
Literature Review: Format, Contoh, dan Cara Membuatnya
- 1.1 1.1: Definisi Literature Review
- 1.2 1.2: Tujuan dan Manfaat Melakukan Literature Review
- 1.3 1.3: Perbedaan Antara Literature Review dengan Review Jurnal
- 2.1 2.1: Memilih Topik Penelitian
- 2.2 2.2: Mencari dan Mengumpulkan Sumber Literatur
- 2.3 2.3: Evaluasi dan Seleksi Sumber Literatur
- 2.4 2.4: Menyusun Kerangka Kerja Literature Review
- 2.5 2.5: Menulis Literature Review
- 3.1 3.1: Struktur Umum Literature Review
- 3.2 3.2: Penulisan Kutipan dan Referensi
- 3.3 3.3: Format Literature Review untuk Jurnal
- 4.1 4.1: Contoh Literature Review dari Berbagai Bidang Studi
- 4.2 4.2: Contoh Literature Review dalam Jurnal
- 4.3 4.3: Contoh Review Literatur dalam Konteks Penelitian
Pengenalan Literature Review
1.1: definisi literature review.
Literature review, atau yang dikenal juga dengan review literatur, adalah suatu proses sistematis dalam mengkaji literatur yang telah ada terkait dengan topik atau masalah penelitian tertentu. Ini bukan hanya sekedar ringkasan dari sumber-sumber literatur, melainkan analisis kritis yang menunjukkan hubungan antara literatur yang satu dengan yang lainnya serta posisi penelitian Anda dalam konteks literatur yang ada.
1.2: Tujuan dan Manfaat Melakukan Literature Review
Melakukan literature review memiliki beberapa tujuan dan manfaat, di antaranya:
- Mengidentifikasi Gap : Dengan memahami literatur yang telah ada, peneliti dapat mengidentifikasi celah atau gap yang belum diteliti sebelumnya.
- Membangun Dasar Teoritis : Literature review membantu dalam membangun dasar teoritis untuk penelitian, dengan merujuk pada teori-teori yang telah ada.
- Menghindari Duplikasi : Dengan mengetahui penelitian-penelitian sebelumnya, peneliti dapat menghindari duplikasi dan fokus pada aspek-aspek baru.
- Menentukan Metodologi : Memahami metodologi yang digunakan dalam literatur sebelumnya dapat membantu peneliti dalam menentukan metodologi yang tepat untuk penelitiannya.
1.3: Perbedaan Antara Literature Review dengan Review Jurnal
Meskipun keduanya melibatkan proses review, literature review dan review jurnal memiliki perbedaan mendasar:
- Fokus : Literature review fokus pada analisis kritis dari berbagai sumber literatur terkait topik penelitian, sedangkan review jurnal lebih fokus pada evaluasi satu artikel jurnal tertentu.
- Tujuan : Literature review bertujuan untuk memberikan gambaran umum tentang apa yang telah diteliti sebelumnya mengenai suatu topik, sementara review jurnal bertujuan untuk menilai kualitas dan relevansi sebuah artikel jurnal.
- Sumber : Literature review mengkaji berbagai sumber literatur seperti buku, artikel jurnal, laporan penelitian, dan lain-lain. Sementara review jurnal hanya mengkaji satu artikel jurnal.
Cara Membuat Literature Review
2.1: memilih topik penelitian.
Sebelum memulai literature review, tentukan terlebih dahulu topik penelitian Anda. Topik harus spesifik dan relevan dengan bidang studi Anda. Pertimbangkan pertanyaan-pertanyaan berikut saat memilih topik:
- Apakah topik tersebut memiliki relevansi dengan bidang studi Anda?
- Apakah ada literatur yang cukup untuk mendukung penelitian Anda?
- Apakah topik tersebut menarik bagi komunitas akademik atau industri tertentu?
2.2: Mencari dan Mengumpulkan Sumber Literatur
Setelah menentukan topik, langkah selanjutnya adalah mencari sumber literatur yang relevan. Beberapa metode pencarian literatur meliputi:
- Pustaka Digital : Gunakan basis data seperti Google Scholar, JSTOR, atau PubMed untuk mencari jurnal, artikel, dan publikasi lainnya.
- Perpustakaan Universitas : Kunjungi perpustakaan universitas Anda untuk mencari buku dan jurnal fisik yang relevan.
- Rujukan dari Artikel : Artikel yang Anda temukan mungkin memiliki daftar pustaka yang bisa Anda gunakan sebagai sumber tambahan.
2.3: Evaluasi dan Seleksi Sumber Literatur
Tidak semua sumber literatur yang Anda temukan akan relevan atau berkualitas. Oleh karena itu, Anda perlu mengevaluasi dan memilih sumber-sumber yang paling sesuai. Beberapa kriteria evaluasi meliputi:
- Relevansi : Apakah sumber tersebut relevan dengan topik penelitian Anda?
- Kredibilitas : Siapa penulisnya? Apakah mereka ahli di bidang tersebut? Apakah sumber tersebut diterbitkan oleh penerbit terpercaya?
- Ketepatan Waktu : Apakah informasi tersebut masih relevan dan up-to-date?
2.4: Menyusun Kerangka Kerja Literature Review
Sebelum mulai menulis, buatlah kerangka kerja untuk literature review Anda. Kerangka kerja ini akan membantu Anda mengorganisir ide dan informasi dari sumber-sumber yang telah Anda kumpulkan. Beberapa langkah dalam menyusun kerangka kerja meliputi:
- Identifikasi Tema Utama : Apa tema-tema utama yang muncul dari literatur yang Anda kumpulkan?
- Susun Tema Secara Logis : Urutkan tema-tema tersebut sesuai dengan logika atau kronologi tertentu.
- Identifikasi Hubungan : Bagaimana hubungan antara satu tema dengan tema lainnya? Apakah ada kontradiksi atau kesepakatan antar sumber?
2.5: Menulis Literature Review
Dengan kerangka kerja yang telah Anda susun, Anda siap untuk mulai menulis. Beberapa tips dalam menulis literature review meliputi:
- Mulai dengan Pengenalan : Jelaskan latar belakang topik dan tujuan literature review Anda.
- Bahasa yang Objektif : Gunakan bahasa yang netral dan objektif saat menyajikan informasi dari sumber literatur.
- Kutip dengan Tepat : Pastikan Anda mengutip sumber literatur dengan benar sesuai dengan format yang diinginkan (misalnya APA, MLA, atau Chicago).
- Kesimpulan : Ringkas temuan utama dari literature review Anda dan jelaskan bagaimana temuan tersebut relevan dengan penelitian Anda.
Baca Juga: Statistik Deskriptif dan Inferensial
Format Literature Review
3.1: struktur umum literature review.
Literature review memiliki struktur tertentu yang memudahkan pembaca untuk mengikuti alur pemikiran penulis. Struktur umum literature review meliputi:
- Pendahuluan : Jelaskan latar belakang topik, tujuan literature review, dan pertanyaan penelitian yang ingin dijawab.
- Tema-tema Utama : Bagilah literatur yang Anda review ke dalam tema-tema atau kategori tertentu. Ini membantu mengorganisir informasi dan memberikan struktur pada review Anda.
- Diskusi : Analisis kritis terhadap literatur yang Anda review. Apakah ada kesepakatan atau kontradiksi antara sumber-sumber literatur? Apa implikasinya bagi penelitian Anda?
- Kesimpulan : Ringkasan dari temuan utama literature review dan bagaimana temuan tersebut relevan dengan penelitian Anda.
- Daftar Pustaka : Daftar semua sumber literatur yang Anda kutip dalam review Anda.
3.2: Penulisan Kutipan dan Referensi
Mengutip sumber literatur dengan benar adalah aspek penting dalam literature review. Hal ini tidak hanya menunjukkan integritas akademik tetapi juga memungkinkan pembaca untuk merujuk kembali ke sumber asli. Beberapa hal yang perlu diperhatikan dalam penulisan kutipan dan referensi:
- Pilih Gaya Sitasi : Ada beberapa gaya sitasi yang umum digunakan, seperti APA, MLA, Chicago, dan lainnya. Pilih salah satu yang sesuai dengan bidang studi Anda atau sesuai dengan instruksi jurnal/lembaga Anda.
- Konsistensi : Pastikan Anda konsisten dalam menggunakan gaya sitasi yang Anda pilih.
- Gunakan Alat Bantu : Ada banyak alat bantu sitasi online yang dapat membantu Anda dalam mengutip sumber literatur dengan benar.
3.3: Format Literature Review untuk Jurnal
Jika Anda berencana untuk menerbitkan literature review Anda di sebuah jurnal, ada beberapa format khusus yang perlu Anda perhatikan:
- Panduan Penulisan Jurnal : Setiap jurnal biasanya memiliki panduan penulisan tersendiri yang mencakup format, gaya sitasi, panjang artikel, dan lainnya.
- Abstrak : Sebagian besar jurnal meminta penulis untuk menyertakan abstrak atau ringkasan singkat dari literature review.
- Kata Kunci : Sertakan kata kunci yang relevan dengan topik Anda. Ini membantu dalam proses indeksasi dan memudahkan pembaca menemukan artikel Anda.
- Format Tabel dan Gambar : Jika Anda menyertakan tabel atau gambar dalam literature review, pastikan Anda mengikuti format yang ditentukan oleh jurnal.
Contoh-Contoh Literature Review
4.1: contoh literature review dari berbagai bidang studi.
Literature review dapat ditemukan di berbagai bidang studi, mulai dari ilmu sosial hingga ilmu alam. Berikut adalah beberapa contoh literature review berdasarkan bidang studi:
- Ilmu Kesehatan : “Pengaruh Diet Mediterania terhadap Penurunan Risiko Penyakit Jantung Koroner: Sebuah Review Literatur.”
- Psikologi : “Dampak Mindfulness Meditation terhadap Kesejahteraan Psikologis: Sebuah Tinjauan Literatur.”
- Teknologi Informasi : “Penerapan Teknologi Blockchain dalam Manajemen Rantai Pasokan: Sebuah Review Literatur.”
4.2: Contoh Literature Review dalam Jurnal
Banyak jurnal yang mempublikasikan literature review sebagai salah satu jenis artikelnya. Berikut adalah contoh-contoh literature review yang diterbitkan dalam jurnal:
- “Tinjauan Literatur tentang Strategi Pemasaran Digital dan Dampaknya terhadap Loyalitas Pelanggan.”
- “Penggunaan Energi Terbarukan di Asia Tenggara: Sebuah Review Literatur.”
- “Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi terhadap Kinerja Karyawan: Sebuah Tinjauan Literatur.”
4.3: Contoh Review Literatur dalam Konteks Penelitian
Dalam konteks penelitian, literature review seringkali menjadi bagian dari proposal atau laporan penelitian. Berikut adalah contoh bagaimana literature review disajikan dalam konteks penelitian:
- Pendahuluan : “Penelitian sebelumnya telah menunjukkan bahwa pola tidur mempengaruhi kinerja akademik siswa. Namun, sedikit penelitian yang mengeksplorasi hubungan antara kualitas tidur dengan konsentrasi siswa.”
- Tema Utama : “Beberapa studi menunjukkan bahwa durasi tidur yang kurang dari 7 jam per malam dapat mengurangi kemampuan kognitif (Smith & Jones, 2010). Sementara itu, studi lain menemukan bahwa kualitas tidur, bukan durasi, yang memiliki dampak lebih besar terhadap konsentrasi (Lee & Kim, 2015).”
- Diskusi : “Meskipun ada bukti yang mendukung hubungan antara tidur dan konsentrasi, masih ada ketidaksepakatan mengenai faktor-faktor apa yang paling berpengaruh.”
Baca Juga: Ketahui Tingkatan dan Urutan Jurnal SINTA, Cek Disini
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
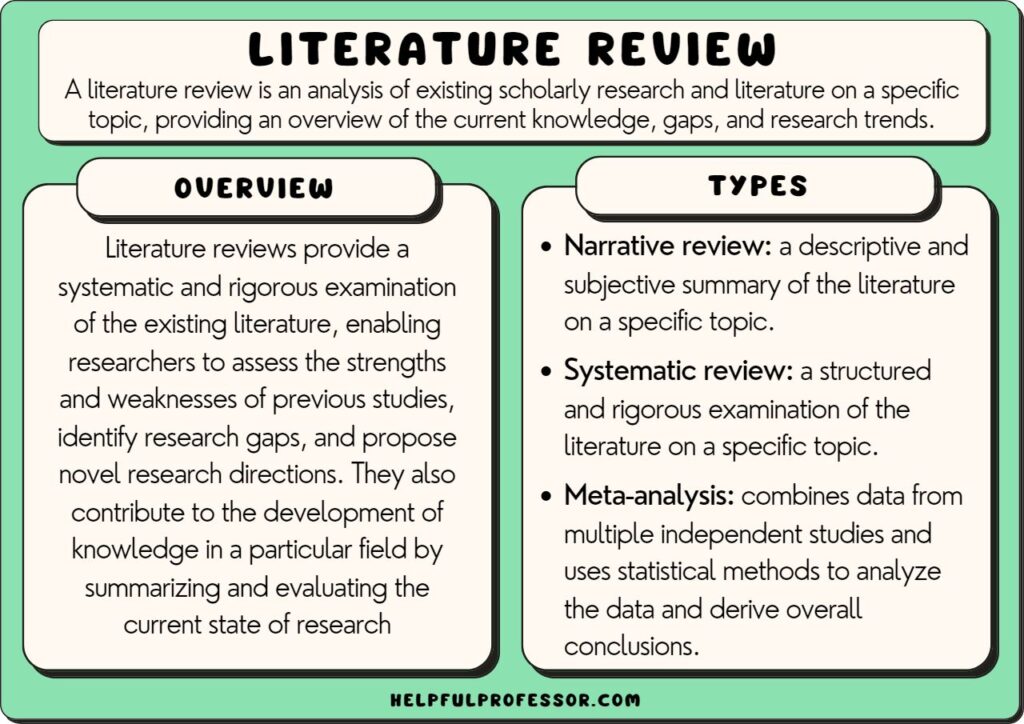
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Oktober 2024
- September 2024
- Agustus 2024
- Februari 2024
- Januari 2024
- Desember 2023
- November 2023
- Oktober 2023
- September 2023
- Januari 2023
- November 2022
- Oktober 2022
- September 2022
- Agustus 2022
- Februari 2022
- Jurnal Internasional
- Karya Ilmiah
- Perguruan Tinggi
- Sertifikasi
- Uncategorized
- Feed komentar
- WordPress.org

Contoh Review Jurnal

Cara Download Jurnal Internasional Gratis Dengan Doi

Contoh Karya Ilmiah PDF
Literature review.

Syarat Pendirian Perguruan Tinggi Swasta 2022
Dalam dunia akademik, literature review atau tinjauan pustaka adalah suatu bentuk kajian yang sangat penting. Proses literatur review melibatkan penelaahan, pengumpulan, dan sintesis berbagai sumber literatur yang relevan dengan topik tertentu. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan membahas pengertian, metode, dan cara membuat literatur review.
Pengertian literatur review adalah proses penelitian yang melibatkan peninjauan serta evaluasi kritis terhadap sumber-sumber literatur yang telah ada. Tujuan utama dari literatur review adalah untuk memahami dan menggambarkan keadaan penelitian terkini di bidang yang berkaitan dengan topik yang diteliti.

Dengan melakukan literatur review, peneliti dapat menemukan pengetahuan terkini, mengidentifikasi kesenjangan penelitian yang ada, serta menyusun dasar teoretis yang kuat untuk penelitian yang akan dilakukan.
Metode yang digunakan dalam literatur review dapat bervariasi tergantung pada tujuan penelitian dan disiplin ilmu yang terkait. Beberapa metode yang umum digunakan meliputi identifikasi sumber literatur yang relevan, pengumpulan data dari sumber-sumber tersebut, analisis dan sintesis data, serta penulisan laporan literatur review yang komprehensif.
Cara membuat literatur review yang efektif melibatkan beberapa langkah penting. Pertama, identifikasi topik atau area penelitian yang akan diteliti. Kemudian, lakukan pencarian literatur yang komprehensif menggunakan basis data akademik, jurnal ilmiah, dan sumber-sumber tepercaya lainnya.
Setelah itu, baca dan pahami sumber-sumber literatur yang relevan secara menyeluruh. Selanjutnya, analisis dan sintesislah data yang ditemukan, temukan pola atau tema yang muncul, dan buat rangkuman yang jelas dan terstruktur.
Dalam artikel ini, kami akan menjelaskan dengan lebih rinci tentang pengertian, metode, dan cara membuat literatur review. Kami juga akan memberikan tips praktis dan saran yang berguna dalam menyusun literatur review yang berkualitas.
Dengan memahami pentingnya literatur review dan mengikuti langkah-langkah yang tepat, Anda akan dapat menciptakan tinjauan pustaka yang berarti dan berkontribusi pada pengembangan pengetahuan dalam bidang yang Anda minati.
Selamat membaca artikel ini dan semoga informasi yang kami sajikan bermanfaat bagi Anda yang ingin mempelajari lebih lanjut tentang literatur review: pengertian, metode, dan cara membuatnya.
Pengertian Literature

Literature, atau yang dikenal juga dengan sebutan literatur dalam bahasa Indonesia, merujuk pada segala jenis tulisan yang dapat digunakan sebagai referensi atau bahan acuan dalam berbagai bidang penelitian atau karya tulis ilmiah. Definisi dalam Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia (KBBI) menyebutkan bahwa literatur merupakan bahan bacaan yang digunakan baik untuk kegiatan intelektual maupun rekreasi.
Keberadaan literature sebagai referensi sangatlah penting karena dianggap memiliki banyak data yang valid. Selain itu, literatur juga dianggap memiliki manfaat abadi, yang artinya literature tidak pernah usang dan selalu berkembang seiring waktu.
Secara umum, segala jenis karya tulis termasuk dalam kategori literature selama terkait dengan topik yang dibahas dalam karya tulis ilmiah. Namun, dalam menggunakan literatur sebagai referensi, penting untuk memeriksa keabsahan data yang terdapat di dalamnya. Hal ini dapat dilakukan melalui pengecekan terhadap penulis literature, editor, dan penerbit literature tersebut.
Literature memiliki peran yang penting dalam dunia akademik dan riset. Dalam melakukan penelitian atau menulis karya ilmiah, penggunaan literature review atau tinjauan pustaka sangatlah diperlukan.
Literature review adalah proses kritis dalam mengumpulkan, mengevaluasi, dan mensintesis berbagai sumber literatur yang relevan dengan topik penelitian. Dengan melakukan literature review, peneliti dapat memperoleh pemahaman mendalam tentang perkembangan penelitian terkini dan mengidentifikasi kesenjangan penelitian yang ada.
Dalam konteks pembuatan karya tulis ilmiah, penggunaan literature review yang baik dapat memberikan dasar teoretis yang kuat, menyediakan kerangka pemikiran, serta mendukung argumen yang disajikan.
Oleh karena itu, memahami pengertian literature, mengakses sumber-sumber literatur yang terpercaya, dan melakukan evaluasi kritis terhadap data-data yang terdapat dalam literature sangatlah penting untuk menciptakan karya tulis ilmiah yang berkualitas.
Dalam artikel ini, kita akan membahas lebih lanjut tentang pengertian literature, peran pentingnya dalam penelitian, dan bagaimana melakukan literature review secara efektif. Kami juga akan memberikan tips dan panduan praktis dalam memanfaatkan literature secara optimal dalam karya tulis ilmiah Anda.
Pengertian Review

Sebagaimana telah dijelaskan sebelumnya, literature review terdiri dari dua kata. Setelah menjelaskan pengertian literature, kita dapat memahami bahwa pengertian review merujuk pada suatu bentuk ringkasan atau evaluasi yang berasal dari berbagai sumber, seperti film, buku, berita, dan jurnal. Selain itu, review juga dapat berkaitan dengan penilaian terhadap berbagai produk yang seringkali dilakukan setelah berbelanja online.
Ulasan yang diberikan setelah berbelanja online memiliki manfaat yang signifikan bagi pemilik toko, karena dapat memberikan wawasan mengenai aspek yang perlu ditingkatkan dan aspek yang perlu dipertahankan.
Oleh karena itu, toko online sangat mengharapkan ulasan dari pelanggan mereka. Dengan adanya ulasan tersebut, pemilik toko dapat meningkatkan kualitas layanan atau produk, yang pada gilirannya dapat meningkatkan omset penjualan.
Secara prinsip, konsep review dalam literature review hampir sama dengan review produk. Dalam konteks literature review, review merujuk pada penilaian seseorang terhadap kualitas sebuah karya tulis. Karya tulis yang dimaksud dalam hal ini dapat berupa artikel jurnal, novel, buku, dan sebagainya.
Melalui literature review, seseorang dapat menentukan apakah sebuah karya tulis dapat digunakan sebagai referensi dalam penelitian atau karya ilmiah. Literature review juga memberikan manfaat bagi penulis karya tulis itu sendiri dengan memberikan wawasan tentang aspek-aspek yang perlu diperbaiki untuk meningkatkan kualitas karya tulis tersebut.
Tidak hanya itu, literature review juga bermanfaat bagi orang lain dengan membantu mereka menemukan karya tulis yang berkualitas dan dapat dijadikan referensi dalam melakukan penelitian.
Mengingat cakupan review yang sangat luas, terdapat beberapa jenis review, seperti review jurnal , review buku, review artikel, dan masih banyak lagi.
Apa Itu Literature Review?

Walaupun literature review terdiri dari dua kata, namun sebenarnya makna dari literature review tidak sekadar merupakan penggabungan dua kata tersebut. Dalam konteks penelitian, terutama dalam pembuatan karya ilmiah, literature review lebih dikenal dengan istilah tinjauan pustaka.
Dengan demikian, literature review dapat diartikan sebagai kegiatan analisis dan kritikan terhadap penelitian yang sedang dilakukan terhadap topik khusus dalam suatu bidang keilmuan.
Isi dari literature review berupa penjelasan atau pembahasan mengenai teori-teori yang terkait dengan temuan atau topik penelitian tersebut. Penjelasan teori-teori ini kemudian menjadi landasan teori yang digunakan dalam pembuatan karya ilmiah atau dalam melakukan kegiatan penelitian.
Penelitian yang sedang dilakukan melalui literature review ini bisa berupa pengembangan dari penelitian sebelumnya atau penelitian yang dilakukan untuk pertama kalinya.
Dalam menyusun literature review, terdapat beberapa langkah yang perlu dilakukan. Pertama, seseorang perlu membaca dan memahami karya tulis yang akan dianalisis. Selanjutnya, kritiklah karya tulis tersebut dan berikan ulasan atau tanggapan terhadap isi karya tulis atau literature yang sedang ditinjau.
Oleh karena itu, kegiatan literature review seringkali dikaitkan dengan mahasiswa atau dosen. Hal ini disebabkan karena mahasiswa atau dosen sering diberi tugas untuk melakukan literature review dalam konteks penelitian atau pembuatan karya ilmiah.
Metode Literature Review

Ketika ingin melakukan atau membuat literature review, terdapat beberapa metode yang dapat digunakan, antara lain systematic mapping study, systematic literature review, dan traditional review.
1. Systematic Mapping Study
Systematic mapping study merupakan salah satu metode literature review yang dilakukan secara sistematis dengan mengikuti langkah-langkah yang telah ditentukan sebelumnya. Dalam metode literature review ini, pemilihan karya tulis yang akan diteliti tidak dapat dilakukan secara subjektif, melainkan harus dilakukan secara objektif.
Systematic mapping study memiliki tingkat kompleksitas yang lebih tinggi dan melibatkan lebih banyak karya tulis dibandingkan traditional review. Selain itu, peneliti yang menggunakan metode ini biasanya telah memiliki standar tertentu, seperti standar dalam pemilihan judul dan jenis karya tulis yang akan digunakan.
Dalam melakukan literature review dengan metode ini, peneliti akan mengumpulkan berbagai jenis karya tulis terlebih dahulu. Setelah itu, karya tulis tersebut akan dibaca satu per satu dan diulas atau dianalisis sesuai dengan topik penelitian yang akan diteliti.
2. Systematic Literature Review
Systematic literature review, atau biasa disingkat sebagai SLR, merupakan metode literature review yang dilakukan secara sistematis dengan tujuan mengumpulkan dan menganalisis kritis data dan temuan dari berbagai penelitian lainnya.
Dalam membuat literature review dengan metode systematic literature review, langkah-langkah dilakukan secara berurutan dan sistematis. Dengan kata lain, literature review dibuat mulai dari hal-hal yang paling mendasar kemudian menuju hal-hal yang lebih kompleks.
Proses dengan metode ini membutuhkan tahapan yang cukup panjang, namun hasil literature review yang dihasilkan akan lebih detail, akurat, dan kompleks. Oleh karena itu, dengan metode ini, penulis dapat memperoleh landasan teori yang lebih tajam dan berkualitas.
3. Traditional Review
Metode kedua yang digunakan dalam membuat literature review adalah traditional review. Traditional review merupakan metode yang umum digunakan oleh peneliti dalam membuat literature review. Hasil dari metode traditional review sering kita jumpai dalam karya tulis survey paper.
Oleh karena itu, literature review yang dihasilkan melalui metode ini lebih terfokus pada satu topik tertentu. Selain itu, karya tulis yang dipilih sudah diketahui oleh penulis sebelumnya.
Dengan metode traditional review, karya tulis yang digunakan sebagai referensi masih berkaitan dengan topik penelitian yang sedang dilakukan. Metode ini dapat membatasi referensi hanya pada topik yang sama, padahal tidak menutup kemungkinan bahwa sumber atau data yang relevan dapat ditemukan dari topik yang berbeda.
Keterbatasan dalam metode traditional review tidak hanya terbatas pada data dan sumber, tetapi juga pada wawasan dan pemahaman peneliti. Dengan kata lain, semakin luas wawasan peneliti, semakin banyak pula karya tulis atau literatur yang telah dibaca, diteliti, atau dianalisis oleh peneliti.
Manfaat Literature Review

Literature review, atau tinjauan pustaka, adalah komponen penting dalam penelitian. Melalui literature review, Anda dapat mengumpulkan dan menganalisis literatur yang relevan dengan topik penelitian Anda. Berikut ini adalah beberapa manfaat penting dari literature review dalam konteks penelitian:
1. Memahami Perkembangan Penelitian Terkini
Dengan melakukan literature review, Anda dapat memahami perkembangan terkini dalam bidang penelitian yang Anda minati. Anda dapat mengidentifikasi studi-studi terbaru, temuan-temuan penting, dan tren penelitian yang sedang berkembang. Hal ini membantu Anda untuk tetap up-to-date dan memastikan bahwa penelitian Anda relevan dengan perkembangan terkini.
2. Mengidentifikasi Kesenjangan Pengetahuan
Melalui literature review, Anda dapat mengidentifikasi kesenjangan pengetahuan atau gap dalam literatur yang ada. Anda dapat melihat area yang belum banyak diteliti atau topik yang masih kontroversial.
Dengan mengetahui kesenjangan ini, Anda dapat merumuskan pertanyaan penelitian yang relevan dan memberikan kontribusi baru dalam bidang tersebut.
3. Memperkuat Rasioanlisasi Penelitian Anda
Dalam literature review, Anda akan menemukan studi-studi terdahulu yang telah dilakukan dalam bidang yang sama atau serupa dengan penelitian Anda. Dengan merujuk pada studi-studi tersebut, Anda dapat memperkuat rasionalisasi penelitian Anda.
Anda dapat menunjukkan kebutuhan untuk penelitian lanjutan atau bagaimana penelitian Anda akan memberikan kontribusi yang berbeda dan berharga.
4. Membangun Kerangka Konseptual
Literature review membantu Anda dalam membangun kerangka konseptual untuk penelitian Anda. Anda dapat mengidentifikasi teori-teori yang relevan, konsep-konsep kunci, dan variabel-variabel yang perlu diperhatikan.
Dengan membangun kerangka konseptual yang kuat, Anda dapat mengarahkan penelitian Anda dan memperjelas hubungan antara variabel-variabel yang akan diteliti.
5. Memilih Metode yang Tepat
Dalam literature review, Anda juga dapat mempelajari metode-metode penelitian yang telah digunakan dalam studi-studi sebelumnya. Anda dapat melihat metode-metode yang telah terbukti efektif dalam bidang penelitian yang sama. Ini membantu Anda dalam memilih metode yang paling tepat untuk penelitian Anda, sehingga hasil penelitian dapat menjadi lebih valid dan dapat diandalkan.
6. Mencegah Pembaruan yang Tidak Perlu
Dengan melakukan literature review, Anda dapat memastikan bahwa penelitian yang Anda lakukan tidak mereplikasi atau mengulang penelitian yang sudah ada. Anda dapat melihat apakah pertanyaan penelitian Anda telah diteliti sebelumnya atau sudah ada jawaban yang jelas.
Jika sudah ada penelitian yang cukup, Anda dapat memfokuskan energi dan sumber daya Anda untuk mengeksplorasi aspek yang belum tercakup.
7. Memvalidasi Temuan Penelitian Anda
Melalui literature review, Anda dapat membandingkan temuan penelitian Anda dengan temuan penelitian sebelumnya. Hal ini memungkinkan Anda untuk memvalidasi hasil penelitian Anda dan melihat sejauh mana hasil Anda konsisten dengan literatur yang ada.
Jika temuan Anda sejalan dengan penelitian sebelumnya, ini akan memperkuat kepercayaan pada hasil Anda.
8. Mendapatkan Pemahaman Mendalam tentang Topik
Dalam literature review, Anda akan membaca dan menganalisis berbagai artikel dan publikasi ilmiah. Hal ini akan membantu Anda untuk mendapatkan pemahaman mendalam tentang topik penelitian Anda.
Anda akan mengembangkan wawasan yang lebih luas dan dapat melihat berbagai perspektif yang ada. Pemahaman yang mendalam ini akan membantu Anda dalam mengembangkan argumen yang kuat dan informasi yang kredibel dalam penelitian Anda.
9. Menemukan Sumber Referensi yang Relevan
Literature review juga membantu Anda dalam menemukan sumber referensi yang relevan untuk penelitian Anda. Anda akan mengidentifikasi artikel-artikel penting, buku, atau publikasi lainnya yang dapat menjadi acuan dalam penelitian Anda.
Dengan memiliki sumber referensi yang kuat, Anda dapat mendukung klaim Anda dan memperkuat argumentasi dalam penelitian Anda.
10. Menghindari Plagiarisme
Dengan melakukan literature review yang cermat, Anda dapat menghindari plagiarisme dalam penelitian Anda. Anda akan mengetahui penelitian-penelitian yang telah ada dan cara mereka menyajikan informasi.
Dengan demikian, Anda dapat memastikan bahwa Anda mengutip dengan benar dan memberikan kredit kepada penulis yang tepat. Ini penting untuk menjaga integritas akademik Anda.
Melalui literature review, Anda tidak hanya memperoleh pemahaman yang lebih mendalam tentang topik penelitian Anda, tetapi juga memperkuat dasar penelitian Anda, mengidentifikasi kesenjangan pengetahuan, dan memperkuat argumen Anda.
Literature review membantu Anda membangun fondasi yang solid untuk penelitian Anda dan memastikan bahwa penelitian Anda memiliki kontribusi yang berharga dalam bidang tersebut.
Contoh Format Literature Review Jurnal

Contoh format literature review jurnal yang disediakan di bawah ini menguraikan bagian-bagian utama dan subjudul yang harus dimasukkan dalam literature review Anda. Ini berfungsi sebagai template yang dapat Anda adaptasi dan modifikasi sesuai dengan persyaratan khusus artikel penelitian Anda.
1. Pendahuluan
Pada bagian ini, berikan gambaran singkat tentang topik dan jelaskan pentingnya melakukan literature review. Hal ini menetapkan konteks untuk review Anda dan menyoroti kesenjangan dalam pengetahuan yang ada yang ingin Anda teliti.
2. Pertanyaan Penelitian atau Tujuan
Tuliskan pertanyaan penelitian atau tujuan Anda dengan jelas dan singkat. Bagian ini harus dengan jelas mengartikulasikan tujuan literature review Anda dan bagaimana hal itu berhubungan dengan tujuan penelitian secara keseluruhan.
3. Strategi Pencarian
Deskripsikan metodologi yang Anda gunakan untuk mencari literature yang relevan. Sertakan rincian seperti basis data yang Anda telusuri, kata kunci yang Anda gunakan, dan kriteria inklusi atau eksklusi yang Anda terapkan. Bagian ini menunjukkan kecermatan proses pencarian literature Anda.
4. Kriteria Inklusi dan Eksklusi
Tentukan kriteria yang Anda gunakan untuk memilih studi yang akan dimasukkan dalam literature review Anda. Ini dapat mencakup faktor seperti tanggal publikasi, desain studi, lokasi geografis, atau bahasa. Dengan mendefinisikan dengan jelas kriteria inklusi dan eksklusi Anda, Anda memastikan bahwa literature review Anda fokus dan relevan.
5. Ekstraksi Data
Jelaskan informasi yang Anda ambil dari setiap studi yang dipilih. Ini dapat mencakup variabel seperti ukuran sampel, desain studi, metodologi yang digunakan, dan temuan-temuan utama. Bagian ini memungkinkan pembaca memahami karakteristik studi yang Anda masukkan dalam literature review Anda.
6. Tema dan Sintesis
Atur literature review Anda menjadi tema atau kategori berdasarkan konsep-konsep kunci, teori, atau variabel yang dieksplorasi dalam studi-studi yang dipilih. Dalam setiap tema, berikan ringkasan temuan utama dan diskusikan pola, ketidaksesuaian, atau kesenjangan dalam literature. Bagian ini menunjukkan kemampuan Anda untuk secara kritis menganalisis dan menyintesis penelitian yang ada.
7. Evaluasi Kritis
Evaluasikan kualitas dan validitas studi yang termasuk dalam literature review Anda. Bahas kekuatan dan kelemahan setiap studi dan nilai secara keseluruhan kualitas bukti tersebut. Bagian ini menyoroti kemampuan Anda dalam menilai kehandalan dan kredibilitas literature yang ada.
8. Diskusi dan Implikasi
Ringkas temuan utama literature review Anda dan diskusikan implikasinya terhadap pertanyaan penelitian atau tujuan Anda. Diskusikan kontribusi Anda terhadap pengetahuan yang ada dan identifikasi arah penelitian masa depan. Bagian ini memperlihatkan kemampuan Anda untuk menghubungkan temuan literature review Anda dengan konteks yang lebih luas.
Contoh Format Literature Review Jurnal PDF

Nah, pada bagian sebelumnya saya hanya memberikan contoh formatnya. Tapi, pada bagian ini kami akan memberikanmu contoh literature review jurnal dalam bentuk PDF yang bisa kamu akses secara langsung dan gratis!

Cara Membuat Literature Review

Literature review adalah elemen penting dalam penelitian akademik. Bagi banyak mahasiswa dan peneliti, membuat literature review sering menjadi tantangan yang membingungkan. Namun, dengan memahami konsep dasar dan mengikuti langkah-langkah yang tepat, Anda dapat menyusun literature review yang efektif dan informatif.
1. Pahami Tujuan dan Lingkup Literature Review
Sebelum memulai, penting untuk memahami tujuan dan lingkup literature review Anda. Pertanyaan yang perlu Anda jawab adalah:
- Apa topik penelitian Anda?
- Apa tujuan literature review Anda?
- Apa lingkup literatur yang akan Anda teliti?
Dengan menjawab pertanyaan-pertanyaan ini, Anda dapat mengarahkan penelitian Anda dan menentukan batasan-batasan yang sesuai.
2. Identifikasi Sumber-Sumber Utama
Langkah pertama dalam membuat literature review adalah mengidentifikasi sumber-sumber utama yang relevan dengan topik penelitian Anda. Berikut adalah beberapa sumber yang dapat Anda gunakan:
- Jurnal ilmiah terkemuka di bidang terkait
- Buku dan monograf
- Konferensi ilmiah dan prosiding
- Skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi terkait
Pastikan untuk menggunakan sumber-sumber yang terpercaya dan terkini. Anda juga dapat menggunakan database akademik seperti Google Scholar atau PubMed untuk mencari literatur yang relevan.
3. Baca dan Analisis Literatur
Setelah mengidentifikasi sumber-sumber utama, langkah berikutnya adalah membaca dan menganalisis literatur yang Anda temukan. Penting untuk mencatat poin-poin kunci dan temuan penting dari setiap artikel atau buku yang Anda baca.
Anda juga dapat membuat tabel atau diagram untuk membantu memvisualisasikan hubungan antara literatur yang berbeda. Hal ini akan memudahkan Anda dalam mengorganisir informasi dan mengidentifikasi tema-tema yang muncul.
4. Buat Rangkuman dan Sinopsis
Setelah membaca dan menganalisis literatur, buat rangkuman dan sinopsis dari setiap sumber. Ini akan membantu Anda memahami secara keseluruhan apa yang telah ditulis tentang topik penelitian Anda.
Pastikan rangkuman dan sinopsis yang Anda buat mencakup poin-poin penting, metodologi penelitian, temuan, dan kesimpulan dari setiap sumber. Anda juga dapat menambahkan komentar pribadi atau pemikiran Anda sendiri tentang setiap sumber.
5. Identifikasi Celah dalam Penelitian yang Ada
Saat menyusun literature review, penting untuk mengidentifikasi celah dalam penelitian yang ada. Tanyakan pada diri Anda:
- Apakah ada perbedaan pendapat atau hasil yang saling bertentangan dalam literatur yang Anda teliti?
- Adakah aspek penelitian yang belum banyak diteliti atau belum ada pemahaman yang mendalam?
- Apakah ada celah dalam penelitian yang dapat Anda jadikan titik fokus dalam literature review Anda?
Dengan mengidentifikasi celah ini, Anda dapat menyajikan kontribusi yang berarti dalam literature review Anda dan memberikan pemahaman baru terhadap topik penelitian.
6. Organisasi dan Struktur
Selanjutnya, Anda perlu mengorganisasi dan memberikan struktur pada literature review Anda. Berikut adalah beberapa tips untuk melakukan hal tersebut:
- Gunakan sub-bab atau sub-topik untuk mengelompokkan literatur berdasarkan tema atau isu yang relevan.
- Pastikan setiap sub-bab memiliki alur yang teratur dan terkait dengan sub-bab sebelumnya dan sesudahnya.
- Gunakan kalimat transisi atau kata penghubung yang tepat untuk menghubungkan ide-ide antara paragraf dan sub-bab.
- Gunakan tabel atau diagram untuk memvisualisasikan hubungan antara literatur yang berbeda.
Dengan memberikan struktur yang jelas, literature review Anda akan lebih mudah dibaca dan dipahami oleh pembaca.
7. Tulis dengan Gaya Bahasa yang Jelas dan Akademik
Saat menulis literature review, pastikan Anda menggunakan gaya bahasa yang jelas dan akademik. Berikut adalah beberapa tips untuk membantu Anda menulis dengan baik:
- Hindari penggunaan frasa berlebihan atau istilah yang terlalu teknis, kecuali jika itu memang diperlukan.
- Gunakan kalimat aktif dan pastikan subjek kalimat jelas.
- Gunakan paragraf pendek dan jelas dengan satu ide utama dalam setiap paragraf.
- Hindari pengulangan kata atau konsep yang sama secara berlebihan.
- Sertakan kutipan langsung atau ringkasan yang tepat dari literatur yang Anda teliti.
Dengan menulis dengan gaya bahasa yang baik, literature review Anda akan lebih profesional dan mudah dipahami oleh pembaca.
8. Periksa Kembali dan Edit Literature Review Anda
Setelah menulis literature review, jangan lupa untuk memeriksa kembali dan mengeditnya. Berikut adalah beberapa hal yang perlu diperhatikan saat melakukan revisi:
- Periksa tata bahasa, ejaan, dan tanda baca yang tepat.
- Pastikan argumen Anda terstruktur dengan baik dan didukung oleh bukti yang kuat.
- Periksa kutipan dan daftar referensi untuk memastikan kesesuaian format yang ditentukan (misalnya, APA, MLA).
- Baca kembali keseluruhan literature review untuk memeriksa alur dan koherensi keseluruhan.
Dengan melakukan revisi yang cermat, literature review Anda akan menjadi lebih baik dan lebih berkualitas.
Daftar Jurnal Literatur Review

Dibawah ini kami paparkan 6 daftar jurnal literatur review yang bisa Anda kunjungi, ini juga bisa Anda jadikan sebagai referensi ilmiah
Dalam artikel ini, kita telah membahas tentang literature review atau tinjauan pustaka. Literature review merupakan kegiatan yang penting dalam dunia akademik dan penelitian, di mana peneliti menganalisis, mengevaluasi, dan mensintesis sumber-sumber literatur yang relevan dengan topik penelitian.
Dalam membuat literature review, terdapat beberapa metode yang dapat digunakan, seperti systematic mapping study, systematic literature review, dan traditional review. Setiap metode memiliki pendekatan yang berbeda dalam mengumpulkan, menganalisis, dan menyajikan data dari sumber-sumber literatur.
TAK : literature review example, literature review artinya, literature review journal, literature review skripsi, literature review menurut para ahli
Sumber : https://www.gramedia.com/literasi/literature-review
Literature review adalah suatu kegiatan yang melibatkan analisis, evaluasi, dan sintesis sumber-sumber literatur yang relevan dengan topik penelitian.
Literature review penting dalam penelitian karena dapat memberikan pemahaman mendalam tentang perkembangan penelitian terkini, mengidentifikasi kesenjangan penelitian yang ada, dan menyusun dasar teoretis yang kuat untuk penelitian yang akan dilakukan.
Systematic mapping study lebih fokus pada pengumpulan dan penyajian data secara sistematis, sedangkan systematic literature review melibatkan analisis kritis terhadap penelitian-penelitian yang ada.
Memilih karya tulis yang relevan dalam literature review dilakukan melalui pencarian berdasarkan topik penelitian, kriteria inklusi dan eksklusi tertentu, serta pengecekan keabsahan dan keandalan sumber literatur.
Publikasi Jurnal Pembelajaran PPG

Nomor Induk Dosen Nasional

Penelitian Studi Kasus : Contoh Judul, Pengertian, Jenis, PDF

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of literature review , a. habitat loss and species extinction: , b. range shifts and phenological changes: , c. ocean acidification and coral reefs: , d. adaptive strategies and conservation efforts: .
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review .
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.
Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as yo u go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free!
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research | Cite feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface. It also allows you auto-cite references in 10,000+ styles and save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research | Cite” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.

- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references in 10,000+ styles into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.

The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 22+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , what are research skills definition, importance, and examples , what is phd dissertation defense and how to..., abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., what is academic integrity, and why is it..., how to make a graphical abstract, academic integrity vs academic dishonesty: types & examples.
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
Note: These are sample literature reviews from a class that were given to us by an instructor when APA 6th edition was still in effect. These were excellent papers from her class, but it does not mean they are perfect or contain no errors. Thanks to the students who let us post!
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Oct 18, 2024 9:43 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview

How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019

Q uality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Learn More About Lit Review:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Literature Review: 4 Time-Saving Hacks
🎙️ PODCAST: Ace The Literature Review 4 Time-Saving Tips To Fast-Track Your Literature...

Research Question 101: Everything You Need To Know
Learn what a research question is, how it’s different from a research aim or objective, and how to write a high-quality research question.

Research Question Examples: The Perfect Starting Point
See what quality research questions look like across multiple topic areas, including psychology, business, computer science and more.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Panduan lengkap untuk memahami dan menyusun literature review. Temukan cara membuat, format yang tepat, serta contoh literature review.
Literature Review Examples. For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. 1. Narrative Review Examples
A literature review is a survey of scholarly knowledge on a topic. Our guide with examples, video, and templates can help you write yours.
A literature review is a compilation of current knowledge on a particular topic derived from the critical evaluation of different scholarly sources such as books, articles, and publications, which is then presented in an organized manner to relate to a specific research problem being investigated.
Dalam artikel ini, kita telah membahas tentang literature review atau tinjauan pustaka. Literature review merupakan kegiatan yang penting dalam dunia akademik dan penelitian, di mana peneliti menganalisis, mengevaluasi, dan mensintesis sumber-sumber literatur yang relevan dengan topik penelitian.
Literature Review Example & Sample: Full Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you’ve come to the right place.
A literature review is a comprehensive analysis of existing research on a topic, identifying trends, gaps, and insights to inform new scholarly contributions. Read this comprehensive article to learn how to write a literature review, with examples.
This guide will provide research and writing tips to help students complete a literature review assignment.
begin by clearing up some misconceptions about what a literature review is and what it is not. Then, I will break the process down into a series of simple steps, looking at examples along the way. In the end, I hope you will have a simple, practical strategy to write an effective literature review.
Learn how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps. Includes free literature review templates and resources.