- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

What Is A Research Hypothesis?
A Plain-Language Explainer + Practical Examples

Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Learn More About Methodology

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.

Research Limitations 101: What You Need To Know
Learn everything you need to know about research limitations (AKA limitations of the study). Includes practical examples from real studies.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.

Process Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about process coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies exploring processes, actions and changes over time.

Qualitative Coding 101: Inductive, Deductive & Hybrid Coding
Inductive, Deductive & Abductive Coding Qualitative Coding Approaches Explained...
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
17 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Hi” best wishes to you and your very nice blog”
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.

Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.

Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Conference Paper vs. Journal Paper: What’s the Difference

What does Ibid. mean? Citation Examples
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
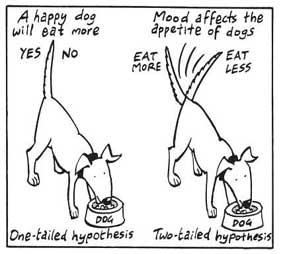
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.

What is Research Hypothesis: Definition, Types, and How to Develop
Read the blog to learn how a research hypothesis provides a clear and focused direction for a study and helps formulate research questions.
June 28, 2024

In this Article
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
AI-generated article summary
- Quota sampling divides a target population into subgroups and sets specific targets for the number of respondents from each subgroup
- It's a non-random sampling method that's useful when researchers need to ensure representation from different demographics or characteristics.
- Use quota sampling when you want to gather data quickly and cheaply while ensuring representation from important subgroups within your target audience.
Get fast AI summaries of customer calls and feedback with magic summarize in Decode
A research hypothesis provides a clear, testable statement that guides the direction and focus of a study.
The benefit is that the hypothesis makes selecting appropriate research methods or statistical means possible, making the analysis more effective and achieving a result. Above all, the idea selected for the research also makes the study more focused, and the hypothesis does that best of all. Finally, when researchers propose and test a hypothesis, they can confirm, enhance, reconsider, or reject any theories.
In this blog, we'll explore the concept of a research hypothesis, its significance in research, and the various types utilized in scientific studies. Additionally, we'll provide a step-by-step guide on formulating your research hypothesis and methods for testing and evaluating it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is a foundational element in both qualitative and quantitative research . It is a precise, testable statement that predicts a possible relationship between two or more variables. This hypothesis is developed based on existing theories, observations, or previous research and aims to provide a direction for further investigation.
A research hypothesis starts with a question a researcher is trying to answer. It implies its effect or outcome and provides a basic ground to construct investigations, surveys, or other methods. It explains what a researcher can expect to find. Once the expectations are clearly stated, a researcher will build the methodology by choosing methods and tools for data collection and analysis.
Examples of Research Hypothesis
Here are some examples of research hypotheses across various fields:
- Hypothesis: Individuals who practice mindfulness meditation daily will report lower levels of stress compared to those who do not practice mindfulness.
- Independent Variable: Mindfulness meditation practice.
- Dependent Variable: Levels of stress.
- Hypothesis: Students who receive personalized tutoring in math will perform better on standardized tests than those who do not.
- Independent Variable: Personalized tutoring in math.
- Dependent Variable: Performance on standardized tests.
- Hypothesis: Consumers exposed to advertisements with emotional appeals will have a higher purchase intention than those with rational appeals.
- Independent Variable: Type of advertisement appeal (emotional vs. rational).
- Dependent Variable: Purchase intent .
- Hypothesis: Increasing the minimum wage will decrease employee turnover rates in the retail sector.
- Independent Variable: Minimum wage increase.
- Dependent Variable: Employee turnover rates in the retail sector.
Technology:
- Hypothesis: Users who receive personalized recommendations on a streaming platform will spend more time watching content than users who do not receive personalized recommendations.
- Independent Variable: Personalized recommendations.
- Dependent Variable: Time spent watching content.
[ Note : Here, Independent Variable is the factor manipulated or controlled in an experiment to observe its effect.
Dependent Variable is the factor that is measured or observed in an experiment to assess the impact of the independent variable.]
What is the Importance of Hypothesis in Research?

The importance of a hypothesis in research cannot be overstated, as it serves several crucial functions in the scientific inquiry process.
Here are the key reasons why hypotheses are fundamental to research:
1. Guides the Research Process
A hypothesis gives a study a clear direction as it outlines what you intend to study and establishes the relationship you are trying to find between variables. It is precise and to the point, which helps formulate your research questions and plan your methods. Using a hypothesis helps organize the testing process from the beginning to the end of the study.
2. Defines the Variables
A well-formulated hypothesis specifies the independent and dependent variables. It defines the object of manipulation and measurement. According to the definition, the hypothesis is an assumption about the relationship between the objects of study. Since statistics is a field of research, the hypothesis is a predictive statement that can be tested empirically.
3. Facilitates Testability and Empirical Investigation
A well-defined hypothesis indicates a clear relationship between the studied variables, thus providing a foundation for designing experiments and observations. In some cases, a null hypothesis is stated to subsequently apply the appropriate statistical test to either validate an already formulated and appropriate hypothesis or reject it.
4. Enhances Objectivity
A hypothesis helps minimize researcher bias by proposing a specific prediction. It forces the researcher to rely on empirical data rather than subjective opinions or beliefs. This objectivity is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the scientific process and ensuring that the findings are credible and reliable.
5. Promotes Critical Thinking and Theoretical Frameworks
Creating a reasonable and viable hypothesis starts with deeply understanding the problem and the field. With a clear sense of the scope of existing evidence and knowledge, there would be a way to go beyond what other researchers have already done. By thoroughly reviewing the literature, researchers are in a position to critically evaluate it and identify problems or questions that remain unresolved.
6. Enables Structured Analysis and Interpretation
A hypothesis is a tentative assumption that provides a context for data analysis and interpretation. It allows for determining specific statistical tests to run and understanding how to interpret them. If the results support the hypothesis, then there is sufficient evidence to claim and infer that the chosen variables are related in a particular way to each other.
If the hypothesis does not match the outcomes, it raises the question of the theoretical assumptions supporting it and additional testing that may be indicated.
7. Drives Scientific Progress
Testing hypotheses continually allows researchers to enrich knowledge beyond merely investigating a particular aspect. The data supporting both hypotheses, the data refuting them, may give rise to new theories, which may serve as the foundation for new research. Such a loop significantly benefits researchers who need to extend their understanding of a particular aspect of the outer world.
{{cta-button}}
What Are The Types of Research Hypotheses?
Research hypotheses can broadly be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes in scientific inquiry.
Here are the main types of research hypotheses:
1. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis posits a relationship between two variables. It suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship without specifying the direction of the effect. For example:
"Increased exercise leads to improved cardiovascular health."
2. Complex Hypothesis
Complex hypotheses involve relationships between multiple variables. These hypotheses may propose how several factors interact to produce a particular outcome. For example:
"The interaction between genetic predisposition, diet, and exercise influences longevity."
3. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis suggests that there is a relationship between two variables, but it does not imply causation. It states that changes in one variable are associated with changes in another. For example:
"There is a correlation between income level and access to healthcare services."
4. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis asserts that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another. It implies a cause-and-effect relationship that can be tested through experimentation or controlled observation. For example:
"Increased consumption of sugary drinks causes an increase in body weight."
5. Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. It specifies whether one variable will increase or decrease in response to changes in another variable. For example:
"Higher levels of education lead to higher income levels."
6. Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis does not predict the direction of the relationship between variables. It simply suggests that there is a relationship without specifying whether one variable will increase or decrease in response to changes in another variable. For example:
"There is a relationship between social media use and levels of anxiety."
7. Null Hypothesis (H₀)
The null hypothesis states no significant relationship exists between the variables being studied. It proposes that any observed differences or effects are due to random chance or sampling error. It is often used to test against the alternative hypothesis (H₁), which proposes the existence of a relationship or effect. For example:
"There is no significant difference in test scores between students who study with music and students who study in silence."
How to Develop a Research Hypothesis?

Developing a research hypothesis involves a systematic process to ensure clarity, testability, and relevance to the research question. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to develop a research hypothesis:
Step 1: Identify the Research Problem or Question
Start by clearly defining the research problem or question you want to investigate. This could be based on gaps in existing literature, observations, theories, or practical issues.
Step 2: Review Existing Literature
Conduct a thorough review of relevant literature to understand what is already known about the topic. Identify theories, findings, and gaps in knowledge that can help inform the development of your hypothesis.
Step 3: Specify Variables
Identify the variables involved in your study. Variables are measurable traits, conditions, or characteristics that can change or vary.
Specifically, determine:
Independent Variable: The factor you manipulate or study in your research.
Dependent Variable: The outcome or response you are measuring or observing about the independent variable.
Step 4: Formulate a Hypothesis
Formulate a clear and specific hypothesis based on your research problem, literature review, and identified variables. A good hypothesis should:
State the expected relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Be testable through empirical research methods (e.g., experiments, surveys, observations).
Be concise and specific, avoiding ambiguity.
Simple hypothesis: "Increased exposure to sunlight leads to higher levels of vitamin D in humans."
Directional hypothesis: "Children who participate in regular physical activity will have lower levels of obesity than children who do not."
Non-directional hypothesis: "There is a relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover."
Step 5: Consider Alternative Hypotheses
While formulating your hypothesis, consider alternative explanations or hypotheses that could also explain the relationship between your variables. This helps in ensuring that your hypothesis is well-grounded and comprehensive.
Step 6: Ensure Testability
Ensure that your hypothesis is testable using appropriate research methods and techniques. Define how to measure or manipulate the variables to gather empirical evidence supporting or refuting your hypothesis.
Step 7: Write and Refine
Write down your hypothesis in a clear and concise statement. Revise and refine it as needed to improve clarity and specificity. Ensure that it aligns with the objectives of your study and effectively addresses the research question.
Step 8: Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your hypothesis, seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or peers in your field. Their input can help identify potential weaknesses or ambiguities in your hypothesis and suggest improvements.
Step 9: Finalize Your Hypothesis
Once you have refined your hypothesis based on feedback and considerations, finalize it as the guiding statement for your research study.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A good research hypothesis possesses several key characteristics that make it effective and suitable for investigation:
1. Clear and Specific
The hypothesis should be precise in its wording and focus. It should clearly state what the researcher intends to investigate or test.
2. Testable
A hypothesis must be capable of being empirically tested and verified or falsified through observation or experimentation. This means there should be a way to gather data that supports or refutes the hypothesis.
3. Falsifiable
There must be a possibility of proving the hypothesis false. A hypothesis that cannot be proven false typically falls outside scientific inquiry. This criterion ensures that research remains objective and open to revision based on evidence.
4. Grounded in Theory
A good hypothesis is usually based on existing theories or literature. It should be informed by a solid understanding of the topic and build upon previous research findings or established principles.
5. Rationale
It should provide a logical rationale or explanation for the expected outcome. This rationale is often derived from the literature review or preliminary observations.
6. Empirical Relevance
The hypothesis should address a question relevant to the field of study and contribute to existing knowledge. It should propose a relationship or difference between variables that is worth investigating.
While the hypothesis should be clear and specific, it should also be concise and to the point. It typically consists of a statement or a few sentences summarizing the expected relationship between variables.
8. Variables
A hypothesis should identify the variables involved and specify how they are expected to relate. This includes independent variables (the factors that are manipulated or controlled) and dependent variables (the outcomes or effects being measured).
9. Observable and Measurable
The variables in the hypothesis should be observable and measurable, allowing for data collection that can be analyzed statistically.
10. Revisable
A hypothesis is not a conclusion but a tentative assumption or prediction that guides the research process. It should be open to revision based on the study's findings.
The Role of Decode in Testing Research Hypotheses

Decode is a powerful survey and consumer research platform powered by Insights AI, that can be instrumental in testing research hypotheses.
Here's how Decode can support you in this process:
- Survey Design and Data Collection: Craft targeted questions using Decode's intuitive interface to gather relevant data for your research.
- Exploratory Research: Conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of your topic—Leverage Decode's functionalities for surveys and feedback mechanisms to gain valuable insights from your target audience.
- Literature Review and Background Research: Supplement your literature review by collecting data on sample populations' opinions, experiences, and preferences through Decode surveys . This combined data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you build a well-grounded hypothesis with a strong foundation in real-world knowledge.
- Identifying Variables: Design targeted survey questions within Decode to pinpoint relevant variables crucial to your research topic.
- Testing Assumptions: Before solidifying your research hypothesis, informally test your assumptions using surveys created on Decode. This allows for early feedback and potential refinement.
- Data Analysis Tools: Decode provides built-in data analysis tools. Utilize these tools to uncover patterns, correlations, and trends within the data you collect through your surveys.
- Refining Your Hypotheses: As you gather data through Decode surveys, you can continuously adjust and refine your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive. This iterative process ensures your hypothesis stays aligned with the insights you uncover.
Final Words
A research hypothesis serves as a guide for scientists. It is a tested idea that applies across different fields, including medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. Integrating theories with hands-on information assists researchers in exploring and discovering new information.
Decode is a valuable tool for researchers. It simplifies creating surveys, gathering data, and analyzing information. It supports all types of research, from forming hypotheses to testing them. Start a free trial to explore its features and maximize your research potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a research hypothesis example.
A research hypothesis example is: "Students who receive daily math tutoring will have higher test scores than students who do not."
What do you write in a research hypothesis?
In a research hypothesis, you write a clear and testable statement predicting the relationship between two or more variables. It should specify the variables and the expected outcome.
What is the purpose of a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis provides a focused direction for research. It guides the study design, data collection, and analysis by predicting a specific outcome that can be tested.
What are the three major types of hypotheses?
The three major types of hypotheses are:
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): States that there is no effect or relationship between variables.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): Suggests that there is an effect or relationship between variables.
- Directional Hypothesis: Specifies the expected direction of the relationship between variables (e.g., positive or negative).
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
With lots of unique blocks, you can easily build a page without coding.
Click on Study templates
Start from scratch
Add blocks to the content
Saving the Template
Publish the Template
Soham is a true Manchester United fan who finds joy in more than just football. Whether navigating the open road, scoring virtual goals in FIFA, reading novels, or enjoying quality time with friends, Soham embraces a life full of diverse passions.
Product Marketing Specialist
Related Articles

Top AI Events You Do Not Want to Miss in 2024
Here are all the top AI events for 2024, curated in one convenient place just for you.

Top Insights Events You Do Not Want to Miss in 2024
Here are all the top Insights events for 2024, curated in one convenient place just for you.

Top CX Events You Do Not Want to Miss in 2024
Here are all the top CX events for 2024, curated in one convenient place just for you.

How to Build an Experience Map: A Complete Guide
An experience map is essential for businesses, as it highlights the customer journey, uncovering insights to improve user experiences and address pain points. Read to find more!

Everything You Need to Know about Intelligent Scoring
Are you curious about Intelligent Scoring and how it differs from regular scoring? Discover its applications and benefits. Read on to learn more!

Qualitative Research Methods and Its Advantages In Modern User Research
Discover how to leverage qualitative research methods, including moderated sessions, to gain deep user insights and enhance your product and UX decisions.


The 10 Best Customer Experience Platforms to Transform Your CX
Explore the top 10 CX platforms to revolutionize customer interactions, enhance satisfaction, and drive business growth.

TAM SAM SOM: What It Means and How to Calculate It?
Understanding TAM, SAM, SOM helps businesses gauge market potential. Learn their definitions and how to calculate them for better business decisions and strategy.

Understanding Likert Scales: Advantages, Limitations, and Questions
Using Likert scales can help you understand how your customers view and rate your product. Here's how you can use them to get the feedback you need.

Mastering the 80/20 Rule to Transform User Research
Find out how the Pareto Principle can optimize your user research processes and lead to more impactful results with the help of AI.

Understanding Consumer Psychology: The Science Behind What Makes Us Buy
Gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer psychology and learn how to apply these insights to inform your research and strategies.

A Guide to Website Footers: Best Design Practices & Examples
Explore the importance of website footers, design best practices, and how to optimize them using UX research for enhanced user engagement and navigation.

Customer Effort Score: Definition, Examples, Tips
A great customer score can lead to dedicated, engaged customers who can end up being loyal advocates of your brand. Here's what you need to know about it.

How to Detect and Address User Pain Points for Better Engagement
Understanding user pain points can help you provide a seamless user experiences that makes your users come back for more. Here's what you need to know about it.

What is Quota Sampling? Definition, Types, Examples, and How to Use It?
Discover Quota Sampling: Learn its process, types, and benefits for accurate consumer insights and informed marketing decisions. Perfect for researchers and brand marketers!

What Is Accessibility Testing? A Comprehensive Guide
Ensure inclusivity and compliance with accessibility standards through thorough testing. Improve user experience and mitigate legal risks. Learn more.

Maximizing Your Research Efficiency with AI Transcriptions
Explore how AI transcription can transform your market research by delivering precise and rapid insights from audio and video recordings.

Understanding the False Consensus Effect: How to Manage it
The false consensus effect can cause incorrect assumptions and ultimately, the wrong conclusions. Here's how you can overcome it.

5 Banking Customer Experience Trends to Watch Out for in 2024
Discover the top 5 banking customer experience trends to watch out for in 2024. Stay ahead in the evolving financial landscape.

The Ultimate Guide to Regression Analysis: Definition, Types, Usage & Advantages
Master Regression Analysis: Learn types, uses & benefits in consumer research for precise insights & strategic decisions.

EyeQuant Alternative
Meet Qatalyst, your best eyequant alternative to improve user experience and an AI-powered solution for all your user research needs.

EyeSee Alternative
Embrace the Insights AI revolution: Meet Decode, your innovative solution for consumer insights, offering a compelling alternative to EyeSee.

Skeuomorphism in UX Design: Is It Dead?
Skeuomorphism in UX design creates intuitive interfaces using familiar real-world visuals to help users easily understand digital products. Do you know how?

Top 6 Wireframe Tools and Ways to Test Your Designs
Wireframe tools assist designers in planning and visualizing the layout of their websites. Look through this list of wireframing tools to find the one that suits you best.

Revolutionizing Customer Interaction: The Power of Conversational AI
Conversational AI enhances customer service across various industries, offering intelligent, context-aware interactions that drive efficiency and satisfaction. Here's how.

User Story Mapping: A Powerful Tool for User-Centered Product Development
Learn about user story mapping and how it can be used for successful product development with this blog.

Understanding Customer Retention: How to Keep Your Customers Coming Back
Understanding customer retention is key to building a successful brand that has repeat, loyal customers. Here's what you need to know about it.

Demographic Segmentation: How Brands Can Use it to Improve Marketing Strategies
Read this blog to learn what demographic segmentation means, its importance, and how it can be used by brands.

Mastering Product Positioning: A UX Researcher's Guide
Read this blog to understand why brands should have a well-defined product positioning and how it affects the overall business.

Discrete Vs. Continuous Data: Everything You Need To Know
Explore the differences between discrete and continuous data and their impact on business decisions and customer insights.

50+ Employee Engagement Survey Questions
Understand how an employee engagement survey provides insights into employee satisfaction and motivation, directly impacting productivity and retention.

What is Experimental Research: Definition, Types & Examples
Understand how experimental research enables researchers to confidently identify causal relationships between variables and validate findings, enhancing credibility.

A Guide to Interaction Design
Interaction design can help you create engaging and intuitive user experiences, improving usability and satisfaction through effective design principles. Here's how.

Exploring the Benefits of Stratified Sampling
Understanding stratified sampling can improve research accuracy by ensuring diverse representation across key subgroups. Here's how.

A Guide to Voice Recognition in Enhancing UX Research
Learn the importance of using voice recognition technology in user research for enhanced user feedback and insights.

The Ultimate Figma Design Handbook: Design Creation and Testing
The Ultimate Figma Design Handbook covers setting up Figma, creating designs, advanced features, prototyping, and testing designs with real users.

The Power of Organization: Mastering Information Architectures
Understanding the art of information architectures can enhance user experiences by organizing and structuring digital content effectively, making information easy to find and navigate. Here's how.

Convenience Sampling: Examples, Benefits, and When To Use It
Read the blog to understand how convenience sampling allows for quick and easy data collection with minimal cost and effort.

What is Critical Thinking, and How Can it be Used in Consumer Research?
Learn how critical thinking enhances consumer research and discover how Decode's AI-driven platform revolutionizes data analysis and insights.

How Business Intelligence Tools Transform User Research & Product Management
This blog explains how Business Intelligence (BI) tools can transform user research and product management by providing data-driven insights for better decision-making.

What is Face Validity? Definition, Guide and Examples
Read this blog to explore face validity, its importance, and the advantages of using it in market research.

What is Customer Lifetime Value, and How To Calculate It?
Read this blog to understand how Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) can help your business optimize marketing efforts, improve customer retention, and increase profitability.

Systematic Sampling: Definition, Examples, and Types
Explore how systematic sampling helps researchers by providing a structured method to select representative samples from larger populations, ensuring efficiency and reducing bias.

Understanding Selection Bias: A Guide
Selection bias can affect the type of respondents you choose for the study and ultimately the quality of responses you receive. Here’s all you need to know about it.

A Guide to Designing an Effective Product Strategy
Read this blog to explore why a well-defined product strategy is required for brands while developing or refining a product.

A Guide to Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in UX: Definition, Strategies, and Examples
Discover what an MVP is, why it's crucial in UX, strategies for creating one, and real-world examples from top companies like Dropbox and Airbnb.

Asking Close Ended Questions: A Guide
Asking the right close ended questions is they key to getting quantitiative data from your users. Her's how you should do it.

Creating Website Mockups: Your Ultimate Guide to Effective Design
Read this blog to learn website mockups- tools, examples and how to create an impactful website design.

Understanding Your Target Market And Its Importance In Consumer Research
Read this blog to learn about the importance of creating products and services to suit the needs of your target audience.

What Is a Go-To-Market Strategy And How to Create One?
Check out this blog to learn how a go-to-market strategy helps businesses enter markets smoothly, attract more customers, and stand out from competitors.

What is Confirmation Bias in Consumer Research?
Learn how confirmation bias affects consumer research, its types, impacts, and practical tips to avoid it for more accurate and reliable insights.

Market Penetration: The Key to Business Success
Understanding market penetration is key to cracking the code to sustained business growth and competitive advantage in any industry. Here's all you need to know about it.

How to Create an Effective User Interface
Having a simple, clear user interface helps your users find what they really want, improving the user experience. Here's how you can achieve it.

Product Differentiation and What It Means for Your Business
Discover how product differentiation helps businesses stand out with unique features, innovative designs, and exceptional customer experiences.

What is Ethnographic Research? Definition, Types & Examples
Read this blog to understand Ethnographic research, its relevance in today’s business landscape and how you can leverage it for your business.

Product Roadmap: The 2024 Guide [with Examples]
Read this blog to understand how a product roadmap can align stakeholders by providing a clear product development and delivery plan.

Product Market Fit: Making Your Products Stand Out in a Crowded Market
Delve into the concept of product-market fit, explore its significance, and equip yourself with practical insights to achieve it effectively.

Consumer Behavior in Online Shopping: A Comprehensive Guide
Ever wondered how online shopping behavior can influence successful business decisions? Read on to learn more.

How to Conduct a First Click Test?
Why are users leaving your site so fast? Learn how First Click Testing can help. Discover quick fixes for frustration and boost engagement.

What is Market Intelligence? Methods, Types, and Examples
Read the blog to understand how marketing intelligence helps you understand consumer behavior and market trends to inform strategic decision-making.

What is a Longitudinal Study? Definition, Types, and Examples
Is your long-term research strategy unclear? Learn how longitudinal studies decode complexity. Read on for insights.

What Is the Impact of Customer Churn on Your Business?
Understanding and reducing customer churn is the key to building a healthy business that keeps customers satisfied. Here's all you need to know about it.

The Ultimate Design Thinking Guide
Discover the power of design thinking in UX design for your business. Learn the process and key principles in our comprehensive guide.

100+ Yes Or No Survey Questions Examples
Yes or no survey questions simplify responses, aiding efficiency, clarity, standardization, quantifiability, and binary decision-making. Read some examples!

What is Customer Segmentation? The ULTIMATE Guide
Explore how customer segmentation targets diverse consumer groups by tailoring products, marketing, and experiences to their preferred needs.

Crafting User-Centric Websites Through Responsive Web Design
Find yourself reaching for your phone instead of a laptop for regular web browsing? Read on to find out what that means & how you can leverage it for business.

How Does Product Placement Work? Examples and Benefits
Read the blog to understand how product placement helps advertisers seek subtle and integrated ways to promote their products within entertainment content.

The Importance of Reputation Management, and How it Can Make or Break Your Brand
A good reputation management strategy is crucial for any brand that wants to keep its customers loyal. Here's how brands can focus on it.

A Comprehensive Guide to Human-Centered Design
Are you putting the human element at the center of your design process? Read this blog to understand why brands must do so.

How to Leverage Customer Insights to Grow Your Business
Genuine insights are becoming increasingly difficult to collect. Read on to understand the challenges and what the future holds for customer insights.

The Complete Guide to Behavioral Segmentation
Struggling to reach your target audience effectively? Discover how behavioral segmentation can transform your marketing approach. Read more in our blog!

Creating a Unique Brand Identity: How to Make Your Brand Stand Out
Creating a great brand identity goes beyond creating a memorable logo - it's all about creating a consistent and unique brand experience for your cosnumers. Here's everything you need to know about building one.

Understanding the Product Life Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the product life cycle, or the stages a product goes through from its launch to its sunset can help you understand how to market it at every stage to create the most optimal marketing strategies.

Empathy vs. Sympathy in UX Research
Are you conducting UX research and seeking guidance on conducting user interviews with empathy or sympathy? Keep reading to discover the best approach.

What is Exploratory Research, and How To Conduct It?
Read this blog to understand how exploratory research can help you uncover new insights, patterns, and hypotheses in a subject area.

First Impressions & Why They Matter in User Research
Ever wonder if first impressions matter in user research? The answer might surprise you. Read on to learn more!

Cluster Sampling: Definition, Types & Examples
Read this blog to understand how cluster sampling tackles the challenge of efficiently collecting data from large, spread-out populations.

Top Six Market Research Trends
Curious about where market research is headed? Read on to learn about the changes surrounding this field in 2024 and beyond.

Lyssna Alternative
Meet Qatalyst, your best lyssna alternative to usability testing, to create a solution for all your user research needs.

What is Feedback Loop? Definition, Importance, Types, and Best Practices
Struggling to connect with your customers? Read the blog to learn how feedback loops can solve your problem!

UI vs. UX Design: What’s The Difference?
Learn how UI solves the problem of creating an intuitive and visually appealing interface and how UX addresses broader issues related to user satisfaction and overall experience with the product or service.

The Impact of Conversion Rate Optimization on Your Business
Understanding conversion rate optimization can help you boost your online business. Read more to learn all about it.

Insurance Questionnaire: Tips, Questions and Significance
Leverage this pre-built customizable questionnaire template for insurance to get deep insights from your audience.

UX Research Plan Template
Read on to understand why you need a UX Research Plan and how you can use a fully customizable template to get deep insights from your users!

Brand Experience: What it Means & Why It Matters
Have you ever wondered how users navigate the travel industry for your research insights? Read on to understand user experience in the travel sector.

Validity in Research: Definitions, Types, Significance, and Its Relationship with Reliability
Is validity ensured in your research process? Read more to explore the importance and types of validity in research.

The Role of UI Designers in Creating Delightful User Interfaces
UI designers help to create aesthetic and functional experiences for users. Here's all you need to know about them.

Top Usability Testing Tools to Try
Using usability testing tools can help you understand user preferences and behaviors and ultimately, build a better digital product. Here are the top tools you should be aware of.

Understanding User Experience in Travel Market Research
Ever wondered how users navigate the travel industry for your research insights? Read on to understand user experience in the travel sector.

Top 10 Customer Feedback Tools You’d Want to Try
Explore the top 10 customer feedback tools for analyzing feedback, empowering businesses to enhance customer experience.

10 Best UX Communities on LinkedIn & Slack for Networking & Collaboration
Discover the significance of online communities in UX, the benefits of joining communities on LinkedIn and Slack, and insights into UX career advancement.

The Role of Customer Experience Manager in Consumer Research
This blog explores the role of Customer Experience Managers, their skills, their comparison with CRMs, their key metrics, and why they should use a consumer research platform.

Product Review Template
Learn how to conduct a product review and get insights with this template on the Qatalyst platform.

What Is the Role of a Product Designer in UX?
Product designers help to create user-centric digital experiences that cater to users' needs and preferences. Here's what you need to know about them.

Top 10 Customer Journey Mapping Tools For Market Research in 2024
Explore the top 10 tools in 2024 to understand customer journeys while conducting market research.

Generative AI and its Use in Consumer Research
Ever wondered how Generative AI fits in within the research space? Read on to find its potential in the consumer research industry.

All You Need to Know About Interval Data: Examples, Variables, & Analysis
Understand how interval data provides precise numerical measurements, enabling quantitative analysis and statistical comparison in research.

How to Use Narrative Analysis in Research
Find the advantages of using narrative analysis and how this method can help you enrich your research insights.
A Guide to Asking the Right Focus Group Questions
Moderated discussions with multiple participants to gather diverse opinions on a topic.
Maximize Your Research Potential
Experience why teams worldwide trust our Consumer & User Research solutions.
Book a Demo

Definition of a Hypothesis
What it is and how it's used in sociology
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
A hypothesis is a prediction of what will be found at the outcome of a research project and is typically focused on the relationship between two different variables studied in the research. It is usually based on both theoretical expectations about how things work and already existing scientific evidence.
Within social science, a hypothesis can take two forms. It can predict that there is no relationship between two variables, in which case it is a null hypothesis . Or, it can predict the existence of a relationship between variables, which is known as an alternative hypothesis.
In either case, the variable that is thought to either affect or not affect the outcome is known as the independent variable, and the variable that is thought to either be affected or not is the dependent variable.
Researchers seek to determine whether or not their hypothesis, or hypotheses if they have more than one, will prove true. Sometimes they do, and sometimes they do not. Either way, the research is considered successful if one can conclude whether or not a hypothesis is true.
Null Hypothesis
A researcher has a null hypothesis when she or he believes, based on theory and existing scientific evidence, that there will not be a relationship between two variables. For example, when examining what factors influence a person's highest level of education within the U.S., a researcher might expect that place of birth, number of siblings, and religion would not have an impact on the level of education. This would mean the researcher has stated three null hypotheses.
Alternative Hypothesis
Taking the same example, a researcher might expect that the economic class and educational attainment of one's parents, and the race of the person in question are likely to have an effect on one's educational attainment. Existing evidence and social theories that recognize the connections between wealth and cultural resources , and how race affects access to rights and resources in the U.S. , would suggest that both economic class and educational attainment of the one's parents would have a positive effect on educational attainment. In this case, economic class and educational attainment of one's parents are independent variables, and one's educational attainment is the dependent variable—it is hypothesized to be dependent on the other two.
Conversely, an informed researcher would expect that being a race other than white in the U.S. is likely to have a negative impact on a person's educational attainment. This would be characterized as a negative relationship, wherein being a person of color has a negative effect on one's educational attainment. In reality, this hypothesis proves true, with the exception of Asian Americans , who go to college at a higher rate than whites do. However, Blacks and Hispanics and Latinos are far less likely than whites and Asian Americans to go to college.
Formulating a Hypothesis
Formulating a hypothesis can take place at the very beginning of a research project , or after a bit of research has already been done. Sometimes a researcher knows right from the start which variables she is interested in studying, and she may already have a hunch about their relationships. Other times, a researcher may have an interest in a particular topic, trend, or phenomenon, but he may not know enough about it to identify variables or formulate a hypothesis.
Whenever a hypothesis is formulated, the most important thing is to be precise about what one's variables are, what the nature of the relationship between them might be, and how one can go about conducting a study of them.
Updated by Nicki Lisa Cole, Ph.D
- What It Means When a Variable Is Spurious
- Understanding Path Analysis
- Pilot Study in Research
- Simple Random Sampling
- Exploitation
- What Is Multiculturalism? Definition, Theories, and Examples
- Convenience Samples for Research
- What Is Cultural Capital? Do I Have It?
- What Does Consumerism Mean?
- Visualizing Social Stratification in the U.S.
- What Is Symbolic Interactionism?
- What Is Cultural Hegemony?
- Understanding Stratified Samples and How to Make Them
- What Is Groupthink? Definition and Examples
- What Is a Reference Group?
- What Is Ethnography?

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

- When did science begin?
- Where was science invented?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Education Resources Information Center - Understanding Hypotheses, Predictions, Laws, and Theories
- Simply Psychology - Research Hypothesis: Definition, Types, & Examples
- Cornell University - The Learning Strategies Center - Hypothesis
- Washington State University - Developing a Hypothesis
- Verywell Mind - Forming a Good Hypothesis for Scientific Research
- BCCampus Publishing - Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction - Hypotheses
hypothesis , something supposed or taken for granted, with the object of following out its consequences (Greek hypothesis , “a putting under,” the Latin equivalent being suppositio ).

In planning a course of action, one may consider various alternatives , working out each in detail. Although the word hypothesis is not typically used in this case, the procedure is virtually the same as that of an investigator of crime considering various suspects. Different methods may be used for deciding what the various alternatives may be, but what is fundamental is the consideration of a supposal as if it were true, without actually accepting it as true. One of the earliest uses of the word in this sense was in geometry . It is described by Plato in the Meno .
The most important modern use of a hypothesis is in relation to scientific investigation . A scientist is not merely concerned to accumulate such facts as can be discovered by observation: linkages must be discovered to connect those facts. An initial puzzle or problem provides the impetus , but clues must be used to ascertain which facts will help yield a solution. The best guide is a tentative hypothesis, which fits within the existing body of doctrine. It is so framed that, with its help, deductions can be made that under certain factual conditions (“initial conditions”) certain other facts would be found if the hypothesis were correct.
The concepts involved in the hypothesis need not themselves refer to observable objects. However, the initial conditions should be able to be observed or to be produced experimentally, and the deduced facts should be able to be observed. William Harvey ’s research on circulation in animals demonstrates how greatly experimental observation can be helped by a fruitful hypothesis. While a hypothesis can be partially confirmed by showing that what is deduced from it with certain initial conditions is actually found under those conditions, it cannot be completely proved in this way. What would have to be shown is that no other hypothesis would serve. Hence, in assessing the soundness of a hypothesis, stress is laid on the range and variety of facts that can be brought under its scope. Again, it is important that it should be capable of being linked systematically with hypotheses which have been found fertile in other fields.
If the predictions derived from the hypothesis are not found to be true, the hypothesis may have to be given up or modified. The fault may lie, however, in some other principle forming part of the body of accepted doctrine which has been utilized in deducing consequences from the hypothesis. It may also lie in the fact that other conditions, hitherto unobserved, are present beside the initial conditions, affecting the result. Thus the hypothesis may be kept, pending further examination of facts or some remodeling of principles. A good illustration of this is to be found in the history of the corpuscular and the undulatory hypotheses about light .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Crit Care Med
- v.23(Suppl 3); 2019 Sep
An Introduction to Statistics: Understanding Hypothesis Testing and Statistical Errors
Priya ranganathan.
1 Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain, Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2 Department of Surgical Oncology, Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
The second article in this series on biostatistics covers the concepts of sample, population, research hypotheses and statistical errors.
How to cite this article
Ranganathan P, Pramesh CS. An Introduction to Statistics: Understanding Hypothesis Testing and Statistical Errors. Indian J Crit Care Med 2019;23(Suppl 3):S230–S231.
Two papers quoted in this issue of the Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine report. The results of studies aim to prove that a new intervention is better than (superior to) an existing treatment. In the ABLE study, the investigators wanted to show that transfusion of fresh red blood cells would be superior to standard-issue red cells in reducing 90-day mortality in ICU patients. 1 The PROPPR study was designed to prove that transfusion of a lower ratio of plasma and platelets to red cells would be superior to a higher ratio in decreasing 24-hour and 30-day mortality in critically ill patients. 2 These studies are known as superiority studies (as opposed to noninferiority or equivalence studies which will be discussed in a subsequent article).
SAMPLE VERSUS POPULATION
A sample represents a group of participants selected from the entire population. Since studies cannot be carried out on entire populations, researchers choose samples, which are representative of the population. This is similar to walking into a grocery store and examining a few grains of rice or wheat before purchasing an entire bag; we assume that the few grains that we select (the sample) are representative of the entire sack of grains (the population).
The results of the study are then extrapolated to generate inferences about the population. We do this using a process known as hypothesis testing. This means that the results of the study may not always be identical to the results we would expect to find in the population; i.e., there is the possibility that the study results may be erroneous.
HYPOTHESIS TESTING
A clinical trial begins with an assumption or belief, and then proceeds to either prove or disprove this assumption. In statistical terms, this belief or assumption is known as a hypothesis. Counterintuitively, what the researcher believes in (or is trying to prove) is called the “alternate” hypothesis, and the opposite is called the “null” hypothesis; every study has a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis. For superiority studies, the alternate hypothesis states that one treatment (usually the new or experimental treatment) is superior to the other; the null hypothesis states that there is no difference between the treatments (the treatments are equal). For example, in the ABLE study, we start by stating the null hypothesis—there is no difference in mortality between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs. We then state the alternate hypothesis—There is a difference between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs. It is important to note that we have stated that the groups are different, without specifying which group will be better than the other. This is known as a two-tailed hypothesis and it allows us to test for superiority on either side (using a two-sided test). This is because, when we start a study, we are not 100% certain that the new treatment can only be better than the standard treatment—it could be worse, and if it is so, the study should pick it up as well. One tailed hypothesis and one-sided statistical testing is done for non-inferiority studies, which will be discussed in a subsequent paper in this series.
STATISTICAL ERRORS
There are two possibilities to consider when interpreting the results of a superiority study. The first possibility is that there is truly no difference between the treatments but the study finds that they are different. This is called a Type-1 error or false-positive error or alpha error. This means falsely rejecting the null hypothesis.
The second possibility is that there is a difference between the treatments and the study does not pick up this difference. This is called a Type 2 error or false-negative error or beta error. This means falsely accepting the null hypothesis.
The power of the study is the ability to detect a difference between groups and is the converse of the beta error; i.e., power = 1-beta error. Alpha and beta errors are finalized when the protocol is written and form the basis for sample size calculation for the study. In an ideal world, we would not like any error in the results of our study; however, we would need to do the study in the entire population (infinite sample size) to be able to get a 0% alpha and beta error. These two errors enable us to do studies with realistic sample sizes, with the compromise that there is a small possibility that the results may not always reflect the truth. The basis for this will be discussed in a subsequent paper in this series dealing with sample size calculation.
Conventionally, type 1 or alpha error is set at 5%. This means, that at the end of the study, if there is a difference between groups, we want to be 95% certain that this is a true difference and allow only a 5% probability that this difference has occurred by chance (false positive). Type 2 or beta error is usually set between 10% and 20%; therefore, the power of the study is 90% or 80%. This means that if there is a difference between groups, we want to be 80% (or 90%) certain that the study will detect that difference. For example, in the ABLE study, sample size was calculated with a type 1 error of 5% (two-sided) and power of 90% (type 2 error of 10%) (1).
Table 1 gives a summary of the two types of statistical errors with an example
Statistical errors
| (a) Types of statistical errors | |||
| : Null hypothesis is | |||
| True | False | ||
| Null hypothesis is actually | True | Correct results! | Falsely rejecting null hypothesis - Type I error |
| False | Falsely accepting null hypothesis - Type II error | Correct results! | |
| (b) Possible statistical errors in the ABLE trial | |||
| There is difference in mortality between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs | There difference in mortality between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs | ||
| Truth | There is difference in mortality between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs | Correct results! | Falsely rejecting null hypothesis - Type I error |
| There difference in mortality between groups receiving fresh RBCs and standard-issue RBCs | Falsely accepting null hypothesis - Type II error | Correct results! | |
In the next article in this series, we will look at the meaning and interpretation of ‘ p ’ value and confidence intervals for hypothesis testing.
Source of support: Nil
Conflict of interest: None
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of hypothesis
Did you know.
The Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
A hypothesis is an assumption, an idea that is proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is usually tentative; it's an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, it is understood to be more likely to be true than a hypothesis is.
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch, with theory being the more common choice.
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
- proposition
- supposition
hypothesis , theory , law mean a formula derived by inference from scientific data that explains a principle operating in nature.
hypothesis implies insufficient evidence to provide more than a tentative explanation.
theory implies a greater range of evidence and greater likelihood of truth.
law implies a statement of order and relation in nature that has been found to be invariable under the same conditions.
Examples of hypothesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'hypothesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Greek, from hypotithenai to put under, suppose, from hypo- + tithenai to put — more at do
1846, in the meaning defined at sense 2
Phrases Containing hypothesis
- counter - hypothesis
- nebular hypothesis
- null hypothesis
- planetesimal hypothesis
- Whorfian hypothesis
Articles Related to hypothesis

This is the Difference Between a...
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
In scientific reasoning, they're two completely different things
Dictionary Entries Near hypothesis
hypothermia
hypothesize
Cite this Entry
“Hypothesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/hypothesis. Accessed 27 Sep. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of hypothesis, medical definition, medical definition of hypothesis, more from merriam-webster on hypothesis.
Nglish: Translation of hypothesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of hypothesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about hypothesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, plural and possessive names: a guide, the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', more commonly misspelled words, absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, weird words for autumn time, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, 15 words that used to mean something different, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, games & quizzes.

Doc’s Things and Stuff
Hypothesis | Definition

Hypothesis refers to a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables in scientific research.
Understanding Hypothesis
In social science research, a hypothesis plays a crucial role in guiding the research process. It is essentially an educated guess or a prediction that researchers formulate based on existing theories, observations, or knowledge. A hypothesis helps define the direction of the study and provides a framework for data collection and analysis.
The Importance of a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is central to the research process for several reasons:
- Focuses the Study : By making a specific prediction, the hypothesis narrows the focus of the research. Instead of exploring a broad question, researchers can zero in on testing the specific prediction made by the hypothesis.
- Guides Research Design : Once a hypothesis is formulated, researchers can design their study in a way that either supports or refutes the hypothesis. This includes choosing appropriate research methods, collecting relevant data, and conducting analyses.
- Provides Direction : A clear hypothesis helps ensure that the research is purposeful and organized. It gives researchers a goal to work toward and a means to measure their findings against their predictions.
- Enables Testing of Theories : Many hypotheses are derived from existing theories. By testing a hypothesis, researchers can assess whether the theory holds up in different contexts or under different conditions.
Components of a Hypothesis
A well-formulated hypothesis usually contains several key components:
- Variables : These are the elements that the researcher is studying. Typically, a hypothesis involves an independent variable (the cause or predictor) and a dependent variable (the effect or outcome). For example, a researcher might hypothesize that “increased study time (independent variable) leads to higher test scores (dependent variable).”
- Relationship : The hypothesis also specifies the expected relationship between the variables. In the example above, the hypothesis predicts a positive relationship between study time and test scores.
- Testability : A hypothesis must be testable through empirical observation or experimentation. If a hypothesis cannot be tested, it remains a speculation or an idea rather than a scientific hypothesis.
- Falsifiability : For a hypothesis to be scientific, it must be falsifiable, meaning that it can be proven wrong. If a hypothesis cannot be disproven, it is not considered scientifically valid.
Types of Hypotheses
There are several types of hypotheses used in social science research, each serving a unique purpose. The most common types are:
1. Null Hypothesis (H0)
The null hypothesis asserts that there is no relationship between the variables being studied. It acts as a default assumption that the researcher tries to disprove or reject. For example, the null hypothesis might state, “There is no relationship between study time and test scores.”
Researchers typically use statistical tests to determine whether they can reject the null hypothesis. If the evidence suggests a significant relationship between the variables, the null hypothesis is rejected.
2. Alternative Hypothesis (H1)
The alternative hypothesis suggests that there is a relationship between the variables. It is the opposite of the null hypothesis. For example, the alternative hypothesis might state, “Increased study time is associated with higher test scores.”
The goal of the research is usually to provide enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
3. Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis makes a specific prediction about the direction of the relationship between variables. In other words, it predicts whether the relationship is positive or negative. For example, “Students who spend more time studying will score higher on tests.”
Directional hypotheses are often used when previous research or theory suggests a specific outcome.
4. Non-Directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis predicts that there will be a relationship between the variables but does not specify the direction of the relationship. For instance, “There is a relationship between study time and test scores.” Non-directional hypotheses are useful when the researcher is unsure whether the variables are positively or negatively correlated.
5. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis involves more than two variables and predicts the relationships among them. For example, “Increased study time and use of study aids will result in higher test scores.” Complex hypotheses are common in social science research, where multiple factors often interact to influence outcomes.
How to Formulate a Hypothesis
Formulating a strong hypothesis requires careful thought and consideration of existing knowledge and research. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
1. Identify the Research Question
The first step in formulating a hypothesis is to identify a research question. This is the broader question you are trying to answer through your study. For example, “What factors influence student test scores?”
2. Conduct a Literature Review
A thorough review of the existing literature helps you understand what is already known about the topic. This step allows you to build on previous research and avoid duplicating studies. It also helps you identify gaps in the literature that your research could fill.
3. Identify the Variables
Next, determine which variables you want to study. In our example, the variables are “study time” and “test scores.” Make sure your variables are measurable and observable.
4. Make an Educated Guess
Based on the literature review and your understanding of the topic, make a prediction about how the variables are related. This prediction forms the basis of your hypothesis. For instance, you might predict that “students who study more will perform better on tests.”
5. Ensure Testability
Finally, ensure that your hypothesis is testable. This means you need to be able to collect data and analyze it to either support or reject your hypothesis.
Testing a Hypothesis
Once a hypothesis is formulated, the next step is to test it. This typically involves collecting data and analyzing it to determine whether the hypothesis is supported. Researchers use various methods to test hypotheses, including experiments, surveys, and observational studies.
1. Data Collection
The method of data collection will depend on the nature of the hypothesis and the research design. For example, if the hypothesis predicts that increased study time leads to better test scores, the researcher could collect data through surveys, test scores, and time logs.
2. Statistical Testing
Statistical tests are used to determine whether the data support the hypothesis. For instance, a common method is to conduct a correlation analysis to examine the relationship between study time and test scores.
3. Interpretation of Results
Once the data have been analyzed, researchers interpret the results to determine whether they support or refute the hypothesis. If the data show a significant relationship between the variables, the hypothesis is supported. If no relationship is found, the hypothesis is rejected.
Hypothesis in the Context of Social Science
In social science, hypotheses are essential for developing new theories, testing existing theories, and exploring relationships between social phenomena. Because social science often deals with complex and multifaceted human behaviors, hypotheses in this field must account for a wide range of variables and external factors.
For instance, a social scientist studying education may hypothesize that smaller class sizes improve student performance. However, they must also consider other variables, such as teacher quality, socioeconomic status, and access to resources. In this way, social science hypotheses often involve multiple variables and interactions.
Hypothesis and Research Ethics
It is important to consider ethics when formulating and testing hypotheses. Ethical considerations ensure that research does not harm participants and that the research process is transparent and unbiased. Researchers should avoid forming hypotheses that could lead to biased or misleading conclusions. Additionally, they must ensure that their testing methods respect participants’ rights and privacy.
A hypothesis is a vital element in the research process. It provides a focused and testable prediction about the relationship between variables, guiding researchers through data collection and analysis. By formulating a clear and testable hypothesis, social scientists can explore complex social phenomena, test theories, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Hypothesis Types and Research
- January 2018

- Eternal University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Intan Angelia Sihombing
- Debora Chaterin Simanjuntak

- Alfatira Gema
- Farah Wulandari Pangestuty
- Agusman Hulu
- Adieli Laoli
- Afore Tahir Harefa
- Elwin Piarawan Zebua

- Bernadette P Hungler
- Dennis F Polit
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

What is Hypothesis? Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Sources
- Post last modified: 10 January 2022
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

- What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
As an example, if we want to explore whether using a specific teaching method at school will result in better school marks (research question), the hypothesis could be that the mean school marks of students being taught with that specific teaching method will be higher than of those being taught using other methods.
In this example, we stated a hypothesis about the expected differences between groups. Other hypotheses may refer to correlations between variables.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Hypothesis?
- 2 Hypothesis Definition
- 3 Meaning of Hypothesis
- 4.1 Conceptual Clarity
- 4.2 Need of empirical referents
- 4.3 Hypothesis should be specific
- 4.4 Hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques
- 4.5 Hypothesis should be consistent with the theory
- 4.6 Hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events
- 4.7 Hypothesis should be simple
- 5.1 Observation
- 5.2 Analogies
- 5.4 State of Knowledge
- 5.5 Culture
- 5.6 Continuity of Research
- 6.1 Null Hypothesis
- 6.2 Alternative Hypothesis
Thus, to formulate a hypothesis, we need to refer to the descriptive statistics (such as the mean final marks), and specify a set of conditions about these statistics (such as a difference between the means, or in a different example, a positive or negative correlation). The hypothesis we formulate applies to the population of interest.
The null hypothesis makes a statement that no difference exists (see Pyrczak, 1995, pp. 75-84).
Hypothesis Definition
A hypothesis is ‘a guess or supposition as to the existence of some fact or law which will serve to explain a connection of facts already known to exist.’ – J. E. Creighton & H. R. Smart
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition not known to be definitely true or false, examined for the sake of determining the consequences which would follow from its truth.’ – Max Black
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition which can be put to a test to determine validity and is useful for further research.’ – W. J. Goode and P. K. Hatt
A hypothesis is a proposition, condition or principle which is assumed, perhaps without belief, in order to draw out its logical consequences and by this method to test its accord with facts which are known or may be determined. – Webster’s New International Dictionary of the English Language (1956)
Meaning of Hypothesis
From the above mentioned definitions of hypothesis, its meaning can be explained in the following ways.
- At the primary level, a hypothesis is the possible and probable explanation of the sequence of happenings or data.
- Sometimes, hypothesis may emerge from an imagination, common sense or a sudden event.
- Hypothesis can be a probable answer to the research problem undertaken for study. 4. Hypothesis may not always be true. It can get disproven. In other words, hypothesis need not always be a true proposition.
- Hypothesis, in a sense, is an attempt to present the interrelations that exist in the available data or information.
- Hypothesis is not an individual opinion or community thought. Instead, it is a philosophical means which is to be used for research purpose. Hypothesis is not to be considered as the ultimate objective; rather it is to be taken as the means of explaining scientifically the prevailing situation.
The concept of hypothesis can further be explained with the help of some examples. Lord Keynes, in his theory of national income determination, made a hypothesis about the consumption function. He stated that the consumption expenditure of an individual or an economy as a whole is dependent on the level of income and changes in a certain proportion.
Later, this proposition was proved in the statistical research carried out by Prof. Simon Kuznets. Matthus, while studying the population, formulated a hypothesis that population increases faster than the supply of food grains. Population studies of several countries revealed that this hypothesis is true.
Validation of the Malthus’ hypothesis turned it into a theory and when it was tested in many other countries it became the famous Malthus’ Law of Population. It thus emerges that when a hypothesis is tested and proven, it becomes a theory. The theory, when found true in different times and at different places, becomes the law. Having understood the concept of hypothesis, few hypotheses can be formulated in the areas of commerce and economics.
- Population growth moderates with the rise in per capita income.
- Sales growth is positively linked with the availability of credit.
- Commerce education increases the employability of the graduate students.
- High rates of direct taxes prompt people to evade taxes.
- Good working conditions improve the productivity of employees.
- Advertising is the most effecting way of promoting sales than any other scheme.
- Higher Debt-Equity Ratio increases the probability of insolvency.
- Economic reforms in India have made the public sector banks more efficient and competent.
- Foreign direct investment in India has moved in those sectors which offer higher rate of profit.
- There is no significant association between credit rating and investment of fund.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Not all the hypotheses are good and useful from the point of view of research. It is only a few hypotheses satisfying certain criteria that are good, useful and directive in the research work undertaken. The characteristics of such a useful hypothesis can be listed as below:
Conceptual Clarity
Need of empirical referents, hypothesis should be specific, hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques, hypothesis should be consistent with the theory, hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events, hypothesis should be simple.
The concepts used while framing hypothesis should be crystal clear and unambiguous. Such concepts must be clearly defined so that they become lucid and acceptable to everyone. How are the newly developed concepts interrelated and how are they linked with the old one is to be very clear so that the hypothesis framed on their basis also carries the same clarity.
A hypothesis embodying unclear and ambiguous concepts can to a great extent undermine the successful completion of the research work.
A hypothesis can be useful in the research work undertaken only when it has links with some empirical referents. Hypothesis based on moral values and ideals are useless as they cannot be tested. Similarly, hypothesis containing opinions as good and bad or expectation with respect to something are not testable and therefore useless.
For example, ‘current account deficit can be lowered if people change their attitude towards gold’ is a hypothesis encompassing expectation. In case of such a hypothesis, the attitude towards gold is something which cannot clearly be described and therefore a hypothesis which embodies such an unclean thing cannot be tested and proved or disproved. In short, the hypothesis should be linked with some testable referents.
For the successful conduction of research, it is necessary that the hypothesis is specific and presented in a precise manner. Hypothesis which is general, too ambitious and grandiose in scope is not to be made as such hypothesis cannot be easily put to test. A hypothesis is to be based on such concepts which are precise and empirical in nature. A hypothesis should give a clear idea about the indicators which are to be used.
For example, a hypothesis that economic power is increasingly getting concentrated in a few hands in India should enable us to define the concept of economic power. It should be explicated in terms of measurable indicator like income, wealth, etc. Such specificity in the formulation of a hypothesis ensures that the research is practicable and significant.
While framing the hypothesis, the researcher should be aware of the available research techniques and should see that the hypothesis framed is testable on the basis of them. In other words, a hypothesis should be researchable and for this it is important that a due thought has been given to the methods and techniques which can be used to measure the concepts and variables embodied in the hypothesis.
It does not however mean that hypotheses which are not testable with the available techniques of research are not to be made. If the problem is too significant and therefore the hypothesis framed becomes too ambitious and complex, it’s testing becomes possible with the development of new research techniques or the hypothesis itself leads to the development of new research techniques.
A hypothesis must be related to the existing theory or should have a theoretical orientation. The growth of knowledge takes place in the sequence of facts, hypothesis, theory and law or principles. It means the hypothesis should have a correspondence with the existing facts and theory.
If the hypothesis is related to some theory, the research work will enable us to support, modify or refute the existing theory. Theoretical orientation of the hypothesis ensures that it becomes scientifically useful. According to Prof. Goode and Prof. Hatt, research work can contribute to the existing knowledge only when the hypothesis is related with some theory.
This enables us to explain the observed facts and situations and also verify the framed hypothesis. In the words of Prof. Cohen and Prof. Nagel, “hypothesis must be formulated in such a manner that deduction can be made from it and that consequently a decision can be reached as to whether it does or does not explain the facts considered.”
If the research work based on a hypothesis is to be successful, it is necessary that the later is as simple and easy as possible. An ambition of finding out something new may lead the researcher to frame an unrealistic and unclear hypothesis. Such a temptation is to be avoided. Framing a simple, easy and testable hypothesis requires that the researcher is well acquainted with the related concepts.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can be derived from various sources. Some of the sources is given below:
Observation
State of knowledge, continuity of research.
Hypotheses can be derived from observation from the observation of price behavior in a market. For example the relationship between the price and demand for an article is hypothesized.
Analogies are another source of useful hypotheses. Julian Huxley has pointed out that casual observations in nature or in the framework of another science may be a fertile source of hypotheses. For example, the hypotheses that similar human types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions come from plant ecology.
This is one of the main sources of hypotheses. It gives direction to research by stating what is known logical deduction from theory lead to new hypotheses. For example, profit / wealth maximization is considered as the goal of private enterprises. From this assumption various hypotheses are derived’.
An important source of hypotheses is the state of knowledge in any particular science where formal theories exist hypotheses can be deduced. If the hypotheses are rejected theories are scarce hypotheses are generated from conception frameworks.
Another source of hypotheses is the culture on which the researcher was nurtured. Western culture has induced the emergence of sociology as an academic discipline over the past decade, a large part of the hypotheses on American society examined by researchers were connected with violence. This interest is related to the considerable increase in the level of violence in America.
The continuity of research in a field itself constitutes an important source of hypotheses. The rejection of some hypotheses leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in subsequent research on the same subject.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null hypothesis.
The hypothesis that are proposed with the intent of receiving a rejection for them are called Null Hypothesis . This requires that we hypothesize the opposite of what is desired to be proved. For example, if we want to show that sales and advertisement expenditure are related, we formulate the null hypothesis that they are not related.
Similarly, if we want to conclude that the new sales training programme is effective, we formulate the null hypothesis that the new training programme is not effective, and if we want to prove that the average wages of skilled workers in town 1 is greater than that of town 2, we formulate the null hypotheses that there is no difference in the average wages of the skilled workers in both the towns.
Since we hypothesize that sales and advertisement are not related, new training programme is not effective and the average wages of skilled workers in both the towns are equal, we call such hypotheses null hypotheses and denote them as H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
Rejection of null hypotheses leads to the acceptance of alternative hypothesis . The rejection of null hypothesis indicates that the relationship between variables (e.g., sales and advertisement expenditure) or the difference between means (e.g., wages of skilled workers in town 1 and town 2) or the difference between proportions have statistical significance and the acceptance of the null hypotheses indicates that these differences are due to chance.
As already mentioned, the alternative hypotheses specify that values/relation which the researcher believes hold true. The alternative hypotheses can cover a whole range of values rather than a single point. The alternative hypotheses are denoted by H 1 .
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
Sampling Method
- Research Methods
Data Collection in Research
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Application of Business Research
Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
Hypothesis Testing
- Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is research design features, components, what is descriptive research types, features, what is sample size determination, formula, determining,, types of errors affecting research design, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, what is hypothesis testing procedure, what is experiments variables, types, lab, field, what is literature review importance, functions, process,, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
Hypothesis | Definition, Meaning and Examples
Hypothesis is a hypothesis is fundamental concept in the world of research and statistics. It is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables.
Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion . Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
In this article, we will learn what hypothesis is, its characteristics, types, and examples. We will also learn how hypothesis helps in scientific research.
Table of Content
What is Hypothesis?
Characteristics of hypothesis, sources of hypothesis, types of hypothesis, functions of hypothesis, how hypothesis help in scientific research.
Hypothesis is a suggested idea or an educated guess or a proposed explanation made based on limited evidence, serving as a starting point for further study. They are meant to lead to more investigation.
It’s mainly a smart guess or suggested answer to a problem that can be checked through study and trial. In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn’t support it.

Hypothesis Meaning
A hypothesis is a proposed statement that is testable and is given for something that happens or observed.
- It is made using what we already know and have seen, and it’s the basis for scientific research.
- A clear guess tells us what we think will happen in an experiment or study.
- It’s a testable clue that can be proven true or wrong with real-life facts and checking it out carefully.
- It usually looks like a “if-then” rule, showing the expected cause and effect relationship between what’s being studied.
Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
- Specific: It needs to be easy and on target, talking about a certain part or connection between things in a study.
- Falsifiable: A good guess should be able to show it’s wrong. This means there must be a chance for proof or seeing something that goes against the guess.
- Logical and Rational: It should be based on things we know now or have seen, giving a reasonable reason that fits with what we already know.
- Predictive: A guess often tells what to expect from an experiment or observation. It gives a guide for what someone might see if the guess is right.
- Concise: It should be short and clear, showing the suggested link or explanation simply without extra confusion.
- Grounded in Research: A guess is usually made from before studies, ideas or watching things. It comes from a deep understanding of what is already known in that area.
- Flexible: A guess helps in the research but it needs to change or fix when new information comes up.
- Relevant: It should be related to the question or problem being studied, helping to direct what the research is about.
- Empirical: Hypotheses come from observations and can be tested using methods based on real-world experiences.
Hypotheses can come from different places based on what you’re studying and the kind of research. Here are some common sources from which hypotheses may originate:
- Existing Theories: Often, guesses come from well-known science ideas. These ideas may show connections between things or occurrences that scientists can look into more.
- Observation and Experience: Watching something happen or having personal experiences can lead to guesses. We notice odd things or repeat events in everyday life and experiments. This can make us think of guesses called hypotheses.
- Previous Research: Using old studies or discoveries can help come up with new ideas. Scientists might try to expand or question current findings, making guesses that further study old results.
- Literature Review: Looking at books and research in a subject can help make guesses. Noticing missing parts or mismatches in previous studies might make researchers think up guesses to deal with these spots.
- Problem Statement or Research Question: Often, ideas come from questions or problems in the study. Making clear what needs to be looked into can help create ideas that tackle certain parts of the issue.
- Analogies or Comparisons: Making comparisons between similar things or finding connections from related areas can lead to theories. Understanding from other fields could create new guesses in a different situation.
- Hunches and Speculation: Sometimes, scientists might get a gut feeling or make guesses that help create ideas to test. Though these may not have proof at first, they can be a beginning for looking deeper.
- Technology and Innovations: New technology or tools might make guesses by letting us look at things that were hard to study before.
- Personal Interest and Curiosity: People’s curiosity and personal interests in a topic can help create guesses. Scientists could make guesses based on their own likes or love for a subject.
Here are some common types of hypotheses:
Simple Hypothesis
Complex hypothesis, directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (H0)
Alternative hypothesis (h1 or ha), statistical hypothesis, research hypothesis, associative hypothesis, causal hypothesis.
Simple Hypothesis guesses a connection between two things. It says that there is a connection or difference between variables, but it doesn’t tell us which way the relationship goes. Example: Studying more can help you do better on tests. Getting more sun makes people have higher amounts of vitamin D.
Complex Hypothesis tells us what will happen when more than two things are connected. It looks at how different things interact and may be linked together. Example: How rich you are, how easy it is to get education and healthcare greatly affects the number of years people live. A new medicine’s success relies on the amount used, how old a person is who takes it and their genes.
Directional Hypothesis says how one thing is related to another. For example, it guesses that one thing will help or hurt another thing. Example: Drinking more sweet drinks is linked to a higher body weight score. Too much stress makes people less productive at work.
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non-Directional Hypothesis are the one that don’t say how the relationship between things will be. They just say that there is a connection, without telling which way it goes. Example: Drinking caffeine can affect how well you sleep. People often like different kinds of music based on their gender.
Null hypothesis is a statement that says there’s no connection or difference between different things. It implies that any seen impacts are because of luck or random changes in the information. Example: The average test scores of Group A and Group B are not much different. There is no connection between using a certain fertilizer and how much it helps crops grow.
Alternative Hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis and shows that there’s a big connection or gap between variables. Scientists want to say no to the null hypothesis and choose the alternative one. Example: Patients on Diet A have much different cholesterol levels than those following Diet B. Exposure to a certain type of light can change how plants grow compared to normal sunlight.
Statistical Hypothesis are used in math testing and include making ideas about what groups or bits of them look like. You aim to get information or test certain things using these top-level, common words only. Example: The average smarts score of kids in a certain school area is 100. The usual time it takes to finish a job using Method A is the same as with Method B.
Research Hypothesis comes from the research question and tells what link is expected between things or factors. It leads the study and chooses where to look more closely. Example: Having more kids go to early learning classes helps them do better in school when they get older. Using specific ways of talking affects how much customers get involved in marketing activities.
Associative Hypothesis guesses that there is a link or connection between things without really saying it caused them. It means that when one thing changes, it is connected to another thing changing. Example: Regular exercise helps to lower the chances of heart disease. Going to school more can help people make more money.
Causal Hypothesis are different from other ideas because they say that one thing causes another. This means there’s a cause and effect relationship between variables involved in the situation. They say that when one thing changes, it directly makes another thing change. Example: Playing violent video games makes teens more likely to act aggressively. Less clean air directly impacts breathing health in city populations.
Hypotheses have many important jobs in the process of scientific research. Here are the key functions of hypotheses:
- Guiding Research: Hypotheses give a clear and exact way for research. They act like guides, showing the predicted connections or results that scientists want to study.
- Formulating Research Questions: Research questions often create guesses. They assist in changing big questions into particular, checkable things. They guide what the study should be focused on.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by saying what connections between variables should be found. They set the targets that scientists try to reach with their studies.
- Testing Predictions: Theories guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By doing tests in a planned way, scientists can check if what they see matches the guesses made by their ideas.
- Providing Structure: Theories give structure to the study process by arranging thoughts and ideas. They aid scientists in thinking about connections between things and plan experiments to match.
- Focusing Investigations: Hypotheses help scientists focus on certain parts of their study question by clearly saying what they expect links or results to be. This focus makes the study work better.
- Facilitating Communication: Theories help scientists talk to each other effectively. Clearly made guesses help scientists to tell others what they plan, how they will do it and the results expected. This explains things well with colleagues in a wide range of audiences.
- Generating Testable Statements: A good guess can be checked, which means it can be looked at carefully or tested by doing experiments. This feature makes sure that guesses add to the real information used in science knowledge.
- Promoting Objectivity: Guesses give a clear reason for study that helps guide the process while reducing personal bias. They motivate scientists to use facts and data as proofs or disprovals for their proposed answers.
- Driving Scientific Progress: Making, trying out and adjusting ideas is a cycle. Even if a guess is proven right or wrong, the information learned helps to grow knowledge in one specific area.
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Initiating Investigations: Hypotheses are the beginning of science research. They come from watching, knowing what’s already known or asking questions. This makes scientists make certain explanations that need to be checked with tests.
- Formulating Research Questions: Ideas usually come from bigger questions in study. They help scientists make these questions more exact and testable, guiding the study’s main point.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by stating what we think will happen between different things. They set the goals that scientists want to reach by doing their studies.
- Designing Experiments and Studies: Assumptions help plan experiments and watchful studies. They assist scientists in knowing what factors to measure, the techniques they will use and gather data for a proposed reason.
- Testing Predictions: Ideas guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By checking these guesses carefully, scientists can see if the seen results match up with what was predicted in each hypothesis.
- Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Hypotheses give us a way to study and make sense of information. Researchers look at what they found and see if it matches the guesses made in their theories. They decide if the proof backs up or disagrees with these suggested reasons why things are happening as expected.
- Encouraging Objectivity: Hypotheses help make things fair by making sure scientists use facts and information to either agree or disagree with their suggested reasons. They lessen personal preferences by needing proof from experience.
- Iterative Process: People either agree or disagree with guesses, but they still help the ongoing process of science. Findings from testing ideas make us ask new questions, improve those ideas and do more tests. It keeps going on in the work of science to keep learning things.
People Also View:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Branches of Mathematics
Hypothesis is a testable statement serving as an initial explanation for phenomena, based on observations, theories, or existing knowledge . It acts as a guiding light for scientific research, proposing potential relationships between variables that can be empirically tested through experiments and observations.
The hypothesis must be specific, testable, falsifiable, and grounded in prior research or observation, laying out a predictive, if-then scenario that details a cause-and-effect relationship. It originates from various sources including existing theories, observations, previous research, and even personal curiosity, leading to different types, such as simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and alternative hypotheses, each serving distinct roles in research methodology .
The hypothesis not only guides the research process by shaping objectives and designing experiments but also facilitates objective analysis and interpretation of data , ultimately driving scientific progress through a cycle of testing, validation, and refinement.
Hypothesis – FAQs
What is a hypothesis.
A guess is a possible explanation or forecast that can be checked by doing research and experiments.
What are Components of a Hypothesis?
The components of a Hypothesis are Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Relationship between Variables, Directionality etc.
What makes a Good Hypothesis?
Testability, Falsifiability, Clarity and Precision, Relevance are some parameters that makes a Good Hypothesis
Can a Hypothesis be Proven True?
You cannot prove conclusively that most hypotheses are true because it’s generally impossible to examine all possible cases for exceptions that would disprove them.
How are Hypotheses Tested?
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data
Can Hypotheses change during Research?
Yes, you can change or improve your ideas based on new information discovered during the research process.
What is the Role of a Hypothesis in Scientific Research?
Hypotheses are used to support scientific research and bring about advancements in knowledge.

Similar Reads
- Geeks Premier League
- School Learning
- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Maths-Class-12
Please Login to comment...
- Top Language Learning Apps in 2024
- Top 20 Free VPN for iPhone in 2024: October Top Picks
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
| ( ) | ||
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person does not differ between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in the textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has on exam scores. | : There is no relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β = 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression.* | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is greater than or equal to the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; ≥ . |
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has an on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person differs between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in a textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has an on exam scores. | : There is a relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β ≠ 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression. | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is less than the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; < . |
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
| A claim that there is in the population. | A claim that there is in the population. | |
|
| ||
| Equality symbol (=, ≥, or ≤) | Inequality symbol (≠, <, or >) | |
| Rejected | Supported | |
| Failed to reject | Not supported |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
| ( ) | ||
| test
with two groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable differs between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| with three groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable of group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) are not all equal in the population. |
| There is no correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ = 0. | There is a correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ ≠ 0. | |
| There is no relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β = 0. | There is a relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β ≠ 0. | |
| Two-proportions test | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion does not differ between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; = . | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion differs between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; ≠ . |
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.
Clinical Research Network
The NIHR Clinical Research Network (CRN) supports patients, the public and health and care organisations across England to participate in high-quality research, thereby advancing knowledge and improving care. The CRN supports research being delivered through 30 specialty therapy areas and 15 Local Clinical Research Networks . These provide a network of research expertise and clinical leadership to deliver research studies on the NIHR CRN Portfolio of studies . Find out more about our performance and key statistics relating to our activity.
From April 2024, the CRN will transition to a new organisation, the NIHR Research Delivery Network (RDN).
Research Delivery Network
The NIHR RDN is being established to support the delivery of high quality research that enables the best care for our population. The new organisation will build on the success of the CRN to support the country's world-class research system to deliver for the future.
The RDN will operate as one organisation across England and will play a critical and active role in implementing government policy, including:
- the Life Sciences Vision
- the Future of UK Clinical Research Delivery vision
- policy for life sciences research and development
- responding to the findings of the Lord O'Shaughnessy review
The RDN will support:
- clinical trials and other well-designed health and social care research studies (including studies that are delivered outside of an NHS setting)
- public health studies that require the recruitment of individuals within an NHS setting - this may include acute, ambulance, mental health, community or primary care
Growing the amount of commercial clinical research will be a key strategic ambition for the new network. The RDN will play a critical role in supporting the implementation of the Government's response to the Lord O'Shaughnessy report, which set out a clear blueprint for how the UK can return to its global leadership role in the support of commercial clinical trials and world-class research.
How will the RDN work in a different way to the CRN?
- The RDN will operate as one organisation across England. The RDN will have a shared vision and purpose, delivering a consistent experience for the research and healthcare communities. Innovations in one region will be shared and replicated across the country. It will be rooted in the local experience and needs of the research system and the populations it serves.
- The 12 Regional Research Delivery Networks will work as one with the Coordinating Centre and the Department of Health and Social Care to deliver a consistent, high quality and responsive service. The RDN will draw strength from its collaborative leadership model, with joint leadership composed from regional leaders, Coordinating Centre and DHSC colleagues. Regional context, expertise and relationships will enhance the quality of national decision making, leadership and coordination.
- The RDN will provide a range of services and support for research delivery, listening and addressing the needs of customers and working in collaboration with R&D teams. It will also support research sites with recruitment resources, tools to support research delivery, analysis and advice, and workforce development.
- The RDN will develop the strategic capacity and capability of the research system. The work of the RDN will build capacity for delivery partners to conduct research, with more researchers, sites, studies and participants involved in research. It will continue to bring research to under-served regions and communities with major health and care needs, considering the need for research inclusion and for the benefits of research to be spread across the whole country.
- The RDN will continuously learn and adapt to the changing domestic and global environment for health and care, life sciences and health research. It will work in collaboration with partners across UK health and care research to help drive improved efficiency across the system.
Regional Research Delivery Networks
NIHR Regional Research Delivery Networks (RRDNs) will develop excellent relationships with organisations commissioning and providing health and social care across their regions. They will help support research and promote the value of research in meeting the needs of local populations.

The NIHR RRDN map (pictured above) shows the geography of the 12 RRDNs that will make up the NIHR RDN from October 2024. These 12 RRDNs and their host organisations are listed below:
- North East and North Cumbria - hosted by The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust- Morag Burton, Director
- Yorkshire and Humber - hosted by Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust- Amber O'Malley, Director
- North West- hosted by Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust- Andy Ustianowski, Director
- East Midlands - hosted by University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust- Elizabeth Moss, Director
- West Midlands - hosted by The Royal Wolverhampton NHS Trust- Matt Brookes, Director
- East of England - hosted by Norfolk and Norwich University NHS Foundation Trust- Helen Macdonald, Director
- North London - hosted by Barts Health NHS Trust- Sharon Barrett, Director
- South London - hosted by Guy's & St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust- James Lyddiard, Director
- South Central - hosted by University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust- Clare Rook, Director
- South East - hosted by Royal Surrey NHS Foundation Trust- Stephen Barnett, Director
- South West Central - hosted by University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust- Kyla Thomas, Director
- South West Peninsula - hosted by Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust- To be announced
The RDN Coordinating Centre will be hosted by the University of Leeds.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
According to the definition, the hypothesis is an assumption about the relationship between the objects of study. Since statistics is a field of research, the hypothesis is a predictive statement that can be tested empirically. 3. Facilitates Testability and Empirical Investigation.
What they need at the start of their research is to formulate a scientific hypothesis that revisits conventional theories, real-world processes, and related evidence to propose new studies and test ideas in an ethical way.3 Such a hypothesis can be of most benefit if published in an ethical journal with wide visibility and exposure to relevant ...
Definition of a Hypothesis. A hypothesis is a prediction of what will be found at the outcome of a research project and is typically focused on the relationship between two different variables studied in the research. It is usually based on both theoretical expectations about how things work and already existing scientific evidence.
William Harvey's research on circulation in animals demonstrates how greatly experimental observation can be helped by a fruitful hypothesis. While a hypothesis can be partially confirmed by showing that what is deduced from it with certain initial conditions is actually found under those conditions, it cannot be completely proved in this way ...
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question. A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on ...
HYPOTHESIS TESTING. A clinical trial begins with an assumption or belief, and then proceeds to either prove or disprove this assumption. In statistical terms, this belief or assumption is known as a hypothesis. Counterintuitively, what the researcher believes in (or is trying to prove) is called the "alternate" hypothesis, and the opposite ...
3 Define your variables. Once you have an idea of what your hypothesis will be, select which variables are independent and which are dependent. Remember that independent variables can only be factors that you have absolute control over, so consider the limits of your experiment before finalizing your hypothesis.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
The meaning of HYPOTHESIS is an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. How to use hypothesis in a sentence. The Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory Synonym Discussion of Hypothesis.
Your hypothesis is what you propose to "prove" by your research. As a result of your research, you will arrive at a conclusion, a theory, or understanding that will be useful or applicable beyond the research itself. 3. Avoid judgmental words in your hypothesis. Value judgments are subjective and are not appropriate for a hypothesis.
Related: Theory vs. Hypothesis: Differences, Definition and Types Types of research hypotheses A scientific hypothesis must be about something that you can prove or disprove through experimentation or observation. This means that hypotheses require extensive research and controlling dependent and independent variables.
A hypothesis helps define the direction of the study and provides a framework for data collection and analysis. The Importance of a Hypothesis. A hypothesis is central to the research process for several reasons: Focuses the Study: By making a specific prediction, the hypothesis narrows the focus of the research. Instead of exploring a broad ...
A hypothesis is a statement of the researcher's expectation or prediction about relationship among study variables. The research process begins and ends with the hypothesis. It is core to the ...
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
Hypothesis is a hypothesis is fundamental concept in the world of research and statistics. It is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that ...
The null hypothesis (H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis (Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the population.". The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That's because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample.
The CRN supports research being delivered through 30 specialty therapy areas and 15 Local Clinical Research Networks. These provide a network of research expertise and clinical leadership to deliver research studies on the NIHR CRN Portfolio of studies. Find out more about our performance and key statistics relating to our activity.