Diabetes-insipidus-diagnosis-and-treatment-
Jan 03, 2023
80 likes | 94 Views
Diabetes insipidus treatment is based on underlying reasons. Family Medicine Austin provides comprehensive diabetic care and tailored treatment regimens.<br><br>

Share Presentation

Presentation Transcript
- More by User

Diabetes Insipidus & ADH hypersecretion
Diabetes Insipidus & ADH hypersecretion. Dr. Abdulmoein Eid Al-Agha Assistant Professor & Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist, King AbdulAziz University & Dr. Erfan Hospital - Jeddah. The Pituitary Gland. The pituitary composed of 2 lobes: anterior lobe “ adenohypophysis”
917 views • 27 slides

DIABETES INSIPIDUS
Dr. Abdelaziz Elamin MD, PhD, FRCPCH Professor of Child Health consultant pediatric endocrinologist Sultan Qaboos University Muscat, Oman. [email protected]. DIABETES INSIPIDUS. DIABETES INSIPIDUS.
1.09k views • 28 slides

A case of DIABETES MELLITUS WITH CENTRAL DIABETES INSIPIDUS
A case of DIABETES MELLITUS WITH CENTRAL DIABETES INSIPIDUS. Prof. DR. M.NATARAJAN MD DR.SYED BAHAVUDEEN HUSSAINI MD DNB DR. VALLI DEVI MD Presentor ; P. Muthukrishnan. 63 years male known case of type 2 diabetes presented complaints of polyuria polydipsia 7 days.
1.46k views • 31 slides

Diabetes Mellitus Classification and Diagnosis
Diabetes Mellitus Classification and Diagnosis. Hengameh Abdi, MD Endocrine Research Center Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences 28 October 2015 [email protected]. 53%. WORLD 592 million people living with diabetes. WORLD
776 views • 17 slides

MEDICAL GRANDROUNDS ON DIABETES INSIPIDUS
MEDICAL GRANDROUNDS ON DIABETES INSIPIDUS. Desiree B. Yano-Simbulan, M.D. Maricel B. Peniero, M.D. November 8, 2007. LEARNING OBJECTIVES. To present a case of a 50 year old female with diabetes insipidus To provide an overview in the diagnostic approach to polyuria and diabetes insipidus
1.87k views • 59 slides

Dementia: Diagnosis and Treatment
Dementia: Diagnosis and Treatment. 2005. Case ….
811 views • 53 slides

DIABETES INSIPIDUS AND ADIPSIA
DIABETES INSIPIDUS AND ADIPSIA. JONATHAN D. LEFFERT, MD SEPTEMBER 22, 2004. CASE PRESENTATION.
570 views • 20 slides

Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus. By Bruna Corrales. Definitons. Diabetes Insipidus ≠ Diabetes M ellitus From the Greek: Diabainein -"to pass through“ From Latin: Insipidus - "having no flavor". Normal Production of ADH.
3.97k views • 12 slides

Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus. Ovidiu Galescu MD. Definition.
480 views • 11 slides

Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment. History Endoscopy. Diagnosis and Treatment. Diagnosis and Treatment. Diagnosis and Treatment.
255 views • 4 slides

Chap44 Diabetes insipidus and aquaporin (ADH, aldosterone and ACTH)
Chap44 Diabetes insipidus and aquaporin (ADH, aldosterone and ACTH). B9902036 洪健睿 B9902045 許仲皓. Diabetes insipidus (DI). Frequency : uncommon, with a prevalence of 1 case per 25,000 population (as in the United States). Signs and symptoms :
697 views • 11 slides

Diabetes insipidus. María Þorsteinsdóttir Læknanemi. Diabetes insipidus. Diabainein: Gríska, “Að renna”, “fara í gegn” Insipidus: Latína, “Bragðlaust” Sjaldgæfur sjúkdómur, einkum sjaldgæft meðal barna DI einkennist af polyuriu og polydipsiu, þvagið er þunnt (250 mosmol/kg).
457 views • 17 slides

DIABETES INSIPIDUS. Vasopressine=antidiuretic hormone Synthesis and actions. Neuhyophisis Is derived from nervous tissue and forms a complex with anterior hypothalamus. Hypothalamus :
903 views • 63 slides

Diagnosis of diabetes
Diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetic symptoms. Diabetic symptoms + venous sample for : Random venous ≥ 11.1 mmol/l (4.4-7.8) Fasting glucose > 7 (<6.1) OGTT ≥ 11.1 (<7.8) HbA1c ≥ 6.5 (<6). Asymptomatic.
270 views • 10 slides

Protocolbespreking Diabetes Insipidus
Protocolbespreking Diabetes Insipidus. Patient met dorst en polyurie. Osmotische diurese Waterdiurese CDI NDI PPD. Regulatie waterbalans via Posm. [Na+] gereguleerd door dorstmechanisme en ADH Posm zeer strak gereguleerd (1 a 2% N) Dorst belangrijkste component
374 views • 15 slides

Diabetes – Diagnosis and assessment
Diabetes – Diagnosis and assessment. M Nasim. Epidemiology. Global prevelance 4.6 % Diabetic population has doubled up in last 13 years
283 views • 13 slides

Diabetes Insipidus. Endocrinology Rounds November 4, 2009 Selina Liu PGY4 Endocrinology. Objectives. To understand and describe the pathophysiology of diabetes insipidus To be able to diagnose and treat diabetes insipidus. Objectives. To name this statue, and its location
6.02k views • 56 slides

Gestational Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatment Long Term Management, and Followup
Gestational Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatment Long Term Management, and Followup. Eric Lind Johnson, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine University of North Dakota School of Medicine And Health Sciences Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes Center
602 views • 49 slides

Diabetes Insipidus in Canines
Diabetes Insipidus in Canines. Lauren Liba Eric Malarney. What is Diabetes Insipidus???. A disorder of water imbalance This disorder is a completely different disease from diabetes mellitus, which is a disorder of glucose metabolism involving the hormone insulin.
832 views • 52 slides

Diabetes Insipidus Causes, Symptoms, Herbal Treatment Diabgon Capsules
This power point presentation describes about Diabetes Insipidus Causes, Symptoms, Herbal Treatment Diabgon Capsules
250 views • 11 slides

Diabetes Mellitus Classification and Diagnosis. By: Dr Mozhgan Karimifar Assistant Prof. of Endocrinology Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences. 53%. WORLD 592 million people living with diabetes. WORLD 387 million. Africa 93%. Middle East and North Africa 85%.
414 views • 30 slides

583 views • 53 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Diabetes Insipidus – Diagnosis and Management
Published by Horace Walters Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Diabetes Insipidus – Diagnosis and Management"— Presentation transcript:

MRI of the Thoracic Spine: Axial T1 wtd.images.
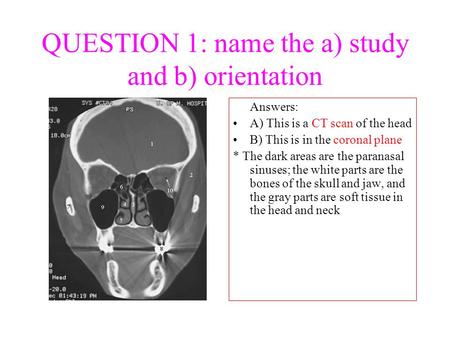
QUESTION 1: name the a) study and b) orientation Answers: A) This is a CT scan of the head B) This is in the coronal plane * The dark areas are the paranasal.
Fig A midline Post-contrast Sagittal T1 Weighted MRI

Goals Be familiar with the extracranial take-off of CN VIII and its relationship to the pons and cerebellum Appreciate how the anatomic position of tumors.
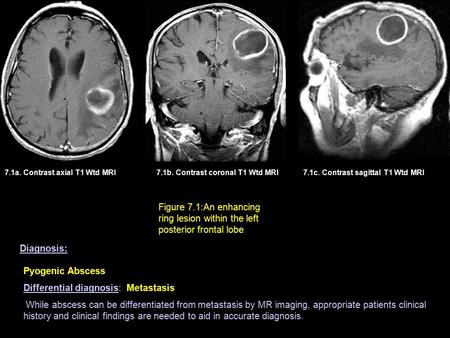
7.1a. Contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI7.1b. Contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI Figure 7.1:An enhancing ring lesion within the left posterior frontal lobe 7.1c. Contrast.

RADIOLOGY ANATOMY OF THE PITUITARY GLAND
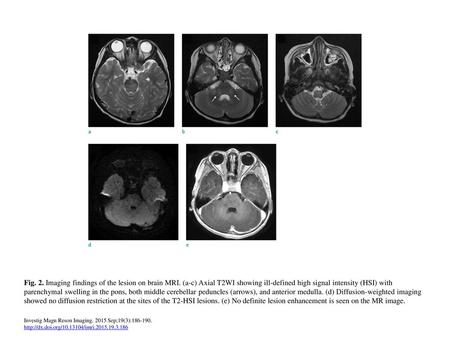
Fig. 2. Imaging findings of the lesion on brain MRI

Diabetes insipidus: Differential diagnosis and management
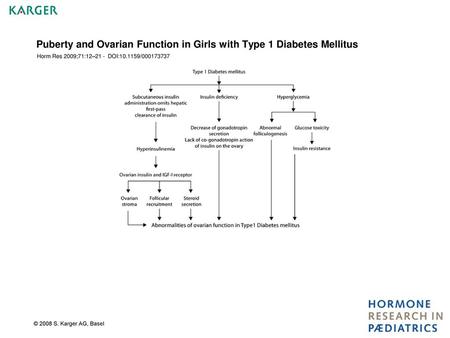
Puberty and Ovarian Function in Girls with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
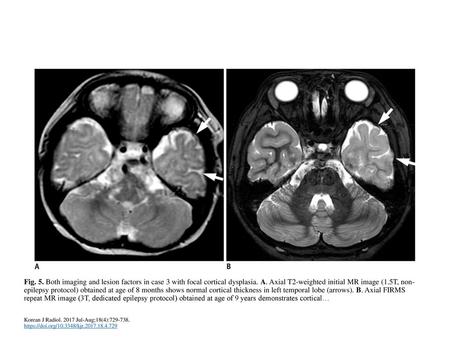
Fig. 5. Both imaging and lesion factors in case 3 with focal cortical dysplasia. A. Axial T2-weighted initial MR image (1.5T, non-epilepsy protocol) obtained.
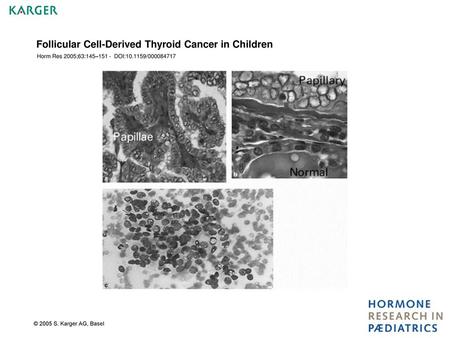
Follicular Cell-Derived Thyroid Cancer in Children

Teaching NeuroImages Neurology Resident and Fellow Section

Symptomatic compression of the optic nerve by the carotid artery
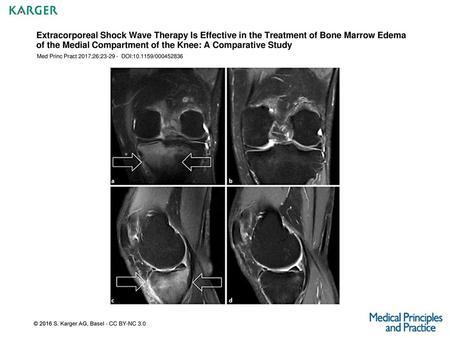
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Marrow Edema of the Medial Compartment of the Knee: A Comparative Study Med Princ.

A Case of Bladder Cancer after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
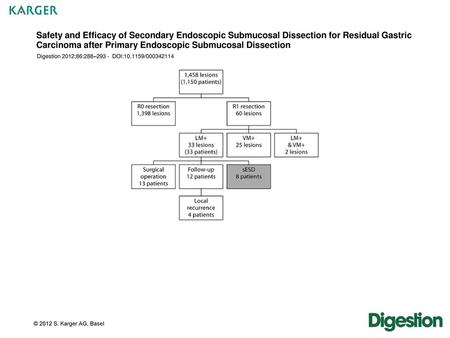
Safety and Efficacy of Secondary Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Residual Gastric Carcinoma after Primary Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Digestion.
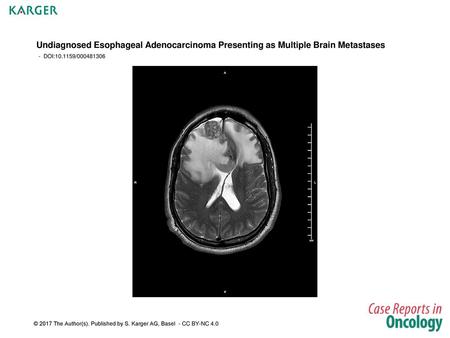
Undiagnosed Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Presenting as Multiple Brain Metastases - DOI: / Fig. 1. MRI-brain T2-weighted image showing an anterior.
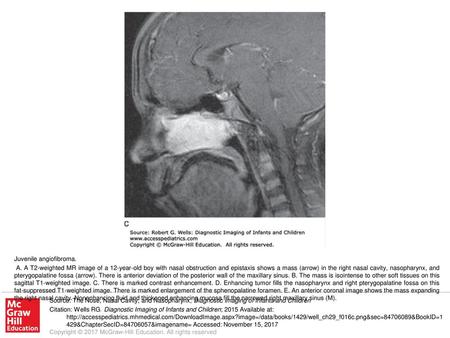
A. A T2-weighted MR image of a 12-year-old boy with nasal obstruction and epistaxis shows a mass (arrow) in the right nasal cavity, nasopharynx, and pterygopalatine.

Treatment of Leptomeningeal Metastases in a Patient with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR T790M Mutation - DOI: / Fig. 1. a Brain.
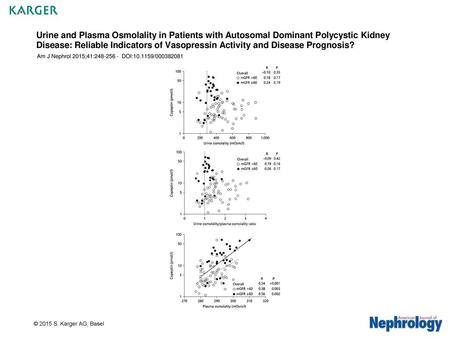
Urine and Plasma Osmolality in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Reliable Indicators of Vasopressin Activity and Disease Prognosis?
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This document discusses diabetes insipidus (DI), a disorder caused by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) characterized by excessive thirst and urination. There are two types: central DI caused by head trauma or pituitary issues reducing ADH production, and nephrogenic DI caused by kidney problems inhibiting ADH response.
Diabetes insipidus is a disorder caused by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or the kidneys' inability to respond to ADH. This results in the excessive production of dilute urine and excessive thirst.
This document discusses diabetes insipidus (DI), which causes excessive urine production (polyuria). There are three main types of DI: primary polydipsia (increased water intake), central DI (deficient vasopressin secretion), and nephrogenic DI (kidneys do not respond to vasopressin).
This power point presentation describes about natural ways to treat diabetes insipidus and mellitus at home. 206 views • 12 slides A novel mutation in the AVPR2 gene in a Palestinian family with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) • Types and causes of DI • Central • Nephrogenic DI • Symptoms and signs of DI • Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion.
Diabetes insipidus treatment is based on underlying reasons. Family Medicine Austin provides comprehensive diabetic care and tailored treatment regimens. Slideshow 11864833 by FamilyMedicineAustin.
Diabetes insipidus.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides an overview of diabetes insipidus, a disorder characterized by excessive urination and thirst.
3 Diabetes Insipidus – Diagnosis and Management Horm Res Paediatr 2012;77:69–84 - DOI: / Fig. 2. Normal MRI findings. a Sagittal T1-weighted image shows normal anterior pituitary (thick arrow), typical posterior pituitary hyperintensity known as ‘bright spot’ (arrowhead), and normal PS (thin arrow).
There are two main types: central diabetes insipidus caused by hypothalamic-pituitary disease and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by kidney problems. Diagnosis involves water deprivation tests and measuring antidiuretic hormone levels.
Diabetes insipidus is a disorder characterized by excessive urine production and thirst due to a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone. There are two main types: central diabetes insipidus caused by issues with the pituitary gland, and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by kidney problems.