- Open access
- Published: 09 March 2020

Rubrics to assess critical thinking and information processing in undergraduate STEM courses
- Gil Reynders 1 , 2 ,
- Juliette Lantz 3 ,
- Suzanne M. Ruder 2 ,
- Courtney L. Stanford 4 &
- Renée S. Cole ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2807-1500 1
International Journal of STEM Education volume 7 , Article number: 9 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
72k Accesses
65 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
Process skills such as critical thinking and information processing are commonly stated outcomes for STEM undergraduate degree programs, but instructors often do not explicitly assess these skills in their courses. Students are more likely to develop these crucial skills if there is constructive alignment between an instructor’s intended learning outcomes, the tasks that the instructor and students perform, and the assessment tools that the instructor uses. Rubrics for each process skill can enhance this alignment by creating a shared understanding of process skills between instructors and students. Rubrics can also enable instructors to reflect on their teaching practices with regard to developing their students’ process skills and facilitating feedback to students to identify areas for improvement.
Here, we provide rubrics that can be used to assess critical thinking and information processing in STEM undergraduate classrooms and to provide students with formative feedback. As part of the Enhancing Learning by Improving Process Skills in STEM (ELIPSS) Project, rubrics were developed to assess these two skills in STEM undergraduate students’ written work. The rubrics were implemented in multiple STEM disciplines, class sizes, course levels, and institution types to ensure they were practical for everyday classroom use. Instructors reported via surveys that the rubrics supported assessment of students’ written work in multiple STEM learning environments. Graduate teaching assistants also indicated that they could effectively use the rubrics to assess student work and that the rubrics clarified the instructor’s expectations for how they should assess students. Students reported that they understood the content of the rubrics and could use the feedback provided by the rubric to change their future performance.
The ELIPSS rubrics allowed instructors to explicitly assess the critical thinking and information processing skills that they wanted their students to develop in their courses. The instructors were able to clarify their expectations for both their teaching assistants and students and provide consistent feedback to students about their performance. Supporting the adoption of active-learning pedagogies should also include changes to assessment strategies to measure the skills that are developed as students engage in more meaningful learning experiences. Tools such as the ELIPSS rubrics provide a resource for instructors to better align assessments with intended learning outcomes.
Introduction
Why assess process skills.
Process skills, also known as professional skills (ABET Engineering Accreditation Commission, 2012 ), transferable skills (Danczak et al., 2017 ), or cognitive competencies (National Research Council, 2012 ), are commonly cited as critical for students to develop during their undergraduate education (ABET Engineering Accreditation Commission, 2012 ; American Chemical Society Committee on Professional Training, 2015 ; National Research Council, 2012 ; Singer et al., 2012 ; The Royal Society, 2014 ). Process skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, information processing, and communication are widely applicable to many academic disciplines and careers, and they are receiving increased attention in undergraduate curricula (ABET Engineering Accreditation Commission, 2012 ; American Chemical Society Committee on Professional Training, 2015 ) and workplace hiring decisions (Gray & Koncz, 2018 ; Pearl et al., 2019 ). Recent reports from multiple countries (Brewer & Smith, 2011 ; National Research Council, 2012 ; Singer et al., 2012 ; The Royal Society, 2014 ) indicate that these skills are emphasized in multiple undergraduate academic disciplines, and annual polls of about 200 hiring managers indicate that employers may place more importance on these skills than in applicants’ content knowledge when making hiring decisions (Deloitte Access Economics, 2014 ; Gray & Koncz, 2018 ). The assessment of process skills can provide a benchmark for achievement at the end of an undergraduate program and act as an indicator of student readiness to enter the workforce. Assessing these skills may also enable instructors and researchers to more fully understand the impact of active learning pedagogies on students.
A recent meta-analysis of 225 studies by Freeman et al. ( 2014 ) showed that students in active learning environments may achieve higher content learning gains than students in traditional lectures in multiple STEM fields when comparing scores on equivalent examinations. Active learning environments can have many different attributes, but they are commonly characterized by students “physically manipulating objects, producing new ideas, and discussing ideas with others” (Rau et al., 2017 ) in contrast to students sitting and listening to a lecture. Examples of active learning pedagogies include POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) (Moog & Spencer, 2008 ; Simonson, 2019 ) and PLTL (Peer-led Team Learning) (Gafney & Varma-Nelson, 2008 ; Gosser et al., 2001 ) in which students work in groups to complete activities with varying levels of guidance from an instructor. Despite the clear content learning gains that students can achieve from active learning environments (Freeman et al., 2014 ), the non-content-gains (including improvements in process skills) in these learning environments have not been explored to a significant degree. Active learning pedagogies such as POGIL and PLTL place an emphasis on students developing non-content skills in addition to content learning gains, but typically only the content learning is assessed on quizzes and exams, and process skills are not often explicitly assessed (National Research Council, 2012 ). In order to fully understand the effects of active learning pedagogies on all aspects of an undergraduate course, evidence-based tools must be used to assess students’ process skill development. The goal of this work was to develop resources that could enable instructors to explicitly assess process skills in STEM undergraduate classrooms in order to provide feedback to themselves and their students about the students’ process skills development.
Theoretical frameworks
The incorporation of these rubrics and other currently available tools for use in STEM undergraduate classrooms can be viewed through the lenses of constructive alignment (Biggs, 1996 ) and self-regulated learning (Zimmerman, 2002 ). The theory of constructivism posits that students learn by constructing their own understanding of knowledge rather than acquiring the meaning from their instructor (Bodner, 1986 ), and constructive alignment extends the constructivist model to consider how the alignment between a course’s intended learning outcomes, tasks, and assessments affects the knowledge and skills that students develop (Biggs, 2003 ). Students are more likely to develop the intended knowledge and skills if there is alignment between the instructor’s intended learning outcomes that are stated at the beginning of a course, the tasks that the instructor and students perform, and the assessment strategies that the instructor uses (Biggs, 1996 , 2003 , 2014 ). The nature of the tasks and assessments indicates what the instructor values and where students should focus their effort when studying. According to Biggs ( 2003 ) and Ramsden ( 1997 ), students see assessments as defining what they should learn, and a misalignment between the outcomes, tasks, and assessments may hinder students from achieving the intended learning outcomes. In the case of this work, the intended outcomes are improved process skills. In addition to aligning the components of a course, it is also critical that students receive feedback on their performance in order to improve their skills. Zimmerman’s theory of self-regulated learning (Zimmerman, 2002 ) provides a rationale for tailoring assessments to provide feedback to both students and instructors.
Zimmerman’s theory of self-regulated learning defines three phases of learning: forethought/planning, performance, and self-reflection. According to Zimmerman, individuals ideally should progress through these three phases in a cycle: they plan a task, perform the task, and reflect on their performance, then they restart the cycle on a new task. If a student is unable to adequately progress through the phases of self-regulated learning on their own, then feedback provided by an instructor may enable the students to do so (Butler & Winne, 1995 ). Thus, one of our criteria when creating rubrics to assess process skills was to make the rubrics suitable for faculty members to use to provide feedback to their students. Additionally, instructors can use the results from assessments to give themselves feedback regarding their students’ learning in order to regulate their teaching. This theory is called self-regulated learning because the goal is for learners to ultimately reflect on their actions to find ways to improve. We assert that, ideally, both students and instructors should be “learners” and use assessment data to reflect on their actions, although with different aims. Students need consistent feedback from an instructor and/or self-assessment throughout a course to provide a benchmark for their current performance and identify what they can do to improve their process skills (Black & Wiliam, 1998 ; Butler & Winne, 1995 ; Hattie & Gan, 2011 ; Nicol & Macfarlane-Dick, 2006 ). Instructors need feedback on the extent to which their efforts are achieving their intended goals in order to improve their instruction and better facilitate the development of process skills through course experiences.
In accordance with the aforementioned theoretical frameworks, tools used to assess undergraduate STEM student process skills should be tailored to fit the outcomes that are expected for undergraduate students and be able to provide formative assessment and feedback to both students and faculty about the students’ skills. These tools should also be designed for everyday classroom use to enable students to regularly self-assess and faculty to provide consistent feedback throughout a semester. Additionally, it is desirable for assessment tools to be broadly generalizable to measure process skills in multiple STEM disciplines and institutions in order to increase the rubrics’ impact on student learning. Current tools exist to assess these process skills, but they each lack at least one of the desired characteristics for providing regular feedback to STEM students.
Current tools to assess process skills
Current tests available to assess critical thinking include the Critical Thinking Assessment Test (CAT) (Stein & Haynes, 2011 ), California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione, 1990a , 1990b ), and Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (Watson & Glaser, 1964 ). These commercially available, multiple-choice tests are not designed to provide regular, formative feedback throughout a course and have not been implemented for this purpose. Instead, they are designed to provide summative feedback with a focus on assessing this skill at a programmatic or university level rather than for use in the classroom to provide formative feedback to students. Rather than using tests to assess process skills, rubrics could be used instead. Rubrics are effective assessment tools because they can be quick and easy to use, they provide feedback to both students and instructors, and they can evaluate individual aspects of a skill to give more specific feedback (Brookhart & Chen, 2014 ; Smit & Birri, 2014 ). Rubrics for assessing critical thinking are available, but they have not been used to provide feedback to undergraduate STEM students nor were they designed to do so (Association of American Colleges and Universities, 2019 ; Saxton et al., 2012 ). The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric is designed specifically to assess K-12 students to enhance college readiness and has not been broadly tested in collegiate STEM courses (Saxton et al., 2012 ). The critical thinking rubric developed by the Association of American Colleges and Universities (AAC&U) as part its Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education (VALUE) Institute and Liberal Education and America’s Promise (LEAP) initiative (Association of American Colleges and Universities, 2019 ) is intended for programmatic assessment rather than specifically giving feedback to students throughout a course. As with tests for assessing critical thinking, current rubrics to assess critical thinking are not designed to act as formative assessments and give feedback to STEM faculty and undergraduates at the course or task level. Another issue with the assessment of critical thinking is the degree to which the construct is measurable. A National Research Council report (National Research Council, 2011 ) has suggested that there is little evidence of a consistent, measurable definition for critical thinking and that it may not be different from one’s general cognitive ability. Despite this issue, we have found that critical thinking is consistently listed as a programmatic outcome in STEM disciplines (American Chemical Society Committee on Professional Training, 2015 ; The Royal Society, 2014 ), so we argue that it is necessary to support instructors as they attempt to assess this skill.
Current methods for evaluating students’ information processing include discipline-specific tools such as a rubric to assess physics students’ use of graphs and equations to solve work-energy problems (Nguyen et al., 2010 ) and assessments of organic chemistry students’ ability to “[manipulate] and [translate] between various representational forms” including 2D and 3D representations of chemical structures (Kumi et al., 2013 ). Although these assessment tools can be effectively used for their intended context, they were not designed for use in a wide range of STEM disciplines or for a variety of tasks.
Despite the many tools that exist to measure process skills, none has been designed and tested to facilitate frequent, formative feedback to STEM undergraduate students and faculty throughout a semester. The rubrics described here have been designed by the Enhancing Learning by Improving Process Skills in STEM (ELIPSS) Project (Cole et al., 2016 ) to assess undergraduate STEM students’ process skills and to facilitate feedback at the classroom level with the potential to track growth throughout a semester or degree program. The rubrics described here are designed to assess critical thinking and information processing in student written work. Rubrics were chosen as the format for our process skill assessment tools because the highest level of each category in rubrics can serve as an explicit learning outcome that the student is expected to achieve (Panadero & Jonsson, 2013 ). Rubrics that are generalizable to multiple disciplines and institutions can enable the assessment of student learning outcomes and active learning pedagogies throughout a program of study and provide useful tools for a greater number of potential users.
Research questions
This work sought to answer the following research questions for each rubric:
Does the rubric adequately measure relevant aspects of the skill?
How well can the rubrics provide feedback to instructors and students?
Can multiple raters use the rubrics to give consistent scores?
This work received Institutional Review Board approval prior to any data collection involving human subjects. The sources of data used to construct the process skill rubrics and answer these research questions were (1) peer-reviewed literature on how each skill is defined, (2) feedback from content experts in multiple STEM disciplines via surveys and in-person, group discussions regarding the appropriateness of the rubrics for each discipline, (3) interviews with students whose work was scored with the rubrics and teaching assistants who scored the student work, and (4) results of applying the rubrics to samples of student work.
Defining the scope of the rubrics
The rubrics described here and the other rubrics in development by the ELIPSS Project are intended to measure process skills, which are desired learning outcomes identified by the STEM community in recent reports (National Research Council, 2012 ; Singer et al., 2012 ). In order to measure these skills in multiple STEM disciplines, operationalized definitions of each skill were needed. These definitions specify which aspects of student work (operations) would be considered evidence for the student using that skill and establish a shared understanding of each skill by members of each STEM discipline. The starting point for this work was the process skill definitions developed as part of the POGIL project (Cole et al., 2019a ). The POGIL community includes instructors from a variety of disciplines and institutions and represented the intended audience for the rubrics: faculty who value process skills and want to more explicitly assess them. The process skills discussed in this work were defined as follows:
Critical thinking is analyzing, evaluating, or synthesizing relevant information to form an argument or reach a conclusion supported with evidence.
Information processing is evaluating, interpreting, and manipulating or transforming information.
Examples of critical thinking include the tasks that students are asked to perform in a laboratory course. When students are asked to analyze the data they collected, combine data from different sources, and generate arguments or conclusions about their data, we see this as critical thinking. However, when students simply follow the so-called “cookbook” laboratory instructions that require them to confirm pre-determined conclusions, we do not think students are engaging in critical thinking. One example of information processing is when organic chemistry students are required to re-draw molecules in different formats. The students must evaluate and interpret various pieces of one representation, and then they recreate the molecule in another representation. However, if students are asked to simply memorize facts or algorithms to solve problems, we do not see this as information processing.
Iterative rubric development
The development process was the same for the information processing rubric and the critical thinking rubric. After defining the scope of the rubric, an initial version was drafted based upon the definition of the target process skill and how each aspect of the skill is defined in the literature. A more detailed discussion of the literature that informed each rubric category is included in the “Results and Discussion” section. This initial version then underwent iterative testing in which the rubric was reviewed by researchers, practitioners, and students. The rubric was first evaluated by the authors and a group of eight faculty from multiple STEM disciplines who made up the ELIPSS Project’s primary collaborative team (PCT). The PCT was a group of faculty members with experience in discipline-based education research who employ active-learning pedagogies in their classrooms. This initial round of evaluation was intended to ensure that the rubric measured relevant aspects of the skill and was appropriate for each PCT member’s discipline. This evaluation determined how well the rubrics were aligned with each instructor’s understanding of the process skill including both in-person and email discussions that continued until the group came to consensus that each rubric category could be applied to student work in courses within their disciplines. There has been an ongoing debate regarding the role of disciplinary knowledge in critical thinking and the extent to which critical thinking is subject-specific (Davies, 2013 ; Ennis, 1990 ). This work focuses on the creation of rubrics to measure process skills in different domains, but we have not performed cross-discipline comparisons. This initial round of review was also intended to ensure that the rubrics were ready for classroom testing by instructors in each discipline. Next, each rubric was tested over three semesters in multiple classroom environments, illustrated in Table 1 . The rubrics were applied to student work chosen by each PCT member. The PCT members chose the student work based on their views of how the assignments required students to engage in process skills and show evidence of those skills. The information processing and critical thinking rubrics shown in this work were each tested in at least three disciplines, course levels, and institutions.
After each semester, the feedback was collected from the faculty testing the rubric, and further changes to the rubric were made. Feedback was collected in the form of survey responses along with in-person group discussions at annual project meetings. After the first iteration of completing the survey, the PCT members met with the authors to discuss how they were interpreting each survey question. This meeting helped ensure that the surveys were gathering valid data regarding how well the rubrics were measuring the desired process skill. Questions in the survey such as “What aspects of the student work provided evidence for the indicated process skill?” and “Are there edits to the rubric/descriptors that would improve your ability to assess the process skill?” allowed the authors to determine how well the rubric scores were matching the student work and identify necessary changes to the rubric. Further questions asked about the nature and timing of the feedback given to students in order to address the question of how well the rubrics provide feedback to instructors and students. The survey questions are included in the Supporting Information . The survey responses were analyzed qualitatively to determine themes related to each research question.
In addition to the surveys given to faculty rubric testers, twelve students were interviewed in fall 2016 and fall 2017. In the United States of America, the fall semester typically runs from August to December and is the first semester of the academic year. Each student participated in one interview which lasted about 30 min. These interviews were intended to gather further data to answer questions about how well the rubrics were measuring the identified process skills that students were using when they completed their assignments and to ensure that the information provided by the rubrics made sense to students. The protocol for these interviews is included in the Supporting Information . In fall 2016, the students interviewed were enrolled in an organic chemistry laboratory course for non-majors at a large, research-intensive university in the United States. Thirty students agreed to have their work analyzed by the research team, and nine students were interviewed. However, the rubrics were not a component of the laboratory course grading. Instead, the first author assessed the students’ reports for critical thinking and information processing, and then the students were provided electronic copies of their laboratory reports and scored rubrics in advance of the interview. The first author had recently been a graduate teaching assistant for the course and was familiar with the instructor’s expectations for the laboratory reports. During the interview, the students were given time to review their reports and the completed rubrics, and then they were asked about how well they understood the content of the rubrics and how accurately each category score represented their work.
In fall 2017, students enrolled in a physical chemistry thermodynamics course for majors were interviewed. The physical chemistry course took place at the same university as the organic laboratory course, but there was no overlap between participants. Three students and two graduate teaching assistants (GTAs) were interviewed. The course included daily group work, and process skill assessment was an explicit part of the instructor’s curriculum. At the end of each class period, students assessed their groups using portions of ELIPSS rubrics, including the two process skill rubrics included in this paper. About every 2 weeks, the GTAs assessed the student groups with a complete ELIPSS rubric for a particular skill, then gave the groups their scored rubrics with written comments. The students’ individual homework problem sets were assessed once with rubrics for three skills: critical thinking, information processing, and problem-solving. The students received the scored rubric with written comments when the graded problem set was returned to them. In the last third of the semester, the students and GTAs were interviewed about how rubrics were implemented in the course, how well the rubric scores reflected the students’ written work, and how the use of rubrics affected the teaching assistants’ ability to assess the student skills. The protocols for these interviews are included in the Supporting Information .
Gathering evidence for utility, validity, and reliability
The utility, validity, and reliability of the rubrics were measured throughout the development process. The utility is the degree to which the rubrics are perceived as practical to experts and practitioners in the field. Through multiple meetings, the PCT faculty determined that early drafts of the rubric seemed appropriate for use in their classrooms, which represented multiple STEM disciplines. Rubric utility was reexamined multiple times throughout the development process to ensure that the rubrics would remain practical for classroom use. Validity can be defined in multiple ways. For example, the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (Joint Committee on Standards for Educational Psychological Testing, 2014 ) defines validity as “the degree to which all the accumulated evidence supports the intended interpretation of test scores for the proposed use.” For the purposes of this work, we drew on the ways in which two distinct types of validity were examined in the rubric literature: content validity and construct validity. Content validity is the degree to which the rubrics cover relevant aspects of each process skill (Moskal & Leydens, 2000 ). In this case, the process skill definition and a review of the literature determined which categories were included in each rubric. The literature review was finished once the data was saturated: when no more new aspects were found. Construct validity is the degree to which the levels of each rubric category accurately reflect the process that students performed (Moskal & Leydens, 2000 ). Evidence of construct validity was gathered via the faculty surveys, teaching assistant interviews, and student interviews. In the student interviews, students were given one of their completed assignments and asked to explain how they completed the task. Students were then asked to explain how well each category applied to their work and if any changes were needed to the rubric to more accurately reflect their process. Due to logistical challenges, we were not able to obtain evidence for convergent validity, and this is further discussed in the “Limitations” section.
Adjacent agreement, also known as “interrater agreement within one,” was chosen as the measure of interrater reliability due to its common use in rubric development projects (Jonsson & Svingby, 2007 ). The adjacent agreement is the percentage of cases in which two raters agree on a rating or are different by one level (i.e., they give adjacent ratings to the same work). Jonsson and Svingby ( 2007 ) found that most of the rubrics they reviewed had adjacent agreement scores of 90% or greater. However, they noted that the agreement threshold varied based on the number of possible levels of performance for each category in the rubric, with three and four being the most common numbers of levels. Since the rubrics discussed in this report have six levels (scores of zero through five) and are intended for low-stakes assessment and feedback, the goal of 80% adjacent agreement was selected. To calculate agreement for the critical thinking and information processing rubrics, two researchers discussed the scoring criteria for each rubric and then independently assessed the organic chemistry laboratory reports.
Results and discussion
The process skill rubrics to assess critical thinking and information processing in student written work were completed after multiple rounds of revision based on feedback from various sources. These sources include feedback from instructors who tested the rubrics in their classrooms, TAs who scored student work with the rubrics, and students who were assessed with the rubrics. The categories for each rubric will be discussed in terms of the evidence that the rubrics measure the relevant aspects of the skill and how they can be used to assess STEM undergraduate student work. Each category discussion will begin with a general explanation of the category followed by more specific examples from the organic chemistry laboratory course and physical chemistry lecture course to demonstrate how the rubrics can be used to assess student work.
Information processing rubric
The definition of information processing and the focus of the rubric presented here (Fig. 1 ) are distinct from cognitive information processing as defined by the educational psychology literature (Driscoll, 2005 ). The rubric shown here is more aligned with the STEM education construct of representational competency (Daniel et al., 2018 ).
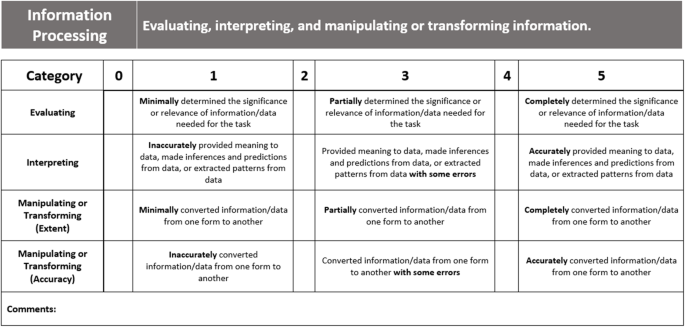
Rubric for assessing information processing
When solving a problem or completing a task, students must evaluate the provided information for relevance or importance to the task (Hanson, 2008 ; Swanson et al., 1990 ). All the information provided in a prompt (e.g., homework or exam questions) may not be relevant for addressing all parts of the prompt. Students should ideally show evidence of their evaluation process by identifying what information is present in the prompt/model, indicating what information is relevant or not relevant, and indicating why information is relevant. Responses with these characteristics would earn high rubric scores for this category. Although students may not explicitly state what information is necessary to address a task, the information they do use can act as indirect evidence of the degree to which they have evaluated all of the available information in the prompt. Evidence for students inaccurately evaluating information for relevance includes the inclusion of irrelevant information or the omission of relevant information in an analysis or in completing a task. When evaluating the organic chemistry laboratory reports, the focus for the evaluating category was the information students presented when identifying the chemical structure of their products. For students who received a high score, this information included their measured value for the product’s melting point, the literature (expected) value for the melting point, and the peaks in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum. NMR spectroscopy is a commonly used technique in chemistry to obtain structural information about a compound. Lower scores were given if students omitted any of the necessary information or if they included unnecessary information. For example, if a student discussed their reaction yield when discussing the identity of their product, they would receive a low Evaluating score because the yield does not help them determine the identity of their product; the yield, in this case, would be unnecessary information. In the physical chemistry course, students often did not show evidence that they determined which information was relevant to answer the homework questions and thus earned low evaluating scores. These omissions will be further addressed in the “Interpreting” section.
Interpreting
In addition to evaluating, students must often interpret information using their prior knowledge to explain the meaning of something, make inferences, match data to predictions, and extract patterns from data (Hanson, 2008 ; Nakhleh, 1992 ; Schmidt et al., 1989 ; Swanson et al., 1990 ). Students earn high scores for this category if they assign correct meaning to labeled information (e.g., text, tables, graphs, diagrams), extract specific details from information, explain information in their own words, and determine patterns in information. For the organic chemistry laboratory reports, students received high scores if they accurately interpreted their measured values and NMR peaks. Almost every student obtained melting point values that were different than what was expected due to measurement error or impurities in their products, so they needed to describe what types of impurities could cause such discrepancies. Also, each NMR spectrum contained one peak that corresponded to the solvent used to dissolve the students’ product, so the students needed to use their prior knowledge of NMR spectroscopy to recognize that peak did not correspond to part of their product.
In physical chemistry, the graduate teaching assistant often gave students low scores for inaccurately explaining changes to chemical systems such as changes in pressure or entropy. The graduate teaching assistant who assessed the student work used the rubric to identify both the evaluating and interpreting categories as weaknesses in many of the students’ homework submissions. However, the students often earned high scores for the manipulating and transforming categories, so the GTA was able to give students specific feedback on their areas for improvement while also highlighting their strengths.
Manipulating and transforming (extent and accuracy)
In addition to evaluating and interpreting information, students may be asked to manipulate and transform information from one form to another. These transformations should be complete and accurate (Kumi et al., 2013 ; Nguyen et al., 2010 ). Students may be required to construct a figure based on written information, or conversely, they may transform information in a figure into words or mathematical expressions. Two categories for manipulating and transforming (i.e., extent and accuracy) were included to allow instructors to give more specific feedback. It was often found that students would either transform little information but do so accurately, or transform much information and do so inaccurately; the two categories allowed for differentiated feedback to be provided. As stated above, the organic chemistry students were expected to transform their NMR spectral data into a table and provide a labeled structure of their final product. Students were given high scores if they converted all of the relevant peaks from their spectrum into the table format and were able to correctly match the peaks to the hydrogen atoms in their products. Students received lower scores if they were only able to convert the information for a few peaks or if they incorrectly matched the peaks to the hydrogen atoms.
Critical thinking rubric
Critical thinking can be broadly defined in different contexts, but we found that the categories included in the rubric (Fig. 2 ) represented commonly accepted aspects of critical thinking (Danczak et al., 2017 ) and suited the needs of the faculty collaborators who tested the rubric in their classrooms.
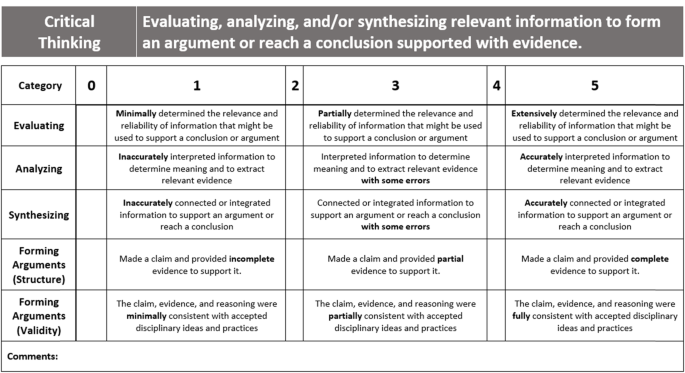
Rubric for assessing critical thinking
When completing a task, students must evaluate the relevance of information that they will ultimately use to support a claim or conclusions (Miri et al., 2007 ; Zohar et al., 1994 ). An evaluating category is included in both critical thinking and information processing rubrics because evaluation is a key aspect of both skills. From our previous work developing a problem-solving rubric (manuscript in preparation) and our review of the literature for this work (Danczak et al., 2017 ; Lewis & Smith, 1993 ), the overlap was seen between information processing, critical thinking, and problem-solving. Additionally, while the Evaluating category in the information processing rubric assesses a student’s ability to determine the importance of information to complete a task, the evaluating category in the critical thinking rubric places a heavier emphasis on using the information to support a conclusion or argument.
When scoring student work with the evaluating category, students receive high scores if they indicate what information is likely to be most relevant to the argument they need to make, determine the reliability of the source of their information, and determine the quality and accuracy of the information itself. The information used to assess this category can be indirect as with the Evaluating category in the information processing rubric. In the organic chemistry laboratory reports, students needed to make an argument about whether they successfully produced the desired product, so they needed to discuss which information was relevant to their claims about the product’s identity and purity. Students received high scores for the evaluating category when they accurately determined that the melting point and nearly all peaks except the solvent peak in the NMR spectrum indicated the identity of their product. Students received lower scores for evaluating when they left out relevant information because this was seen as evidence that the student inaccurately evaluated the information’s relevance in supporting their conclusion. They also received lower scores when they incorrectly stated that a high yield indicated a pure product. Students were given the opportunity to demonstrate their ability to evaluate the quality of information when discussing their melting point. Students sometimes struggled to obtain reliable melting point data due to their inexperience in the laboratory, so the rubric provided a way to assess the student’s ability to critique their own data.
In tandem with evaluating information, students also need to analyze that same information to extract meaningful evidence to support their conclusions (Bailin, 2002 ; Lai, 2011 ; Miri et al., 2007 ). The analyzing category provides an assessment of a student’s ability to discuss information and explore the possible meaning of that information, extract patterns from data/information that could be used as evidence for their claims, and summarize information that could be used as evidence. For example, in the organic chemistry laboratory reports, students needed to compare the information they obtained to the expected values for a product. Students received high scores for the analyzing category if they could extract meaningful structural information from the NMR spectrum and their two melting points (observed and expected) for each reaction step.
Synthesizing
Often, students are asked to synthesize or connect multiple pieces of information in order to draw a conclusion or make a claim (Huitt, 1998 ; Lai, 2011 ). Synthesizing involves identifying the relationships between different pieces of information or concepts, identifying ways that different pieces of information or concepts can be combined, and explaining how the newly synthesized information can be used to reach a conclusion and/or support an argument. While performing the organic chemistry laboratory experiments, students obtained multiple types of information such as the melting point and NMR spectrum in addition to other spectroscopic data such as an infrared (IR) spectrum. Students received high scores for this category when they accurately synthesized these multiple data types by showing how the NMR and IR spectra could each reveal different parts of a molecule in order to determine the molecule’s entire structure.
Forming arguments (structure and validity)
The final key aspect of critical thinking is forming a well-structured and valid argument (Facione, 1984 ; Glassner & Schwarz, 2007 ; Lai, 2011 ; Lewis & Smith, 1993 ). It was observed that students can earn high scores for evaluating, analyzing, and synthesizing, but still struggle to form arguments. This was particularly common in assessing problem sets in the physical chemistry course.
As with the manipulating and transforming categories in the information processing rubric, two forming arguments categories were included to allow instructors to give more specific feedback. Some students may be able to include all of the expected structural elements of their arguments but use faulty information or reasoning. Conversely, some students may be able to make scientifically valid claims but not necessarily support them with evidence. The two forming arguments categories are intended to accurately assess both of these scenarios. For the forming arguments (structure) category, students earn high scores if they explicitly state their claim or conclusion, list the evidence used to support the argument, and provide reasoning to link the evidence to their claim/conclusion. Students who do not make a claim or who provide little evidence or reasoning receive lower scores.
For the forming arguments (validity) category, students earn high scores if their claim is accurate and their reasoning is logical and clearly supports the claim with provided evidence. Organic chemistry students earned high scores for the forms and supports arguments categories if they made explicit claims about the identity and purity of their product and provided complete and accurate evidence for their claim(s) such as the melting point values and positions of NMR peaks that correspond to their product. Additionally, the students provided evidence for the purity of their products by pointing to the presence or absence of peaks in their NMR spectrum that would match other potential side products. They also needed to provide logical reasoning for why the peaks indicated the presence or absence of a compound. As previously mentioned, the physical chemistry students received lower scores for the forming arguments categories than for the other aspects of critical thinking. These students were asked to make claims about the relationships between entropy and heat and then provide relevant evidence to justify these claims. Often, the students would make clearly articulated claims but would provide little evidence to support them. As with the information processing rubric, the critical thinking rubric allowed the GTAs to assess aspects of these skills independently and identify specific areas for student improvement.
Validity and reliability
The goal of this work was to create rubrics that can accurately assess student work (validity) and be consistently implemented by instructors or researchers within multiple STEM fields (reliability). The evidence for validity includes the alignment of the rubrics with literature-based descriptions of each skill, review of the rubrics by content experts from multiple STEM disciplines, interviews with undergraduate students whose work was scored using the rubrics, and interviews of the GTAs who scored the student work.
The definitions for each skill, along with multiple iterations of the rubrics, underwent review by STEM content experts. As noted earlier, the instructors who were testing the rubrics were given a survey at the end of each semester and were invited to offer suggested changes to the rubric to better help them assess their students. After multiple rubric revisions, survey responses from the instructors indicated that the rubrics accurately represented the breadth of each process skill as seen in each expert’s content area and that each category could be used to measure multiple levels of student work. By the end of the rubrics’ development, instructors were writing responses such as “N/A” or “no suggestions” to indicate that the rubrics did not need further changes.
Feedback from the faculty also indicated that the rubrics were measuring the intended constructs by the ways they responded to the survey item “What aspects of the student work provided evidence for the indicated process skill?” For example, one instructor noted that for information processing, she saw evidence of the manipulating and transforming categories when “students had to transform their written/mathematical relationships into an energy diagram.” Another instructor elicited evidence of information processing during an in-class group quiz: “A question on the group quiz was written to illicit [sic] IP [information processing]. Students had to transform a structure into three new structures and then interpret/manipulate the structures to compare the pKa values [acidity] of the new structures.” For this instructor, the structures written by the students revealed evidence of their information processing by showing what information they omitted in the new structures or inaccurately transformed. For critical thinking, an instructor assessed short research reports with the critical thinking rubric and “looked for [the students’] ability to use evidence to support their conclusions, to evaluate the literature studies, and to develop their own judgements by synthesizing the information.” Another instructor used the critical thinking rubric to assess their students’ abilities to choose an instrument to perform a chemical analysis. According to the instructor, the students provided evidence of their critical thinking because “in their papers, they needed to justify their choice of instrument. This justification required them to evaluate information and synthesize a new understanding for this specific chemical analysis.”
Analysis of student work indicates multiple levels of achievement for each rubric category (illustrated in Fig. 3 ), although there may have been a ceiling effect for the evaluating and the manipulating and transforming (extent) categories in information processing for organic chemistry laboratory reports because many students earned the highest possible score (five) for those categories. However, other implementations of the ELIPSS rubrics (Reynders et al., 2019 ) have shown more variation in student scores for the two process skills.
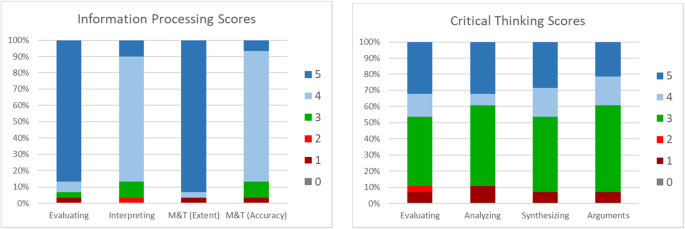
Student rubric scores from an organic chemistry laboratory course. The two rubrics were used to evaluate different laboratory reports. Thirty students were assessed for information processing and 28 were assessed for critical thinking
To provide further evidence that the rubrics were measuring the intended skills, students in the physical chemistry course were interviewed about their thought processes and how well the rubric scores reflected the work they performed. During these interviews, students described how they used various aspects of information processing and critical thinking skills. The students first described how they used information processing during a problem set where they had to answer questions about a diagram of systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Students described how they evaluated and interpreted the graph to make statements such as “diastolic [pressure] is our y-intercept” and “volume is the independent variable.” The students then demonstrated their ability to transform information from one form to another, from a graph to a mathematic equation, by recognizing “it’s a linear relationship so I used Y equals M X plus B ” and “integrated it cause it’s the change, the change in V [volume]. For critical thinking, students described their process on a different problem set. In this problem set, the students had to explain why the change of Helmholtz energy and the change in Gibbs free energy were equivalent under a certain given condition. Students first demonstrated how they evaluated the relevant information and analyzed what would and would not change in their system. One student said, “So to calculate the final pressure, I think I just immediately went to the ideal gas law because we know the final volume and the number of moles won’t change and neither will the temperature in this case. Well, I assume that it wouldn’t.” Another student showed evidence of their evaluation by writing out all the necessary information in one place and stating, “Whenever I do these types of problems, I always write what I start with which is why I always have this line of information I’m given.” After evaluating and analyzing, students had to form an argument by claiming that the two energy values were equal and then defending that claim. Students explained that they were not always as clear as they could be when justifying their claim. For instance, one student said, “Usually I just write out equations and then hope people understand what I’m doing mathematically” but they “probably could have explained it a little more.”
Student feedback throughout the organic chemistry course and near the end of the physical chemistry course indicated that the rubric scores were accurate representations of the students’ work with a few exceptions. For example, some students felt like they should have received either a lower or higher score for certain categories, but they did say that the categories themselves applied well to their work. Most notably, one student reported that the forms and supports arguments categories in the critical thinking rubric did not apply to her work because she “wasn’t making an argument” when she was demonstrating that the Helmholtz and Gibbs energy values were equal in her thermodynamics assignment. We see this as an instance where some students and instructors may define argument in different ways. The process skill definitions and the rubric categories are meant to articulate intended learning outcomes from faculty members to their students, so if a student defines the skills or categories differently than the faculty member, then the rubrics can serve to promote a shared understanding of the skill.
As previously mentioned, reliability was measured by two researchers assessing ten laboratory reports independently to ensure that multiple raters could use the rubrics consistently. The average adjacent agreement scores were 92% for critical thinking and 93% for information processing. The exact agreement scores were 86% for critical thinking and 88% for information processing. Additionally, two different raters assessed a statistics assignment that was given to sixteen first-year undergraduates. The average pairwise adjacent agreement scores were 89% for critical thinking and 92% for information processing for this assignment. However, the exact agreement scores were much lower: 34% for critical thinking and 36% for information processing. In this case, neither rater was an expert in the content area. While the exact agreement scores for the statistics assignment are much lower than desirable, the adjacent agreement scores do meet the threshold for reliability as seen in other rubrics (Jonsson & Svingby, 2007 ) despite the disparity in expertise. Based on these results, it may be difficult for multiple raters to give exactly the same scores to the same work if they have varying levels of content knowledge, but it is important to note that the rubrics are primarily intended for formative assessment that can facilitate discussions between instructors and students about the ways for students to improve. The high level of adjacent agreement scores indicates that multiple raters can identify the same areas to improve in examples of student work.
Instructor and teaching assistant reflections
The survey responses from faculty members determined the utility of the rubrics. Faculty members reported that when they used the rubrics to define their expectations and be more specific about their assessment criteria, the students seemed to be better able to articulate the areas in which they needed improvement. As one instructor put it, “having the rubrics helped open conversations and discussions” that were not happening before the rubrics were implemented. We see this as evidence of the clear intended learning outcomes that are an integral aspect of achieving constructive alignment within a course. The instructors’ specific feedback to the students, and the students’ increased awareness of their areas for improvement, may enable the students to better regulate their learning throughout a course. Additionally, the survey responses indicated that the faculty members were changing their teaching practices and becoming more cognizant of how assignments did or did not elicit the process skill evidence that they desired. After using the rubrics, one instructor said, “I realize I need to revise many of my activities to more thoughtfully induce process skill development.” We see this as evidence that the faculty members were using the rubrics to regulate their teaching by reflecting on the outcomes of their practices and then planning for future teaching. These activities represent the reflection and forethought/planning aspects of self-regulated learning on the part of the instructors. Graduate teaching assistants in the physical chemistry course indicated that the rubrics gave them a way to clarify the instructor’s expectations when they were interacting with the students. As one GTA said, “It’s giving [the students] feedback on direct work that they have instead of just right or wrong. It helps them to understand like ‘Okay how can I improve? What areas am I lacking in?’” A more detailed account of how the instructors and teaching assistants implemented the rubrics has been reported elsewhere (Cole et al., 2019a ).
Student reflections
Students in both the organic and physical chemistry courses reported that they could use the rubrics to engage in the three phases of self-regulated learning: forethought/planning, performing, and reflecting. In an organic chemistry interview, one student was discussing how they could improve their low score for the synthesizing category of critical thinking by saying “I could use the data together instead of trying to use them separately,” thus demonstrating forethought/planning for their later work. Another student described how they could use the rubric while performing a task: “I could go through [the rubric] as I’m writing a report…and self-grade.” Finally, one student demonstrated how they could use the rubrics to reflect on their areas for improvement by saying that “When you have the five column [earn a score of five], I can understand that I’m doing something right” but “I really need to work on revising my reports.” We see this as evidence that students can use the rubrics to regulate their own learning, although classroom facilitation can have an effect on the ways in which students use the rubric feedback (Cole et al., 2019b ).
Limitations
The process skill definitions presented here represent a consensus understanding among members of the POGIL community and the instructors who participated in this study, but these skills are often defined in multiple ways by various STEM instructors, employers, and students (Danczak et al., 2017 ). One issue with critical thinking, in particular, is the broadness of how the skill is defined in the literature. Through this work, we have evidence via expert review to indicate that our definitions represent common understandings among a set of STEM faculty. Nonetheless, we cannot claim that all STEM instructors or researchers will share the skill definitions presented here.
There is currently a debate in the STEM literature (National Research Council, 2011 ) about whether the critical thinking construct is domain-general or domain-specific, that is, whether or not one’s critical thinking ability in one discipline can be applied to another discipline. We cannot make claims about the generalness of the construct based on the data presented here because the same students were not tested across multiple disciplines or courses. Additionally, we did not gather evidence for convergent validity, which is “the degree to which an operationalized construct is similar to other operationalized constructs that it theoretically should be similar to” (National Research Council, 2011 ). In other words, evidence for convergent validity would be the comparison of multiple measures of information processing or critical thinking. However, none of the instructors who used the ELIPSS rubrics also used a secondary measure of the constructs. Although the rubrics were examined by a multidisciplinary group of collaborators, this group was primarily chemists and included eight faculties from other disciplines, so the content validity of the rubrics may be somewhat limited.
Finally, the generalizability of the rubrics is limited by the relatively small number of students who were interviewed about their work. During their interviews, the students in the organic and physical chemistry courses each said that they could use the rubric scores as feedback to improve their skills. Additionally, as discussed in the “Validity and Reliability” section, the processes described by the students aligned with the content of the rubric and provided evidence of the rubric scores’ validity. However, the data gathered from the student interviews only represents the views of a subset of students in the courses, and further study is needed to determine the most appropriate contexts in which the rubrics can be implemented.
Conclusions and implications
Two rubrics were developed to assess and provide feedback on undergraduate STEM students’ critical thinking and information processing. Faculty survey responses indicated that the rubrics measured the relevant aspects of each process skill in the disciplines that were examined. Faculty survey responses, TA interviews, and student interviews over multiple semesters indicated that the rubric scores accurately reflected the evidence of process skills that the instructors wanted to see and the processes that the students performed when they were completing their assignments. The rubrics showed high inter-rater agreement scores, indicating that multiple raters could identify the same areas for improvement in student work.
In terms of constructive alignment, courses should ideally have alignment between their intended learning outcomes, student and instructor activities, and assessments. By using the ELIPSS rubrics, instructors were able to explicitly articulate the intended learning outcomes of their courses to their students. The instructors were then able to assess and provide feedback to students on different aspects of their process skills. Future efforts will be focused on modifying student assignments to enable instructors to better elicit evidence of these skills. In terms of self-regulated learning, students indicated in the interviews that the rubric scores were accurate representations of their work (performances), could help them reflect on their previous work (self-reflection), and the feedback they received could be used to inform their future work (forethought). Not only did the students indicate that the rubrics could help them regulate their learning, but the faculty members indicated that the rubrics had helped them regulate their teaching. With the individual categories on each rubric, the faculty members were better able to observe their students’ strengths and areas for improvement and then tailor their instruction to meet those needs. Our results indicated that the rubrics helped instructors in multiple STEM disciplines and at multiple institutions reflect on their teaching and then make changes to better align their teaching with their desired outcomes.
Overall, the rubrics can be used in a number of different ways to modify courses or for programmatic assessment. As previously stated, instructors can use the rubrics to define expectations for their students and provide them with feedback on desired skills throughout a course. The rubric categories can be used to give feedback on individual aspects of student process skills to provide specific feedback to each student. If an instructor or department wants to change from didactic lecture-based courses to active learning ones, the rubrics can be used to measure non-content learning gains that stem from the adoption of such pedagogies. Although the examples provided here for each rubric were situated in chemistry contexts, the rubrics were tested in multiple disciplines and institution types. The rubrics have the potential for wide applicability to assess not only laboratory reports but also homework assignments, quizzes, and exams. Assessing these tasks provides a way for instructors to achieve constructive alignment between their intended outcomes and their assessments, and the rubrics are intended to enhance this alignment to improve student process skills that are valued in the classroom and beyond.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
American Association of Colleges and Universities
Critical Thinking Assessment Test
Comprehensive University
Enhancing Learning by Improving Process Skills in STEM
Liberal Education and America’s Promise
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Primary Collaborative Team
Peer-led Team Learning
Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning
Primarily Undergraduate Institution
Research University
Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics
Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education
ABET Engineering Accreditation Commission. (2012). Criteria for Accrediting Engineering Programs . Retrieved from http://www.abet.org/accreditation/accreditation-criteria/criteria-for-accrediting-engineering-programs-2016-2017/ .
American Chemical Society Committee on Professional Training. (2015). Unergraduate Professional Education in Chemistry: ACS Guidelines and Evaluation Procedures for Bachelor's Degree Programs . Retrieved from https://www.acs.org/content/dam/acsorg/about/governance/committees/training/2015-acs-guidelines-for-bachelors-degree-programs.pdf
Association of American Colleges and Universities. (2019). VALUE Rubric Development Project. Retrieved from https://www.aacu.org/value/rubrics .
Bailin, S. (2002). Critical Thinking and Science Education. Science and Education, 11 , 361–375.
Article Google Scholar
Biggs, J. (1996). Enhancing teaching through constructive alignment. Higher Education, 32 (3), 347–364.
Biggs, J. (2003). Aligning teaching and assessing to course objectives. Teaching and learning in higher education: New trends and innovations, 2 , 13–17.
Google Scholar
Biggs, J. (2014). Constructive alignment in university teaching. HERDSA Review of higher education, 1 (1), 5–22.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and Classroom Learning. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 5 (1), 7–74.
Bodner, G. M. (1986). Constructivism: A theory of knowledge. Journal of Chemical Education, 63 (10), 873–878.
Brewer, C. A., & Smith, D. (2011). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: a call to action. American Association for the Advancement of Science . DC : Washington .
Brookhart, S. M., & Chen, F. (2014). The quality and effectiveness of descriptive rubrics. Educational Review , 1–26.
Butler, D. L., & Winne, P. H. (1995). Feedback and Self-Regulated Learning: A Theoretical Synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 65 (3), 245–281.
Cole, R., Lantz, J., & Ruder, S. (2016). Enhancing Learning by Improving Process Skills in STEM. Retrieved from http://www.elipss.com .
Cole, R., Lantz, J., & Ruder, S. (2019a). PO: The Process. In S. R. Simonson (Ed.), POGIL: An Introduction to Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning for Those Who Wish to Empower Learners (pp. 42–68). Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Cole, R., Reynders, G., Ruder, S., Stanford, C., & Lantz, J. (2019b). Constructive Alignment Beyond Content: Assessing Professional Skills in Student Group Interactions and Written Work. In M. Schultz, S. Schmid, & G. A. Lawrie (Eds.), Research and Practice in Chemistry Education: Advances from the 25 th IUPAC International Conference on Chemistry Education 2018 (pp. 203–222). Singapore: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Danczak, S., Thompson, C., & Overton, T. (2017). ‘What does the term Critical Thinking mean to you?’A qualitative analysis of chemistry undergraduate, teaching staff and employers' views of critical thinking. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 18 , 420–434.
Daniel, K. L., Bucklin, C. J., Leone, E. A., & Idema, J. (2018). Towards a Definition of Representational Competence. In Towards a Framework for Representational Competence in Science Education (pp. 3–11). Switzerland: Springer.
Davies, M. (2013). Critical thinking and the disciplines reconsidered. Higher Education Research & Development, 32 (4), 529–544.
Deloitte Access Economics. (2014). Australia's STEM Workforce: a survey of employers. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/au/en/pages/economics/articles/australias-stem-workforce-survey.html .
Driscoll, M. P. (2005). Psychology of learning for instruction . Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Ennis, R. H. (1990). The extent to which critical thinking is subject-specific: Further clarification. Educational researcher, 19 (4), 13–16.
Facione, P. A. (1984). Toward a theory of critical thinking. Liberal Education, 70 (3), 253–261.
Facione, P. A. (1990a). The California Critical Thinking Skills Test--College Level . In Technical Report #1 . Experimental Validation and Content : Validity .
Facione, P. A. (1990b). The California critical thinking skills test—college level . In Technical Report #2 . Factors Predictive of CT : Skills .
Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., & Wenderoth, M. P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111 (23), 8410–8415.
Gafney, L., & Varma-Nelson, P. (2008). Peer-led team learning: evaluation, dissemination, and institutionalization of a college level initiative (Vol. 16): Springer Science & Business Media, Netherlands.
Glassner, A., & Schwarz, B. B. (2007). What stands and develops between creative and critical thinking? Argumentation? Thinking Skills and Creativity, 2 (1), 10–18.
Gosser, D. K., Cracolice, M. S., Kampmeier, J. A., Roth, V., Strozak, V. S., & Varma-Nelson, P. (2001). Peer-led team learning: A guidebook: Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ .
Gray, K., & Koncz, A. (2018). The key attributes employers seek on students' resumes. Retrieved from http://www.naceweb.org/about-us/press/2017/the-key-attributes-employers-seek-on-students-resumes/ .
Hanson, D. M. (2008). A cognitive model for learning chemistry and solving problems: implications for curriculum design and classroom instruction. In R. S. Moog & J. N. Spencer (Eds.), Process-Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (pp. 15–19). Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Hattie, J., & Gan, M. (2011). Instruction based on feedback. Handbook of research on learning and instruction , 249-271.
Huitt, W. (1998). Critical thinking: an overview. In Educational psychology interactive Retrieved from http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/topics/cogsys/critthnk.html .
Joint Committee on Standards for Educational Psychological Testing. (2014). Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing : American Educational Research Association.
Jonsson, A., & Svingby, G. (2007). The use of scoring rubrics: Reliability, validity and educational consequences. Educational Research Review, 2 (2), 130–144.
Kumi, B. C., Olimpo, J. T., Bartlett, F., & Dixon, B. L. (2013). Evaluating the effectiveness of organic chemistry textbooks in promoting representational fluency and understanding of 2D-3D diagrammatic relationships. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 14 , 177–187.
Lai, E. R. (2011). Critical thinking: a literature review. Pearson's Research Reports, 6 , 40–41.
Lewis, A., & Smith, D. (1993). Defining higher order thinking. Theory into Practice, 32 , 131–137.
Miri, B., David, B., & Uri, Z. (2007). Purposely teaching for the promotion of higher-order thinking skills: a case of critical thinking. Research in Science Education, 37 , 353–369.
Moog, R. S., & Spencer, J. N. (Eds.). (2008). Process oriented guided inquiry learning (POGIL) . Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Moskal, B. M., & Leydens, J. A. (2000). Scoring rubric development: validity and reliability. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation, 7 , 1–11.
Nakhleh, M. B. (1992). Why some students don't learn chemistry: Chemical misconceptions. Journal of Chemical Education, 69 (3), 191.
National Research Council. (2011). Assessing 21st Century Skills: Summary of a Workshop . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
National Research Council. (2012). Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Nguyen, D. H., Gire, E., & Rebello, N. S. (2010). Facilitating Strategies for Solving Work-Energy Problems in Graphical and Equational Representations. 2010 Physics Education Research Conference, 1289 , 241–244.
Nicol, D. J., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education, 31 (2), 199–218.
Panadero, E., & Jonsson, A. (2013). The use of scoring rubrics for formative assessment purposes revisited: a review. Educational Research Review, 9 , 129–144.
Pearl, A. O., Rayner, G., Larson, I., & Orlando, L. (2019). Thinking about critical thinking: An industry perspective. Industry & Higher Education, 33 (2), 116–126.
Ramsden, P. (1997). The context of learning in academic departments. The experience of learning, 2 , 198–216.
Rau, M. A., Kennedy, K., Oxtoby, L., Bollom, M., & Moore, J. W. (2017). Unpacking “Active Learning”: A Combination of Flipped Classroom and Collaboration Support Is More Effective but Collaboration Support Alone Is Not. Journal of Chemical Education, 94 (10), 1406–1414.
Reynders, G., Suh, E., Cole, R. S., & Sansom, R. L. (2019). Developing student process skills in a general chemistry laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education , 96 (10), 2109–2119.
Saxton, E., Belanger, S., & Becker, W. (2012). The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments. Assessing Writing, 17 , 251–270.
Schmidt, H. G., De Volder, M. L., De Grave, W. S., Moust, J. H. C., & Patel, V. L. (1989). Explanatory Models in the Processing of Science Text: The Role of Prior Knowledge Activation Through Small-Group Discussion. J. Educ. Psychol., 81 , 610–619.
Simonson, S. R. (Ed.). (2019). POGIL: An Introduction to Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning for Those Who Wish to Empower Learners . Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Singer, S. R., Nielsen, N. R., & Schweingruber, H. A. (Eds.). (2012). Discipline-Based education research: understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington D.C.: The National Academies Press.
Smit, R., & Birri, T. (2014). Assuring the quality of standards-oriented classroom assessment with rubrics for complex competencies. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 43 , 5–13.
Stein, B., & Haynes, A. (2011). Engaging Faculty in the Assessment and Improvement of Students' Critical Thinking Using the Critical Thinking Assessment Test. Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning, 43 , 44–49.
Swanson, H. L., Oconnor, J. E., & Cooney, J. B. (1990). An Information-Processing Analysis of Expert and Novice Teachers Problem-Solving. American Educational Research Journal, 27 (3), 533–556.
The Royal Society. (2014). Vision for science and mathematics education: The Royal Society Science Policy Centre . London: England.
Watson, G., & Glaser, E. M. (1964). Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Manual . New York, NY: Harcourt, Brace, and World.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41 (2), 64–70.
Zohar, A., Weinberger, Y., & Tamir, P. (1994). The Effect of the Biology Critical Thinking Project on the Development of Critical Thinking. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 31 , 183–196.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank members of our Primary Collaboration Team and Implementation Cohorts for collecting and sharing data. We also thank all the students who have allowed us to examine their work and provided feedback.
Supporting information
• Product rubric survey
• Initial implementation survey
• Continuing implementation survey
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation under collaborative grants #1524399, #1524936, and #1524965. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Chemistry, University of Iowa, W331 Chemistry Building, Iowa City, Iowa, 52242, USA
Gil Reynders & Renée S. Cole
Department of Chemistry, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia, 23284, USA
Gil Reynders & Suzanne M. Ruder
Department of Chemistry, Drew University, Madison, New Jersey, 07940, USA
Juliette Lantz
Department of Chemistry, Ball State University, Muncie, Indiana, 47306, USA
Courtney L. Stanford
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
RC, JL, and SR performed an initial literature review that was expanded by GR. All authors designed the survey instruments. GR collected and analyzed the survey and interview data with guidance from RC. GR revised the rubrics with extensive input from all other authors. All authors contributed to reliability measurements. GR drafted all manuscript sections. RC provided extensive comments during manuscript revisions; JL, SR, and CS also offered comments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Renée S. Cole .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1..
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Reynders, G., Lantz, J., Ruder, S.M. et al. Rubrics to assess critical thinking and information processing in undergraduate STEM courses. IJ STEM Ed 7 , 9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00208-5
Download citation
Received : 01 October 2019
Accepted : 20 February 2020
Published : 09 March 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00208-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Constructive alignment
- Self-regulated learning
- Process skills
- Professional skills
- Critical thinking
- Information processing
- DOI: 10.1016/J.ASW.2012.07.002
- Corpus ID: 143117282
The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments
- Emily Saxton , Secret Belanger , W. Becker
- Published 1 October 2012
- Assessing Writing
59 Citations
Development of critical thinking skills instruments : cases for essay tests, testing inter-rater reliability in rubrics for large scale undergraduate independent projects, assessing efl university students' writing: a study of score reliability, validating an academic group tutorial discussion speaking test, development of rubric of higher order thinking skills assessment on mathematics learning, a robust and generalisable rubric design framework for critical thinking assessment, students’ perceptions on using rubrics as a peer and self-assessment tool in efl speaking courses, measuring critical thinking as learning outcome: a pilot study from the ideas and exposition module, evidences of critical thinking in the writing of first-year college students, analytic rubrics for decision making, 28 references, exploring the structure of the watson–glaser critical thinking appraisal: one scale or many subscales, the use of scoring rubrics: reliability, validity, and educational consequences, assessing students' critical thinking performance: urging for measurements using multi-response format., reliability and validity of rubrics for assessment through writing, inter-rater reliability on various types of assessments scored by school district staff., validation of authentic performance assessment: a process suited for rasch modeling, sampling variability of performance assessments., critical thinking assessment, practical assessment, research, and evaluation practical assessment, research, and evaluation a comparison of consensus, consistency, and measurement a comparison of consensus, consistency, and measurement approaches to estimating interrater reliability approaches to estimating interrater reliabilit, learning to improve: using writing to increase critical thinking performance in general education biology., related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
VALUE Rubrics - Critical Thinking
The VALUE rubrics were developed by teams of faculty experts representing colleges and universities across the United States through a process that examined many existing campus rubrics and related documents for each learning outcome and incorporated additional feedback from faculty. The rubrics articulate fundamental criteria for each learning outcome, with performance descriptors demonstrating progressively more sophisticated levels of attainment. The rubrics are intended for institutional-level use in evaluating and discussing student learning, not for grading. The core expectations articulated in all 16 of the VALUE rubrics can and should be translated into the language of individual campuses, disciplines, and even courses. The utility of the VALUE rubrics is to position learning at all undergraduate levels within a basic framework of expectations such that evidence of learning can by shared nationally through a common dialog and understanding of student success.
The Critical Thinking VALUE Rubric is available for free download in Word and PDF formats.
Preview the Critical Thinking VALUE Rubric:

- Institute of Effectiveness
- Developing Program Learning Outcomes
- Developing Course Learning Outcomes
- Curriculum Mapping
- Sample Rubrics
- Examples of Direct Evidence of Student Learning
- Examples of Indirect Evidence of Student Learning
- Assessment Management System
- Assessment Coordinators List (PDF)
- Student Learning Outcomes at the Program Level
- Institutional Learning Outcome
- Mission Fulfillment Indicators
SAMPLE RUBRICS
Examples of scoring rubrics:, value rubrics (valid assessment of learning in undergraduate education):.
The VALUE Rubrics are meta-rubrics sponsored by the Association of American Colleges and Universities (AAC&U) and reflect expectations for the AAC&U Essential Learning Outcomes (LEAP project). Each rubric contains the most commonly and broadly shared criteria considered critical for judging the quality of student work for each respective outcome.
Click each learning outcome below to retrieve the corresponding VALUE rubric. If you would like to download all of the rubrics in one PDF document, please click here.
Intellectual and Practical Skills
- Inquiry and Analysis
- Critical Thinking
- Creative Thinking
- Written Communication
Oral Communication
- Quantitative Literacy
- Information Literacy
- Problem Solving
Personal and Social Responsibility
- Civic Engagement
- Intercultural Knowledge and Competence
- Ethical Reasoning
- Foundations and Skills for Lifelong Learning
- Global Learning
Integrative and Applied Learning
- Integrative Learning
Samples of Rubrics from Other Institutions
Below is a sample of rubrics that can be found on the websites of other institutions. If you have a rubric you’d like to share, please email it to us.
Collaboration, Teamwork, Participation
- Group Participation (analytic rubric)
- Participation (holistic rubric)
Critical Thinking, Creative Thinking
- Design Project (analytic rubric)
- Critical Thinking (analytic rubric)
Ethical Deliberation
- Focus Contemporary Ethical Issues, UH Mānoa General Education
Reflection/Metacognition
- Rubric to evaluate students’ reflective essays, Mānoa General Education
- Focus Oral Communication rubric to score oral presentations, UH Mānoa General Education
- Foundations Written Communication rubric to score essays and narratives, UH Mānoa General Education
- Writing (holistic rubric; portfolio)
- Media and Design Elements (analytic rubric; portfolio)

An Initial Development of an Analytic Rubric for Assessing Critical Thinking in English Argumentative Essays of EFL College Students
Article sidebar, main article content.
This study aims to initially develop a Critical-Thinking-in-Argumentative-Essay Rubric (CTER) for EFL college students. Participants of this study were five experts and two groups of raters. Data sources included the experts’ validation survey for the CTER, interviews and writing samples. Three phases for developing the CTER were conducted, and the evaluative descriptors of the rubric were revised based on the experts’ comments. To complete the initial development of the rubric, the raters and the first researcher used the CTER to evaluate the writing samples. The scores obtained from the evaluation were analyzed to examine the inter-rater reliability of the rubric. The findings showed that the CTER contained six clear and valid domains for assessing critical thinking in argumentative essays of EFL students. The total scoring results from the six domains achieved a moderate inter-rater reliability with ICC of 0.70 and Kendall’s W of 0.5 (p < 0.05). The raters perceived that the CTER could be used to promote learning and critical thinking of EFL learners. Pedagogical implications were presented based on the findings.
Article Details
Adunyarittigun, D. (2015). Developing a scale to measure reader self-perception for EFL students PASAA, 50, 1-30.
Anderson, N. J. (2012). Student involvement in assessment: Healthy self-assessment and effective peer assessment. In C. Coombe, P. Davidson, B. O’Sullivan & S. Stoynoff (Eds.), The Cambridge guide to second language assessment (pp.187-197). Cambridge United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Angeli, C., & Valanides, N. (2009). Instructional effects on critical thinking: Performance on ill- defined issues. Learning and Instruction, 19, 322-334.
Bailey, A., Zanchetta, M., Velasco, D., Pon, G., & Hassan, A. (2015). Building a scholar in writing (BSW): A model for developing students’ critical writing skills. Nurse Education in Practice, 15, 524-529.
Bauer, J. A. (2016). A new approach: Closing the writing gap by using reliable assessment to guide and evaluate cross-curricular argumentative writing (Master’s thesis). University of Wisconsin, Wisconsin, U.S.A.
Brown, G. T. L., Glasswell, K., & Harland, D. (2004). Accuracy in the scoring of writing: Studies of reliability an validity using a New Zealand writing assessment system. Assessing Writing, 9, 105-121.
Castilleja, M. F. P. (2012). Developing a process to create and validate an instrument assessing student attainment of competencies at an intercultural university in Mexico (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Florida International University, Florida, united States of America.
Celuch, K., & Slama, M. (2010). Teaching critical thinking skills for the 21st century: An advertising principles case study. Journal of Education for Business, 74(3), 134-139.
Chatfield, T. (2018). Critical thinking: Your guide to effective argument, successful analysis and independent study. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Cheng, F. (2003). The effects of rhetorical specification in writing assignments on EFL (English as a foreign language) writing (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Boston University, Boston, U.S.A.
Chinda, B. (2013). Consideration in performance-based language assessment: Rating scales and rater training. PASAA, 46, 141-159.
Chinda, B. (2014). Teachers’ reactions towards performance-based language assessment. PASAA, 48, 57-88.
Daud, N. S. B. M. (2012). Developing critical thinking skills in tertiary academic writing through the use of an instructional rubric for peer evaluation (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). The University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand.
Denzin, N. K. (1978). The research act: A theoretical introduction to sociological methods (2nd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Dhanarattigannon, J. (1995). Journal writing: Language activity and teaching/learning evaluation. Humanities Journal, 3(1), 69-80.
Dong, Y. (2015). Critical thinking in second language writing: Concept, theory, and pedagogy (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada.
Epstein, R. L. (1999). Critical thinking. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. Gardner, R. C. (1985). Social psychology and language learning: The role of attitudes and motivation. London, United Kingdom: Edward Arnold.
Gebril, A., & Plakans, L. (2014). Assembling validity evidence for assessing academic writing: Rater reactions to integrated tasks. Assessing Writing, 21, 56-73.
Green, A. (2014). Exploring language assessment and testing: Language in action. New York, NY: Routledge.
Green, A., & Hawkey, R. (2012). Marking assessments: Rating scales and rubrics. In C. A. Coombe, P. Davidson, B. O’Sullivan & S. Stoynoff (Eds.), The Cambridge guide to second language assessment (pp. 299-306). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Greene, J. C., Caracelli, V. J., & Graham, W. F. (1989). Toward a conceptual framework for mixed-method evaluation designs. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 11(3), 255-274.
Han, T., & Huang, J. (2017). Examining the impact of scoring methods on the instructional EFL writing assessment: A Turkish perspective. PASAA, 53, 112-147.
Hodges, T. S., Wright, K. L., Winda, S. A., Matthews, S. D., Zimmer, W. K., & McTigue, E. (2019). Developing and examining validity evidence for the Writing Rubric to Inform Teacher Educators (WRITE). Assessing Writing, 40, 1-13.
Hughes, C. (2000). A comparative study of teaching critical thinking through persuasive writing to average, gifted and students with learning disabilities (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). The College of William and Mary, Virginia, U.S.A.
Janssen, G., Meier, V., & Trace, J. (2015). Building a better rubric: Mixed methods rubric revision. Assessing Writing, 26, 51-66.
Johnson, B., & Onwuegbuzie, A. (2004). Mixed methods research: A research paradigm whose time has come. Educational Researcher, 33(7), 14-26.
Kalchayanant, T. (2009). Writing essays. Bangkok, Thailand: Thammasat University Press.
Katz, A. (2012). Linking assessment with instructional aims and learning. In C. A. Coombe, P. Davidson, B. O’Sullivan & S. Stoynoff (Eds.), The Cambridge guide to second language assessment (pp. 66-73). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Kirby, G. R., & Goodpaster, J. R. (2007). Thinking: An interdisciplinary approach to critical and creative thought (4th ed.). Cranbury, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc.
Koo, T. K., & Li, BPS. M. L. (2016). A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, 15, 155-163.
Lau, J. Y. F. (2011). An introduction to critical thinking and creativity: Think more, think better. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Liu, F., & Stapleton, P. (2014). Counterargumentation and the cultivation of critical thinking in argumentative writing: Investigating washback from a high-stakes test. System, 45, 117-128.
Liu, F., & Stapleton, P. (2018). Connecting writing assessment with critical thinking: An exploratory study of alternative rhetorical functions and objects of enquiry in writing prompts. Assessing Writing, 38, 10–20.
Liu, P. E., Wu, W. V., & Shieh, R. (2015). Enhancing EFL students’ critical thinking and writing: An asynchronous debate instructional design. English Teaching & Learning, 39(3), 33-59.
Malcolm, B. (2011). Say What?: The use of voice in teaching creative writing. Journal of Letters, Special Issue, 40(2), 104-125.
Manalo, E., & Sheppard, C. (2016). How might language affect critical thinking performance? Thinking Skills and Creativity, 21, 41–49.
Matsuda, P. K., & Hammill, M. J. (2014). Second language writing pedagogy. In G. Tate, A. R. Taggart, K. Schick & H. B. Hessler (Eds.), A guide to composition pedagogies (2nd ed., pp. 266-282). Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Maybin, J., & Swann, J. (Eds.) (2006). The art of English: Everyday creativity. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Mayweg-Paus, E., Thiebach, M., & Jucks, R. (2016). Let me critically question this! Insights from a training study on the role of questioning on argumentative discourse. International Journal of Educational Research, 79, 195-210.
McKitrick, S. A., & Barnes, S. M. (2012). Assessment of critical thinking: An evolutionary approach. Journal of Assessment and Institutional Effectiveness, 2(1), 1-29.
McLaughlin, F., & Moore, M. (2012). Integrating critical thinking into the assessment of college writing. TETYC, 40(2), 145-162.
McLendon, N. C. G. (2008). The effects of teaching critical thinking and reading comprehension strategies on students’ writing in developmental English in a community college (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Auburn University, Albama, U.S.A.
Merriam, S. B. (1998). Qualitative research and case study applications in education. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Messick, S. (1996). Validity and washback in language testing. Language Testing, 13(3), 241-256.
Moskal, B. M., & Leydens, J. A. (2000). Scoring rubric development: Validity and reliability. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 7(10), 1-10.
Mulnix, J. W., & Mulnix, M. J. (2010). Using a writing portfolio project to teach critical thinking skills. Teaching Philosophy, 33(1), 27-54.
Newell, G. E., Beach, R., Smith, J., VanDerHeide, J., Kuhn, D., & Andriessen, J. (2011). Teaching and learning argumentative reading and writing: A review of research. Reading Research Quarterly, 46(3), 273- 304.
Nussbaum, E. M., & Schraw, G. (2007). Promoting argument–counterargument integration in students’ writing. The Journal of Experimental Education, 76(1), 59-92.
Oshima, A., & Hogue, A. (2006). Writing academic English (4th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson Education.
Payutto, P. A. (2010). The language and the truth. Bangkok, Thailand: Chandpen Publishing.
Plakans, L., & Gebril, A. (2017). An assessment perspective on argumentation in writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 36, 85-86.
Qin, J. (2009). The analysis of Toulmin elements and use of sources in Chinese university EFL argumentative writing (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Northern Arizona University, Arigona, U.S.A.
Quintieri, M. (2005). Measuring rater consistency: An investigation into the effects of two testing instruments on raters’ scores (Unpublished master’s thesis). Concordia University, Montreal, Canada.
Reznitskaya, A., Kuo, L., Glina, M., & Anderson, R. C. (2009). Measuring argumentative reasoning: What’s behind the numbers? Learning and Individual Differences, 19(2), 219-224.
Rosenwasser, D., & Stephen, J. (2012). Writing analytically (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth.
Ross, J. A. (2006). The reliability, validity, and utilization of self-assessment. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 11(10), 1-13.
Rowicki, M. A. (2001). A study of the relationship between reflective writing and critical thinking in seventh grade integrated science students (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Auburn University, Albama, U.S.A.
Saxton, E., Belanger, S., & Becker, W. (2012). The critical thinking analytic rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments. Assessing Writing, 17, 251-270.
Schmidt, R. C. (1997). Managing Delphi surveys using nonparametric statistical techniques. Decision Sciences, 28(3), 763-774.
Shepard, L. (2000). The role of assessment in a learning culture. Educational Researcher, 29(7), 4-14.
Stapleton, P. (2001). Assessing critical thinking in the writing of Japanese university students: Insights about assumptions and content familiarity. Written Communication, 18(4), 506-548.
Stapleton, P., & Wu, Y. (2015). Assessing the quality of arguments in students’ persuasive writing: A case study analyzing the relationship between surface structure and substance. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 7, 12–23.
Stevens, D. D., & Levi, A. (2005). Introduction to rubric: An assessment tool to save grading time, convey effective feedback, and promote student learning. Herndon, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Tangkiengsirisin, S. (2014). Links between teacher written feedback and student revision. LEARN Journal, Special Issue, 50-60.
Tapinta, P. (2006). Exploring Thai EFL university students’ awareness of their knowledge, use, and control of strategies in reading and writing (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of North Texas, Texas, U.S.A.
Thongrin, S. (2002). E-mail peer response in collectivist Thai culture: Task, social, and cultural dimensions (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Indiana University of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.
Tittle, P. (2011). Critical thinking: An appeal to reason. New York, NY: Routedge.
Tulgar, A. T., Yagiz, O., & Han, T. (2017). Bridging the gap between linguistic and pragmatic assessment in Turkish contexts. PASAA, 54, 58-81.
Verlinden, J. (2005). Critical thinking and everyday argument. Boston, MA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning.
Weigle, S. C. (2002). Assessing writing. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Welch, K. C., Hieb, J., & Graham, J. (2015). A systematic approach to teaching critical thinking skills to electrical and computer engineering undergraduates. American Journal of Engineering Education, 6(2), 113-123.
Williams, R. L. (1999). Operational definitions and assessment of higher-order cognitive constructs. Educational Psychology Review, 11(4), 411-427.
Yu, H. J. (2008). Interactional structure in the writing process: A comparison of three ESL writing classes (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Arizona State University, Arizona, U.S.A.
Zhao, C. G. (2010). The role of voice in high-stakes second language writing assessment (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). New York University, New York, U.S.A.
Login to your account
If you don't remember your password, you can reset it by entering your email address and clicking the Reset Password button. You will then receive an email that contains a secure link for resetting your password
If the address matches a valid account an email will be sent to __email__ with instructions for resetting your password
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Status | |
| Version | |
| Ad File | |
| Disable Ads Flag | |
| Environment | |
| Moat Init | |
| Moat Ready | |
| Contextual Ready | |
| Contextual URL | |
| Contextual Initial Segments | |
| Contextual Used Segments | |
| AdUnit | |
| SubAdUnit | |
| Custom Targeting | |
| Ad Events | |
| Invalid Ad Sizes |

- Submit Member Login
Access provided by
Assessing Written Evidence of Critical Thinking Using an Analytic Rubric
Download started
- Add to Mendeley

Get full text access
Log in, subscribe or purchase for full access.
Article metrics
Related articles.
- Download Hi-res image
- Download .PPT
- Access for Developing Countries
- Articles & Issues
- Articles In Press
- Current Issue
- List of Issues
- Supplements
- For Authors
- Author Guidelines
- Submit Your Manuscript
- Statistical Methods
- Guidelines for Authors of Educational Material Reviews
- Permission to Reuse
- About Open Access
- Researcher Academy
- For Reviewers
- General Guidelines
- Methods Paper Guidelines
- Qualitative Guidelines
- Quantitative Guidelines
- Questionnaire Methods Guidelines
- Statistical Methods Guidelines
- Systematic Review Guidelines
- Perspective Guidelines
- GEM Reviewing Guidelines
- Journal Info
- About the Journal
- Disclosures
- Abstracting/Indexing
- Impact/Metrics
- Contact Information
- Editorial Staff and Board
- Info for Advertisers
- Member Access Instructions
- New Content Alerts
- Sponsored Supplements
- Statistical Reviewers
- Reviewer Appreciation
- New Resources
- New Resources for Nutrition Educators
- Submit New Resources for Review
- Guidelines for Writing Reviews of New Resources for Nutrition Educators
- Podcast/Webinars
- New Resources Podcasts
- Press Release & Other Podcasts
- Collections
- Society News
The content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Accessibility
- Help & Contact

Society Member Access
SNEB Members, full access to the journal is a member benefit. Login via the SNEB Website to access all journal content and features.
- Institutional Access: Log in to ScienceDirect
- Existing Subscriber: Log in
- New Subscriber: Claim access with activation code. New subscribers select Claim to enter your activation code.
Academic & Personal
Corporate r&d professionals.
- Full online access to your subscription and archive of back issues
- Table of Contents alerts
- Access to all multimedia content, e.g. podcasts, videos, slides
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments

2012, Assessing Writing
Related papers
Education Sciences, 2022
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally and focuses on deciding what to do or what to believe (Facione, 2000). It includes the ability to conceptualize, apply, analyze, synthesize, and/or evaluate the information gathered from observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication (Valenzuela, Nieto, & Saiz, 2011). Therefore, critical thinking has always been viewed as a goal of academic work of all successful students (Stupnisky, Renaud, Daniels, Haynes, & Perry, 2008).Educational researchers and theorists (e.g., Ennis, 1996; Halpern, 1998) posit that any conceptualization of critical thinking must include both skills (ability to interpret, analyze, and evaluate data, knowledge, and insight) and dispositions (tendency or willingness to use analytical thinking skills) (Bohlin, 2009; Facione, 1990; Perkins, Jay, & Tishman, 1993; Siegel, 1999). As the critical thinking is a mental process that connected to cognitive activity which is not activated au...
Frontiers in Education, 2020
Tennessee Technological University has been exploring methods of assessing critical thinking skills as part of a performance funding initiative since 2000. Our experiences over the last three and half years provide useful information about both a process for developing an assessment tool and a product for assessing critical thinking skills. Our approach has been to empower our faculty to both identify and evaluate a core set of skills they believe to be an important part of critical thinking in our graduates. Our initial test has demonstrated good face validity and high criterion validity when correlated with scores on the American College Test (ACT) and the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (CCTST).
Journal of Veterinary Medical Education, 2012
Education Research International, 2013
This study deals with verbal reports of thinking in relation to determining the construct validity of each item of The CEU-Lopez Critical Thinking Test (Lopez, 2012) which is multi-aspect general knowledge critical thinking test designed for Filipino tertiary students. The procedure is based on the adapted methodology of Norris (1992) in validating his co-authored Test on Appraising Observations (Norris & King, 1983). Seven methodological phases were utilized in this study: determining the participants who would be part of sets of interviewees, adapting an interviewing methodology for eliciting trustworthy reports of thinking, collecting verbal reports of thinking, scoring verbal reports of thinking and choice of answer, comparing performance and thinking scores as basis for judging items, modifying suspected items, and retrying the revised or the replaced items in accord with steps 3 to 6. Items were revised, retained, and discarded based on the correlation of thinking and performa...
Jurnal Ilmiah Psikologi Terapan, 2018
Critical-thinking dispositions are integral to drive and maintain students' use of critical-thinking in their academic and daily life setting. Yet, critical-thinking dispositions have received small attention from researchers. The present study developed and tested a novel strategy aimed to foster three Indonesian Master Students' critical-thinking dispositions. The strategy represented by a table consisting of a set of critical-thinking criteria and phases of critical-thinking self-regulation. The strategy intended to make explicit and to enhance the students' metacognition and self-regulation in the process of critical-thinking. Scores retrieved from critical-thinking dispositions scale shows that the intervention successfully increased the overall students' level of critical-thinking dispositions. The qualitative data from individual interviews revealed some valuable insights about the students' learning difficulties and that the strategy successfully made students aware of their thinking process and reinforced the students' metacognition and self-regulation process. The limitation and implication of the strategy are discussed.
The landmark 1990 APA Delphi Report presents the findings of the two year project to articulate an international expert consensus definition of “critical thinking. Over the past 25 years this report has been adopted by educators at every level and in every discipline, as well as by business, military, healthcare, and technology professionals seeking to make the idea of “critical thinking” practical, positive, and applicable. Today the Delphi conceptualization grounds is used throughout the world. It grounds academic requirements, courses, textbooks, peer-reviewed research, dissertations, competitively funded grants, institutional accreditation projects, and numerous assessment tools used for educational and employment purposes when evaluating an individual’s or a group’s reasoning skills and mindset attributes are important. The international panel of experts who participated in the APA Delphi research project come to the consensus that critical thinking is best understood, taught, and modeled for students as the process of purposeful and reflective judgment. When engaging in critical thinking we solve problems and make decisions by considering the questions, evidence, conceptualizations, context, and standards to apply to the problem or issue at hand. The process is non-linear and the application of our specific critical thinking skills can be recursive, for we can analyze our interpretations, evaluate our inferences, or explain our analyses. The key, of course, is that we are being reflective and fair-minded and truth-seeking throughout the process of determining what to believe or what to do in any given context. Defined in this way, critical thinking is a powerful tool for learning as well as for our professional and civic lives. We all may have different beliefs, values, perspectives, and experiences influencing our problem solving and decision making. But we share the human capacity to be reflective, analytical, open-minded, and systematic about thinking through our problems and choices, so that we can make the best judgments possible about what to believe or what to do. That human process of well-reasoned, reflective judgment is critical thinking. In the Delphi Report the international panel of experts identify the attributes of ideal critical thinker as well as the specific skills that are engaged in the process of purposeful, reflective judgment. The report includes detailed pedagogically focused tables and specific recommendations relating to critical thinking instruction and assessment.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Marmara Eleştirel Düşünme Eğilimleri Ölçeği'nin Geliştirilmesi: Geçerlik ve Güvenirlik Çalışması, 2018
Critical Thinking and Reasoning, 2021
MARKETING IDENTITY New changes, New challenges. Conference Proceedings from the International Scientific Conference 9th November 2021, Faculty of Mass Media Communication, University of SS. Cyril and Methodius in Trnava, Slovakia, , 2021
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018
Thinking Skills and Creativity, 2012
Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psychology
Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in the South, 2019
Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice, 1991
International Education Studies, 2015
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
This page uses technologies your browser does not support.
Many of our new website's features will not function and basic layout will appear broken.
Visit browsehappy.com to learn how to upgrade your browser.

- university of new orleans
- general education
- evaluation rubrics
- critical thinking rubric
Critical Thinking Rubric
This rubric is designed to evaluate the extent to which undergraduate students evaluate claims, arguments, evidence, and hypotheses.
Results will be used for program improvement purposes only.
Download the Critical Thinking Rubric (PDF version)
| Course: | Instructor: | Student: | Date: |
| | | | | ||
| Accurately interpret evidence and thoughtfully evaluate alternative points of view | Information is taken from source(s) with enough interpretation/evaluation to develop a comprehensive analysis or synthesis. Viewpoints of experts are questioned thoroughly. | Information is taken from source(s) with enough interpretation/evaluation to develop a coherent analysis or synthesis. Viewpoints of experts are subject to questioning. | Information is taken from source(s) with some interpretation/evaluation, but not enough to develop a coherent analysis or synthesis. Viewpoints of experts are taken as mostly fact, with little questioning. | Information is taken from source(s) without any interpretation/ evaluation. Viewpoints of experts are taken as fact, without question. | |
| Draw judicious conclusions, justify results, and explain reasoning | Not only develops a logical, consistent plan to solve problem, but recognizes consequences of solution and can articulate reason for choosing solution. Conclusions and related outcomes (consequences and implications) are logical and reflect student’s informed evaluation and ability to place evidence and perspectives discussed in priority order. | Having selected from among alternatives, develops a logical, consistent plan to solve the problem. Conclusion is logically tied to a range of information, including opposing viewpoints; related outcomes (consequences and implications) are identified clearly. | Considers and rejects less acceptable approaches to solving problem. Conclusion is logically tied to information (because information is chosen to fit the desired conclusion); some related outcomes (consequences and implications) are identified clearly. | Only a single approach is considered and is used to solve the problem. Conclusion is inconsistently tied to some of the information discussed; related outcomes (consequences and implications) are oversimplified. | |
| Engage in skepticism, judgment, and free thinking | Extends a novel or unique idea, question, format, or product to create new knowledge or knowledge that crosses boundaries. | Creates a novel or unique idea, question, format, or product. | Experiments with creating a novel or unique idea, question, format, or product. | Reformulates a collection of available ideas. | |
| Engage in abstract reasoning, questioning and understanding | Actively seeks out and follows through on untested and potentially risky directions or approaches to the assignment in the final product. Integrates alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas fully. | Incorporates new directions or approaches to the assignment in the final product. Incorporates alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas in a exploratory way. | Considers new directions or approaches without going beyond the guidelines of the assignment. Includes (recognizes the value of) alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas in a small way. | Stays strictly within the guidelines of the assignment. Acknowledges (mentions in passing) alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas. | |
| Notes: | |||||

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Simplified Rubric for Assessing CRITICAL & ANALYTICAL THINKING Details Behind Simplified Rubric Novice Developing Proficient Critical and Analytical Thinking: Students will comprehensively explore issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating opinions or conclusions. Student demonstrates some awareness of assumptions when
The analytic rubric is an assessment tool that shows promise of meeting this need for the measurement of critical thinking sub-skills and disposition towards critical thinking. The benefits of analytic rubrics include (1) greater level of detail in the information derived from the assessment scores, (2) clear designation of what is being ...
Adapted from the AAC&U Critical Thinking, Inquiry & Analysis, and Creative Thinking VALUE Rubrics. This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Texas A&M University Core Curriculum Critical Thinking Rubric Advanced 8 7 Competent 6 5 Developing 4 3 Beginner 2 1 Not Present 0 Explanation of Issue/Problem Issue/problem to be considered
Microsoft PowerPoint - Designing Rubrics to Assess Critical Thinking.pptx. 3:00. Traditional assessment measures such as multiple choice questions are a form of selected response measures designed for knowledge recall and sometimes for decision‐making from a selection of options. In such measures, students are asked to think critically in the ...
The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric is designed specifically to assess K-12 students to enhance college readiness and has not been broadly tested in collegiate STEM courses (Saxton et al., 2012). The critical thinking rubric developed by the Association of American Colleges and Universities (AAC&U) as part its Valid Assessment of Learning ...
Critical thinking is a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion. Framing Language This rubric is designed to be transdisciplinary, reflecting the recognition that success in all disciplines requires habits of inquiry and analysis ...
The purpose of this study was to investigate the intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of the Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR). The CTAR is composed of 6 rubric categories: interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and disposition. To investigate inter-rater reliability, two trained raters scored four sets of ...
DEVELOPMENT OF CRITICAL THINKING RUBRIC. Definition: Critical thinking is a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion. The capacity to combine or synthesize existing ideas, images, or expertise in original ways; thinking ...
The critical thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments. Assessing Writing, 17(4), 251-270. Crossref. Google Scholar. Cite article Cite article. Cite article Copy Citation OR. Download to reference manager ...
DOI: 10.1016/J.ASW.2012.07.002 Corpus ID: 143117282; The Critical Thinking Analytic Rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments
VALUE Rubrics - Critical Thinking. The VALUE rubrics were developed by teams of faculty experts representing colleges and universities across the United States through a process that examined many existing campus rubrics and related documents for each learning outcome and incorporated additional feedback from faculty.
Using the Holistic Critical Thinking Scoring Rubric. 1. Understand What this Rubric is Intended to Address. Critical thinking is the process of making purposeful, reflective and fair‐minded judgments about what to believe or what to do. Individuals and groups use critical thinking in problem solving and decision making.
To assess student statements as an outcome of a critical thinking exercise, an analytic scoring rubric was devised (Table).A rubric is a matrix with a concise description of expectations at different levels of accomplishment and an organized approach to evaluating the conclusion of a multistep exercise. 8 Analytic rubrics feature multiple scales that provide diagnostic information useful to ...
Critical thinking is a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion. Framing Language This rubric is designed to be transdisciplinary, reflecting the recognition that success in all disciplines requires habits of inquiry and analysis ...
Below is a sample of rubrics that can be found on the websites of other institutions. If you have a rubric you'd like to share, please email it to us. Collaboration, Teamwork, Participation. Group Participation (analytic rubric) Participation (holistic rubric) Critical Thinking, Creative Thinking. Design Project (analytic rubric)
A valid and reliable rubric is crucial for critical thinking assessment since it can be used to evaluate critical thinking accurately and provide students with diagnostic data for improving their critical thinking. However, the existing rubrics for assessing critical thinking in English argumentative writing suffer from four striking flaws.
The critical thinking analytic rubric (CTAR): Investigating intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a scoring mechanism for critical thinking performance assessments. Assessing Writing, 17, 251-270. Schmidt, R. C. (1997). Managing Delphi surveys using nonparametric statistical techniques. Decision Sciences, 28(3), 763-774.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills: The Key to Professional Competencies. A tool kit. Sarasota, FL: American Accounting Association. Skills in the Scoring Manual for the Reflective Judgment Interview Rubrics Based on a Model of Open-Ended Problem Solving Skills: Steps for Better Thinking Rubric Steps for Better Thinking Competency Rubric
The EAG is a practical approach for the design of a critical thinking exercise in nutrition that climaxes in a written statement. Combining reflection with writing fosters independent thinking, enhances tolerance for uncertainty, and curbs emotional reasoning that is common in oral expression. 11 An analytical scoring rubric is a reliable ...
To assess student statements as an outcome of a critical thinking exercise, an analytic scoring rubric was devised . A rubric is a matrix with a concise description of expectations at different levels of accomplishment and an organized approach to evaluating the conclusion of a multistep exercise. 8 Analytic rubrics feature multiple scales that ...
The analytic rubric is an assessment tool that shows promise of meeting this need for the measurement of critical thinking Author's personal copy 254 E. Saxton et al. / Assessing Writing 17 (2012) 251-270 sub-skills and disposition towards critical thinking. The benefits of analytic rubrics include (1) greater level of detail in the ...
Critical Thinking Rubric. This rubric is designed to evaluate the extent to which undergraduate students evaluate claims, arguments, evidence, and hypotheses. Results will be used for program improvement purposes only. Download the Critical Thinking Rubric (PDF version) Course: Instructor: Student: Date: Component.