Is MasterClass right for me?
Take this quiz to find out.

What Is a Narrative Essay? Learn How to Write A Narrative Essay With Tips and Examples
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Sep 22, 2021 • 5 min read
Not every form of essay writing involves meticulous research. One form in particular—the narrative essay—combines personal storytelling with academic argument. Narrative essay authors illustrate universal lessons in their unique experiences of the world. Below, you’ll find some tips to guide in this style of narrative writing.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
Narrative essays make an argument or impart a lesson through personal experience.
- Narrative essays are always non-fiction and usually autobiographical.
- They are written with a more creative style versus the strictly objective, fact-based language of academic writing or journalism.
- Narrative essays are often part of the coursework in high school and during college admissions.


Library Updates and News
Get the latest information | upcoming events, english research: narrative essay, narrative essay.
- Expository Essay
- Analysis paper
- Persuasive Essay
- Your Research Question
- Find Background Information
- Find Sources
- Read and Evaluate
- Write and Cite
- Subject Library Instruction Survey
WHAT IS A NARRATIVE ESSAY?
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Example of a narrative essay
This type of essay is focused on your life and experiences. This task gives you a certain advantage since you can speak from your point of view and tell about things that actually happened to you. On the other hand, it’s not an easy task, since you need to shorten all your emotions and claims into a brief essay form, which usually consists of only five paragraphs. You need to highlight the most important moments and don’t focus on unnecessary details. Even though it’s an essay about yourself, make sure that you don’t sound self-centered. Think about what would be interesting for your readers and what is really worth sharing with others.
First of all, your essay must highlight the following things:
- Your challenges,
- Your talents,
- Your interests,
- Your background,
- Your important achievements,
- Interesting things about who you are.
We decided to tell you the key features of writing an autobiographical essay, so you could understand what rules to follow. We suggest you adhere to the following sequence of actions:
- Brainstorm and find the best ideas;
- Introduce yourself to readers;
- Write the body part;
- Make conclusions;
- Check and polish your essay.
Choose the Most Interesting and Important Information
If you have no ideas about what exactly to write about, we suggest you take the time and brainstorm. Write down all things you consider important about yourself: your achievements, experiences, skills, and everything that you like. Don’t forget that your essay should be remembered by readers, so it should be different from any other paper that they will read. This thing is of key significance, especially for those who write a narrative essay for an admission committee.
Try to impress your readers from the very first words. To help you with it, we collected some good topics.
Examples of the Best Topics
- The most difficult choice in your life;
- Your experience between life and death;
- What you’d like to change about yourself;
- The most important moment in your life;
- Your biggest loss ever.
For this essay type, we suggest you stay away from controversial issues, such as:
Introduce Yourself
Try to avoid too obvious descriptions, such as “My name is Joe, I was born in the A and then moved to the B, and the most important moment in my life is…” Use your creativity; find a more interesting way to introduce yourself.
For example, write “I was born after my father came back from the army… There was an unexpected moment that changed my whole life…”
Writing in this manner, you’ll get readers’ attention and make them want to continue reading your essay.
The Body Part
Here you need to describe your experience, interests, or background in more detail. Try to not jump from one subject to another, because it makes your text hard to perceive, and you get a chance that readers will just stop reading your essay. Define your key points and write about them in a certain order. We suggest you pay special attention to transitions between paragraphs, to keep your text holistic and easy to read.
Summarize Your Essay
Every good essay includes a conclusion part. Define your key point, and what is most important about this story. Maybe you’ve learned something new or developed some new skills. Maybe this story pushed you to rethink your whole life. Explain how it happened and what you consider useful for others. One of the good approaches for you is a “so what?” method. Read your entire essay and ask yourself, “So what?” Usually, it’s easy to find the answer. Write your conclusions based on it.
Source: https://college-writers.com/narrative-essay-about-yourself/
Video on Narrative Essay
Newspaper Source Plus
- Newspaper Source Plus Provides the latest news from the leading national and international news sources.
- StudySC Know where you live. Explore South Carolina through StudySC! Learn about your community, South Carolina history, and the people who have made a significant impact on the state and the world.
- National Public Radio
- The New York Times
ProQuest Research Library
- ProQuest Research Library A collection of database modules that contain full-text journal and newspaper articles about art, business, children, education, health, humanities, law, military, science, psychology, social science, women´s interest, etc.
CultureGrams
- CultureGrams Country reports that provide snapshots of the world’s cultures.
The State Paper
- The State Newspaper
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Expository Essay >>
- Last Updated: Oct 17, 2023 3:37 PM
- URL: https://scsu.libguides.com/English
Telephone (803) 536-8640 Fax: (803) 536-8902

Make a difference! Give to the libraries.
Stay Connected!
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Narrative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a narrative essay?
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay.
- If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a story.
This means that you must include an introduction, plot, characters, setting, climax, and conclusion.
- When would a narrative essay not be written as a story?
A good example of this is when an instructor asks a student to write a book report. Obviously, this would not necessarily follow the pattern of a story and would focus on providing an informative narrative for the reader.
- The essay should have a purpose.
Make a point! Think of this as the thesis of your story. If there is no point to what you are narrating, why narrate it at all?
- The essay should be written from a clear point of view.
It is quite common for narrative essays to be written from the standpoint of the author; however, this is not the sole perspective to be considered. Creativity in narrative essays oftentimes manifests itself in the form of authorial perspective.
- Use clear and concise language throughout the essay.
Much like the descriptive essay, narrative essays are effective when the language is carefully, particularly, and artfully chosen. Use specific language to evoke specific emotions and senses in the reader.
- The use of the first person pronoun ‘I’ is welcomed.
Do not abuse this guideline! Though it is welcomed it is not necessary—nor should it be overused for lack of clearer diction.
- As always, be organized!
Have a clear introduction that sets the tone for the remainder of the essay. Do not leave the reader guessing about the purpose of your narrative. Remember, you are in control of the essay, so guide it where you desire (just make sure your audience can follow your lead).
- How it works

How to Write a Narrative Essay
Published by Grace Graffin at August 17th, 2021 , Revised On July 26, 2023
What is a Narrative Essay?
“Narrative essays let the authors account for their personal experiences in the form of a story.”
Unlike most other essay types , you can let your creativity and ideas flow freely in a narrative essay, although it should still be factual. They are a common assignment in high schools, colleges, and universities.
While you are certainly free to rely upon your imagination to express personal experiences in a narrative essay, it is equally important to follow the suitable narrative essay structure and format. Here are some strategies to write a narrative essay that would surely hook your audience.
Why Should I Write a Narrative Essay?
When assigned a narrative essay, many students are unsure about why they have been asked to write a narrative essay and of the significance of storytelling in academic writing. While the topic of a narrative essay can range from the most important to the most insignificant, it is not the topic but how you tell a story that will be evaluated.
This is partly because much of the writing discipline will be in containing what could be a detailed or complex story within a tight word limit.
You will achieve a higher grade in your narrative essay assignment if you follow a logical structure and tell your story clearly and intriguingly. Decide where your story must start and end and how you can get your thoughts across to the readers smoothly without losing the plot.
This writing style is very different from other forms of academic writing. Narrative essay writing involves the use of suspense, conversation, metaphorical language, and the use of first-person (’I’). It is possible to write about what happened to someone else, in which case you would use the third-person point of view (using ‘he’, ‘she’, and ‘they’ ).
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Essay
You could receive extensive, moderate, or even very little guidance about the topic for your narrative essay assignment. If you get very little, then you will be required to find a topic to work with.
The topic you are assigned will be either specific or open-ended.
Examples of a specific topic
- Write a story about your most notable achievement at college.
- Write about your interactive experiences on your final day at university.
Examples of an open-ended topic
- Reflect upon an experience where you learned from your mistake.
- Write about a professional achievement you are proud of. How did it help you excel in your career?
Think about the story you want to tell. It is best to use a story that encompasses a surprise, a lesson, or a particular theme, so you can keep the readers interested throughout the essay.
For example , if you talk about an achievement that encompasses a twist or a challenge that you had to overcome, it will be far more engaging than a story where everything went according to plan. Narrate an experience that would end in a lesson for the readers.
Stuck on a difficult essay? We can help!
Our Essay Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

Writing a Narrative Essay for a College Application
Most colleges require candidates to submit a narrative essay describing their achievements or ambitions , along with their admission application.
College Application Topic Example
Please submit a one-page, single-spaced essay that describes why you have chosen to apply to Oxford University.
For a narrative essay for college application, think about a story or an experience that would enable you to express the qualities and achievements desired by the college you are applying to. For example , you could talk about your proven ability to learn from your mistakes, your calculated approach, and your love for the subject you wish to study.
Narrative Essay Structure
A narrative essay should follow an appropriate academic structure, even though it will be based on an experience from your life. Like other essay types , a narrative essay comprises an introduction paragraph , the main body , and a conclusion paragraph.
Narrative Essay Introduction
The introduction paragraph should start with the background statement to explain why the topic is essential to you. The last sentence of the paragraph introduces the theme of the essay.
Narrative Essay Main Body
The main body is where you tell the story, develop the plot, and provide facts and details of the experience you are talking about. Make sure to include all the points in a clear and exciting way. When did it happen? Who was involved? What was at stake? Staying true to your feelings and using appropriate transition words is the key to telling an interesting story.
Four points you should consider following in the narrative main body:
- Include lifelike and relevant detail : In the narrative essay, you present a scene and aim to share the experience with the reader. Include plenty of detail where necessary but do not waste your word count. Each sentence must advance or enhance the story.
- Use dialogue: The use of direct speech, that which is in quotation marks, makes events more real. Use it where most effective; if you use it too much, or include long monologues, it will lose its effect.
- Apply chronological order: Tell the story as it happened. This aids clarity and ease of understanding. It is better if your readers read it twice because they enjoyed it, not because they could not understand it.
- Focus on the story only: Keep checking as you write that everything you say relates to the story. It is easy to deviate, and doing so also takes away the reader’s attention.
It is important to note what is not included in the narrative essay main body; you will not be making any arguments , criticising, or trying to persuade your readers in any way. It is also unlikely that you will be required to quote other works and cite them.
Narrative Essay Conclusion
The concluding paragraph should link back to the background statement and the main theme of your essay, you can also restate some important points mentioned in the body here. The conclusion should emphasise how your experience helped you or others involved to attain an improved overall understanding of the situation.
Want to know what essay structure and style will work best for your assignment?
Problem fixed! We can write any type of essay in any referencing style. We ensure every essay written is beyond your expectations.

Example of a Narrative Essay
Here is an example of a narrative essay that explains “why you have chosen to apply to Oxford University.”
Important: Our essay writing help get better results for the students who use ResearchProspect’s professional service; along with using writing service, you can also learn to write an impressive piece of your own.
What is the difference between a descriptive and a narrative essay?
A descriptive essay provides an extensive description of a particular place, object, topic, or idea. On the other hand, a narrative essay is used to tell a complete story of a personal experience. However, both narrative and descriptive essays allow the authors to use their creativity and personal reflections. Other types of essays do not permit this style of writing.
How long is a narrative essay?
Narrative essays are generally 800-1000 words long. The length of your narrative essay depends on who you are writing the essay for. For example, the high school narrative essay will be shorter than a college application narrative essay.
When should I write a narrative essay?
Narrative essays are assigned to students to evaluate their creative storytelling skills in high schools, colleges, and universities. They may also form part of a college application. When you are asked to reflect upon your personal experiences in the form of a story, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
How to choose a suitable topic for my narrative essay?
If you have not been given direction on what the topic of your narrative essay should be, think about the scope and background of the task. Choose to tell a story that is relevant to the audience. A story that includes a lesson, a surprise, or a particular theme is the best kind of story for a narrative essay. You can build your story around any experience that made you a better person or taught you a valuable lesson.
You May Also Like
The length of an academic essay depends on your level and the nature of subject. If you are unsure how long is an essay then this article will guide you.
The following article will discuss the five elements that are essential to report writing. These components should be considered when beginning any report.
This article explains the important conceptions of rhetorical writing and provides tips on writing a first-class rhetorical analysis essay.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
Have a question?
Try our Ask a Librarian service. Chat with a librarian 24/7, take a look at our FAQs,or send us a message.

- Hampton: (757) 825-2877 | Historic Triangle: (757) 258-6500
- Virginia Peninsula Community College Library and Learning Resources
- Research Guides
- Library Services
Writing Center
Narrative essays.
- Argumentative Essays
- Descriptive Essays
- Expository Essays
- Citation Guide
- Other Helpful Links
How to Write a Narrative Essay
- Narrative Essay Structure A handout that goes over how to write a narrative essay to help you outline and write your narrative essay.
- Writing Narrative Essays From the Excelsior Writing Lab, here is an overview of narrative essays with some writing tips.
- << Previous: Expository Essays
- Next: Citation Guide >>
Hampton Campus
- (757) 825-2700
- 99 Thomas Nelson Drive
- Hampton, VA 23666
Historic Triangle campus
- (757) 253-4300
- 4601 Opportunity Way
- Williamsburg, VA 23188
ACADEMIC INFORMATION
- Accreditation
- College Catalog
- Class Schedule
- Programs of Study
COLLEGE INFORMATION
- For the Media
- Information & Accessibility
- Non-Discrimination
- Policy & Consumer Information
- Privacy Policy
- Virginia Freedom of Information Act
- Join our Mailing List
- Explore our Programs
- Request Info
SAFETY INFORMATION
- Safety at Virginia Peninsula Community College
- Closings & Emergency Information
- e2Campus Text Alerts

Virginia Peninsula Community College is one of Virginia's Community Colleges , primarily serving the cities of Hampton, Newport News, Poquoson and Williamsburg, and the counties of James City and York.
- Last Update: Aug 19, 2024 2:01 PM
- URL: https://guides.vpcc.edu/writingcenter

What is a Narrative Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)

Narrative essays are a type of storytelling in which writers weave a personal experience into words to create a fascinating and engaging narrative for readers. A narrative essay explains a story from the author’s point of view to share a lesson or memory with the reader. Narrative essays, like descriptive essays , employ figurative language to depict the subject in a vivid and creative manner to leave a lasting impact on the readers’ minds. In this article, we explore the definition of narrative essays, list the key elements to be included, and provide tips on how to craft a narrative that captivates your audience.
Table of Contents
What is a narrative essay, choosing narrative essay topics, key elements in a narrative essay, creating a narrative essay outline, types of narrative essays, the pre-writing stage, the writing stage, the editing stage, narrative essay example, frequently asked questions.
Narrative essays are often based on one’s personal experience which allows the author to express himself/herself in compelling ways for the reader. They employ storytelling elements to convey the plot and captivate the reader while disclosing the story’s theme or purpose. The author must always have a purpose or theme in mind when writing a narrative essay. These essays may be assigned to high school students to assess their ability to create captivating stories based on personal experiences, or they may be required as part of a college application to assess the applicant’s personal traits. Narrative essays might be based on true events with minor tweaks for dramatic purposes, or they can be adapted from a fictional scenario. Whatever the case maybe, the goal is to tell a story, a good story!
In narrative essays, the emphasis is not so much on the narrative itself as it is on how you explain it. Narrative essay topics cover a range of experiences, from noteworthy to mundane, but when storytelling elements are used well, even a simple account can have weight. Notably, the skills required for narrative writing differ significantly from those needed for formal academic essays, and we will delve deeper into this in the next section.
You can talk about any narrative, but consider whether it is fascinating enough, has enough twists and turns, or teaches a lesson (It’s a plus if the story contains an unexpected twist at the end). The potential topics for a narrative essay are limitless—a triumphant story, a brief moment of introspection, or a voyage of self-discovery. These essays provide writers with the opportunity to share a fragment of their lives with the audience, enriching both the writer’s and the reader’s experiences. Narrative essay examples could be a write-up on “What has been your biggest achievement in life so far and what did it teach you?” or “Describe your toughest experience and how you dealt with it?”.

While narrative essays allow you to be creative with your ideas, language, and format, they must include some key components to convey the story clearly, create engaging content and build reader interest. Follow these guidelines when drafting your essay:
- Tell your story using the first person to engage users.
- Use sufficient sensory information and figurative language.
- Follow an organized framework so the story flows chronologically.
- Include interesting plot components that add to the narrative.
- Ensure clear language without grammar, spelling, or word choice errors.
Narrative essay outlines serve as the foundational structure for essay composition, acting as a framework to organize thoughts and ideas prior to the writing process. These outlines provide writers with a means to summarize the story, and help in formulating the introduction and conclusion sections and defining the narrative’s trajectory.
Unlike conventional essays that strictly adhere to the five-paragraph structure, narrative essays allow for more flexibility as the organization is dictated by the flow of the story. The outline typically encompasses general details about the events, granting writers the option to prioritize writing the body sections first while deferring the introduction until later stages of the writing process. This approach allows for a more organic and fluid writing process. If you’re wondering how to start writing a narrative essay outline, here is a sample designed to ensure a compelling and coherent narrative:
Introduction
- Hook/Opening line: The introduction should have an opening/hook sentence that is a captivating quote, question, or anecdote that grabs the reader’s attention.
- Background: Briefly introduce the setting, time, tone, and main characters.
- Thesis statement: State clearly the main theme or lesson acquired from the experience.
- Event 1 (according to occurrence): Describe the first major event in detail. Introduce the primary characters and set the story context; include sensory elements to enrich the narrative and give the characters depth and enthusiasm.
- Event 2: Ensure a smooth transition from one event to the next. Continue with the second event in the narrative. For more oomph, use suspense or excitement, or leave the plot with cliffhanger endings. Concentrate on developing your characters and their relationships, using dialog to bring the story to life.
- Event 3: If there was a twist and suspense, this episode should introduce the climax or resolve the story. Keep the narrative flowing by connecting events logically and conveying the feelings and reactions of the characters.
- Summarize the plot: Provide a concise recap of the main events within the narrative essay. Highlight the key moments that contribute to the development of the storyline. Offer personal reflections on the significance of the experiences shared, emphasizing the lasting impact they had on the narrator. End the story with a clincher; a powerful and thought-provoking sentence that encapsulates the essence of the narrative. As a bonus, aim to leave the reader with a memorable statement or quote that enhances the overall impact of the narrative. This should linger in the reader’s mind, providing a satisfying and resonant conclusion to the essay.
There are several types of narrative essays, each with their own unique traits. Some narrative essay examples are presented in the table below.
| Narrative essay type | Features | |
| 1. | Personal | Based on personal experience, insight, reflection, and emotion |
| 2. | Autobiographical | Covers life events, full length |
| 3. | Descriptive | Emphasizes detailed description for reader immersion |
| 4. | Experiential | Based on a specific experience, involving emotional responses |
| 5. | Historical | Focuses on historical events, non-fictional, facts stated using figurative language |
| 6. | Biographical | Explores an individual’s life, personality, achievements, and challenges |
| 7. | Travel | Chronicles experiences and thoughtful observations during a journey |
| 8. | Literary | Analyzes or interprets literature, includes a narrative element |
How to write a narrative essay: Step-by-step guide
A narrative essay might be inspired by personal experiences, stories, or even imaginary scenarios that resonate with readers, immersing them in the imaginative world you have created with your words. Here’s an easy step-by-step guide on how to write a narrative essay.
- Select the topic of your narrative
If no prompt is provided, the first step is to choose a topic to write about. Think about personal experiences that could be given an interesting twist. Readers are more likely to like a tale if it contains aspects of humor, surprising twists, and an out-of-the-box climax. Try to plan out such subjects and consider whether you have enough information on the topic and whether it meets the criteria of being funny/inspiring, with nice characters/plot lines, and an exciting climax. Also consider the tone as well as any stylistic features (such as metaphors or foreshadowing) to be used. While these stylistic choices can be changed later, sketching these ideas early on helps you give your essay a direction to start.
- Create a framework for your essay
Once you have decided on your topic, create an outline for your narrative essay. An outline is a framework that guides your ideas while you write your narrative essay to keep you on track. It can help with smooth transitions between sections when you are stuck and don’t know how to continue the story. It provides you with an anchor to attach and return to, reminding you of why you started in the first place and why the story matters.

- Compile your first draft
A perfect story and outline do not work until you start writing the draft and breathe life into it with your words. Use your newly constructed outline to sketch out distinct sections of your narrative essay while applying numerous linguistic methods at your disposal. Unlike academic essays, narrative essays allow artistic freedom and leeway for originality so don’t stop yourself from expressing your thoughts. However, take care not to overuse linguistic devices, it’s best to maintain a healthy balance to ensure readability and flow.
- Use a first-person point of view
One of the most appealing aspects of narrative essays is that traditional academic writing rules do not apply, and the narration is usually done in the first person. You can use first person pronouns such as I and me while narrating different scenarios. Be wary of overly using these as they can suggest lack of proper diction.
- Use storytelling or creative language
You can employ storytelling tactics and linguistic tools used in fiction or creative writing, such as metaphors, similes, and foreshadowing, to communicate various themes. The use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense is encouraged in narrative essays.
- Follow a format to stay organized
There’s no fixed format for narrative essays, but following a loose format when writing helps in organizing one’s thoughts. For example, in the introduction part, underline the importance of creating a narrative essay, and then reaffirm it in the concluding paragraph. Organize your story chronologically so that the reader can follow along and make sense of the story.
- Reread, revise, and edit
Proofreading and editing are critical components of creating a narrative essay, but it can be easy to become weighed down by the details at this stage. Taking a break from your manuscript before diving into the editing process is a wise practice. Stepping away for a day or two, or even just a few hours, provides valuable time to enhance the plot and address any grammatical issues that may need correction. This period of distance allows for a fresh perspective, enabling you to approach the editing phase with renewed clarity and a more discerning eye.
One suggestion is to reconsider the goals you set out to cover when you started the topic. Ask yourself these questions:
- Is there a distinct beginning and end to your story?
- Does your essay have a topic, a memory, or a lesson to teach?
- Does the tone of the essay match the intended mood?
Now, while keeping these things in mind, modify and proofread your essay. You can use online grammar checkers and paraphrase tools such as Paperpal to smooth out any rough spots before submitting it for publication or submission.
It is recommended to edit your essay in the order it was written; here are some useful tips:
- Revise the introduction
After crafting your narrative essay, review the introduction to ensure it harmonizes with the developed narrative. Confirm that it adeptly introduces the story and aligns seamlessly with the conclusion.
- Revise the conclusion and polish the essay
The conclusion should be the final element edited to ensure coherence and harmony in the entire narrative. It must reinforce the central theme or lesson outlined initially.
- Revise and refine the entire article
The last step involves refining the article for consistent tone, style, and tense as well as correct language, grammar, punctuation, and clarity. Seeking feedback from a mentor or colleague can offer an invaluable external perspective at this stage.
Narrative essays are true accounts of the writer’s personal experiences, conveyed in figurative language for sensory appeal. Some narrative essay topic examples include writing about an unforgettable experience, reflecting on mistakes, or achieving a goal. An example of a personal narrative essay is as follows:
Title: A Feline Odyssey: An Experience of Fostering Stray Kittens
Introduction:
It was a fine summer evening in the year 2022 when a soft meowing disrupted the tranquility of my terrace. Little did I know that this innocent symphony would lead to a heartwarming journey of compassion and companionship. Soon, there was a mama cat at my doorstep with four little kittens tucked behind her. They were the most unexpected visitors I had ever had.
The kittens, just fluffs of fur with barely open eyes, were a monument to life’s fragility. Their mother, a street-smart feline, had entrusted me with the care of her precious offspring. The responsibility was sudden and unexpected, yet there was an undeniable sense of purpose in the air , filling me with delight and enthusiasm.
As the days unfolded, my terrace transformed into a haven for the feline family. Cardboard boxes became makeshift cat shelters and my once solitary retreat was filled with purrs and soothing meows. The mother cat, Lily, who initially observ ed me from a safe distance, gradually began to trust my presence as I offered food and gentle strokes.
Fostering the kittens was a life-changing , enriching experience that taught me the true joy of giving as I cared for the felines. My problems slowly faded into the background as evenings were spent playing with the kittens. Sleepless nights turned into a symphony of contented purring, a lullaby filled with the warmth of trust and security . Although the kittens were identical, they grew up to have very distinct personalities, with Kuttu being the most curious and Bobo being the most coy . Every dawn ushered in a soothing ritual of nourishing these feline companions, while nights welcomed their playful antics — a daily nocturnal delight.
Conclusion:
As the kittens grew, so did the realization that our paths were destined to part. Finally, the day arrived when the feline family, now confident and self-reliant, bid farewell to my terrace. It was a bittersweet moment, filled with a sense of love and accomplishment and a tinge of sadness.
Fostering Kuttu, Coco, Lulu, and Bobo became one of the most transformative experiences of my life. Their arrival had brought unexpected joy, teaching me about compassion and our species’ ability to make a difference in the world through love and understanding. The terrace, once a quiet retreat, now bore the echoes of a feline symphony that had touched my heart in ways I could have never imagined.

The length of a narrative essay may vary, but it is typically a brief to moderate length piece. Generally, the essay contains an introductory paragraph, two to three body paragraphs (this number can vary), and a conclusion. The entire narrative essay could be as short as five paragraphs or much longer, depending on the assignment’s requirements or the writer’s preference.
You can write a narrative essay when you have a personal experience to share, or a story, or a series of events that you can tell in a creative and engaging way. Narrative essays are often assigned in academic settings as a form of writing that allows students to express themselves and showcase their storytelling skills. However, you can also write a narrative essay for personal reflection, entertainment, or to communicate a message.
A narrative essay usually follows a three-part structure: – Introduction (To set the stage for the story) – Body paragraphs (To describe sequence of events with details, descriptions, and dialogue) – Conclusion (To summarize the story and reflect on the significance)
Paperpal is an AI academic writing assistant that helps authors write better and faster with real-time writing suggestions and in-depth checks for language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of published scholarly articles and 20+ years of STM experience, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to Paperpal Copilot and premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks, submission readiness and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
Webinar: how to use generative ai tools ethically in your academic writing.
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Chemistry Terms: 7 Commonly Confused Words in Chemistry Manuscripts
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
What is a Descriptive Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)
You may also like, machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal....
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a narrative essay [Updated 2024]

A narrative essay is an opportunity to flex your creative muscles and craft a compelling story. In this blog post, we define what a narrative essay is and provide strategies and examples for writing one.
What is a narrative essay?
Similarly to a descriptive essay or a reflective essay, a narrative essay asks you to tell a story, rather than make an argument and present evidence. Most narrative essays describe a real, personal experience from your own life (for example, the story of your first big success).
Alternately, your narrative essay might focus on an imagined experience (for example, how your life would be if you had been born into different circumstances). While you don’t need to present a thesis statement or scholarly evidence, a narrative essay still needs to be well-structured and clearly organized so that the reader can follow your story.
When you might be asked to write a narrative essay
Although less popular than argumentative essays or expository essays, narrative essays are relatively common in high school and college writing classes.
The same techniques that you would use to write a college essay as part of a college or scholarship application are applicable to narrative essays, as well. In fact, the Common App that many students use to apply to multiple colleges asks you to submit a narrative essay.
How to choose a topic for a narrative essay
When you are asked to write a narrative essay, a topic may be assigned to you or you may be able to choose your own. With an assigned topic, the prompt will likely fall into one of two categories: specific or open-ended.
Examples of specific prompts:
- Write about the last vacation you took.
- Write about your final year of middle school.
Examples of open-ended prompts:
- Write about a time when you felt all hope was lost.
- Write about a brief, seemingly insignificant event that ended up having a big impact on your life.
A narrative essay tells a story and all good stories are centered on a conflict of some sort. Experiences with unexpected obstacles, twists, or turns make for much more compelling essays and reveal more about your character and views on life.
If you’re writing a narrative essay as part of an admissions application, remember that the people reviewing your essay will be looking at it to gain a sense of not just your writing ability, but who you are as a person.
In these cases, it’s wise to choose a topic and experience from your life that demonstrates the qualities that the prompt is looking for, such as resilience, perseverance, the ability to stay calm under pressure, etc.
It’s also important to remember that your choice of topic is just a starting point. Many students find that they arrive at new ideas and insights as they write their first draft, so the final form of your essay may have a different focus than the one you started with.
How to outline and format a narrative essay
Even though you’re not advancing an argument or proving a point of view, a narrative essay still needs to have a coherent structure. Your reader has to be able to follow you as you tell the story and to figure out the larger point that you’re making.
You’ll be evaluated on is your handling of the topic and how you structure your essay. Even though a narrative essay doesn’t use the same structure as other essay types, you should still sketch out a loose outline so you can tell your story in a clear and compelling way.
To outline a narrative essay, you’ll want to determine:
- how your story will start
- what points or specifics that you want to cover
- how your story will end
- what pace and tone you will use
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.” Also, most narrative essays will follow typical formatting guidelines, so you should choose a readable font like Times New Roman in size 11 or 12. Double-space your paragraphs and use 1” margins.
To get your creative wheels turning, consider how your story compares to archetypes and famous historical and literary figures both past and present. Weave these comparisons into your essay to improve the quality of your writing and connect your personal experience to a larger context.
How to write a narrative essay
Writing a narrative essay can sometimes be a challenge for students who typically write argumentative essays or research papers in a formal, objective style. To give you a better sense of how you can write a narrative essay, here is a short example of an essay in response to the prompt, “Write about an experience that challenged your view of yourself.”
Narrative essay example
Even as a child, I always had what people might call a reserved personality. It was sometimes framed as a positive (“Sarah is a good listener”) and at other times it was put in less-than-admiring terms (“Sarah is withdrawn and not very talkative”). It was the latter kind of comments that caused me to see my introverted nature as a drawback and as something I should work to eliminate. That is, until I joined my high school’s student council.
The first paragraph, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
The other four students making up the council were very outspoken and enthusiastic. I enjoyed being around them, and I often agreed with their ideas. However, when it came to overhauling our school’s recycling plan, we butted heads. When I spoke up and offered a different point of view, one of my fellow student council members launched into a speech, advocating for her point of view. As her voice filled the room, I couldn’t get a word in edgewise. I wondered if I should try to match her tone, volume, and assertiveness as a way to be heard. But I just couldn’t do it—it’s not my way, and it never has been. For a fleeting moment, I felt defeated. But then, something in me shifted.
In this paragraph, the writer goes into greater depth about how her existing thinking brought her to this point.
I reminded myself that my view was valid and deserved to be heard. So I waited. I let my fellow council member speak her piece and when she was finished, I deliberately waited a few moments before calmly stating my case. I chose my words well, and I spoke them succinctly. Just because I’m not a big talker doesn’t mean I’m not a big thinker. I thought of the quotation “still waters run deep” and I tried to embody that. The effect on the room was palpable. People listened. And I hadn’t had to shout my point to be heard.
This paragraph demonstrates the turn in the story, the moment when everything changed. The use of the quotation “still waters run deep” imbues the story with a dash of poetry and emotion.
We eventually reached a compromise on the matter and concluded the student council meeting. Our council supervisor came to me afterward and said: “You handled that so well, with such grace and poise. I was very impressed.” Her words in that moment changed me. I realized that a bombastic nature isn't necessarily a powerful one. There is power in quiet, too. This experience taught me to view my reserved personality not as a character flaw, but as a strength.
The final paragraph, or conclusion, closes with a statement about the significance of this event and how it ended up changing the writer in a meaningful way.
Narrative essay writing tips
1. pick a meaningful story that has a conflict and a clear “moral.”.
If you’re able to choose your own topic, pick a story that has meaning and that reveals how you became the person your are today. In other words, write a narrative with a clear “moral” that you can connect with your main points.
2. Use an outline to arrange the structure of your story and organize your main points.
Although a narrative essay is different from argumentative essays, it’s still beneficial to construct an outline so that your story is well-structured and organized. Note how you want to start and end your story, and what points you want to make to tie everything together.
3. Be clear, concise, concrete, and correct in your writing.
You should use descriptive writing in your narrative essay, but don’t overdo it. Use clear, concise, and correct language and grammar throughout. Additionally, make concrete points that reinforce the main idea of your narrative.
4. Ask a friend or family member to proofread your essay.
No matter what kind of writing you’re doing, you should always plan to proofread and revise. To ensure that your narrative essay is coherent and interesting, ask a friend or family member to read over your paper. This is especially important if your essay is responding to a prompt. It helps to have another person check to make sure that you’ve fully responded to the prompt or question.
Frequently Asked Questions about narrative essays
A narrative essay, like any essay, has three main parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Structuring and outlining your essay before you start writing will help you write a clear story that your readers can follow.
The first paragraph of your essay, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.”
The 4 main types of essays are the argumentative essay, narrative essay, exploratory essay, and expository essay. You may be asked to write different types of essays at different points in your education.
Most narrative essays will be around five paragraphs, or more, depending on the topic and requirements. Make sure to check in with your instructor about the guidelines for your essay. If you’re writing a narrative essay for a college application, pay close attention to word or page count requirements.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Narrative Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples
Narrative Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Narrative Analysis
Definition:
Narrative analysis is a qualitative research methodology that involves examining and interpreting the stories or narratives people tell in order to gain insights into the meanings, experiences, and perspectives that underlie them. Narrative analysis can be applied to various forms of communication, including written texts, oral interviews, and visual media.
In narrative analysis, researchers typically examine the structure, content, and context of the narratives they are studying, paying close attention to the language, themes, and symbols used by the storytellers. They may also look for patterns or recurring motifs within the narratives, and consider the cultural and social contexts in which they are situated.
Types of Narrative Analysis
Types of Narrative Analysis are as follows:
Content Analysis
This type of narrative analysis involves examining the content of a narrative in order to identify themes, motifs, and other patterns. Researchers may use coding schemes to identify specific themes or categories within the text, and then analyze how they are related to each other and to the overall narrative. Content analysis can be used to study various forms of communication, including written texts, oral interviews, and visual media.
Structural Analysis
This type of narrative analysis focuses on the formal structure of a narrative, including its plot, character development, and use of literary devices. Researchers may analyze the narrative arc, the relationship between the protagonist and antagonist, or the use of symbolism and metaphor. Structural analysis can be useful for understanding how a narrative is constructed and how it affects the reader or audience.
Discourse Analysis
This type of narrative analysis focuses on the language and discourse used in a narrative, including the social and cultural context in which it is situated. Researchers may analyze the use of specific words or phrases, the tone and style of the narrative, or the ways in which social and cultural norms are reflected in the narrative. Discourse analysis can be useful for understanding how narratives are influenced by larger social and cultural structures.
Phenomenological Analysis
This type of narrative analysis focuses on the subjective experience of the narrator, and how they interpret and make sense of their experiences. Researchers may analyze the language used to describe experiences, the emotions expressed in the narrative, or the ways in which the narrator constructs meaning from their experiences. Phenomenological analysis can be useful for understanding how people make sense of their own lives and experiences.
Critical Analysis
This type of narrative analysis involves examining the political, social, and ideological implications of a narrative, and questioning its underlying assumptions and values. Researchers may analyze the ways in which a narrative reflects or reinforces dominant power structures, or how it challenges or subverts those structures. Critical analysis can be useful for understanding the role that narratives play in shaping social and cultural norms.
Autoethnography
This type of narrative analysis involves using personal narratives to explore cultural experiences and identity formation. Researchers may use their own personal narratives to explore issues such as race, gender, or sexuality, and to understand how larger social and cultural structures shape individual experiences. Autoethnography can be useful for understanding how individuals negotiate and navigate complex cultural identities.
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying themes or patterns that emerge from the data, and then interpreting these themes in relation to the research question. Researchers may use a deductive approach, where they start with a pre-existing theoretical framework, or an inductive approach, where themes are generated from the data itself.
Narrative Analysis Conducting Guide
Here are some steps for conducting narrative analysis:
- Identify the research question: Narrative analysis begins with identifying the research question or topic of interest. Researchers may want to explore a particular social or cultural phenomenon, or gain a deeper understanding of a particular individual’s experience.
- Collect the narratives: Researchers then collect the narratives or stories that they will analyze. This can involve collecting written texts, conducting interviews, or analyzing visual media.
- Transcribe and code the narratives: Once the narratives have been collected, they are transcribed into a written format, and then coded in order to identify themes, motifs, or other patterns. Researchers may use a coding scheme that has been developed specifically for the study, or they may use an existing coding scheme.
- Analyze the narratives: Researchers then analyze the narratives, focusing on the themes, motifs, and other patterns that have emerged from the coding process. They may also analyze the formal structure of the narratives, the language used, and the social and cultural context in which they are situated.
- Interpret the findings: Finally, researchers interpret the findings of the narrative analysis, and draw conclusions about the meanings, experiences, and perspectives that underlie the narratives. They may use the findings to develop theories, make recommendations, or inform further research.
Applications of Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis is a versatile qualitative research method that has applications across a wide range of fields, including psychology, sociology, anthropology, literature, and history. Here are some examples of how narrative analysis can be used:
- Understanding individuals’ experiences: Narrative analysis can be used to gain a deeper understanding of individuals’ experiences, including their thoughts, feelings, and perspectives. For example, psychologists might use narrative analysis to explore the stories that individuals tell about their experiences with mental illness.
- Exploring cultural and social phenomena: Narrative analysis can also be used to explore cultural and social phenomena, such as gender, race, and identity. Sociologists might use narrative analysis to examine how individuals understand and experience their gender identity.
- Analyzing historical events: Narrative analysis can be used to analyze historical events, including those that have been recorded in literary texts or personal accounts. Historians might use narrative analysis to explore the stories of survivors of historical traumas, such as war or genocide.
- Examining media representations: Narrative analysis can be used to examine media representations of social and cultural phenomena, such as news stories, films, or television shows. Communication scholars might use narrative analysis to examine how news media represent different social groups.
- Developing interventions: Narrative analysis can be used to develop interventions to address social and cultural problems. For example, social workers might use narrative analysis to understand the experiences of individuals who have experienced domestic violence, and then use that knowledge to develop more effective interventions.
Examples of Narrative Analysis
Here are some examples of how narrative analysis has been used in research:
- Personal narratives of illness: Researchers have used narrative analysis to examine the personal narratives of individuals living with chronic illness, to understand how they make sense of their experiences and construct their identities.
- Oral histories: Historians have used narrative analysis to analyze oral histories to gain insights into individuals’ experiences of historical events and social movements.
- Children’s stories: Researchers have used narrative analysis to analyze children’s stories to understand how they understand and make sense of the world around them.
- Personal diaries : Researchers have used narrative analysis to examine personal diaries to gain insights into individuals’ experiences of significant life events, such as the loss of a loved one or the transition to adulthood.
- Memoirs : Researchers have used narrative analysis to analyze memoirs to understand how individuals construct their life stories and make sense of their experiences.
- Life histories : Researchers have used narrative analysis to examine life histories to gain insights into individuals’ experiences of migration, displacement, or social exclusion.
Purpose of Narrative Analysis
The purpose of narrative analysis is to gain a deeper understanding of the stories that individuals tell about their experiences, identities, and beliefs. By analyzing the structure, content, and context of these stories, researchers can uncover patterns and themes that shed light on the ways in which individuals make sense of their lives and the world around them.
The primary purpose of narrative analysis is to explore the meanings that individuals attach to their experiences. This involves examining the different elements of a story, such as the plot, characters, setting, and themes, to identify the underlying values, beliefs, and attitudes that shape the story. By analyzing these elements, researchers can gain insights into the ways in which individuals construct their identities, understand their relationships with others, and make sense of the world.
Narrative analysis can also be used to identify patterns and themes across multiple stories. This involves comparing and contrasting the stories of different individuals or groups to identify commonalities and differences. By analyzing these patterns and themes, researchers can gain insights into broader cultural and social phenomena, such as gender, race, and identity.
In addition, narrative analysis can be used to develop interventions that address social and cultural problems. By understanding the stories that individuals tell about their experiences, researchers can develop interventions that are tailored to the unique needs of different individuals and groups.
Overall, the purpose of narrative analysis is to provide a rich, nuanced understanding of the ways in which individuals construct meaning and make sense of their lives. By analyzing the stories that individuals tell, researchers can gain insights into the complex and multifaceted nature of human experience.
When to use Narrative Analysis
Here are some situations where narrative analysis may be appropriate:
- Studying life stories: Narrative analysis can be useful in understanding how individuals construct their life stories, including the events, characters, and themes that are important to them.
- Analyzing cultural narratives: Narrative analysis can be used to analyze cultural narratives, such as myths, legends, and folktales, to understand their meanings and functions.
- Exploring organizational narratives: Narrative analysis can be helpful in examining the stories that organizations tell about themselves, their histories, and their values, to understand how they shape the culture and practices of the organization.
- Investigating media narratives: Narrative analysis can be used to analyze media narratives, such as news stories, films, and TV shows, to understand how they construct meaning and influence public perceptions.
- Examining policy narratives: Narrative analysis can be helpful in examining policy narratives, such as political speeches and policy documents, to understand how they construct ideas and justify policy decisions.
Characteristics of Narrative Analysis
Here are some key characteristics of narrative analysis:
- Focus on stories and narratives: Narrative analysis is concerned with analyzing the stories and narratives that people tell, whether they are oral or written, to understand how they shape and reflect individuals’ experiences and identities.
- Emphasis on context: Narrative analysis seeks to understand the context in which the narratives are produced and the social and cultural factors that shape them.
- Interpretive approach: Narrative analysis is an interpretive approach that seeks to identify patterns and themes in the stories and narratives and to understand the meaning that individuals and communities attach to them.
- Iterative process: Narrative analysis involves an iterative process of analysis, in which the researcher continually refines their understanding of the narratives as they examine more data.
- Attention to language and form : Narrative analysis pays close attention to the language and form of the narratives, including the use of metaphor, imagery, and narrative structure, to understand the meaning that individuals and communities attach to them.
- Reflexivity : Narrative analysis requires the researcher to reflect on their own assumptions and biases and to consider how their own positionality may shape their interpretation of the narratives.
- Qualitative approach: Narrative analysis is typically a qualitative research method that involves in-depth analysis of a small number of cases rather than large-scale quantitative studies.
Advantages of Narrative Analysis
Here are some advantages of narrative analysis:
- Rich and detailed data : Narrative analysis provides rich and detailed data that allows for a deep understanding of individuals’ experiences, emotions, and identities.
- Humanizing approach: Narrative analysis allows individuals to tell their own stories and express their own perspectives, which can help to humanize research and give voice to marginalized communities.
- Holistic understanding: Narrative analysis allows researchers to understand individuals’ experiences in their entirety, including the social, cultural, and historical contexts in which they occur.
- Flexibility : Narrative analysis is a flexible research method that can be applied to a wide range of contexts and research questions.
- Interpretive insights: Narrative analysis provides interpretive insights into the meanings that individuals attach to their experiences and the ways in which they construct their identities.
- Appropriate for sensitive topics: Narrative analysis can be particularly useful in researching sensitive topics, such as trauma or mental health, as it allows individuals to express their experiences in their own words and on their own terms.
- Can lead to policy implications: Narrative analysis can provide insights that can inform policy decisions and interventions, particularly in areas such as health, education, and social policy.
Limitations of Narrative Analysis
Here are some of the limitations of narrative analysis:
- Subjectivity : Narrative analysis relies on the interpretation of researchers, which can be influenced by their own biases and assumptions.
- Limited generalizability: Narrative analysis typically involves in-depth analysis of a small number of cases, which limits its generalizability to broader populations.
- Ethical considerations: The process of eliciting and analyzing narratives can raise ethical concerns, particularly when sensitive topics such as trauma or abuse are involved.
- Limited control over data collection: Narrative analysis often relies on data that is already available, such as interviews, oral histories, or written texts, which can limit the control that researchers have over the quality and completeness of the data.
- Time-consuming: Narrative analysis can be a time-consuming research method, particularly when analyzing large amounts of data.
- Interpretation challenges: Narrative analysis requires researchers to make complex interpretations of data, which can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Limited statistical analysis: Narrative analysis is typically a qualitative research method that does not lend itself well to statistical analysis.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Probability Histogram – Definition, Examples and...

Inferential Statistics – Types, Methods and...

Content Analysis – Methods, Types and Examples

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Symmetric Histogram – Examples and Making Guide

Discourse Analysis – Methods, Types and Examples
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!

People also read
Narrative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide with Examples
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2024 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
|
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
|
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
|
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now that you have essay examples and tips to get started, you're well on your way to crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our custom essay writing service for help. Our service features skilled writers who can tackle any type of essay with great expertise. With their experience, you'll receive a top-quality, 100% plagiarism-free essay every time.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Narrative Essay Guide
Narrative Essay Outline
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023
How to Write a Narrative Essay Outline - Tips & Examples
By: Nathan D.
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Jun 2, 2020

A narrative essay is a type of academic essay in which the writer narrates a story. It is the most commonly assigned form of academic writing. Students have to face the narrative essay writing task quite often, so it is essential to know how to handle it.
A narrative essay is a story, so it's important to know how to write one. The best way to start your outline is by brainstorming ideas.
Who are the characters? What do they want? How does this conflict with their goals and who wins in the end?
There are many different types of essays you can write about, but all will have some sort of conflict. Once you've figured out the basics, be creative! You could explore an event that happened in your life or tell a fictional story.
In this blog, you’ll learn to write an outline for a narrative essay with examples. Start reading!

On this Page
A narrative essay is a type of academic essay in which the writer narrates a story. It is the most commonly assigned form of academic writing. Students have to face the narrative essay writing task quite often, so it is essential to know how to handle it.
Narrative Essay Outline Format
The narrative essay outline follows the standard structure. Like other types of essays, this essay normally follows a typical 5 paragraph essay format. The 5 paragraph outline includes one introduction paragraph, three body paragraphs, and one conclusion paragraph.
However, unlike other essays, the paragraphs of the narrative essay have specifically designated purposes:
1. Introduction Paragraph: Gives an insight into the story
2. First Body Paragraph: Discuss the rising action
3. Second Body Paragraph: Present the climax of the story
4. Third Body Paragraph: Provide the falling action
5. Conclusion Paragraph: Discussion of the lesson learned from the story
Paragraph Narrative Essay Outline Template
Let's look at the detailed 5 paragraph narrative essay outline for college students.
How to Write a Narrative Essay Outline?
A narrative essay is all about sharing the stories. Therefore, you need to organize your story into an essay format. As a writer, you are supposed to tell a story from your personal experience and why you are sharing that specific experience. Later, you need to discuss why this story or experience is important to share.
Let's look at how to craft an outline for a narrative essay. Follow the steps in the same sequence, and at the end, you’ll get a perfect outline. The writing process will become less stressful and daunting if you follow the steps given below.
1. Write the Introduction
The introduction paragraph is meant to engage the reader with the story. The first paragraph plays the most crucial role in making an impression on the reader’s mind. It allows you to share your perspective and how it relates to you. The following elements are involved in writing a strong narrative essay introduction.
- Create a Hook Statement Draw the reader in with an intriguing and attention-grabbing hook statement. Create a strong hook that makes your reader want to read further. You can use a quote, rhetorical question, or fact to create a persuasive hook statement.
- Set the Scene: Give your reader an idea of what is going to happen. Do not tell the whole story; just give a glimpse into it and keep your reader intrigued. Tell the reader how the points of the story relate to you.
- Define the Thesis Statement: Finally, tell your reader what your story is all about with the help of a thesis statement. Give a sneak peek of what is about to come but avoid telling the lesson you have learned from the situation yet; just give a hint.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
2. Draft the Body Paragraphs
The main body of a narrative essay is the most important part because it tells the whole story. This is where you state the facts, provide examples, give details, and guide the reader through the plot. According to the five paragraphs essay structure, it has three body paragraphs, but it can depend on the length and word count.
Below elements must be kept in mind while writing the narrative essay body paragraphs:
- Write Chronologically: The timelines of a story should be presented in chronological order. Otherwise, the reader will get confused, and it becomes hard for them to understand the story. To keep your paper organized, you should present things in sequential order.
- Share the Relevant and Vivid Details: As a narrative essay is all about creating a mood and scene to follow, do that creatively. Set up the story with descriptive and concise language. Provide the reader with the most important details of your story. These details may include the characters, setting, plot, and the onset of the story.
- Avoid Narration Deviation: The narrative essay is usually written in the first person unless you share someone else’s story. The third-person narrative only works best when you are telling a story you heard from someone else.
3. Write a Compelling Conclusion
The conclusion paragraph is the final section of the essay where you give some final comments about the story. Summarize your essay and connect your reader back to the story. Follow these steps to write an impressive conclusion.
- Restate Some Key Details: Restate the thesis statement and some key details you have shared in the body. It will help you connect your reader with your story.
- Share the Lesson: Stress the lesson you have learned from the story and leave the reader with something to think about.
- Call to Action: In the end, provide a call to action that convinces the reader to think more about the topic.
Narrative Essay Outline Worksheet
Use the given worksheet below to write a narrative essay with ease.
Narrative Essay Outline Example
Here are some narrative essay examples and samples for your convenience. Use these templates and learn to write a good narrative essay easily.
Narrative Essay Outline for Middle School
College Narrative Essay Outline
Personal Narrative Essay Outline Template
Descriptive Narrative Essay Outline
Literacy Narrative Essay Outline
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
However, if you still have some concerns about writing a perfect outline, you can contact our essay writers. 5StarEssays.com is a legit and reliable ‘ write my essay for me? ’ service that provides you with highly qualified and professional writers.
You can trust us with all of your academic writing assignments. So waste no more time and place your order now!

Literature, College Essay
Nathan completed his Ph.D. in journalism and has been writing articles for well-respected publications for many years now. His work is carefully researched and insightful, showing a true passion for the written word. Nathan's clients appreciate his expertise, deep understanding of the process, and ability to communicate difficult concepts clearly.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Narrative Essay - An Ultimate Guide With Examples & Topics

- Narrative Essay Topics - Best Topic Ideas for Your Essay

- Narrative Essay Examples: Samples & Tips

People Also Read
- personal statement prompts
- autobiography vs memoir
- list of social issues
- elements of press release
- press release example
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
The Ultimate Narrative Essay Guide for Beginners

A narrative essay tells a story in chronological order, with an introduction that introduces the characters and sets the scene. Then a series of events leads to a climax or turning point, and finally a resolution or reflection on the experience.
Speaking of which, are you in sixes and sevens about narrative essays? Don’t worry this ultimate expert guide will wipe out all your doubts. So let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Everything You Need to Know About Narrative Essay
What is a narrative essay.
When you go through a narrative essay definition, you would know that a narrative essay purpose is to tell a story. It’s all about sharing an experience or event and is different from other types of essays because it’s more focused on how the event made you feel or what you learned from it, rather than just presenting facts or an argument. Let’s explore more details on this interesting write-up and get to know how to write a narrative essay.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of a narrative essay:
A narrative essay has a beginning, middle, and end. It builds up tension and excitement and then wraps things up in a neat package.
Real people, including the writer, often feature in personal narratives. Details of the characters and their thoughts, feelings, and actions can help readers to relate to the tale.
It’s really important to know when and where something happened so we can get a good idea of the context. Going into detail about what it looks like helps the reader to really feel like they’re part of the story.
Conflict or Challenge
A story in a narrative essay usually involves some kind of conflict or challenge that moves the plot along. It could be something inside the character, like a personal battle, or something from outside, like an issue they have to face in the world.
Theme or Message
A narrative essay isn’t just about recounting an event – it’s about showing the impact it had on you and what you took away from it. It’s an opportunity to share your thoughts and feelings about the experience, and how it changed your outlook.
Emotional Impact
The author is trying to make the story they’re telling relatable, engaging, and memorable by using language and storytelling to evoke feelings in whoever’s reading it.
Narrative essays let writers have a blast telling stories about their own lives. It’s an opportunity to share insights and impart wisdom, or just have some fun with the reader. Descriptive language, sensory details, dialogue, and a great narrative voice are all essentials for making the story come alive.
The Purpose of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is more than just a story – it’s a way to share a meaningful, engaging, and relatable experience with the reader. Includes:
Sharing Personal Experience
Narrative essays are a great way for writers to share their personal experiences, feelings, thoughts, and reflections. It’s an opportunity to connect with readers and make them feel something.
Entertainment and Engagement
The essay attempts to keep the reader interested by using descriptive language, storytelling elements, and a powerful voice. It attempts to pull them in and make them feel involved by creating suspense, mystery, or an emotional connection.
Conveying a Message or Insight
Narrative essays are more than just a story – they aim to teach you something. They usually have a moral lesson, a new understanding, or a realization about life that the author gained from the experience.
Building Empathy and Understanding
By telling their stories, people can give others insight into different perspectives, feelings, and situations. Sharing these tales can create compassion in the reader and help broaden their knowledge of different life experiences.
Inspiration and Motivation
Stories about personal struggles, successes, and transformations can be really encouraging to people who are going through similar situations. It can provide them with hope and guidance, and let them know that they’re not alone.
Reflecting on Life’s Significance
These essays usually make you think about the importance of certain moments in life or the impact of certain experiences. They make you look deep within yourself and ponder on the things you learned or how you changed because of those events.
Demonstrating Writing Skills
Coming up with a gripping narrative essay takes serious writing chops, like vivid descriptions, powerful language, timing, and organization. It’s an opportunity for writers to show off their story-telling abilities.
Preserving Personal History
Sometimes narrative essays are used to record experiences and special moments that have an emotional resonance. They can be used to preserve individual memories or for future generations to look back on.
Cultural and Societal Exploration
Personal stories can look at cultural or social aspects, giving us an insight into customs, opinions, or social interactions seen through someone’s own experience.
Format of a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays are quite flexible in terms of format, which allows the writer to tell a story in a creative and compelling way. Here’s a quick breakdown of the narrative essay format, along with some examples:
Introduction
Set the scene and introduce the story.
Engage the reader and establish the tone of the narrative.
Hook: Start with a captivating opening line to grab the reader’s attention. For instance:
Example: “The scorching sun beat down on us as we trekked through the desert, our water supply dwindling.”
Background Information: Provide necessary context or background without giving away the entire story.
Example: “It was the summer of 2015 when I embarked on a life-changing journey to…”
Thesis Statement or Narrative Purpose
Present the main idea or the central message of the essay.
Offer a glimpse of what the reader can expect from the narrative.
Thesis Statement: This isn’t as rigid as in other essays but can be a sentence summarizing the essence of the story.
Example: “Little did I know, that seemingly ordinary hike would teach me invaluable lessons about resilience and friendship.”
Body Paragraphs
Present the sequence of events in chronological order.
Develop characters, setting, conflict, and resolution.
Story Progression : Describe events in the order they occurred, focusing on details that evoke emotions and create vivid imagery.
Example : Detail the trek through the desert, the challenges faced, interactions with fellow hikers, and the pivotal moments.
Character Development : Introduce characters and their roles in the story. Show their emotions, thoughts, and actions.
Example : Describe how each character reacted to the dwindling water supply and supported each other through adversity.
Dialogue and Interactions : Use dialogue to bring the story to life and reveal character personalities.
Example : “Sarah handed me her last bottle of water, saying, ‘We’re in this together.'”
Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance.
Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative.
Example: “As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team’s helicopters.”
Provide closure to the story.
Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact.
Reflection : Summarize the key lessons learned or insights gained from the experience.
Example : “That hike taught me the true meaning of resilience and the invaluable support of friendship in challenging times.”
Closing Thought : End with a memorable line that reinforces the narrative’s message or leaves a lasting impression.
Example : “As we boarded the helicopters, I knew this adventure would forever be etched in my heart.”
Example Summary:
Imagine a narrative about surviving a challenging hike through the desert, emphasizing the bonds formed and lessons learned. The narrative essay structure might look like starting with an engaging scene, narrating the hardships faced, showcasing the characters’ resilience, and culminating in a powerful realization about friendship and endurance.
Different Types of Narrative Essays
There are a bunch of different types of narrative essays – each one focuses on different elements of storytelling and has its own purpose. Here’s a breakdown of the narrative essay types and what they mean.

Personal Narrative
Description : Tells a personal story or experience from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Reflects on personal growth, lessons learned, or significant moments.
Example of Narrative Essay Types:
Topic : “The Day I Conquered My Fear of Public Speaking”
Focus: Details the experience, emotions, and eventual triumph over a fear of public speaking during a pivotal event.
Descriptive Narrative
Description : Emphasizes vivid details and sensory imagery.
Purpose : Creates a sensory experience, painting a vivid picture for the reader.
Topic : “A Walk Through the Enchanted Forest”
Focus : Paints a detailed picture of the sights, sounds, smells, and feelings experienced during a walk through a mystical forest.
Autobiographical Narrative
Description: Chronicles significant events or moments from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Provides insights into the writer’s life, experiences, and growth.
Topic: “Lessons from My Childhood: How My Grandmother Shaped Who I Am”
Focus: Explores pivotal moments and lessons learned from interactions with a significant family member.
Experiential Narrative
Description: Relays experiences beyond the writer’s personal life.
Purpose: Shares experiences, travels, or events from a broader perspective.
Topic: “Volunteering in a Remote Village: A Journey of Empathy”
Focus: Chronicles the writer’s volunteering experience, highlighting interactions with a community and personal growth.
Literary Narrative
Description: Incorporates literary elements like symbolism, allegory, or thematic explorations.
Purpose: Uses storytelling for deeper explorations of themes or concepts.
Topic: “The Symbolism of the Red Door: A Journey Through Change”
Focus: Uses a red door as a symbol, exploring its significance in the narrator’s life and the theme of transition.
Historical Narrative
Description: Recounts historical events or periods through a personal lens.
Purpose: Presents history through personal experiences or perspectives.
Topic: “A Grandfather’s Tales: Living Through the Great Depression”
Focus: Shares personal stories from a family member who lived through a historical era, offering insights into that period.
Digital or Multimedia Narrative
Description: Incorporates multimedia elements like images, videos, or audio to tell a story.
Purpose: Explores storytelling through various digital platforms or formats.
Topic: “A Travel Diary: Exploring Europe Through Vlogs”
Focus: Combines video clips, photos, and personal narration to document a travel experience.
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Essay?
Selecting a compelling topic for your narrative essay is crucial as it sets the stage for your storytelling. Choosing a boring topic is one of the narrative essay mistakes to avoid . Here’s a detailed guide on how to choose the right topic:
Reflect on Personal Experiences
- Significant Moments:
Moments that had a profound impact on your life or shaped your perspective.
Example: A moment of triumph, overcoming a fear, a life-changing decision, or an unforgettable experience.
- Emotional Resonance:
Events that evoke strong emotions or feelings.
Example: Joy, fear, sadness, excitement, or moments of realization.
- Lessons Learned:
Experiences that taught you valuable lessons or brought about personal growth.
Example: Challenges that led to personal development, shifts in mindset, or newfound insights.
Explore Unique Perspectives
- Uncommon Experiences:
Unique or unconventional experiences that might captivate the reader’s interest.
Example: Unusual travels, interactions with different cultures, or uncommon hobbies.
- Different Points of View:
Stories from others’ perspectives that impacted you deeply.
Example: A family member’s story, a friend’s experience, or a historical event from a personal lens.
Focus on Specific Themes or Concepts
- Themes or Concepts of Interest:
Themes or ideas you want to explore through storytelling.
Example: Friendship, resilience, identity, cultural diversity, or personal transformation.
- Symbolism or Metaphor:
Using symbols or metaphors as the core of your narrative.
Example: Exploring the symbolism of an object or a place in relation to a broader theme.
Consider Your Audience and Purpose
- Relevance to Your Audience:
Topics that resonate with your audience’s interests or experiences.
Example: Choose a relatable theme or experience that your readers might connect with emotionally.
- Impact or Message:
What message or insight do you want to convey through your story?
Example: Choose a topic that aligns with the message or lesson you aim to impart to your readers.
Brainstorm and Evaluate Ideas
- Free Writing or Mind Mapping:
Process: Write down all potential ideas without filtering. Mind maps or free-writing exercises can help generate diverse ideas.
- Evaluate Feasibility:
The depth of the story, the availability of vivid details, and your personal connection to the topic.
Imagine you’re considering topics for a narrative essay. You reflect on your experiences and decide to explore the topic of “Overcoming Stage Fright: How a School Play Changed My Perspective.” This topic resonates because it involves a significant challenge you faced and the personal growth it brought about.
Narrative Essay Topics
50 easy narrative essay topics.
- Learning to Ride a Bike
- My First Day of School
- A Surprise Birthday Party
- The Day I Got Lost
- Visiting a Haunted House
- An Encounter with a Wild Animal
- My Favorite Childhood Toy
- The Best Vacation I Ever Had
- An Unforgettable Family Gathering
- Conquering a Fear of Heights
- A Special Gift I Received
- Moving to a New City
- The Most Memorable Meal
- Getting Caught in a Rainstorm
- An Act of Kindness I Witnessed
- The First Time I Cooked a Meal
- My Experience with a New Hobby
- The Day I Met My Best Friend
- A Hike in the Mountains
- Learning a New Language
- An Embarrassing Moment
- Dealing with a Bully
- My First Job Interview
- A Sporting Event I Attended
- The Scariest Dream I Had
- Helping a Stranger
- The Joy of Achieving a Goal
- A Road Trip Adventure
- Overcoming a Personal Challenge
- The Significance of a Family Tradition
- An Unusual Pet I Owned
- A Misunderstanding with a Friend
- Exploring an Abandoned Building
- My Favorite Book and Why
- The Impact of a Role Model
- A Cultural Celebration I Participated In
- A Valuable Lesson from a Teacher
- A Trip to the Zoo
- An Unplanned Adventure
- Volunteering Experience
- A Moment of Forgiveness
- A Decision I Regretted
- A Special Talent I Have
- The Importance of Family Traditions
- The Thrill of Performing on Stage
- A Moment of Sudden Inspiration
- The Meaning of Home
- Learning to Play a Musical Instrument
- A Childhood Memory at the Park
- Witnessing a Beautiful Sunset
Narrative Essay Topics for College Students
- Discovering a New Passion
- Overcoming Academic Challenges
- Navigating Cultural Differences
- Embracing Independence: Moving Away from Home
- Exploring Career Aspirations
- Coping with Stress in College
- The Impact of a Mentor in My Life
- Balancing Work and Studies
- Facing a Fear of Public Speaking
- Exploring a Semester Abroad
- The Evolution of My Study Habits
- Volunteering Experience That Changed My Perspective
- The Role of Technology in Education
- Finding Balance: Social Life vs. Academics
- Learning a New Skill Outside the Classroom
- Reflecting on Freshman Year Challenges
- The Joys and Struggles of Group Projects
- My Experience with Internship or Work Placement
- Challenges of Time Management in College
- Redefining Success Beyond Grades
- The Influence of Literature on My Thinking
- The Impact of Social Media on College Life
- Overcoming Procrastination
- Lessons from a Leadership Role
- Exploring Diversity on Campus
- Exploring Passion for Environmental Conservation
- An Eye-Opening Course That Changed My Perspective
- Living with Roommates: Challenges and Lessons
- The Significance of Extracurricular Activities
- The Influence of a Professor on My Academic Journey
- Discussing Mental Health in College
- The Evolution of My Career Goals
- Confronting Personal Biases Through Education
- The Experience of Attending a Conference or Symposium
- Challenges Faced by Non-Native English Speakers in College
- The Impact of Traveling During Breaks
- Exploring Identity: Cultural or Personal
- The Impact of Music or Art on My Life
- Addressing Diversity in the Classroom
- Exploring Entrepreneurial Ambitions
- My Experience with Research Projects
- Overcoming Impostor Syndrome in College
- The Importance of Networking in College
- Finding Resilience During Tough Times
- The Impact of Global Issues on Local Perspectives
- The Influence of Family Expectations on Education
- Lessons from a Part-Time Job
- Exploring the College Sports Culture
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education
- The Journey of Self-Discovery Through Education
Narrative Essay Comparison
Narrative essay vs. descriptive essay.
Here’s our first narrative essay comparison! While both narrative and descriptive essays focus on vividly portraying a subject or an event, they differ in their primary objectives and approaches. Now, let’s delve into the nuances of comparison on narrative essays.
Narrative Essay:
Storytelling: Focuses on narrating a personal experience or event.
Chronological Order: Follows a structured timeline of events to tell a story.
Message or Lesson: Often includes a central message, moral, or lesson learned from the experience.
Engagement: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling storyline and character development.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, using “I” and expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a plot with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Focuses on describing characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Conflict or Challenge: Usually involves a central conflict or challenge that drives the narrative forward.
Dialogue: Incorporates conversations to bring characters and their interactions to life.
Reflection: Concludes with reflection or insight gained from the experience.
Descriptive Essay:
Vivid Description: Aims to vividly depict a person, place, object, or event.
Imagery and Details: Focuses on sensory details to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
Emotion through Description: Uses descriptive language to evoke emotions and engage the reader’s senses.
Painting a Picture: Creates a sensory-rich description allowing the reader to visualize the subject.
Imagery and Sensory Details: Focuses on providing rich sensory descriptions, using vivid language and adjectives.
Point of Focus: Concentrates on describing a specific subject or scene in detail.
Spatial Organization: Often employs spatial organization to describe from one area or aspect to another.
Objective Observations: Typically avoids the use of personal opinions or emotions; instead, the focus remains on providing a detailed and objective description.
Comparison:
Focus: Narrative essays emphasize storytelling, while descriptive essays focus on vividly describing a subject or scene.
Perspective: Narrative essays are often written from a first-person perspective, while descriptive essays may use a more objective viewpoint.
Purpose: Narrative essays aim to convey a message or lesson through a story, while descriptive essays aim to paint a detailed picture for the reader without necessarily conveying a specific message.
Narrative Essay vs. Argumentative Essay
The narrative essay and the argumentative essay serve distinct purposes and employ different approaches:
Engagement and Emotion: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling story.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience or lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, sharing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a storyline with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Message or Lesson: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Argumentative Essay:
Persuasion and Argumentation: Aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s viewpoint on a specific topic.
Logical Reasoning: Presents evidence, facts, and reasoning to support a particular argument or stance.
Debate and Counterarguments: Acknowledge opposing views and counter them with evidence and reasoning.
Thesis Statement: Includes a clear thesis statement that outlines the writer’s position on the topic.
Thesis and Evidence: Starts with a strong thesis statement and supports it with factual evidence, statistics, expert opinions, or logical reasoning.
Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints and provides rebuttals with evidence.
Logical Structure: Follows a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, and a conclusion reaffirming the thesis.
Formal Language: Uses formal language and avoids personal anecdotes or emotional appeals.
Objective: Argumentative essays focus on presenting a logical argument supported by evidence, while narrative essays prioritize storytelling and personal reflection.
Purpose: Argumentative essays aim to persuade and convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, while narrative essays aim to engage, entertain, and share personal experiences.
Structure: Narrative essays follow a storytelling structure with character development and plot, while argumentative essays follow a more formal, structured approach with logical arguments and evidence.
In essence, while both essays involve writing and presenting information, the narrative essay focuses on sharing a personal experience, whereas the argumentative essay aims to persuade the audience by presenting a well-supported argument.
Narrative Essay vs. Personal Essay
While there can be an overlap between narrative and personal essays, they have distinctive characteristics:
Storytelling: Emphasizes recounting a specific experience or event in a structured narrative form.
Engagement through Story: Aims to engage the reader through a compelling story with characters, plot, and a central theme or message.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience and the lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s viewpoint, expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Focuses on developing a storyline with a clear beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Includes descriptions of characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Central Message: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Personal Essay:
Exploration of Ideas or Themes: Explores personal ideas, opinions, or reflections on a particular topic or subject.
Expression of Thoughts and Opinions: Expresses the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and perspectives on a specific subject matter.
Reflection and Introspection: Often involves self-reflection and introspection on personal experiences, beliefs, or values.
Varied Structure and Content: Can encompass various forms, including memoirs, personal anecdotes, or reflections on life experiences.
Flexibility in Structure: Allows for diverse structures and forms based on the writer’s intent, which could be narrative-like or more reflective.
Theme-Centric Writing: Focuses on exploring a central theme or idea, with personal anecdotes or experiences supporting and illustrating the theme.
Expressive Language: Utilizes descriptive and expressive language to convey personal perspectives, emotions, and opinions.
Focus: Narrative essays primarily focus on storytelling through a structured narrative, while personal essays encompass a broader range of personal expression, which can include storytelling but isn’t limited to it.
Structure: Narrative essays have a more structured plot development with characters and a clear sequence of events, while personal essays might adopt various structures, focusing more on personal reflection, ideas, or themes.
Intent: While both involve personal experiences, narrative essays emphasize telling a story with a message or lesson learned, while personal essays aim to explore personal thoughts, feelings, or opinions on a broader range of topics or themes.

A narrative essay is more than just telling a story. It’s also meant to engage the reader, get them thinking, and leave a lasting impact. Whether it’s to amuse, motivate, teach, or reflect, these essays are a great way to communicate with your audience. This interesting narrative essay guide was all about letting you understand the narrative essay, its importance, and how can you write one.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
Narrative Essay Topics: TOP 200 Choices for Students

Imagine yourself facing a blank page, ready to fill it with your memories and imagination. What story will you tell today?
As students, you often have to write narratives that capture people's attention. But with so many stories to choose from, where do you start? How do you find the perfect topic that will grab our readers' interest and make them think?
Join our essay service experts as we explore 200 topics for college where stories are waiting to be told, and experiences are ready to be shared. From everyday events to unforgettable moments, each topic is a chance to connect with your readers and make them feel something.

Do You Need Professional Help with Your Hometask?
Ideas for Narrative Essay Topics
After exploring how students write narrative paragraphs, we've put together a list of narrative essay topics designed specifically for college and school students. This list covers a wide range of subjects, so pick one that speaks to you!
Literacy Narrative Essay Topics for College Students
How about delving into captivating literacy narrative essay topics designed specifically for college-level writing? Exciting, isn't it?
- How did a childhood book shape your view of the world?
- What challenges did you face when learning to read in a second language?
- How has storytelling within your family influenced your literacy journey?
- Can you recall a pivotal moment that ignited your love for reading?
- How did a specific teacher inspire your passion for literature?
- Have you ever encountered a character in a book who profoundly impacted your perspective on life?
- What role did writing play in helping you navigate a difficult period in your life?
- How has your relationship with technology affected your reading habits?
- What cultural or historical event sparked your interest in a particular genre of literature?
- How has poetry shaped your understanding of language and emotion?
- Have you ever experienced a breakthrough moment in your writing process?
- How has reading aloud impacted your comprehension and enjoyment of literature?
- Can you recall a time when a book challenged your beliefs or worldview?
- How has participating in a book club enriched your reading experience?
- What strategies have you developed to overcome reading difficulties or distractions?
Personal Narrative Essay Topics on Relationships
Take a moment to reflect on your past experiences and craft compelling personal narratives with these essay ideas.
- How did a specific friendship shape who you are today?
- Can you recount a moment that strengthened your bond with a family member?
- What challenges have you faced in maintaining a long-distance relationship?
- How has a mentor influenced your personal and professional development?
- Have you experienced a betrayal in a relationship? How did it impact you?
- Can you describe a memorable conflict resolution process within a relationship?
- How has your relationship with a pet affected your emotional well-being?
- What lessons have you learned from navigating a romantic relationship?
- How has your relationship with a sibling evolved over time?
- Can you recall a time when you had to set boundaries in a friendship?
- How has volunteering or community involvement enriched your relationships?
- What cultural differences have influenced your relationships with others?
- Can you share a moment when you felt truly understood by someone?
- How has technology affected the dynamics of your relationships?
- Have you ever experienced a reconciliation that transformed a strained relationship?
Best Narrative Essay Topics on Education and Learning
Consider the beauty of sharing your personal experiences and emotions in a captivating manner through these ideas for personal narrative essays.
- What was the most valuable lesson you learned outside of the classroom?
- Can you recount a moment when a teacher's unconventional method transformed your understanding of a subject?
- How has a field trip or experiential learning opportunity impacted your education?
- What challenges have you faced in balancing extracurricular activities with academics?
- Have you ever had a "Eureka!" moment while studying? Describe it.
- How has learning a new skill outside of school influenced your academic performance?
- Can you recall a time when a peer's perspective challenged your own understanding of a topic?
- How has technology enhanced or hindered your learning experience?
- What role does creativity play in your approach to learning?
- Have you ever experienced a setback that ultimately propelled you forward academically?
- How has your cultural background influenced your learning style?
- Can you describe a time when you had to advocate for yourself within an educational setting?
- How has mentorship shaped your educational journey?
- What strategies have you employed to overcome academic challenges or obstacles?
- Can you reflect on a time when failure taught you a valuable lesson about learning?
At this point, we think you might've already been interested in our term paper writing service that helps busy students succeed in college.
Personal Narrative Essay Ideas on Reflection on Life
Why not ignite your creativity with a range of narrative essay topics, from extraordinary moments to everyday experiences?
- How has a moment of failure ultimately led to personal growth and resilience?
- Can you recount a pivotal decision that significantly altered the course of your life?
- What lessons have you learned from navigating a crossroads or major life transition?
- How has your perspective on success evolved over time?
- Can you reflect on a time when you had to confront and overcome a deeply held fear?
- What role has gratitude played in shaping your outlook on life?
- How have your values and beliefs been influenced by significant life experiences?
- Can you describe a moment when you found clarity and purpose amidst chaos or uncertainty?
- What impact has traveling to a new place had on your understanding of the world and yourself?
- How has adversity strengthened your character and determination?
- Can you recall a time when a random act of kindness profoundly impacted your life?
- What lessons have you learned from embracing vulnerability and authenticity in relationships?
- How has practicing mindfulness or self-reflection enhanced your well-being and happiness?
- Can you reflect on a period of personal transformation or self-discovery?
- How have you found meaning and fulfillment in pursuing your passions and interests?
Ideas for a Narrative Essay on Culture and Society
Engaging your readers with narrative essays on culture and society is a great way to spark interest, offering captivating ideas for exploration.
- How has your family's unique culinary heritage influenced your cultural identity?
- Can you reflect on a specific cultural artifact or heirloom that holds deep significance for your family?
- What challenges have you faced in preserving traditional customs while adapting to modern societal expectations?
- How has a local festival or celebration revealed the intricacies of your community's cultural tapestry?
- Can you recount a moment when you navigated a cultural clash between your upbringing and the dominant culture?
- How has your experience as a first-generation immigrant shaped your understanding of cultural assimilation?
- What lessons have you learned from participating in intercultural exchange programs or initiatives?
- Can you describe a unique cultural practice or tradition within your community that outsiders might find intriguing or misunderstood?
- How has the revitalization of indigenous languages contributed to the preservation of cultural heritage in your region?
- Can you reflect on a personal journey of reconnecting with your cultural roots after a period of assimilation or disconnection?
- What role does storytelling play in passing down cultural wisdom and values within your family or community?
- How has the portrayal of your culture in mainstream media affected your sense of belonging and self-perception?
- Can you recount a moment when you challenged cultural stereotypes through creative expression or advocacy?
- How has the migration of a specific cultural group enriched the social fabric and economic landscape of your community?
- What initiatives or grassroots movements are currently underway to promote cross-cultural understanding and cooperation in your society?
Since you're working on essays, we think it's suitable to suggest you learn more about the case study format , which is another common college assignment.
Narrative Writing Topics on Hobbies and Interests
Wow your readers by turning your passions and hobbies into compelling narrative essay topics that will get them thinking.
- How has your passion for urban gardening transformed neglected spaces in your community?
- Can you recount a thrilling adventure from your hobby of urban exploration?
- What lessons have you learned from restoring vintage motorcycles in your spare time?
- How has your fascination with birdwatching deepened your connection to nature and conservation efforts?
- Can you describe a memorable moment from your hobby of foraging wild edibles in the wilderness?
- What unique skills have you developed through your hobby of beekeeping, and how have they impacted your daily life?
- How has your interest in historical reenactment brought the past to life in unexpected ways?
- Can you reflect on a transformative experience from your hobby of landscape photography?
- What insights have you gained from practicing the art of bonsai cultivation and nurturing miniature ecosystems?
- How has your passion for stargazing inspired awe and wonder in the vastness of the universe?
- Can you recount a challenging project from your hobby of woodworking and the satisfaction it brought upon completion?
- What cultural connections have you discovered through your hobby of traditional folk dancing?
- How has your interest in sustainable fashion influenced your consumer habits and environmental awareness?
- Can you describe a moment of serenity and mindfulness experienced while practicing the art of tea ceremony?
- How has your hobby of letterpress printing preserved the tactile beauty of handmade craftsmanship in a digital age?
Narrative Essay Titles on Life-Changing Moments
Life is full of unexpected twists that can lead to life-changing moments. Take a look at these narrative essay titles for stories that have had a lasting impact on your life.
- How did surviving a natural disaster reshape your perspective on life?
- Can you recall a single conversation that drastically altered the course of your life?
- What was the pivotal moment that inspired you to pursue your dreams against all odds?
- How did a chance encounter lead to a life-changing friendship or partnership?
- Can you reflect on the decision that transformed your career trajectory?
- What profound lesson did you learn from facing a life-threatening illness or injury?
- How did traveling to a new country open your eyes to new possibilities and opportunities?
- Can you recount the moment when you discovered your true passion or calling in life?
- What was the turning point that allowed you to break free from a toxic relationship or environment?
- How did experiencing failure or rejection ultimately lead to personal growth and resilience?
- Can you describe the moment when you found the strength to overcome a deep-seated fear or insecurity?
- What life-changing realization did you have while experiencing a period of solitude or introspection?
- How did a profound act of kindness from a stranger restore your faith in humanity?
- Can you reflect on the moment when you forgave someone who had deeply hurt you, and how it changed your perspective on forgiveness?
- What pivotal decision did you make that allowed you to reclaim control over your own happiness and destiny?
Have you ever wondered about the challenges of essay writing? What happens when you're assigned a larger paper, like coursework? Make a preemptive strike by exploring coursework writing service right now!
Good Narrative Topics on Travel and Adventure
Consider creating intriguing titles for your narrative essay ideas by exploring thrilling travel adventures.
- Can you recount a memorable encounter with wildlife during your solo hiking adventure?
- How did a spontaneous decision to explore an unfamiliar city lead to unexpected discoveries?
- What lessons did you learn from navigating a foreign country with only a map and your instincts?
- Can you describe the exhilaration of conquering a challenging mountain peak for the first time?
- How did immersing yourself in a local culture during your travels broaden your perspective on the world?
- What unexpected obstacles did you encounter while embarking on a backpacking journey through rugged terrain?
- Can you reflect on the transformative experience of volunteering abroad in a community-driven project?
- How did getting lost in a labyrinthine city alleyway lead to serendipitous encounters and newfound friendships?
- What was the most memorable meal you had while sampling street food in a bustling market abroad?
- Can you recount the adrenaline rush of participating in an extreme sports activity in a foreign land?
- How did witnessing a breathtaking natural phenomenon during your travels leave a lasting impression on you?
- What cultural traditions or rituals did you participate in during a homestay experience with a local family?
- Can you describe the sense of wonder and awe you felt while exploring ancient ruins or historical sites?
- How did navigating a language barrier challenge and ultimately enrich your travel experience?
- What valuable life lessons did you learn from the mishaps and misadventures encountered during your journey off the beaten path?
Narrative Essay Topic Ideas on Career and Work Experience
College students can uncover captivating narrative essay ideas by exploring potential career paths or reminiscing about past job experiences.
- How did a challenging project at work showcase your problem-solving skills and resilience?
- Can you reflect on a pivotal mentorship experience that guided your career trajectory?
- What valuable lessons did you learn from a career setback or failure, and how did it shape your future success?
- How did a workplace conflict lead to personal growth and improved communication skills?
- Can you recount a moment when taking a professional risk paid off in unexpected ways?
- What insights did you gain from transitioning to a new industry or career path?
- How did participating in a cross-functional team project enhance your collaboration and leadership abilities?
- Can you describe the satisfaction of achieving a long-term career goal after years of hard work and perseverance?
- What impact did a meaningful recognition or award have on your motivation and sense of accomplishment?
- How did volunteering or pro bono work contribute to your professional development and sense of purpose?
- Can you reflect on the decision to leave a stable job in pursuit of passion or fulfillment?
- What strategies did you employ to navigate a toxic work environment and maintain your well-being?
- How did a career setback lead to unexpected opportunities for personal and professional growth?
- Can you describe a moment when mentorship or sponsorship played a crucial role in advancing your career?
- What lessons did you learn from a challenging client or customer interaction, and how did it shape your approach to customer service and relationship-building?
Interesting Narrative Essay Topics about Challenges and Obstacles
If you're not sure what to write about for your narrative essay, think back to the tough times you've had and how you managed to get through them.
- How did you conquer a once-paralyzing fear to chase your dreams?
- What new strengths did you discover while adapting to a physical challenge?
- Can you recall a creative solution you used during a tough financial period?
- When did you bravely stand against injustice, despite opposition?
- How did overcoming a language barrier broaden your horizons?
- What key lessons did you learn from a major setback in your life?
- How did you manage overwhelming stress and responsibilities?
- What inner reserves of resilience did you draw upon after personal loss?
- Describe a time when you defied societal norms to pursue your goals.
- Reflect on a moment when failure fueled your determination for success.
- When did you find the courage to leave your comfort zone behind?
- How did community support bolster you through a challenging time?
- Share a time when self-doubt led to newfound confidence.
- Can you recount a tragedy that spurred your personal growth?
- What insights did overcoming a monumental obstacle reveal about life?
Best Narrative Essay Topics: How to Choose the One That Resonates
A narrative essay is a type of writing that tells a personal story, including characters, plot, setting, and the order of events. Its main goal is to connect with readers emotionally and share a specific message or insight through the retelling of a meaningful experience.
Students write narrative essays as part of their studies for several reasons. Firstly, it allows them to express themselves creatively by sharing their unique experiences, thoughts, and feelings. Secondly, it helps them develop important writing skills like organizing ideas and thoughts effectively.
.webp)
Choosing good narrative essay ideas involves looking at personal experiences, interests, and the potential for engaging storytelling. Here's a simple guide to help you pick the right topic:
- Think about significant moments in your life that had a lasting impact, such as personal growth or overcoming challenges.
- Choose topics related to your hobbies, interests, or areas of expertise to make your story more engaging.
- Consider what your audience would be interested in and choose topics that resonate with them.
- Focus on a specific event or detail to make your narrative more focused and impactful.
- Look for universal themes like love or personal transformation that connect with readers on a deeper level.
- Brainstorm ideas and write freely to uncover compelling topics.
- Decide on storytelling techniques like flashbacks or foreshadowing and choose a topic that fits.
- Get feedback from friends, peers, or instructors to see if your topics are interesting and impactful.
- Choose topics that evoke strong emotions for a more compelling narrative.
- Select a topic that you personally connect with to make your story authentic.
Once you've chosen a topic, brainstorm ideas and create an outline for your essay. Follow your professor's instructions carefully and consider seeking help from our narrative essay writing service if needed.
Bring your stories to life with EssayPro. Select from a vast array of narrative essay topics and let our professionals help you weave your tales into captivating essays. Whether it's adventure, reflection, or imagination, we're here to assist.
Final Remarks
As we wrap up, our list of 200 narrative essay topics is here to fuel your creativity for your next writing project! Whether you're sharing a memorable event, reliving a childhood memory, or expressing a profound insight, crafting a narrative essay can be an uplifting experience that resonates deeply with readers.
And if you're gearing up for college admissions, why not check out our admission essay writing service ? We've already assisted countless students in securing their spots at their dream colleges, and we'd love to help you, too!
Give Us Your Task
We provide assistance as well as editing and proofreading. Every paper we deal with is written and triple-checked by a team of experts—which means that you are guaranteed to get top-quality work from our term paper writing service . Order now!

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)

Narrative Analysis 101
Everything you need to know to get started
By: Ethar Al-Saraf (PhD)| Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to research, the host of qualitative analysis methods available to you can be a little overwhelming. In this post, we’ll unpack the sometimes slippery topic of narrative analysis . We’ll explain what it is, consider its strengths and weaknesses , and look at when and when not to use this analysis method.
Overview: Narrative Analysis
- What is narrative analysis (simple definition)
- The two overarching approaches
- The strengths & weaknesses of narrative analysis
- When (and when not) to use it
- Key takeaways
What Is Narrative Analysis?
Simply put, narrative analysis is a qualitative analysis method focused on interpreting human experiences and motivations by looking closely at the stories (the narratives) people tell in a particular context.
In other words, a narrative analysis interprets long-form participant responses or written stories as data, to uncover themes and meanings . That data could be taken from interviews , monologues, written stories, or even recordings. In other words, narrative analysis can be used on both primary and secondary data to provide evidence from the experiences described.
That’s all quite conceptual, so let’s look at an example of how narrative analysis could be used.
Let’s say you’re interested in researching the beliefs of a particular author on popular culture. In that case, you might identify the characters , plotlines , symbols and motifs used in their stories. You could then use narrative analysis to analyse these in combination and against the backdrop of the relevant context.
This would allow you to interpret the underlying meanings and implications in their writing, and what they reveal about the beliefs of the author. In other words, you’d look to understand the views of the author by analysing the narratives that run through their work.

The Two Overarching Approaches
Generally speaking, there are two approaches that one can take to narrative analysis. Specifically, an inductive approach or a deductive approach. Each one will have a meaningful impact on how you interpret your data and the conclusions you can draw, so it’s important that you understand the difference.
First up is the inductive approach to narrative analysis.
The inductive approach takes a bottom-up view , allowing the data to speak for itself, without the influence of any preconceived notions . With this approach, you begin by looking at the data and deriving patterns and themes that can be used to explain the story, as opposed to viewing the data through the lens of pre-existing hypotheses, theories or frameworks. In other words, the analysis is led by the data.
For example, with an inductive approach, you might notice patterns or themes in the way an author presents their characters or develops their plot. You’d then observe these patterns, develop an interpretation of what they might reveal in the context of the story, and draw conclusions relative to the aims of your research.
Contrasted to this is the deductive approach.
With the deductive approach to narrative analysis, you begin by using existing theories that a narrative can be tested against . Here, the analysis adopts particular theoretical assumptions and/or provides hypotheses, and then looks for evidence in a story that will either verify or disprove them.
For example, your analysis might begin with a theory that wealthy authors only tell stories to get the sympathy of their readers. A deductive analysis might then look at the narratives of wealthy authors for evidence that will substantiate (or refute) the theory and then draw conclusions about its accuracy, and suggest explanations for why that might or might not be the case.
Which approach you should take depends on your research aims, objectives and research questions . If these are more exploratory in nature, you’ll likely take an inductive approach. Conversely, if they are more confirmatory in nature, you’ll likely opt for the deductive approach.
Need a helping hand?
Strengths & Weaknesses
Now that we have a clearer view of what narrative analysis is and the two approaches to it, it’s important to understand its strengths and weaknesses , so that you can make the right choices in your research project.
A primary strength of narrative analysis is the rich insight it can generate by uncovering the underlying meanings and interpretations of human experience. The focus on an individual narrative highlights the nuances and complexities of their experience, revealing details that might be missed or considered insignificant by other methods.
Another strength of narrative analysis is the range of topics it can be used for. The focus on human experience means that a narrative analysis can democratise your data analysis, by revealing the value of individuals’ own interpretation of their experience in contrast to broader social, cultural, and political factors.
All that said, just like all analysis methods, narrative analysis has its weaknesses. It’s important to understand these so that you can choose the most appropriate method for your particular research project.
The first drawback of narrative analysis is the problem of subjectivity and interpretation . In other words, a drawback of the focus on stories and their details is that they’re open to being understood differently depending on who’s reading them. This means that a strong understanding of the author’s cultural context is crucial to developing your interpretation of the data. At the same time, it’s important that you remain open-minded in how you interpret your chosen narrative and avoid making any assumptions .
A second weakness of narrative analysis is the issue of reliability and generalisation . Since narrative analysis depends almost entirely on a subjective narrative and your interpretation, the findings and conclusions can’t usually be generalised or empirically verified. Although some conclusions can be drawn about the cultural context, they’re still based on what will almost always be anecdotal data and not suitable for the basis of a theory, for example.
Last but not least, the focus on long-form data expressed as stories means that narrative analysis can be very time-consuming . In addition to the source data itself, you will have to be well informed on the author’s cultural context as well as other interpretations of the narrative, where possible, to ensure you have a holistic view. So, if you’re going to undertake narrative analysis, make sure that you allocate a generous amount of time to work through the data.

When To Use Narrative Analysis
As a qualitative method focused on analysing and interpreting narratives describing human experiences, narrative analysis is usually most appropriate for research topics focused on social, personal, cultural , or even ideological events or phenomena and how they’re understood at an individual level.
For example, if you were interested in understanding the experiences and beliefs of individuals suffering social marginalisation, you could use narrative analysis to look at the narratives and stories told by people in marginalised groups to identify patterns , symbols , or motifs that shed light on how they rationalise their experiences.
In this example, narrative analysis presents a good natural fit as it’s focused on analysing people’s stories to understand their views and beliefs at an individual level. Conversely, if your research was geared towards understanding broader themes and patterns regarding an event or phenomena, analysis methods such as content analysis or thematic analysis may be better suited, depending on your research aim .

Let’s recap
In this post, we’ve explored the basics of narrative analysis in qualitative research. The key takeaways are:
- Narrative analysis is a qualitative analysis method focused on interpreting human experience in the form of stories or narratives .
- There are two overarching approaches to narrative analysis: the inductive (exploratory) approach and the deductive (confirmatory) approach.
- Like all analysis methods, narrative analysis has a particular set of strengths and weaknesses .
- Narrative analysis is generally most appropriate for research focused on interpreting individual, human experiences as expressed in detailed , long-form accounts.
If you’d like to learn more about narrative analysis and qualitative analysis methods in general, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach blog here . Alternatively, if you’re looking for hands-on help with your project, take a look at our 1-on-1 private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Thanks. I need examples of narrative analysis
Here are some examples of research topics that could utilise narrative analysis:
Personal Narratives of Trauma: Analysing personal stories of individuals who have experienced trauma to understand the impact, coping mechanisms, and healing processes.
Identity Formation in Immigrant Communities: Examining the narratives of immigrants to explore how they construct and negotiate their identities in a new cultural context.
Media Representations of Gender: Analysing narratives in media texts (such as films, television shows, or advertisements) to investigate the portrayal of gender roles, stereotypes, and power dynamics.
Where can I find an example of a narrative analysis table ?
Please i need help with my project,
how can I cite this article in APA 7th style?
please mention the sources as well.
My research is mixed approach. I use interview,key_inforamt interview,FGD and document.so,which qualitative analysis is appropriate to analyze these data.Thanks
Which qualitative analysis methode is appropriate to analyze data obtain from intetview,key informant intetview,Focus group discussion and document.
I’ve finished my PhD. Now I need a “platform” that will help me objectively ascertain the tacit assumptions that are buried within a narrative. Can you help?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Narrative Essay Writing
Narrative Essay Examples

20+ Top Narrative Essay Examples by Experts
12 min read
Published on: Apr 12, 2020
Last updated on: Mar 24, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Narrative Essay in Simple Steps
Interesting Narrative Essay Topics and Ideas
Personal Narrative Essay - Easy Guide & Examples
Share this article
Narrative essays are a common assignment in school, but many students struggle to write them.
The problem with narrative essays is that they can be difficult to write. They require students to think about their own experiences and to put those experiences into words. This can be a challenge, especially for students who are not used to writing about themselves.
The solution to the problem of writing narrative essays is to provide students with examples. By reading examples of narrative essays, students can see how other students have successfully written about their own experiences.
In this blog post, we will provide you with examples of narrative essays.By the end of this blog post, you will have a better understanding of how to write a narrative essay.
On This Page On This Page -->
Before writing, go through narrative essay examples to ensure that outlining and formatting are done correctly. Moreover, looking at examples will allow the writer to understand sensory details and vocabulary to describe events, settings, characters, and emotions.
Here are some famous narrative essays that you can consider adding to your reading wishlist:
âA Modest Proposalâ by Jonathan Swift
âOnce More to the Lakeâ by EB White
âThe Fourth of Julyâ by Audre Lorde
âThe Story of an Hourâ by Kate Chopin
âThe Crisisâ by Thomas Paine
But it doesn't end here! To help our students, CollegeEssay.org has gathered many other narrative essay sample. These examples will help you learn the correct formation of a narrative essay.
Read on to discover!
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Are you looking for a sample to draft a personal narrative essay ? Go through the example provided below to understand how the first-person and third-person perspectives are used in a narrative essay.
|
Sample Personal Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Example for Middle School
A narrative essay is frequently assigned to middle school students to assess their writing and creative skills. If you are a student looking for a sample narrative essay for your middle school assignment, go through the example provided below.
Narrative Essay Example: 7th Grade
Narrative Essay Example for Grade 8
Grade 9 Narrative Essay Example
Sample Narrative Essay Grade 12
Narrative Essay Example for High School
When drafting assignments for high school, professional writing is essential. Your essays and papers should be well structured and written in order to achieve better grades. If you are assigned a narrative essay, go through the sample provided to see how an effective essay is written.
Sample Narrative Essay For High School
Good Narrative Essay Examples for College
College essays are more complex in nature than other academic levels. They require a better understanding of the concept, following a proper writing procedure, and an outline.
Although you are to draft a narrative essay for your college assignment, make sure it is professionally written. Read the sample narrative essay provided below.
|
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
If you are to draft a document on the recreation of an event, a descriptive narrative essay is written. It presents an incident that happened to the writer and the backed-up information that supports the story.
The following is a perfect example of a descriptive narrative essay.
Sample Descriptive Narrative Essay

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Literacy Narrative Essay Example
Academic assignments often require students to draft essays on education. Education is the most significant topic of discussion, and for this purpose, almost every essay type and research paper studies it.
If you are drafting a narrative essay on literacy, go through the sample provided.
Fictional Narrative Essay Example
Drafting a fictional piece of document requires a more vivid description and detail. If you are assigned a narrative essay to draft on a fictional theme, read the example provided below.
Sample Fictional Narrative Essay
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
In a narrative essay, the goal is to write a story from one person's perspective. To do this well requires incorporating all of these aspects:
Below are some golden points that you should keep in mind when writing a narrative essay.
- Chronological order is the most common way to present information.
- A thesis statement has a function in an essay. This is typically evident in the opening paragraph.
- The writer's argument is clearly communicated through the use of sensory details and vivid language.
- This draws the reader in and makes them interested in what the writer has to say. Everything in the passage is somehow related to the main point.
How to Start a Narrative Essay?
When you start writing the narrative essay, you should follow some steps and make your writing process easy.
For your help, we gathered some steps that you should follow when starting writing the essay.
- Choose a narrative essay topic that is engaging and interesting.
- Do some research and then start writing the essay.
- Create an outline.
- Start writing the essay. The way you describe things should be creative and colorful. Thus, the reader can feel as if they are right there with what's happening.
- Proofread the essay before submitting it.
Watch the video below for tips on how to write a narrative essay:
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Professional essay writers of CollegeEssay.org have gathered some tips and tricks for you to follow to make your narrative essay remarkable. Even if you are aware of the writing procedure, it is advised to use expert tips to make your documents flawless.
Follow the tips provided below to draft an exceptional narrative essay.
- Clear Content: The narrative essay content should be clear. All the details and descriptions provided should be readable and understandable by the audience. Avoid using complex words and distribute content into paragraphs.
- Keep it concise: Avoid describing every minor detail or movement. Provide only explanations that are important for the readers to imagine.
- Use first-person perspective: To make something believable and interesting for the readers, state it from the first-person perspective. Share your personal experiences, stories, and opinions to make the content impactful.
- Use limited referencing: When drafting an essay, according to the instructed format, avoid using frequent in-text citations.
- Use Clear Stance: Write your point of view clearly, so the readers feel that it is a genuine piece of writing.
Keep in mind that a narrative essay is different from an expository essay but the same as a descriptive essay .
In conclusion,
Using the tips provided by the professionals and going through the narrative essay examples will let you draft an effective paper.
Looking for top-tier essay writing help online ?
Our narrative essay writing service offers unparalleled expertise to bring your stories to life with clarity and creativity.
Also, elevate your writing journey with the best essay writer , our AI-driven tool that combines cutting-edge technology with user-friendly functionality. Experience the blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern innovation in your next essay. Try it now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a narrative paragraph.
Paragraphs vary in length depending on the content, but a standard 5-sentence paragraph usually isn't enough to tell an interesting story.
How do I write a narrative essay?
Here are some steps that will help you to write a great narrative essay.
- Consider the topic
- Start writing the draft
- Provide supporting facts
- Revise your essay
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
3 Great Narrative Essay Examples + Tips for Writing
General Education

A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story .
But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif —a recurring theme or idea that you’ll explore throughout. Narrative essays are less rigid, more creative in expression, and therefore pretty different from most other essays you’ll be writing.
But not to fear—in this article, we’ll be covering what a narrative essay is, how to write a good one, and also analyzing some personal narrative essay examples to show you what a great one looks like.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
At first glance, a narrative essay might sound like you’re just writing a story. Like the stories you're used to reading, a narrative essay is generally (but not always) chronological, following a clear throughline from beginning to end. Even if the story jumps around in time, all the details will come back to one specific theme, demonstrated through your choice in motifs.
Unlike many creative stories, however, your narrative essay should be based in fact. That doesn’t mean that every detail needs to be pure and untainted by imagination, but rather that you shouldn’t wholly invent the events of your narrative essay. There’s nothing wrong with inventing a person’s words if you can’t remember them exactly, but you shouldn’t say they said something they weren’t even close to saying.
Another big difference between narrative essays and creative fiction—as well as other kinds of essays—is that narrative essays are based on motifs. A motif is a dominant idea or theme, one that you establish before writing the essay. As you’re crafting the narrative, it’ll feed back into your motif to create a comprehensive picture of whatever that motif is.
For example, say you want to write a narrative essay about how your first day in high school helped you establish your identity. You might discuss events like trying to figure out where to sit in the cafeteria, having to describe yourself in five words as an icebreaker in your math class, or being unsure what to do during your lunch break because it’s no longer acceptable to go outside and play during lunch. All of those ideas feed back into the central motif of establishing your identity.
The important thing to remember is that while a narrative essay is typically told chronologically and intended to read like a story, it is not purely for entertainment value. A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning.
Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays. If you’re writing a story about yourself, it’s natural to refer to yourself within the essay. It’s also okay to use other perspectives, such as third- or even second-person, but that should only be done if it better serves your motif. Generally speaking, your narrative essay should be in first-person perspective.
Though your motif choices may feel at times like you’re making a point the way you would in an argumentative essay, a narrative essay’s goal is to tell a story, not convince the reader of anything. Your reader should be able to tell what your motif is from reading, but you don’t have to change their mind about anything. If they don’t understand the point you are making, you should consider strengthening the delivery of the events and descriptions that support your motif.
Narrative essays also share some features with analytical essays, in which you derive meaning from a book, film, or other media. But narrative essays work differently—you’re not trying to draw meaning from an existing text, but rather using an event you’ve experienced to convey meaning. In an analytical essay, you examine narrative, whereas in a narrative essay you create narrative.
The structure of a narrative essay is also a bit different than other essays. You’ll generally be getting your point across chronologically as opposed to grouping together specific arguments in paragraphs or sections. To return to the example of an essay discussing your first day of high school and how it impacted the shaping of your identity, it would be weird to put the events out of order, even if not knowing what to do after lunch feels like a stronger idea than choosing where to sit. Instead of organizing to deliver your information based on maximum impact, you’ll be telling your story as it happened, using concrete details to reinforce your theme.

3 Great Narrative Essay Examples
One of the best ways to learn how to write a narrative essay is to look at a great narrative essay sample. Let’s take a look at some truly stellar narrative essay examples and dive into what exactly makes them work so well.
A Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Today is Press Day at the Illinois State Fair in Springfield, and I’m supposed to be at the fairgrounds by 9:00 A.M. to get my credentials. I imagine credentials to be a small white card in the band of a fedora. I’ve never been considered press before. My real interest in credentials is getting into rides and shows for free. I’m fresh in from the East Coast, for an East Coast magazine. Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish. I think they asked me to do this because I grew up here, just a couple hours’ drive from downstate Springfield. I never did go to the state fair, though—I pretty much topped out at the county fair level. Actually, I haven’t been back to Illinois for a long time, and I can’t say I’ve missed it.
Throughout this essay, David Foster Wallace recounts his experience as press at the Illinois State Fair. But it’s clear from this opening that he’s not just reporting on the events exactly as they happened—though that’s also true— but rather making a point about how the East Coast, where he lives and works, thinks about the Midwest.
In his opening paragraph, Wallace states that outright: “Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish.”
Not every motif needs to be stated this clearly , but in an essay as long as Wallace’s, particularly since the audience for such a piece may feel similarly and forget that such a large portion of the country exists, it’s important to make that point clear.
But Wallace doesn’t just rest on introducing his motif and telling the events exactly as they occurred from there. It’s clear that he selects events that remind us of that idea of East Coast cynicism , such as when he realizes that the Help Me Grow tent is standing on top of fake grass that is killing the real grass beneath, when he realizes the hypocrisy of craving a corn dog when faced with a real, suffering pig, when he’s upset for his friend even though he’s not the one being sexually harassed, and when he witnesses another East Coast person doing something he wouldn’t dare to do.
Wallace is literally telling the audience exactly what happened, complete with dates and timestamps for when each event occurred. But he’s also choosing those events with a purpose—he doesn’t focus on details that don’t serve his motif. That’s why he discusses the experiences of people, how the smells are unappealing to him, and how all the people he meets, in cowboy hats, overalls, or “black spandex that looks like cheesecake leotards,” feel almost alien to him.
All of these details feed back into the throughline of East Coast thinking that Wallace introduces in the first paragraph. He also refers back to it in the essay’s final paragraph, stating:
At last, an overarching theory blooms inside my head: megalopolitan East Coasters’ summer treats and breaks and literally ‘getaways,’ flights-from—from crowds, noise, heat, dirt, the stress of too many sensory choices….The East Coast existential treat is escape from confines and stimuli—quiet, rustic vistas that hold still, turn inward, turn away. Not so in the rural Midwest. Here you’re pretty much away all the time….Something in a Midwesterner sort of actuates , deep down, at a public event….The real spectacle that draws us here is us.
Throughout this journey, Wallace has tried to demonstrate how the East Coast thinks about the Midwest, ultimately concluding that they are captivated by the Midwest’s less stimuli-filled life, but that the real reason they are interested in events like the Illinois State Fair is that they are, in some ways, a means of looking at the East Coast in a new, estranging way.
The reason this works so well is that Wallace has carefully chosen his examples, outlined his motif and themes in the first paragraph, and eventually circled back to the original motif with a clearer understanding of his original point.
When outlining your own narrative essay, try to do the same. Start with a theme, build upon it with examples, and return to it in the end with an even deeper understanding of the original issue. You don’t need this much space to explore a theme, either—as we’ll see in the next example, a strong narrative essay can also be very short.

Death of a Moth by Virginia Woolf
After a time, tired by his dancing apparently, he settled on the window ledge in the sun, and, the queer spectacle being at an end, I forgot about him. Then, looking up, my eye was caught by him. He was trying to resume his dancing, but seemed either so stiff or so awkward that he could only flutter to the bottom of the window-pane; and when he tried to fly across it he failed. Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure. After perhaps a seventh attempt he slipped from the wooden ledge and fell, fluttering his wings, on to his back on the window sill. The helplessness of his attitude roused me. It flashed upon me that he was in difficulties; he could no longer raise himself; his legs struggled vainly. But, as I stretched out a pencil, meaning to help him to right himself, it came over me that the failure and awkwardness were the approach of death. I laid the pencil down again.
In this essay, Virginia Woolf explains her encounter with a dying moth. On surface level, this essay is just a recounting of an afternoon in which she watched a moth die—it’s even established in the title. But there’s more to it than that. Though Woolf does not begin her essay with as clear a motif as Wallace, it’s not hard to pick out the evidence she uses to support her point, which is that the experience of this moth is also the human experience.
In the title, Woolf tells us this essay is about death. But in the first paragraph, she seems to mostly be discussing life—the moth is “content with life,” people are working in the fields, and birds are flying. However, she mentions that it is mid-September and that the fields were being plowed. It’s autumn and it’s time for the harvest; the time of year in which many things die.
In this short essay, she chronicles the experience of watching a moth seemingly embody life, then die. Though this essay is literally about a moth, it’s also about a whole lot more than that. After all, moths aren’t the only things that die—Woolf is also reflecting on her own mortality, as well as the mortality of everything around her.
At its core, the essay discusses the push and pull of life and death, not in a way that’s necessarily sad, but in a way that is accepting of both. Woolf begins by setting up the transitional fall season, often associated with things coming to an end, and raises the ideas of pleasure, vitality, and pity.
At one point, Woolf tries to help the dying moth, but reconsiders, as it would interfere with the natural order of the world. The moth’s death is part of the natural order of the world, just like fall, just like her own eventual death.
All these themes are set up in the beginning and explored throughout the essay’s narrative. Though Woolf doesn’t directly state her theme, she reinforces it by choosing a small, isolated event—watching a moth die—and illustrating her point through details.
With this essay, we can see that you don’t need a big, weird, exciting event to discuss an important meaning. Woolf is able to explore complicated ideas in a short essay by being deliberate about what details she includes, just as you can be in your own essays.

Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
On the twenty-ninth of July, in 1943, my father died. On the same day, a few hours later, his last child was born. Over a month before this, while all our energies were concentrated in waiting for these events, there had been, in Detroit, one of the bloodiest race riots of the century. A few hours after my father’s funeral, while he lay in state in the undertaker’s chapel, a race riot broke out in Harlem. On the morning of the third of August, we drove my father to the graveyard through a wilderness of smashed plate glass.
Like Woolf, Baldwin does not lay out his themes in concrete terms—unlike Wallace, there’s no clear sentence that explains what he’ll be talking about. However, you can see the motifs quite clearly: death, fatherhood, struggle, and race.
Throughout the narrative essay, Baldwin discusses the circumstances of his father’s death, including his complicated relationship with his father. By introducing those motifs in the first paragraph, the reader understands that everything discussed in the essay will come back to those core ideas. When Baldwin talks about his experience with a white teacher taking an interest in him and his father’s resistance to that, he is also talking about race and his father’s death. When he talks about his father’s death, he is also talking about his views on race. When he talks about his encounters with segregation and racism, he is talking, in part, about his father.
Because his father was a hard, uncompromising man, Baldwin struggles to reconcile the knowledge that his father was right about many things with his desire to not let that hardness consume him, as well.
Baldwin doesn’t explicitly state any of this, but his writing so often touches on the same motifs that it becomes clear he wants us to think about all these ideas in conversation with one another.
At the end of the essay, Baldwin makes it more clear:
This fight begins, however, in the heart and it had now been laid to my charge to keep my own heart free of hatred and despair. This intimation made my heart heavy and, now that my father was irrecoverable, I wished that he had been beside me so that I could have searched his face for the answers which only the future would give me now.
Here, Baldwin ties together the themes and motifs into one clear statement: that he must continue to fight and recognize injustice, especially racial injustice, just as his father did. But unlike his father, he must do it beginning with himself—he must not let himself be closed off to the world as his father was. And yet, he still wishes he had his father for guidance, even as he establishes that he hopes to be a different man than his father.
In this essay, Baldwin loads the front of the essay with his motifs, and, through his narrative, weaves them together into a theme. In the end, he comes to a conclusion that connects all of those things together and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of completion—though the elements may have been initially disparate, in the end everything makes sense.
You can replicate this tactic of introducing seemingly unattached ideas and weaving them together in your own essays. By introducing those motifs, developing them throughout, and bringing them together in the end, you can demonstrate to your reader how all of them are related. However, it’s especially important to be sure that your motifs and clear and consistent throughout your essay so that the conclusion feels earned and consistent—if not, readers may feel mislead.
5 Key Tips for Writing Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can be a lot of fun to write since they’re so heavily based on creativity. But that can also feel intimidating—sometimes it’s easier to have strict guidelines than to have to make it all up yourself. Here are a few tips to keep your narrative essay feeling strong and fresh.
Develop Strong Motifs
Motifs are the foundation of a narrative essay . What are you trying to say? How can you say that using specific symbols or events? Those are your motifs.
In the same way that an argumentative essay’s body should support its thesis, the body of your narrative essay should include motifs that support your theme.
Try to avoid cliches, as these will feel tired to your readers. Instead of roses to symbolize love, try succulents. Instead of the ocean representing some vast, unknowable truth, try the depths of your brother’s bedroom. Keep your language and motifs fresh and your essay will be even stronger!
Use First-Person Perspective
In many essays, you’re expected to remove yourself so that your points stand on their own. Not so in a narrative essay—in this case, you want to make use of your own perspective.
Sometimes a different perspective can make your point even stronger. If you want someone to identify with your point of view, it may be tempting to choose a second-person perspective. However, be sure you really understand the function of second-person; it’s very easy to put a reader off if the narration isn’t expertly deployed.
If you want a little bit of distance, third-person perspective may be okay. But be careful—too much distance and your reader may feel like the narrative lacks truth.
That’s why first-person perspective is the standard. It keeps you, the writer, close to the narrative, reminding the reader that it really happened. And because you really know what happened and how, you’re free to inject your own opinion into the story without it detracting from your point, as it would in a different type of essay.
Stick to the Truth
Your essay should be true. However, this is a creative essay, and it’s okay to embellish a little. Rarely in life do we experience anything with a clear, concrete meaning the way somebody in a book might. If you flub the details a little, it’s okay—just don’t make them up entirely.
Also, nobody expects you to perfectly recall details that may have happened years ago. You may have to reconstruct dialog from your memory and your imagination. That’s okay, again, as long as you aren’t making it up entirely and assigning made-up statements to somebody.
Dialog is a powerful tool. A good conversation can add flavor and interest to a story, as we saw demonstrated in David Foster Wallace’s essay. As previously mentioned, it’s okay to flub it a little, especially because you’re likely writing about an experience you had without knowing that you’d be writing about it later.
However, don’t rely too much on it. Your narrative essay shouldn’t be told through people explaining things to one another; the motif comes through in the details. Dialog can be one of those details, but it shouldn’t be the only one.
Use Sensory Descriptions
Because a narrative essay is a story, you can use sensory details to make your writing more interesting. If you’re describing a particular experience, you can go into detail about things like taste, smell, and hearing in a way that you probably wouldn’t do in any other essay style.
These details can tie into your overall motifs and further your point. Woolf describes in great detail what she sees while watching the moth, giving us the sense that we, too, are watching the moth. In Wallace’s essay, he discusses the sights, sounds, and smells of the Illinois State Fair to help emphasize his point about its strangeness. And in Baldwin’s essay, he describes shattered glass as a “wilderness,” and uses the feelings of his body to describe his mental state.
All these descriptions anchor us not only in the story, but in the motifs and themes as well. One of the tools of a writer is making the reader feel as you felt, and sensory details help you achieve that.
What’s Next?
Looking to brush up on your essay-writing capabilities before the ACT? This guide to ACT English will walk you through some of the best strategies and practice questions to get you prepared!
Part of practicing for the ACT is ensuring your word choice and diction are on point. Check out this guide to some of the most common errors on the ACT English section to be sure that you're not making these common mistakes!
A solid understanding of English principles will help you make an effective point in a narrative essay, and you can get that understanding through taking a rigorous assortment of high school English classes !
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Social Science
- Qualitative Social Research
- Narrative Research
A Narrative Research Approach: The Experiences of Social Media Support in Higher Education
- Conference: International Conference on Learning and Collaboration Technologies

- YüksekÖğretim MEsleki Gelişim Ağı Derneği - YÖMEGA

- Eastern Mediterranean University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Dianne M Ramirez
- Mecaella Joy D. Liwag

- Ayobami Ojebode

- Rexford Assasie Oppong

- Purwohandoko
- Dr. Nargis Khan
- Musta'in Musta'in
- Wildan Isna Asyhar

- M.Pd. Drs. Musta’in
- M.Pd. Wildan Isna Asyhar
- Sarah Cousins
- Dounia Bissar

- Hester Tinti-Kane
- F. Michael Connelly

- John W. Creswell
- J.W. Cresswell
- Vicki L. Plano Clark
- M.L. Gutmann
- William E. Hanson

- Yu-Chih Sun
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Peer Reviewed
The role of narrative in misinformation games
Article metrics.
CrossRef Citations
Altmetric Score
PDF Downloads
Several existing media literacy games aim to increase resilience to misinformation. However, they lack variety in their approaches. The vast majority focus on assessing information accuracy, with limited exploration of socio-emotional influences of misinformation adoption. Misinformation correction and educational games have explored how narrative persuasion influences personal beliefs, as identification with certain narratives can frame the interpretation of information. We created a preliminary framework for designers seeking to develop narrative-driven misinformation games that synthesizes findings from psychology, narrative theory, and game design. In addition, we conducted a narrative-centered content analysis of existing media literacy games.
Human Centered Design & Engineering, University of Washington, USA
Information School, University of Washington, USA

Research Questions
- How can the narratives of existing misinformation games help address psychological drivers of misinformation?
- What aspects of narrative design are important to consider in the context of games for misinformation education?
Essay Summary
- We compiled findings from misinformation psychology, game studies, and narrative theory to inform a content analysis of how existing misinformation education games are utilizing narrative to address psychological drivers of misinformation.
- Researchers across the fields of misinformation, educational games, and communication theory have used narrative to 1) promote identification with opposing viewpoints, 2) reduce counterarguing and reactance, and 3) facilitate connection to educational outcomes.
- We summarize our findings into the misinformation game narrative design (MGND) framework, which can be used by researchers and designers to create game-based misinformation interventions targeted at specific audiences.
Implications
Misinformation and disinformation have many widespread and often harmful effects on society due to their ability to shape people’s beliefs and behaviors (Ecker et al., 2022). This has led to calls to feature misinformation more predominantly in mainstream media literacy curricula (Dame Adjin-Tettey, 2022). Media literacy was shown to positively correlate with correct determination of the accuracy of online information (Kahne & Bowyer, 2017).
Games have been suggested as a promising educational medium for effective media literacy interventions (Chang et al., 2020). The immersive nature of games allows players to creatively engage with real-world situations as thought experiments (Schulzke, 2014), allowing for a safe space to investigate complex issues. Indeed, researchers and educators have created games that aim to improve media literacy (Contreras-Espinosa & Eguia-Gomez, 2023; Kiili et al., 2023) and effectively inoculate players from misinformation and disinformation (Basol et al., 2020; Maertens et al., 2021; Roozenbeek & van der Linden, 2019; van der Linden et al., 2017). However, there are limitations to the existing body of game-based misinformation interventions, namely their lack of theoretical variance. The majority are based in inoculation theory (Kiili et al., 2023), and recent work has suggested that inoculation-based interventions may simply increase the likelihood of conservative reporting, rather than critical engagement with misinformation (Modirrousta-Galian & Higham, 2023). While informative, these interventions primarily address rational processes of misinformation correction (i.e., teaching basic media literacy competencies). However, the processing and subsequent adoption of misinformation is also heavily influenced by psychological drivers and personal belief (Ecker et al., 2022). Thus, it is essential for designers of misinformation education games to facilitate player exploration of the socio-emotional influences that can lead to the acceptance and spread of misinformation.
Research on misinformation correction and educational games has explored a common method to engage with people on an emotional basis: narrative (Cohen et al., 2015; Domínguez et al., 2016; Iten et al., 2018; Mahood & Hanus, 2017; Ophir et al., 2020; Sangalang et al., 2019). We define narrative as a story that contains event(s), character(s), setting(s), structure, a clear point of view, and a sense of time (Chatman, 1978). Reading, processing, and identifying with narratives is a fundamental component of how we organize our interpretations of reality (Bruner, 1990). However, despite the effectiveness of narrative persuasion in both misinformation correction (Cohen et al., 2015; Ophir et al., 2020; Sangalang et al., 2019) and educational games (Domínguez et al., 2016; Iten et al., 2018; Mahood & Hanus, 2017), current misinformation games are notably lacking in narrative-driven learning mechanisms, as their primary focus tends to be on improving skill-based or knowledge-based information literacy (Contreras-Espinosa & Eguia-Gomez, 2023). There is a strong potential for using narrative as a tool for prompting player empathy and emotional connection within misinformation education (Grace & Liang, 2024).
Misinformation game narrative design (MGND) framework
We synthesized possible benefits of narrative-based education games from communication theory and game design and developed an understanding of how key narrative elements, such as those presented in Chatman (1978), may synergize with game mechanics to emotionally connect with players. Using these learnings as a basis, we then performed a content analysis of current misinformation education games. We used our findings to map an initial framework for designers seeking to create narrative-driven misinformation games. We intend to aid these designers, as well as educators and practitioners, in tying certain narrative elements to their intended learning outcomes. Our proposed design framework, the misinformation game narrative design (MGND) framework, consists of ten dimensions, each of which contains several elements. We began by choosing relevant dimensions (i.e., structure, setting, and characters) from Chatman’s definition of narrative (1978). We then integrated game design elements, such as player agency and dynamics , as well as considerations from misinformation psychology, namely the psychological drivers and the correction type the designer is creating. The intended audience must also be centered through the design. It is possible for a game narrative to have multiple elements within each dimension or exist on a sliding scale between two elements. The dimensions are as follows: educational goals, intended audience, psychological drivers, narrative structure, setting, tone, player agency, player morality, ending, and player dynamics.
Educational goals: What arethe intended educational goals? We derived the following goals from Barzilai and Chinn’s (2020) educational lenses for a post-truth world:
- Addressing not knowing how to know . Learners may have gaps in their knowledge and skills for critically dealing with misinformation in digital spheres. Educational games can remedy this by promoting civic, digital, and scientific literacy, as well as inoculating against misinformation.
- Addressing fallible ways of knowing . Adoption of misinformation is strongly influenced by cognitive biases. Educational games can mitigate this by teaching players about cognitive and socioemotional biases and cultivating epistemic vigilance through evaluating the reliability and trustworthiness of information.
- Addressing not caring enough about truth . Misinformation is often propagated by actors who do not necessarily care that they are being misleading or if they are being misled. Educational games can address this by teaching players about the potential consequences of not taking misleading information seriously.
- Addressing disagreeing about how to know . People have ways of seeing the world that are often in conflict with each other. Educational games should emphasize authoritative sources and incorporate debunking strategies when necessary. At the same time, they should teach players how to discuss and evaluate differing beliefs while recognizing and coordinating various epistemologies.
Goals 1 and 2 focus on information literacy and prebunking and are frequently addressed in the current body of misinformation games . However, there is currently limited exploration of goals 3 and 4, and we provide examples of how games can be framed around those goals in Appendix C. All approaches have benefits and drawbacks, but one might be preferable depending on the context, such as the audience or the type of misinformation.
Intended audience : Who is the intended audience? Games can be created for a (1) general audience , (2) specific audience , or (3) somewhere in between . Designing for general audiences increases the potential reach of the game, while designing for targeted communities creates avenues for designers to utilize narrative affordances. For example, designers could consider creating characters with which target groups may very strongly identify and use those characters as vehicles to explore various aspects of players’ beliefs. This has the potential to engage players in discussions with reduced risk of reactance and counterarguing.
Psychological drivers : What psychological aspects of misinformation does the game touch upon? In our content analysis, we used Shane’s (2020) framework as a basis for identifying a handful of psychological drivers addressed by existing misinformation games (1–5), and we also included one additional driver, emotion, as some games address the influence of emotive information and emotional state on false beliefs (Ecker et al., 2022):
- Third person effect (the tendency to assume that misinformation affects others more than oneself)
- Social pressure (the inclination to repost and believe misinformation shared by one’s social circles)
- Confirmation bias (the tendency to believe information that verifies one’s existing beliefs)
- The rabbit hole effect (a pathway leading towards more extreme misinformation)
- Heuristics (indicators used to make quick judgments)
In addition, designers could also consider other psychological drivers or social factors, such as cognitive dissonance, motivated reasoning, or cognitive miserliness. This would also help establish more specific learning outcomes of the game.
Narrative structure: How does the story progress from beginning to end? We identified three possibilities for the progression of the story: (1) linear , where the story follows a fixed and predictable path, (2) plot twist , where players are abruptly introduced to new information halfway through an otherwise linear story, and (3) branching , where there are multiple paths and multiple endings that the player can discover based on their actions. These choices may have an impact on how people feel at the end of the game and prompt reflection on their role or agency. Furthermore, different modalities may afford different structures. For example, a linear structure would work better for a digital escape room than a physical one, where players can more efficiently examine different parts of the puzzle in parallel.
Setting : Where does the story take place? The story can take place in either realistic or fantastical setting. A realistic setting provides an opportunity for a game to reflect prominent mis- or disinformation issues from the modern day. On the contrary, a fantastical setting may allow for a narrative that can appeal to broader audiences, especially in polarized communities and increase the longevity of the game as it will not feel out of date when new misinformation issues become prevalent. Several existing misinformation games chose a dystopian approach, a fantastical setting that still affords serious conversations about the harm of disinformation present today. Designers could also choose to integrate elements from both: realistic elements to keep the game grounded, but with added fantastical elements to engage younger audiences.
Tone : How does the story convey the topic of misinformation to players? Games can take a humorous tone to lighten the situation, a serious tone to underline the importance of the topic, or incorporate elements of both. This can be determined by considering the audience and the type of misinformation issues that are being discussed in the game. For instance, it would be important to be respectful when incorporating certain misinformation scenarios that harmed people in the real world.
Player agency: Do the game mechanics allow the player to make choices that affect the narrative in significant ways? Based on players’ ability to influence the narrative, the game can allow for different levels of their agency: (1) high agency that permits players to make impactful choices and witness their effects, (2) no agency that keeps players bounded within a set narrative, and (3) limited agency that allows players to make choices, but none that are particularly impactful. In some situations, providing agency may be deemed especially important (e.g., creating a game that empowers players to take action against misinformation), but in other situations, having players experience one particular path is critical for meeting the learning goals (e.g., having players fall for misinformation themselves to discuss the third-person effect).
Player morality : What role does the player character serve within the narrative? In terms of ethical considerations, characters can take on different roles: (1) a hero , by choosing morally correct options, (2) a villain, by actively sowing discord, or (3) a morally gray character , by carrying out questionable actions despite their personal reservations. Taking the perspective of a villain may make the game more engaging, but it might be less suitable in certain misinformation situations. Taking on a role of a morally gray charactermay prompt players to reflect on the choices they make after the gameplay.
Ending : What note does the story finish on? Depending on the finishing note, the story can conclude with (1) a positive ending that might provide players with hope that their actions can make real change, (2) a negative ending that may serve as a reminder of the real harm caused by misinformation, and (3) variable endings , in which the ending is determined by players’ in-game actions. Variable endings may work especially well in social play situations where players get to discuss their choices with others and empathize with the decisions others may have made in the game (Yin & Xiao, 2022).
Player dynamics : How do players interact with each other, if at all? Players’ ability (or lack thereof) to interact with each other during the game determines player dynamics. Many narrative games are individual , but some modalities, such as escape rooms or tabletop games, are suited to social play, in which players can progress through the narrative and construct elements of the story together. Social play could especially be useful for games that require deeper reflection and discussion or that aim to influence players’ attitudes or beliefs, as opposed to more skill- or knowledge-based games.
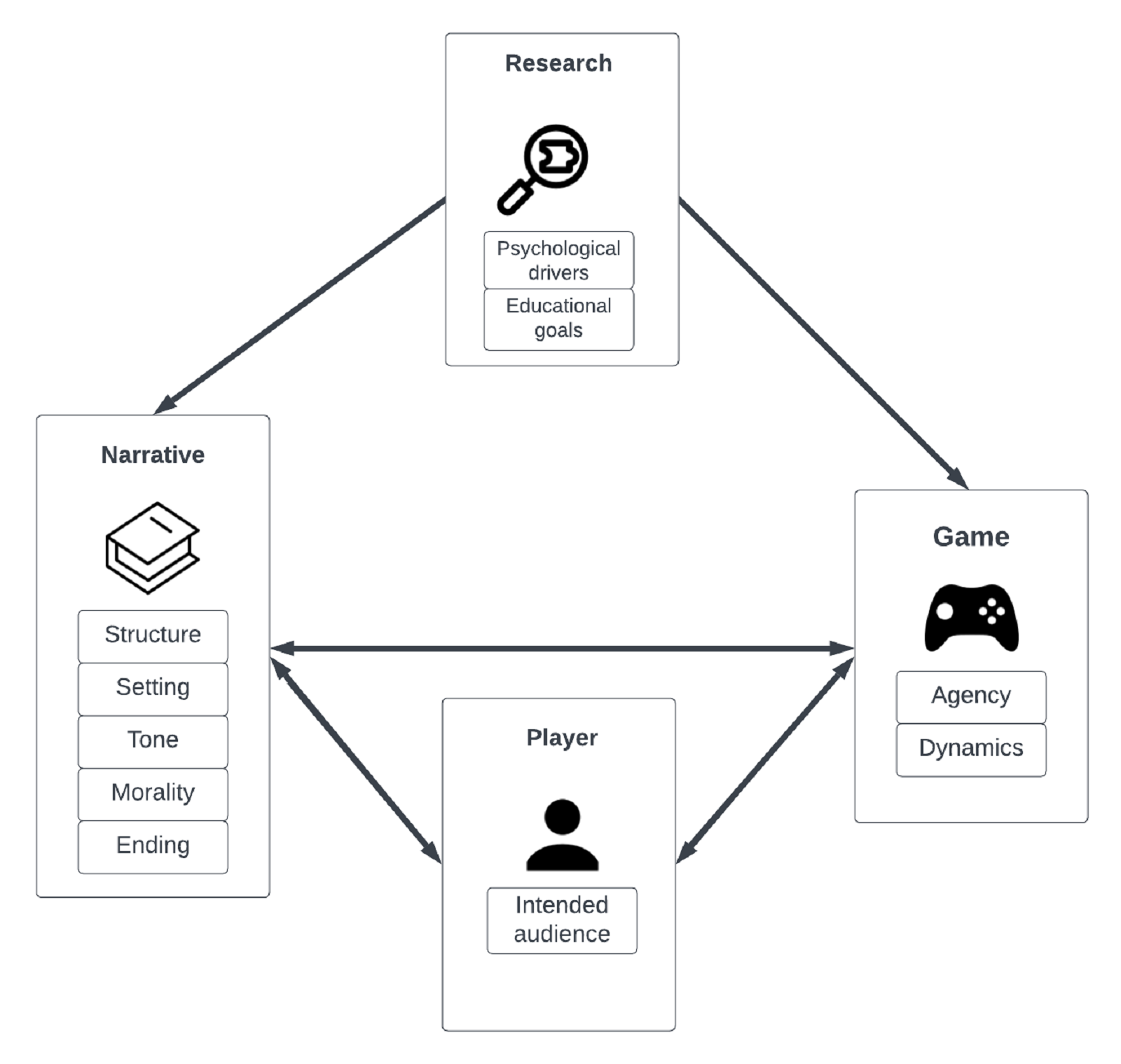
In sum, the MGND framework allows the designer to carefully consider with which misinformation-related experiences they would like the players to engage through the narrative and game mechanics. This framework could be used in tandem with other game design frameworks, such as the Mechanics, Dynamics, Aesthetics (MDA) framework (Hunicke et al., 2004), to co-design experiences for specific stakeholders and their associated misinformation contexts. We plan to use the MGND framework to co-design culturally specific narratives through our work with universities and libraries internationally.
We build from the theoretical background and present three specific hypotheses as to how narrative could supplement the outcomes of playing misinformation games.
Hypothesis 1: Narrative can facilitate identification with opposing viewpoints.
People who have already adopted misinformed beliefs require debunking rather than prebunking. This has led to the suggestion of implementing counter-narratives as a way to deconstruct strongly held beliefs (White, 2022), such as counteracting misinformed beliefs among smokers (Ophir et al., 2020; Sangalang et al., 2019). Evoking a strong emotional response and identification with the main character was shown to have mediating effects on misinformed beliefs (Cohen et al., 2015; de Graaf et al., 2012; Ophir et al., 2020). In game studies, research has shown that perspective taking in virtual environments increases empathy (Estrada Villalba & Jacques-García, 2021). Players are capable of feeling deep emotional attachment to and identification with characters in narrative games (Bopp et al., 2019; Hefner et al., 2007; Sierra Rativa et al., 2020). This increases situational empathy for that character, regardless of their morality (Happ et al., 2013; Iten et al., 2018). Narrative game environments also provide a medium for players to understand other players with whom they may not necessarily identify closely in real life (Burgess & Jones, 2021). Though players may choose different narrative branches, they are capable of empathizing with the rationale behind other players’ decisions without necessarily agreeing with said reasons (Yin & Xiao, 2022).
Hypothesis 2: Narrative can reduce reactance and counterarguing.
Counterarguing against an attempted misinformation correction can strengthen an individual’s belief in it (Ecker, 2017). Narrative’s ability to reduce reactance offers a solution in this respect (Moyer-Gusé, 2008). Slater and Rouner’s (2002) extended Elaboration Likelihood Model, which builds from Petty and Cacioppo’s (2012) Elaboration Likelihood Model, suggests that the cognitive processing of narratives suppresses resistance to persuasive messages contained within the story. The effectiveness of the messaging is associated with the degree of transportation into the story and identification with the characters (Green & Brock, 2000), which led Slater and Rouner (2002) to further argue that transportation and counterarguing are mutually exclusive. In previous work, Slater and Rouner (1996) found that narrative messages were more persuasive than factual arguments, particularly for participants with pre-existing attitudes that countered the persuasive messaging in question. There is also evidence that narratives can overwrite preexisting attitudes regarding controversial issues (Igartua & Barrios, 2012; Slater et al., 2006): Both narrative and effective debunking correctives require an individual to continuously update their mental models (de Vega, 1995; Wilkes & Leatherbarrow, 1988). The process of creating an alternative mental model that replaces the original can reduce the effects of misinformation (Johnson & Seifert, 1994).
Hypothesis 3: Narrative can facilitate educational gains.
Narrative-centered learning environments (Lester et al., 2013) are more effective in promoting enjoyment and knowledge acquisition than traditional game-based learning environments (Abdul Jabbar & Felicia, 2015; Jackson et al., 2018; McQuiggan, Rowe, Lee, et al., 2008; McQuiggan, Rowe, & Lester, 2008; Naul & Liu, 2020). Similar to practitioners building expertise in a domain, games allow players to develop increasingly complex skills through continuously challenging them to achieve mastery in order to progress (Gee, 2003). In addition to skill acquisition, narrative-centered educational games can also spur attitude change. In a review of narrative-centered educational games, skill acquisition (measured in 33 out of 130 reviewed studies) and attitude change (measured in 15 out of 130 reviewed studies) were the most effective educational outcomes (Jackson et al., 2018). This presents an opportunity for designers of misinformation education games to not only allow for skill-building, but to also engage in the attitude changes required for debunking false beliefs.
Our investigation was two-fold. First, we synthesized findings from misinformation psychology, narrative theory, and game design principles to compile three affordances of narrative in gamified misinformation education contexts. These were presented in the Evidence section and served as guiding principles for our content analysis, described below.
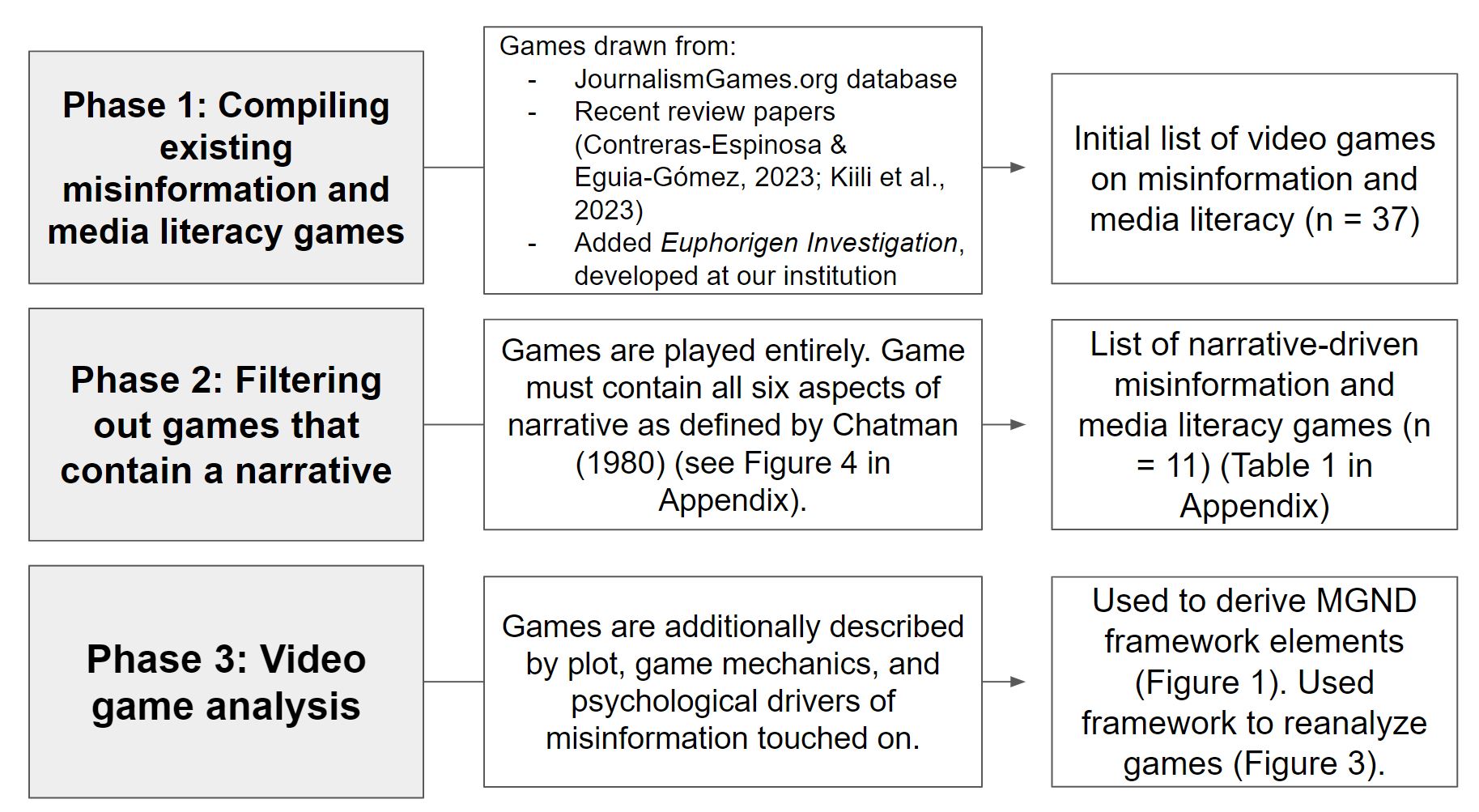
Content analysis
We compiled a list of 37 digital misinformation education games from recent review papers (Contreras-Espinosa & Eguia-Gomez, 2023; Kiili et al., 2023) and from the JournalismGames.org database (Grace & Huang, 2020). We focused on digital games as they are the dominant medium in this space. We excluded games no longer available online or not in English, and we additionally included The Euphorigen Investigation , a recent game developed at our university. We identified 11 games that qualified as narrative-driven (i.e., games containing events, character(s), setting(s), structure, point of view, and time) according to Jackson et al.’s (2018) heuristic. The authors used a consensus model to agree upon the set of games, using the heuristic to make initial selections and discussing conflicts to agreement. The entire process is summarized in Figure 2. We identified and described different aspects of these games’ narrative design, which consequently informed the design of the MGND framework. We then re-analyzed the games using the MGND framework, as presented in Figure 3.
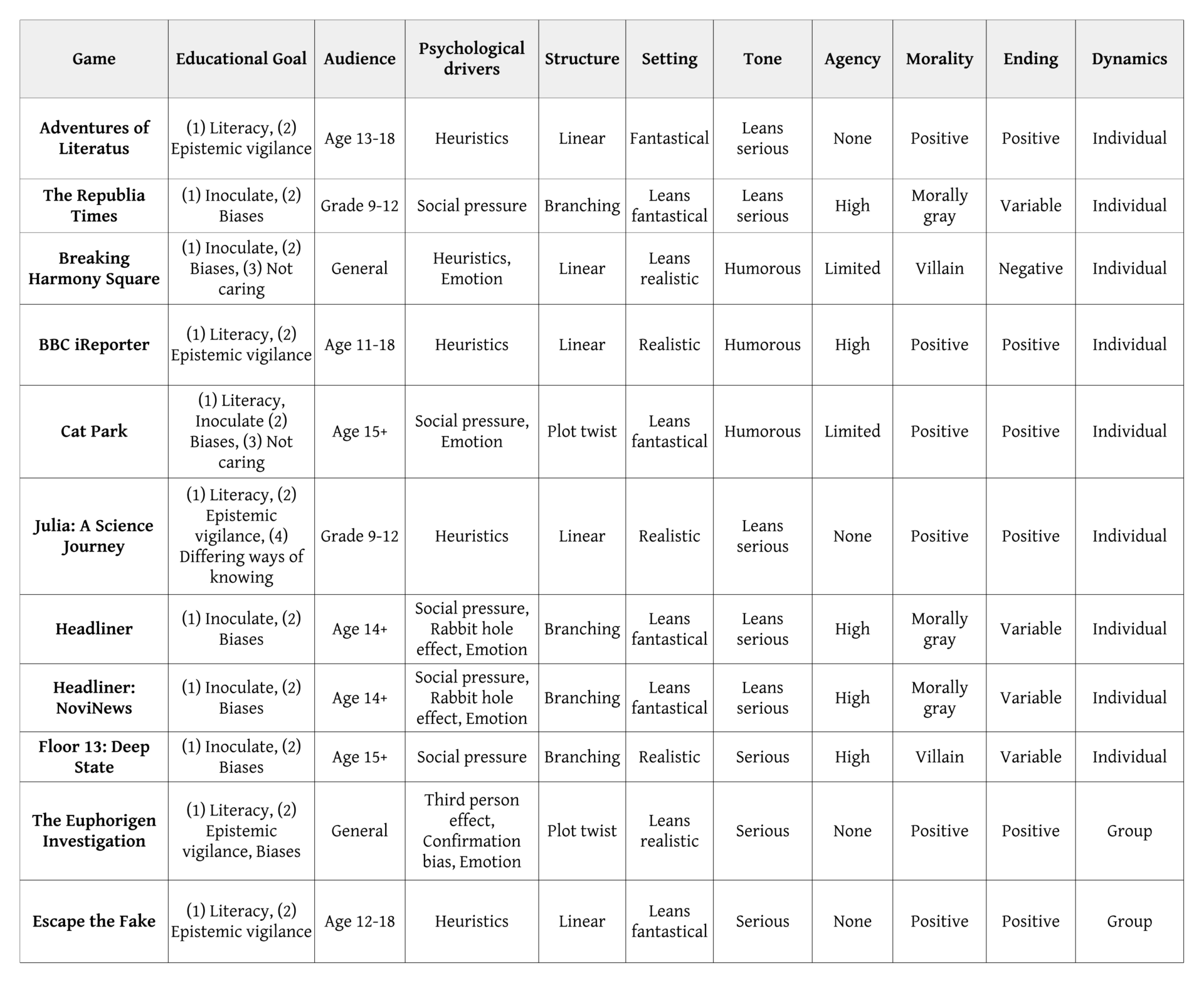
Cite this Essay
Devasia, N., & Lee, J. H. (2024). The role of narrative in misinformation games. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-158
- / Appendix B
- / Appendix C
Bibliography
Abdul Jabbar, A. I., & Felicia, P. (2015). Gameplay engagement and learning in game-based learning: A systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 85 (4), 740–779. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315577210
Barzilai, S., & Chinn, C. A. (2020). A review of educational responses to the “post-truth” condition: Four lenses on “post-truth” problems. Educational Psychologist, 55 (3), 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2020.1786388
Basol, M., Roozenbeek, J., & van der Linden, S. (2020). Good news about bad news: Gamified inoculation boosts confidence and cognitive immunity against fake news. Journal of Cognition, 3 (1). https://doi.org/10.5334/joc.91
Bopp, J. A., Müller, L. J., Aeschbach, L. F., Opwis, K., & Mekler, E. D. (2019). Exploring emotional attachment to game characters. In Proceedings of the Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play (pp. 313–324). Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/3311350.3347169
Bruner, J. (1990). Acts of meaning . Harvard University Press.
Burgess, J., & Jones, C. (2021). The female video game player-character persona and emotional attachment. Persona Studies, 6 (2), 7–21. https://doi.org/10.21153/psj2020vol6no2art963
Chang, Y. K., Literat, I., Price, C., Eisman, J. I., Gardner, J., Chapman, A., & Truss, A. (2020). News literacy education in a polarized political climate: How games can teach youth to spot misinformation. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review, 1 (4). https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-020
Chatman, S. B. (1978). Story and discourse: Narrative structure in fiction and film . Cornell University Press.
Cohen, J., Tal-Or, N., & Mazor-Tregerman, M. (2015). The tempering effect of transportation: Exploring the effects of transportation and identification during exposure to controversial two-sided narratives. Journal of Communication, 65 (2), 237–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcom.12144
Contreras-Espinosa, R. S., & Eguia-Gomez, J. L. (2023). Evaluating video games as tools for education on fake news and misinformation. Computers, 12 (9). https://doi.org/10.3390/computers12090188
Dame Adjin-Tettey, T. (2022). Combating fake news, disinformation, and misinformation: Experimental evidence for media literacy education. Cogent Arts & Humanities, 9 (1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311983.2022.2037229
de Graaf, A., Hoeken, H., Sanders, J., & Beentjes, J. W. J. (2012). Identification as a mechanism of narrative persuasion. Communication Research, 39 (6), 802–823. https://doi.org/10.1177/0093650211408594
de Vega, M. (1995). Backward updating of mental models during continuous reading of narratives. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21 (2), 373–385. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.21.2.373
Domínguez, I. X., Cardona-Rivera, R. E., Vance, J. K., & Roberts, D. L. (2016). The mimesis effect: The effect of roles on player choice in interactive narrative role-playing games. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems , (pp. 3438–3449). Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/2858036.2858141
Ecker, U. K. H. (2017). Why rebuttals may not work: The psychology of misinformation. Media Asia, 44 (2), 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/01296612.2017.1384145
Ecker, U. K. H., Lewandowsky, S., Cook, J., Schmid, P., Fazio, L. K., Brashier, N., Kendeou, P., Vraga, E. K., & Amazeen, M. A. (2022). The psychological drivers of misinformation belief and its resistance to correction. Nature Reviews Psychology, 1 (1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-021-00006-y
Estrada Villalba, É., & Jacques-García, F. A. (2021). Immersive virtual reality and its use in developing empathy in undergraduate students. In S. Latifi (Ed.), ITNG 2021 18th International Conference on Information Technology-New Generations (pp. 361–365). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70416-2_46
Gee, J. P. (2003). What video games have to teach us about learning and literacy. Computers in Entertainment, 1 (1), 20. https://doi.org/10.1145/950566.950595
Grace, L. D., & Huang, K. (2020). State of newsgames 2020 . JournalismGames.com. http://journalismgames.org/Research Overview_newsgames_report_Grace_ Haung.pdf
Grace, L. D., & Liang, S. (2024). Exposure, emotion, and empathy: A theory-informed approach to misinformation and disinformation behavior change through games. In Proceedings of the 57th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences . https://aisel.aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1292&context=hicss-57
Green, M. C., & Brock, T. C. (2000). The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79 (5), 701–721. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.79.5.701
Happ, C., Melzer, A., & Steffgen, G. (2013). Superman vs. bad man? The effects of empathy and game character in violent video games. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 16 (10), 774–778. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2012.0695
Hefner, D., Klimmt, C., & Vorderer, P. (2007). Identification with the player character as determinant of video game enjoyment. In L. Ma, M. Rauterberg, & R. Nakatsu (Eds.), Entertainment computing – ICEC 2007 (pp. 39–48). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74873-1_6
Hunicke, R., LeBlanc, M., & Zubek, R. (2004). MDA: A formal approach to game design and game research. Proceedings of the AAAI Workshop on Challenges in Game AI, 4 . https://cdn.aaai.org/Workshops/2004/WS-04-04/WS04-04-001.pdf
Igartua, J.-J., & Barrios, I. (2012). Changing real-world beliefs with controversial movies: Processes and mechanisms of narrative persuasion. Journal of Communication, 62 (3), 514–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.2012.01640.x
Iten, G. H., Steinemann, S. T., & Opwis, K. (2018). Choosing to help monsters: A mixed-method examination of meaningful choices in narrative-rich games and interactive narratives. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–13). Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/3173574.3173915
Jackson, L. C., O’Mara, J., Moss, J., & Jackson, A. C. (2018). A critical review of the effectiveness of narrative-driven digital educational games. International Journal of Game-Based Learning, 8 (4), 32–49. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJGBL.2018100103
Johnson, H. M., & Seifert, C. M. (1994). Sources of the continued influence effect: When misinformation in memory affects later inferences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 20 (6), 1420–1436. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.20.6.1420
Kahne, J., & Bowyer, B. (2017). Educating for democracy in a partisan age: Confronting the challenges of motivated reasoning and misinformation. American Educational Research Journal, 54 (1), 3–34. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831216679817
Kiili, K., Siuko, J., & Ninaus, M. (2023). Tackling misinformation with critical reading games: A systematic literature review [Preprint]. Open Science Framework. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/8qrx3
Kshetri, N. (2023). The economics of deepfakes. Computer , 56 (8), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2023.3276068
Lester, J. C., Rowe, J. P., & Mott, B. W. (2013). Narrative-centered learning environments: A story-centric approach to educational games. In C. Mouza & N. Lavigne (Eds.), Emerging technologies for the classroom: A learning sciences perspective (pp. 223–237). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4696-5_15
Maertens, R., Roozenbeek, J., Basol, M., & van der Linden, S. (2021). Long-term effectiveness of inoculation against misinformation: Three longitudinal experiments. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 27 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1037/xap0000315
Mahood, C., & Hanus, M. (2017). Role-playing video games and emotion: How transportation into the narrative mediates the relationship between immoral actions and feelings of guilt. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 6 (1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000084
McQuiggan, S. W., Rowe, J. P., Lee, S., & Lester, J. C. (2008). Story-based learning: The impact of narrative on learning experiences and outcomes. In B. P. Woolf, E. Aïmeur, R. Nkambou, & S. Lajoie (Eds.), Intelligent tutoring systems (pp. 530–539). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69132-7_56
McQuiggan, S. W., Rowe, J. P., & Lester, J. C. (2008). The effects of empathetic virtual characters on presence in narrative-centered learning environments. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1511–1520). Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/1357054.1357291
Modirrousta-Galian, A., & Higham, P. A. (2023). Gamified inoculation interventions do not improve discrimination between true and fake news: Reanalyzing existing research with receiver operating characteristic analysis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 152 (9), 2411–2437. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001395
Moyer-Gusé, E. (2008). Toward a theory of entertainment persuasion: Explaining the persuasive effects of entertainment-education messages. Communication Theory, 18 (3), 407–425. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2885.2008.00328.x
Naul, E., & Liu, M. (2020). Why story matters: A review of narrative in serious games. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58 (3), 687–707. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633119859904
Ophir, Y., Romer, D., Jamieson, P. E., & Jamieson, K. H. (2020). Counteracting misleading protobacco YouTube videos: The effects of text-based and narrative correction interventions and the role of identification. International Journal of Communication , 4973–4989. https://ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/15276
Papadamou, K. (2021). Characterizing abhorrent, misinformative, and mistargeted content on YouTube. arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.09819
Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2012). Communication and persuasion: Central and peripheral routes to attitude change . Springer Science & Business Media.
Roozenbeek, J., & van der Linden, S. (2019). The fake news game: Actively inoculating against the risk of misinformation. Journal of Risk Research, 22 (5), 570–580. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2018.1443491
Sangalang, A., Ophir, Y., & Cappella, J. N. (2019). The potential for narrative correctives to combat misinformation. Journal of Communication, 69 (3), 298–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/joc/jqz014
Schulzke, M. (2014). Simulating philosophy: Interpreting video games as executable thought experiments. Philosophy & Technology, 27 (2), 251–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13347-013-0102-2
Shane, T. (2020, June 30). The psychology of misinformation: Why we’re vulnerable. First Draft. https://firstdraftnews.org/articles/the-psychology-of-misinformation-why-were-vulnerable/
Sierra Rativa, A., Postma, M., & Van Zaanen, M. (2020). The influence of game character appearance on empathy and immersion: Virtual non-robotic versus robotic animals. Simulation & Gaming, 51 (5), 685–711. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878120926694
Slater, M. D., & Rouner, D. (1996). How message evaluation and source attributes may influence credibility assessment and belief change. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, 73 (4), 974–991. https://doi.org/10.1177/107769909607300415
Slater, M. D., & Rouner, D. (2002). Entertainment-education and elaboration likelihood: Understanding the processing of narrative persuasion. Communication Theory, 12 (2), 173–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2885.2002.tb00265.x
Slater, M. D., Rouner, D., & Long, M. (2006). Television dramas and support for controversial public policies: Effects and mechanisms. Journal of Communication, 56 (2), 235–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.2006.00017.x
Tang, L., Fujimoto, K., Amith, M. T., Cunningham, R., Costantini, R. A., York, F., Xiong, G., Boom, J. A., & Tao, C. (2021). “Down the rabbit hole” of vaccine misinformation on YouTube: Network exposure study. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23 (1), e23262. https://doi.org/10.2196/23262
van der Linden, S., Maibach, E., Cook, J., Leiserowitz, A., & Lewandowsky, S. (2017). Inoculating against misinformation. Science, 358 (6367), 1141–1142. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar4533
Warner, E. L., Basen-Engquist, K. M., Badger, T. A., Crane, T. E., & Raber-Ramsey, M. (2022). The online cancer nutrition misinformation: A framework of behavior change based on exposure to cancer nutrition misinformation. Cancer, 128 (13), 2540–2548. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.34218
White, A. (2022). Overcoming ‘confirmation bias’ and the persistence of conspiratorial types of thinking. Continuum, 36 (3), 364–376. https://doi.org/10.1080/10304312.2021.1992352
Wilkes, A. L., & Leatherbarrow, M. (1988). Editing episodic memory following the identification of error. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 40 (2), 361–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/02724988843000168
Yin, M., & Xiao, R. (2022). How should I respond to “Good morning?”: Understanding choice in narrative-rich games. Designing Interactive Systems Conference , 726–744. https://doi.org/10.1145/3532106.3533459
This work was supported by the University of Washington’s Center for an Informed Public.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
This work did not involve human subjects, and therefore did not require approval by an institutional review board.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original author and source are properly credited.
Data Availability
Replication data is not available for this study.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the rest of the Loki’s Loop team for inspiring this work. The authors also thank Kate Starbird for her helpful feedback on the first iteration of this project.
- Open access
- Published: 27 September 2024
Narrative Medicine: theory, clinical practice and education - a scoping review
- Ilaria Palla 1 ,
- Giuseppe Turchetti 1 &
- Stefania Polvani 2 , 3
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 1116 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The origin of Narrative Medicine dates back to more than 20 years ago at an international level. Narrative Medicine is not an alternative to evidence-based medicine, however these two approaches are integrated. Narrative Medicine is a methodology based on specific communication skills where storytelling is a fundamental tool to acquire, understand and integrate several points of view related to persons involving in the disease and in the healthcare process. Narrative Medicine, henceforth NM, represents a union between disease and illness between the doctor’s clinical knowledge and the patient’s experience. According to Byron Good, “we cannot have direct access to the experience of others’ illness , not even through in-depth investigations: one of the ways in which we can learn more from the experience of others is to listen to the stories of what has happened to other people.” Several studies have been published on NM; however, to the best of our knowledge, no scoping review of the literature has been performed.
This paper aims to map and synthetize studies on NM according to theory, clinical practice and education/training.
The scoping review was carried out in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist. A search was conducted in PubMed, APA PsycNet and Jstor. Two authors independently assessed the eligibility and methodological quality of the studies and extracted the data. This review refers to the period from 1998 to 2022.
A total of 843 abstracts were identified of which 274 papers were selected based on the title/abstract. A total of 152 papers in full text were evaluated and 76 were included in the review. Papers were classified according to three issues:
✘ Nineteen studies focused on the definition and concept of NM (Theoretical).
✘ Thirty-eight papers focused on the collection of stories, projects and case reports (Clinical practice).
✘ Nineteen papers focused on the implementation of the Narrative Medicine approach in the education and training of medical doctors (Education and training).
Conclusions
This scoping review presents an overview of the state of the art of the Narrative Medicine. It collect studies performed mainly in Italy and in the United States as these are the countries developing the Narrative Medicine approach in three identified areas, theoretical, clinical practice and education and training. This scoping review will help to promote the power of Narrative Medicine in all three areas supporting the development of methods to evaluate and to measure the Narrative Medicine approach using key performance indicators.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The role and involvement of patients in healthcare have changed, as has their relationship with healthcare professionals. The patient is no longer a passive subject but part of the healthcare process. Over the years, many approaches to patients’ involvement in healthcare have been developed in the literature, with significant differences in terms of concept and significance.
NM represents a focus on the patient’s needs and the empowerment of their active participation in the healthcare process.
Narrative Medicine enables patients to share their stories with healthcare professionals so that the latter can gain the necessary skills to recognize, interpret and relate to patients [ 1 ]. Stories of illness have an important impact on patients and their caregivers, healthcare professionals and organisational systems [ 2 ].
Trisha Greenhalgh, an academic in primary healthcare who trained as a General Practitioner, and Brian Hurwitz, an Emeritus Professor of Medicine and The Arts at King’s College (London) [ 3 , 4 ], affirmed that the core clinical skills in terms of listening, questioning, outlining, collecting, explaining and interpreting can provide a way of navigating among the very different worlds of patients and health professionals. These tasks need to be performed well because they can affect disease outcomes from the patient’s perspective and the scientific aspects of diagnosis and treatment.
In 2013, Rita Charon, a general internist and professor at Columbia University (New York), and Brian Hurwitz promoted “a narrative future for healthcare” , the first global conference on Narrative Based Medicine (NBM). The global conference took place in London in June 2013, where experts in humanities, social sciences and professionals interested in shaping a narrative future for healthcare discussed several topics, such as increasing the visibility of narrative-based concepts and methods; developing strategies that can influence traditional clinical institutions; spreading appreciation for the role of creativity in caring for the sick; articulating the risks of narrative practices in health care; providing a space for Narrative Medicine in the context of other fields, including personalized medicine; and sharing goals for training, research, and clinical care. The conference was the first important opportunity to share different points of view and perspectives at the global level involving several stakeholders with different backgrounds [ 5 ].
In the early 2000s, the first Italian experience of Narrative Medicine occurred in Florence with NaMe, a project endorsed by the Local Health Authority aimed at diffusing the culture of patient-centered medicine and integrating strategies to improve doctor‒patient communication in clinical practice [ 6 ]. This project was inspired by the articles of Hurwitz and Greenhalgh [ 3 , 4 ]. In addition, significant input was derived from Arthur Kleinman [ 7 ] and Byron Good [ 8 ], psychiatrists and anthropologists who studied medicine as a cultural system, as a set of symbolic meanings involving the story of the sick person. Health and illness represent the subjective experience of the person.
Kleinmann [ 7 ] defines three dimensions to explain the illness using three different significances:
✘ Disease: “only as an alteration in biological structure or functioning” .
✘ Illness: the subjective experience of suffering and discomfort.
✘ Sickness: the social representation.
Narrative Medicine can be used in several areas such as prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation; adherence to treatment; organization of the care team; awareness of the professional role and the emotional world by health and social workers; prevention of the burnout of professionals and caregivers; promotion and implementation of Patient Care Pathways (PCPs); and prevention of legal disputes and defensive medicine.
The Italian guidelines established by the National Institute of Health in 2015 [ 9 ] represent a fundamental step in the process of diffusion and implementation of Narrative Medicine in Italy and currently represents the only document. The guidelines define Narrative Medicine as an intervention methodology based on specific communication skills. Storytelling is a fundamental instrument for acquiring, understanding and integrating the different perspectives of those involved in the disease and in the healthcare process. Storytelling represents a moment of contact between a healthcare professional and the patient’s world. The story told involves people, those who narrate and those who listen. Telling stories is a way of transferring knowledge and experience, connecting, reflecting and feeling emotions.
In the last few years, several studies have been carried out with different objectives and perspectives, but no literature review on Medicine Narrative has been performed. We founded the study of Rui et al. [ 10 ] performing a bibliometric analysis of the literature on medical narratives published from 2011 to 2021 showing that the field of narrative medicine is dominated by a few countries. Respect to 736 studies included in the review, 48% (369) are performed in US and 98 papers in Italy.
The objective of scoping review was to map and synthetize studies on NM according to theory, clinical practice and education/training, three settings where NM was developed.
The research questions formulated: (1) What is Narrative Medicine?; (2) How is Narrative Medicine implemented in clinical practice?; (3) What is the role of Narrative Medicine in education and training for medical doctors?
The study protocol follows the PRISMA-ScR checklist (PRISMA extension for Scoping Reviews) but it is not registered (Additional file 1).
We included peer-reviewed papers published from 1998 to December 2022 written in Italian or in English. We excluded papers written in other languages. We included articles according to one of these issues: studies on theory of Narrative Medicine, on clinical practice or education/training of Narrative Medicine. We excluded books, case reports, reviews. To identify potentially relevant studies, the following databases were searched from 1998 to December 2022: PubMed, APA PsycNet and Jstor. The search strategy can be founded in Additional file 2. A data charting form was developed by two reviewers to define which variables can be extracted. The reviewers independently charted the data and discussed the results. We grouped the studies by type of application related to the Narrative Medicine and summarized objective, methods and reflections/conclusions. The scoping review maps the evidence on Narrative Medicine according one of the three fields of diffusion and implementation (Fig. 1 ). Furthermore, the studies classified in “theoretical field “are grouped in subcategories to explain in best way the concepts and permit a clearer and more streamlined reading.
Categories of Narrative Medicine
Review process
After removing duplicates, 843 abstracts from PubMed, Jstor and APA PsycNet were screened. A total of 274 papers were screened based on the abstracts, of which 122 were excluded. A total of 152 full texts were evaluated, and 76 were included in the review (Fig. 2 ).
PRISMA Flow-chart
The studies included were classified into the three fields where the Narrative Medicine is implemented:
✘ Theoretical studies: 19.
✘ Clinical Practice: 38.
✘ Education and training: 19.
The scoping review did not present the results of papers included but the main objectives and the methods used as the aim of the scoping review was to map the studies performed in terms of theory, clinical practice and education/training. We have tried to organize the studies published so far, making it increasingly clear how Narrative Medicine has developed.
Theoretical studies
This section presents the 19 selected theoretical studies grouped into subcategories (Additional file 3).
Narrative Medicine: advantages
In this section, we present seven papers that highlight the benefits of narrative medicine.
Of the seven papers considered, four were performed by Rita Charon emphasizing the value of Narrative Medicine in four different contexts. In the first [ 11 ], the study by Goupy et al. evaluated a Narrative Medicine elective course at the Paris-Descartes School of Medicine. In the second [ 12 ], Charon rewrote a patient’s family illness to demonstrate how medicine that respects the narrative dimension of illness and care can improve the care of individual patients, their colleagues and effective medical practice. The third paper [ 13 ] describes a visit to the Rothko Room at the Tate Modern in London as a pretext to emphasize how for narrative medicine, creativity is at the heart of health care and that the care of the sick is a work of art.
In the fourth [ 14 ], Charon provides the elements of narrative theory through a careful reading of the form and content of an excerpt from a medical record. This is part of an audio-recorded interview with a medical student and a reflection on a short section of a modernist novel to show how to determine the significance of patients’ situations.
According to Abettan [ 15 ], Narrative Medicine can play a key role in the reform of current medical practice, although to date, there has been little focus on how and why it can deliver results and be cost-effective.
Cenci [ 16 ] underlines that the existential objective of the patient is fundamental to know the person’s life project and how they would like to live their future years.
Zaharias [ 17 ], whose main sources are Charon and Launer, has published three articles on NM as a valid approach that, if practiced more widely by general practitioners, could significantly benefit both patients and doctors. If the patient’s condition is central, the NM shifts the doctor’s focus from the need to solve the problem to the need to understand. Consequently, the patient‒physician relationship is strengthened, and patients’ needs and concerns are addressed more effectively and with better results.
Narrative Medicine: the role of digital technologies
This section includes 3 papers on the role of digital technologies in Narrative Medicine. Digital narrative medicine is diffusing in care relationship as presents an opportunity for the patient and the clinician. The patient has more time to reflect on his/her needs and communicate in best way with the healthcare professionals. The clinician can access to more information as quantitative and qualitative information and data provided by the patient. These information represent an instrument for the clinician to personalize the care and respond to patient’s unmet needs.
The use of digital technologies, particularly the digital health storymap tool described by Cenci [ 16 ], for obtaining a multidisciplinary understanding of the patient’s medical history facilitates communication between the patient and caregiver. According to Charon [ 18 ], the relentless specialization and technologization of medicine damages the therapeutic importance of recognizing the context of patients’ lives and witnessing their suffering.
Rosti [ 19 ] affirms that e-health technologies will build new bridges and permit professionals to have more time to use narrative techniques with patients.
The increased use of digital technologies could reduce the opportunity for narrative contact but provide a starting point for discussion through the use of electronically transmitted patient pain diaries.
Narrative Medicine: integration with evidence-based medicine
Greenhalgh’s [ 20 ] and Rosti’s [ 19 ] studies address one of the most significant issues, the integration of Narrative Medicine with Evidence Based Medicine. Narrative Medicine is not an alternative to Evidence Based Medicine, they coexist and can complement each other in clinical practice.
Greenhalgh’s work [ 20 ] clearly shows how NM and EBM can be integrated. EBM requires an interpretative paradigm in which the patient experiences the disease in a unique and contextual way and the clinician can draw on all aspects of the evidence and thus arrive at an integrated clinical judgement.
Rosti [ 19 ] believes that even “evidence-based” physicians sustain the importance of competence and clinical judgement. Clinicians also need to rely on patients’ narratives to integrate more objective clinical results. Clinical methods are not without their limitations, which Narrative Medicine can help to overcome. Lederman [ 21 ] enphatises the importance of social sciences to analyze the stories and to improve the care.
Narrative-based Medicine: insidious
Three papers in this section focus on the possible risks of the Narrative Medicine approach. It is needing a more awareness on role of Narrative Medicine as a robust methodology.
The study by Kalitzus [ 22 ] shows how a narrative approach in medicine will be successful only if it has a positive effect on daily clinical practice instead of merely increasing existing problems.
Complex narratives on diseases published in biographies or collected by social scientists are useful only for training and research purposes. NM requires time and effort and cannot be considered the only important issue in medicine. According to Abettan [ 15 ], Narrative Medicine can make the treatment more personalised for each patient, but it is not the only way.
Zaharias [ 17 ] affirms that Narrative Medicine is often described simplistically as listening to the patient’s story, whereas it is much more common and requires special communication skills. Perhaps for these reasons, and despite its advantages, NM is not as widely practiced as it could be. Narrative skills are an integral part of practice and learning them takes time. As the author also states, “the healing power of storytelling is repeatedly attested to while evidence of effectiveness is scarce”. Lanphier [ 23 ] underlines the need to explain the term "narrative medicine" to avoid misunderstandings and to analyze the use of narrative as a tool.
Narrative Medicine: training
Liao et al. [ 24 ] presented a study aimed at helping students improve their relationships with patients by listening to them. These results, similar to those described by Charon [ 25 ], suggest that Narrative Medicine is worth recommending in academic training. The essay by O’Mahony [ 26 ] aims to provoke a debate on how and what the medical humanities should teach. Narratology and narrative medicine are linked to empathy.
Narrative Medicine: clinician-patient communication
Papers included within this category focus on the relationship between the clinician and patient, which is important in the healthcare context.
American healthcare institutions recognize the use of the Narrative Medicine approach to develop quality patient care. As a gastroenterologist at a health centre in Minnesota (US), Rian [ 27 ] concluded that the practice of Narrative Medicine should not be kept on the fringes of medicine as a hobby or ancillary treatment for the benefit of the patients but should be considered key to the healthcare process. Improving doctor‒patient communication merits more attention.
According to Rosti [ 19 ], NM can be seen as a tool to promote better communication. Although time constraints are often mentioned as an obstacle, the time needed to listen to patients is not excessive, and all healthcare professionals should consider giving patients more freedom from time constraints during consultations by encouraging them to talk about their experiences. The use of NM may also be associated with better diagnosis and treatment of pain.
Zaharias [ 28 ] underlines that communication skills are crucial. General practitioners can further develop the strong communication skills they already possess by practicing NM through neutrality, circular questions and hypotheses, and reflective skills.
Narrative Medicine: bioethics in qualitative research
The use of qualitative research in bioethics and narrative approaches to conducting and analysing qualitative interviews are becoming increasingly widespread. As Roest [ 29 ] states, this approach enables more “diagnostic thinking”. It is about promoting listening skills and the careful reading of people and healthcare practices, as well as quality criteria for the ethical evaluation of research and training.
- Clinical practice
In this classification, we included case studies performed in clinical care. We focused on methods used to guide the patients’ stories or narratives written by healthcare professionals. We analysed how Narrative Medicine has been implemented in clinical healthcare practice.
The studies included (38) were performed in the following countries: Italy (28), USA (4), Australia (1), Canada (1), China (1), Colombia (1), Norway (1), and several European countries (1) (Table 1 ). The main methods used were semi-structured interviews that guided the patient’s and physician’s narration [ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ], narrative diaries written by patients [ 34 ], and paper parallel charts (an instrument to integrate the patients’ stories in clinical practice) written by clinicians [ 34 , 35 , 36 ].
The studies underlined the usefulness of narrative medicine not only in qualitative research but also in integration with quantitative analysis. Gargiulo et al. [ 45 ] highlighted the importance of integrating narrative medicine and evidence-based approaches to improve therapeutic effectiveness and organizational pathways. Cappuccio et al. [ 36 ] affirmed that narrative medicine can be effective in supporting clinicians in their relationships with patients and caregivers.
Narrative Medicine is an important instrument for patients, caregivers and healthcare professionals [ 63 ]. Suter et al. [ 60 ] affirmed that patients’ stories can help other patients with similar experiences. The studies performed by Cercato [ 39 , 40 ] and Zocher [ 67 ] highlighted the role of digital diaries in the care process from the perspective of healthcare professionals and patients. Sansone et al. [ 55 ] highlighted that the use of diaries in the intensive care unit is helpful in facilitating communication between healthcare professionals and the family.
Education and training
This section includes studies on the role of Narrative Medicine in the education and training of medical students and healthcare professionals. The studies discuss the experiences, roles and programmes of the Narrative Medicine programme in education and training. Nineteen studies were carried out, 10 of which were in the USA (Table 2 ). Only two studies were carried out in Europe, 4 in Taiwan, 1 in Canada, 1 in Iran and 1 in Israel. Seven studies focused on the role of narrative medicine for healthcare professionals [ 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 ], and 11 were aimed at medical students from different disciplines. All studies underlined the positive role of Narrative Medicine in training. Chou et al. [ 75 ] affirmed that the new model of narrative medicine training, “community-based participatory narrative medicine”, which focuses on shared narrative work between healthcare trainees and patients, facilitates the formation of therapeutic patient-clinician relationships but also creates new opportunities to evaluate those relationships. Darayazadeh et al. [ 70 ] underlined the effectiveness of Narrative Medicine in improving students’ reflections and empathy with patients. Additionally, Lam et al. [ 76 ] highlighted that Narrative Medicine could be a useful tool for improving clinical empathy skills. The studies used different approaches to implement the Narrative Medicine method. Arntfield et al. [ 77 ] proposed three tools at different steps of the study (survey, focus group and open-ended questions). Chou et al. [ 75 ] asked participants to write a personal narrative. DasGupta and Charon [ 78 ] used a reflective writing exercise to analyse personal experiences of illness.
In this scoping review we identified 76 studies addressing dissemination and implementation of Narrative Medicine across three settings between 1998 and 2022. The studies performed by Hurwitz [ 3 ] and Greenhalgh [ 4 ] provide a path towards the Narrative Medicine affirm that sickness episodes are important milestones in patient life stories. Not only we live through storytelling, but often, with our doctor or nurse as a witness, we get sick, we improve, we get worse, we are stable and finally we also die through the story. affirms that the stories are often evocative and memorable. They are image rich, action packed and laden with emotions. Most people recall them better than they recall lists, graphs or numbers. Stories can convey important elements of nuance, including mood, tone and urgency. We learn through stories because the story form allows our existing schemas to be modified in the light of emerging experiential knowledge. The stories can capture tacit knowledge: in healthcare organizations they can bridge the gap between explicit, codified and formal knowledge (job descriptions, guidelines and protocols) and informal, not codified knowledge (knowing how to get things done in a particular organization or team, sometimes referred to as knowing the ropes). The “story” is the focal point in the studies related to the clinical practice as these discuss about the patient’s experience, illness story thought tools as questionnaires, narrative diary, chart parallels. The patient is an expert patient able to interact with the healthcare professionals, he/she had not a passive role; the patient is part of the process with the other involved stakeholders. Also, the Italian guidelines on Narrative Medicine [ 9 ] considers the storytelling as a fundamental instrument to acquire, understand and integrate several points of view related to persons involving in the disease and in the healthcare process. Storytelling represents the interaction between a healthcare professional and the patient’s world. According to this perspective, it is useful to educate in Narrative Medicine the healthcare professionals from the University to provide instruments to communicate and interact with their patients. Charon [ 11 ] emphasizes the role of training in narrative skills as an important tool permitting to physicians and medical students to improve their care. Charon [ 24 ] underlines that narrative training permits to explore the clinician’s attention to patients and to establish a relationship with patients, colleagues, and the self. The study of Liao [ 22 ] underlines that Narrative Medicine is worth recommending for healthcare education as resource for interdisciplinary collaboration among students from different discipline.
John Launer in The Art of Medicine. Narrative medicine , narrative practice , and the creation of meaning (2023) [ 87 ] affirm that Narrative Medicine could be complemented by the skills and pedagogy of narrative practice. In addition to the creation and study of words on the page, learners could bring their spoken accounts of their experiences at work and interview each other using narrative practice techniques. He also affirms that narrative practice and narrative medicine could both do more to build alliances with advocacy groups.
We have performed a picture of Narrative Medicine from its origin to today hoping that it will help to promote the power of Narrative Medicine in all three areas becoming increasingly integrated.
Strengths and limitations
The scoping review does not present the results of studies included but objectives, methodology and conclusions/suggestions as it aims to map the evidence related to the Narrative Medicine using a classification defined for the review. This classification had permit to make even clearer the “world” of Narrative Medicine and present a mapping.
English- and Italian-language articles were included because, as seen from the preceding pages, most of the studies were carried out in the United States and Italy.
This could be a limitation, as we may have excluded papers written in other languages. However, the United States and Italy are the countries where Narrative Medicine has developed the most.
The scoping review presents an overview of the literature considering three settings in which Narrative Medicine has emerged from its origins until today highlighting evidence in terms of theory, clinical practice, and education. Currently, a methodology to “measure” Narrative Medicine with indicators, a method assessing the effectiveness and promoting a greater diffusion of Narrative Medicine using objective and measurable indicators, is not available. Furthermore, the literature analysis doesn’t show an integration across three settings. We hope that the review will be a first step towards future projects in which it will be possible to measure Narrative Medicine according to an integrated approach between clinical practice and education/training.
Availability of data and materials
Availability of data and materials: All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- Narrative Medicine
Narrative-Based Medicine
Evidence-Based Medicine
Polvani S. Cura alle stelle. Manuale di salute narrativa. Bulgarini; 2022.
Google Scholar
Polvani S, Sarti A. Medicina narrativa in terapia intensiva. Storie di Malattia e di cura. FrancoAngeli; 2013.
Greenhalgh T, Hurwitz B. Narrative based medicine Why study narrative? BMJ. 1999;318:48–50.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Greenhalgh T, Hurwitz B. Narrative-Based Medicine: Dialogue and Discourse in Clinical Practice. London: BMJ Books; 1998.
Hurwitz B, Charon R. A narrative future for health care. Lancet. 2013;381:1886–7.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ballo P, Milli M, Slater C, Bandini F, Trentanove F, Comper G, Zuppiroli A, Polvani S. Prospective Validation of the Decalogue, a Set of Doctor-Patient Communication Recommendations to Improve Patient Illness Experience and Mood States within a Hospital Cardiologic Ambulatory Setting. Biomed Res Int. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2792131 .
Kleinman A. The Illness Narratives: Suffering, Healing, and the Human Condition. New York: Basic Books; 1988.
Good BJ. Medicine, Rationality, and Experience: An anthropological perspective. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
Book Google Scholar
Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Linee di indirizzo per l’utilizzo della Medicina Narrativa in ambito clinico-assistenziale, per le malattie rare e cronico-degenerative. Sole24Ore Sanità. 2015.
Rui L. Wang L. Global Trends and Hotspots in Narrative Medicine Studies: A Bibliometric Analysis. 2023. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2816041/v1 .
Article Google Scholar
Charon R. Narrative medicine in the international education of physicians. Presse Med. 2013;42(1):3–5.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Charon R. Narrative Medicine. A model for empathy, Reflection, profession and Trust. JAMA. 2001;286(15):1897–902.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Charon R. Narrative Medicine: Caring for the sick is a work of art. JAAPA. 2013;26(12):8.
Charon R. The membranes of care: stories in Narrative Medicine. Acad Med. 2012;87(3):342–7.
Abettan C. From method to hermeneutics: which epistemological framework for narrative medicine? Theor Med Bioeth. 2017;38:179–93.
Cenci C, Fatati G. Conversazioni online per comprendere la malattia e favorire il rapporto medico-paziente. Recenti Prog Med. 2020;111:682–4.
PubMed Google Scholar
Zaharias G. What is narrative-based medicine? Narrative-based medicine 1. Canadian Family Physician|Le Médecin de famille canadien. 2018;64:176–80.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Charon R. Form Function, and Ethics. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:83–7.
Rosti G. Role of narrative-based medicine in proper patient assessment. Support Care Cancer. 2017;25(Suppl 1):3–6.
Greenhalgh T. Narrative based medicine in an evidence-based word. BMJ. 1999;318:323–5.
Lederman M. Social and gendered readings of illness narratives. J Med Humanit. 2016;37:275–88.
Kalitzkus V, Matthiessen PF. Narrative-Based Medicine: Potential, Pitfalls, and Practice. Permanente J. 2009;13(1):80–6.
Lanphier E. Narrative and Medicine premises, practices, pragmatism. Perspective in Biology and Medicine. 2021;64(2):211–34.
Liao HC, Wang YH. Storytelling in Medical Education: Narrative Medicine as a Resource for Interdisciplinary Collaboration. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041135 .
Charon R. Close Reading and Creative Writing in Clinical Education: teaching attention, representation, and affiliation. Acad Med. 2016;91(3):345–50.
O’Mahony S. Against Narrative Medicine. Perspect Biol Med. 2013;56(4):611–9.
Rian J, Hammer R. The Practical Application of Narrative Medicine at Mayo Clinic: Imagining the Scaffold of a Worthy House. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2013;37:670–80.
Zaharias G. Narrative-based medicine and the general practice consultation. Narrative-based medicine 2. Canadian Family Physician|Le Médecin de famille canadien. 2018;64(4):286–90.
Roest B, Milota M, Carlo LC. Developing new ways to listen: the value of narrative approaches in empirical (bio)ethics. BMC Med Ethics. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-021-00691-7 .
Breccia M, Graffigna G, Galimberti S, Iurlo A, Pungolino E, Pizzuti M, Maggi A, et al. Personal history and quality of life in chronic myeloid leukemia patients: a cross-sectional study using narrative medicine and quantitative analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(11):4487–93.
Cappuccio A, Limonta T, Parodi A, Cristaudo A, Bugliaro F, Cannavò SP, Rossi O. Living with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria in Italy: A Narrative Medicine Project to Improve the Pathway of Patient Care. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97(1):81–5.
Ceccarelli F, Covelli V, Olivieri G, Natalucci F, Conti F. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus before and after COVID-19 Lockdown: How the Perception of Disease Changes through the Lenses of Narrative Medicine. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060726 .
Cenci C, Mecarelli O. Digital narrative medicine for the personalization of epilepsy care pathways. Epilepsy Behav. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107143 .
Banfi P, Cappuccio A, Latella M, Reale L, Muscianisi E, Marini MG. Narrative medicine to improve the management and quality of life of patients with COPD: the first experience applying parallel chart in Italy. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:287–97.
Cappuccio A, Sanduzzi Zamparelli A, Verga M, Nardini S, Policreti A, Porpiglia PA, Napolitano S, Marini MG. Narrative medicine educational project to improve the care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. ERJ Open Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1183/23120541.00155-2017 .
Cappuccio A, Napolitano S, Menzella F, Pellegrini G, Policreti A, Pelaia G, Porpiglia PA, Marini MG. Use of narrative medicine to identify key factors for effective doctor-patient relationships in severe asthma. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40248-019-0190-7 .
Caputo A. Exploring quality of life in Italian patients with rare disease: a computer-aided content analysis of illness stories. Psychol Health Med. 2014;19(2):211–21.
Cepeda MS, Chapman CR, Miranda N, Sanchez R, Rodriguez CH, Restrepo AE, Ferrer LM, Linares RA, Carr DB. Emotional disclosure through patient narrative may improve pain and well-being: results of a randomized controlled trial in patients with cancer pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2008;35(6):623–31.
Cercato MC, Colella E, Fabi A, Bertazzi I, Giardina BG, Di Ridolfi P, Mondati M, et al. Narrative medicine: feasibility of a digital narrative diary application in oncology. J Int Med Res. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211045507 .
Cercato MC, Vari S, Maggi G, Faltyn W, Onesti CE, Baldi J, Scotto di Uccio A et al. Narrative Medicine: A Digital Diary in the Management of Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcoma Patients. Preliminary Results of a Multidisciplinary Pilot Study. J Clin Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020406 .
De Vincentis G, Monari F, Baldari S, Salgarello M, Frantellizzi V, Salvi E, Reale L, Napolitano S. Narrative medicine in metastatic prostate cancer reveals ways to improve patient awareness & quality of care. Future Oncol. 2018;14(27):2821–32.
Di Gangi S, Naretto G, Cravero N, Livigni S. A narrative-based study on communication by family members in intensive care unit. J Crit Care. 2013;28(4):483–9.
Donzelli G, Paddeu EM, D’Alessandro F, Nanni CA. The role of narrative medicine in pregnancy after liver transplantation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28(2):158–61.
Fox DA, Hauser JM. Exploring perception and usage of narrative medicine by physician specialty: a qualitative analysis. Philos Ethics Humanit Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13010-021-00106-w .
Gargiulo G, Sansone V, Rea T, Artioli G, Botti S, Continisio GI, Ferri P, et al. Narrative Based Medicine as a tool for needs assessment of patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Acta Biomed. 2017;88:18–24.
Graffigna G, Cecchini I, Breccia M, Capochiani E, Della Seta R, Galimberti S, Melosi A, et al. Recovering from chronic myeloid leukemia: the patients’ perspective seen through the lens of narrative medicine. Qual Life Res. 2017;26(10):2739–54.
Herrington ER, Parker LS. Narrative methods for assessing “quality of life” in hand transplantation: five case studies with bioethical commentary. Med Health Care Philos. 2019;22(3):407–25.
Kvåle K, Haugen DF, Synnes O. Patients’ illness narratives-From being healthy to living with incurable cancer: Encounters with doctors through the disease trajectory. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnr2.1227 .
Lamprell K, Braithwaite J. Reading Between the Lines: A Five-Point Narrative Approach to Online Accounts of Illness. J Med Humanit. 2019;40(4):569–90.
Marini MG, Chesi P, Bruscagnin M, Ceccatelli M, Ruzzon E. Digits and narratives of the experience of Italian families facing premature births. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31(17):2258–64.
Marini MG, Chesi P, Mazzanti L, Guazzarotti L, Toni TD, Salerno MC, Officioso A, et al. Stories of experiences of care for growth hormone deficiency: the CRESCERE project. Future Sci OA. 2016. https://doi.org/10.4155/fso.15.82 .
Midena E, Varano M, Pilotto E, Staurenghi G, Camparini M, Pece A, Battaglia PM. Real-life patient journey in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a narrative medicine analysis in the Italian setting. Eye (Lond). 2022;36(1):182–92.
Palandri F, Benevolo G, Iurlo A, Abruzzese E, Carella AM, Paoli C, Palumbo GA, et al. Life for patients with myelofibrosis: the physical, emotional and financial impact, collected using narrative medicine-Results from the Italian “Back to Life” project. Qual Life Res. 2018;27(6):1545–54.
Rushforth A, Ladds E, Wieringa S, Taylor S, Husain L, Greenhalgh T. Long Covid-The illness narratives. Soc Sci Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114326 .
Sansone V, Cancani F, Gagliardi C, Satta T, Cecchetti C, de Ranieri C, Di Nardo M, Rossi A, et al. Narrative diaries in the paediatric intensive care unit: A thematic analysis. Nurs Crit Care. 2022;27(1):45–54.
Scaratti C, Zorzi G, Guastafierro E, Leonardi M, Covelli V, Toppo C, Nardocci N. Long term perceptions of illness and self after Deep Brain Stimulation in pediatric dystonia: A narrative research. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2020;26:61–7.
Simonelli F, Sodi A, Falsini B, Bacci G, Iarossi G, Di Iorio V, Giorgio D, et al. Care Pathway of RPE65-Related Inherited Retinal Disorders from Early Symptoms to Genetic Counseling: A Multicenter Narrative Medicine Project in Italy. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021;2(15):4591–605.
Slocum RB, Howard TA, Villano JL. Narrative Medicine perspectives on patient identity and integrative care in neuro-oncology. J Neuroncol. 2017;134(2):417–21.
Slocum RB, Hart AL, Guglin ME. Narrative medicine applications for patient identity and quality of life in ventricular assist device (VAD) patients. Heart Lung. 2019;48(1):18–21.
Suter N, Ardizzone G, Giarelli G, Cadorin L, Gruarin N, Cipolat Mis C, Michilin N, et al. The power of informal cancer caregivers’ writings: results from a thematic and narrative analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2021;29(8):4381–8.
Talarico R, Cannizzo S, Lorenzoni V, Marinello D, Palla I, Pirri S, Ticciati S, et al. RarERN Path: a methodology towards the optimisation of patients’ care pathways in rare and complex diseases developed within the European Reference Networks. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-021-01778-5 .
Testa M, Cappuccio A, Latella M, Napolitano S, Milli M, Volpe M, Marini MG. The emotional and social burden of heart failure: integrating physicians’, patients’, and caregivers’ perspectives through narrative medicine. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01809-2 .
Tonini MC, Fiorencis A, Iannacchero R, Zampolini M, Cappuccio A, Raddino R, Grillo E, et al. Narrative Medicine to integrate patients’, caregivers’ and clinicians ’migraine experiences: the DRONE multicentre project. Neurol Sci. 2021;42:5277–88.
Vanstone M, Toledo F, Clarke F, Boyle A, Giacomini M, Swinton M, Saunders L, et al. Narrative medicine and death in the ICU: word clouds as a visual legacy. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjspcare-2016-001179 .
Volpato E, Centanni S, Banfi P, D’Antonio S, Peterle E, Bugliaro F, Grattagliano I, et al. Narrative Analysis of the Impact of COVID-19 on Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Their Caregivers, and Healthcare Professionals in Italy. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:2181–201.
Zhang Y, Pi B, Xu X, Li Y, Chen X, Yang N. Influence of Narrative Medicine-Based Health Education Combined With An Online Patient Mutual Assistance Group On The Health Of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Arthritis. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2020;7(13):1–10.
Zocher U, Bertazzi I, Colella E, Fabi A, Scarinci V, Franceschini A, Cenci C, et al. Application of narrative medicine in oncological clinical practice: impact on health care professional. Recenti Prog Med. 2020;111(3):154–9.
Chen PJ, Huang CD, Yeh SJ. Impact of a narrative medicine programme on healthcare providers’ empathy scores over time. BMC Med Educ. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-017-0952-x .
Chu SY, Wen CC, Lin CW. A qualitative study of clinical narrative competence of medical personnel. BMC Med Educ. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02336-6 .
Daryazadeh S, Adibi P, Yamani N. The role of narrative medicine program in promoting professional ethics: perceptions of Iranian medical students. J Med Ethics Hist Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.18502/jmehm.v14i21.8181 .
Karkabi K, Wald HS, Castel OC. The use of abstract paintings and narratives to foster reflective capacity in medical educators: a multinational faculty development workshop. Med Humanit. 2014;40(1):44–8.
Lijoi AF, Tovar AD. Narrative medicine: Re-engaging and re-energizing ourselves through story. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2020;55(5):321–30.
Wallace CL, Trees A, Ohs J, Hinyard L. Narrative Medicine for Healthcare Providers: Improving Practices of Advance Care Planning. Omega (Westport). 2023;87(1):87–102.
Winkel AF, Feldman N, Moss H, Jakalow H, Simon J, Blank S. Narrative Medicine Workshops for Obstetrics and Gynecology Residents and Association with Burnout Measures. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128(Suppl 1):27–33.
Chou JC, Schepel IRM, Vo AT, Kapetanovic S, Schaff PB. Patient Co-Participation in Narrative Medicine Curricula as a Means of Engaging Patients as Partners in Healthcare: a pilot study involving medical students and patient living with HIV. J Med Humanit. 2021;42(4):641–57.
Lam JA, Feingold-Link M, Noguchi J, Quinn A, Chofay D, Cahill K, Rougas S. My Life, My Story: Integrating a Life Story Narrative Component into Medical Student Curricula. MedEdPORTAL. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11211 .
Arntfield SL, Slesar K, Dickson J, Charon R. Narrative medicine as a means of training medical students toward residency competencies. Patient Educ Couns. 2013;91(3):280–6.
DasGupta S, Charon R. Personal illness narratives: using reflective writing to teach empathy. Acad Med. 2004;79(4):351–6.
Gowda D, Curran T, Khedagi A, Mangold M, Jiwani F, Desai U, Charon R, Balmer D. Implementing an interprofessional narrative medicine program in academic clinics: Feasibility and program evaluation. Perspect Med Educ. 2019;8(1):52–9.
Lemogne C, Buffel du Vaure C, Hoertel N, Catu-Pinault A, Limosin F, Ghasarossian C, Le Jeunne C, Jaury P. Balint groups and narrative medicine compared to a control condition in promoting students’ empathy. BMC Med Educ. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02316-w .
Liao KC, Peng CH, Snell L, Wang X, Huang CD, Saroyan A. Understanding the lived experiences of medical learners in a narrative medicine course: a phenomenological study. BMC Med Educ. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02741-5 .
Lorenz JF, Darok MC, Ho L, Holstrom-Mercader MS, Freiberg AS, Dellasega CA. The Impact of an Unconventional Elective in Narrative Medicine and Pediatric Psycho-oncology on Humanism in Medical Students. J Cancer Educ. 2022;37(6):1798–805.
Miller E, Balmer D, Hermann N, Graham G, Charon R. Sounding narrative medicine: studying students’ professional identity development at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. Acad Med. 2014;89(2):335–42.
Shaw AC, McQuade JL, Reilley MJ, Nixon B, Baile WF, Epner DE. Integrating Storytelling into a Communication Skills Teaching Program for Medical Oncology Fellows. J Cancer Educ. 2019;34(6):1198–203.
Skelton JR, O’Riordan M, Berenguera Ossȯ A, Beavan J, Weetman K. Learning from patients: trainers’ use of narratives for learning and teaching. BJGP Open. 2017. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgpopen17X100581 .
Launer J, Wohlmann A. Narrative medicine, narrative practice, and the creation of meaning. Lancet. 2023;401(10371):98–9.
Download references
The work has not been financed.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Management, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna Pisa, Piazza Martiri della Libertà 33, Pisa, 56127, Italy
Ilaria Palla & Giuseppe Turchetti
SIMeN, Società Italiana Medicina Narrativa, Arezzo, Italy
Stefania Polvani
Azienda USL Toscana Sud Est, Arezzo, Italy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
I.P. and S.P. carried out the scoping review, conceived the study, data collection process and drafted the manuscript. G.T. participated in the coordination of the study. All authors read, reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ilaria Palla .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Palla, I., Turchetti, G. & Polvani, S. Narrative Medicine: theory, clinical practice and education - a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 1116 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11530-x
Download citation
Received : 01 February 2024
Accepted : 03 September 2024
Published : 27 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11530-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Healthcare professional
- Scoping review
- Personalized medicine
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
Narrative essay authors illustrate universal lessons in their unique experiences of the world. Below, you'll find some tips to guide in this style of narrative writing. What Is a Narrative Essay? Narrative essays make an argument or impart a lesson through personal experience. Narrative essays are always non-fiction and usually autobiographical.
WHAT IS A NARRATIVE ESSAY? When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
What is a narrative essay? When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Narrative essays let the authors provide an account of their personal experiences in the form of a story and let their ideas flow freely.
When you have a personal story to tell, a narrative essay may be the perfect fit. Learn how to write a narrative essay step-by-step, with tips and examples.
Narrative Essay Structure. A handout that goes over how to write a narrative essay to help you outline and write your narrative essay. Writing Narrative Essays. From the Excelsior Writing Lab, here is an overview of narrative essays with some writing tips. Aug 19, 2024 2:01 PM.
Learn how to write a narrative essay with tips, samples, and FAQs. Find everything you need to excel in your writing process in this comprehensive guide.
Framing a compelling narrative essay involves a captivating story with a clear purpose. Check out this detailed article to understand what a narrative essay is, its key elements and types, and how to write a narrative essay with examples.
A narrative essay tells a story about a personal experience. In this blog post, we define what a narrative essay is and provide strategies and examples for writing one.
Narrative analysis is a qualitative research methodology that involves examining and interpreting the stories or narratives people tell in order to gain insights into the meanings, experiences, and perspectives that underlie them. Narrative analysis can be applied to various forms of communication, including written texts, oral interviews, and ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Need help writing narrative essays? Check out these narrative essay examples and learn how to develop engaging stories and enhance your narrative skills!
Narrative essay outline consists of three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. Learn how to write a perfect outline here in this blog. Get started.
A narrative essay depends on what your story is about. If you're curious about it, want to learn more, this comprehensive narrative essay guide is for you!
Not sure what story you will tell next? You just stumbled upon the best narrative essay topics! Check out this article for endless ideas and inspiration.
Simply put, narrative analysis is a qualitative analysis method focused on interpreting human experiences and motivations by looking closely at the stories (the narratives) people tell in a particular context. In other words, a narrative analysis interprets long-form participant responses or written stories as data, to uncover themes and ...
Narrative essays are unique in that research is conducted within the scope of your personal life and experiences. This means that research may consist of utilizing personal artifacts, memorabilia, anecdotes, and conversations.
Find great narrative essays examples here. Learn to write to an effective paper using our samples. Read this guide to know the writing process and tips.
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes. Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan. A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay. It usually comes near the end of your introduction. Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you're writing. But the thesis statement ...
Looking for a narrative essay sample to inspire your writing? Check out our analysis of 3 great personal narrative essay examples, plus tips for writing.
The research also includes the study of writing the narrative essay, how to write it, its patterns, and knowledge. The study ends with a conclusion that summarizes the current study.
Narrative research is started to be used in educational context recently. This article focuses on a discussion of the reasons for choosing narrative research approach in discovering the ...
Several existing media literacy games aim to increase resilience to misinformation. However, they lack variety in their approaches. The vast majority focus on assessing information accuracy, with limited exploration of socio-emotional influences of misinformation adoption. Misinformation correction and educational games have explored how narrative persuasion influences personal beliefs, as ...
The origin of Narrative Medicine dates back to more than 20 years ago at an international level. Narrative Medicine is not an alternative to evidence-based medicine, however these two approaches are integrated. Narrative Medicine is a methodology based on specific communication skills where storytelling is a fundamental tool to acquire, understand and integrate several points of view related ...
The stolen narrative of the Bulgarian Jews and the Holocaust by Jacky Comforty with Martha Aladjem Bloomfield, with a foreword by Omer Bartov, Lanham, MD, Lexington Books, 2021, xxxiv + 370 pp., US$46.99 (paperback), ISBN 978-1-7936-3292-