

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an essay introduction paragraph with paperpal – step -by -step, how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Unsure of how to start your essay introduction? Leverage Paperpal’s Generative AI templates to provide a base for your essay introduction. Here’s an example of an essay outline generated by Paperpal.

Use Paperpal’s Preditive AI writing features to maintain your writing flow
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Write essays 2x faster with Paperpal. Try for free
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.
Write strong essays in academic English with Paperpal. Try it for free
Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write a Good Hook for Essays, with Examples
- What is a Narrative Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal....
How to Start an Essay: 13 Engaging Strategies
ThoughtCo / Hugo Lin
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
There are countless ways to start an essay effectively. A solid introductory paragraph both informs and motivates. It lets readers know what your piece is about and it encourages them to keep reading.
For folks new to learning how to start an essay, here are 13 introductory strategies accompanied by examples from a wide range of professional writers.
State Your Thesis Briefly and Directly
One straightforward way to begin is to get right to the point. But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...".
"It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving." The Camera Age: Essays on Television . Penguin, 1982)
Pose a Question Related to Your Subject
A thought-provoking way to start an essay is by asking a relevant question that needs to be unpacked. Follow up the question with an answer, or an invitation for your readers to answer the question.
"What is the charm of necklaces? Why would anyone put something extra around their neck and then invest it with special significance? A necklace doesn't afford warmth in cold weather, like a scarf, or protection in combat, like chain mail; it only decorates. We might say, it borrows meaning from what it surrounds and sets off, the head with its supremely important material contents, and the face, that register of the soul. When photographers discuss the way in which a photograph reduces the reality it represents, they mention not only the passage from three dimensions to two, but also the selection of a point de vue that favors the top of the body rather than the bottom, and the front rather than the back. The face is the jewel in the crown of the body, and so we give it a setting." (Emily R. Grosholz, "On Necklaces." Prairie Schooner , Summer 2007)
State an Interesting Fact About Your Subject
Leading with a fact that draws readers in immediately can grab their attention effectively.
" The peregrine falcon was brought back from the brink of extinction by a ban on DDT, but also by a peregrine falcon mating hat invented by an ornithologist at Cornell University. If you cannot buy this, Google it. Female falcons had grown dangerously scarce. A few wistful males nevertheless maintained a sort of sexual loitering ground. The hat was imagined, constructed, and then forthrightly worn by the ornithologist as he patrolled this loitering ground, singing, Chee-up! Chee-up! and bowing like an overpolite Japanese Buddhist trying to tell somebody goodbye...." (David James Duncan, "Cherish This Ecstasy." The Sun , July 2008)
Present Your Thesis as a Recent Discovery or Revelation
"I've finally figured out the difference between neat people and sloppy people. The distinction is, as always, moral. Neat people are lazier and meaner than sloppy people." (Suzanne Britt Jordan, "Neat People vs. Sloppy People." Show and Tell . Morning Owl Press, 1983)
Briefly Describe the Primary Setting of Your Essay
"It was in Burma, a sodden morning of the rains. A sickly light, like yellow tinfoil, was slanting over the high walls into the jail yard. We were waiting outside the condemned cells, a row of sheds fronted with double bars, like small animal cages. Each cell measured about ten feet by ten and was quite bare within except for a plank bed and a pot of drinking water. In some of them brown silent men were squatting at the inner bars, with their blankets draped round them. These were the condemned men, due to be hanged within the next week or two." (George Orwell, "A Hanging," 1931)
Recount an Incident That Dramatizes Your Subject
Sharing an incident from your life or history in general is an impactful way to start an essay.
"One October afternoon three years ago while I was visiting my parents, my mother made a request I dreaded and longed to fulfill. She had just poured me a cup of Earl Grey from her Japanese iron teapot, shaped like a little pumpkin; outside, two cardinals splashed in the birdbath in the weak Connecticut sunlight. Her white hair was gathered at the nape of her neck, and her voice was low. “Please help me get Jeff’s pacemaker turned off,” she said, using my father’s first name. I nodded, and my heart knocked." (Katy Butler, "What Broke My Father's Heart." The New York Times Magazine , June 18, 2010)
Use the Narrative Strategy of Delay
The narrative strategy of delay allows you to put off identifying your subject just long enough to pique your readers' interest without frustrating them.
"They woof. Though I have photographed them before, I have never heard them speak, for they are mostly silent birds. Lacking a syrinx, the avian equivalent of the human larynx, they are incapable of song. According to field guides the only sounds they make are grunts and hisses, though the Hawk Conservancy in the United Kingdom reports that adults may utter a croaking coo and that young black vultures, when annoyed, emit a kind of immature snarl...." (Lee Zacharias, "Buzzards." Southern Humanities Review , 2007)
Use the Historical Present Tense
An effective way to start an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now.
"Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother’s station wagon. We face glowing white headlights of cars following us, our sneakers pressed against the back hatch door. This is our joy—his and mine—to sit turned away from our moms and dads in this place that feels like a secret, as though they are not even in the car with us. They have just taken us out to dinner, and now we are driving home. Years from this evening, I won’t actually be sure that this boy sitting beside me is named Ben. But that doesn’t matter tonight. What I know for certain right now is that I love him, and I need to tell him this fact before we return to our separate houses, next door to each other. We are both five." (Ryan Van Meter, "First." The Gettysburg Review , Winter 2008)
Briefly Describe a Process That Leads Into Your Subject
"I like to take my time when I pronounce someone dead. The bare-minimum requirement is one minute with a stethoscope pressed to someone’s chest, listening for a sound that is not there; with my fingers bearing down on the side of someone’s neck, feeling for an absent pulse; with a flashlight beamed into someone’s fixed and dilated pupils, waiting for the constriction that will not come. If I’m in a hurry, I can do all of these in sixty seconds, but when I have the time, I like to take a minute with each task." (Jane Churchon, "The Dead Book." The Sun , February 2009)
Reveal a Secret or Make a Candid Observation
"I spy on my patients. Ought not a doctor to observe his patients by any means and from any stance, that he might the more fully assemble evidence? So I stand in doorways of hospital rooms and gaze. Oh, it is not all that furtive an act. Those in bed need only look up to discover me. But they never do." ( Richard Selzer , "The Discus Thrower." Confessions of a Knife . Simon & Schuster, 1979)
Open with a Riddle, Joke, or Humorous Quotation
A fun way to start an essay is to use a riddle , joke, or humorous quotation that reveals something about your subject.
" Q: What did Eve say to Adam on being expelled from the Garden of Eden? A: 'I think we're in a time of transition.' The irony of this joke is not lost as we begin a new century and anxieties about social change seem rife. The implication of this message, covering the first of many periods of transition, is that change is normal; there is, in fact, no era or society in which change is not a permanent feature of the social landscape...." (Betty G. Farrell, Family: The Making of an Idea, an Institution, and a Controversy in American Culture . Westview Press, 1999)
Offer a Contrast Between Past and Present
"As a child, I was made to look out the window of a moving car and appreciate the beautiful scenery, with the result that now I don't care much for nature. I prefer parks, ones with radios going chuckawaka chuckawaka and the delicious whiff of bratwurst and cigarette smoke." (Garrison Keillor, "Walking Down The Canyon." Time , July 31, 2000)
Offer a Contrast Between Image and Reality
A compelling way to start an essay is with a contrast between a common misconception and the opposing truth.
"They aren’t what most people think they are. Human eyes, touted as ethereal objects by poets and novelists throughout history, are nothing more than white spheres, somewhat larger than your average marble, covered by a leather-like tissue known as sclera and filled with nature’s facsimile of Jell-O. Your beloved’s eyes may pierce your heart, but in all likelihood they closely resemble the eyes of every other person on the planet. At least I hope they do, for otherwise he or she suffers from severe myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness), or worse...." (John Gamel, "The Elegant Eye." Alaska Quarterly Review , 2009)
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Essay Assignment: Descriptive and Informative Profile
- Practice in Supporting a Topic Sentence with Specific Details
- How to Start a Book Report
- What Is Expository Writing?
- An Essay Revision Checklist
- Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech (With Topic Ideas)
- Writing an Opinion Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services, how to start an essay: 4 introduction paragraph examples.

- Tags: Essay , Essay Writing
Staring at a blank page, not knowing how to start your essay introduction can certainly be daunting! You may spend hours pondering over the introduction of your essay, while the deadline draws closer each day. However, the formula for a great introduction paragraph is not that complex.
Different types of essays use different forms of introductions. But a good introduction should grab the reader’s attention from the get-go! It should also equip the reader with essential background information and acquaint them with the main idea of your essay.
In this article, we’ll guide you on how to start off an essay with a bang. We’ll also brief you on a few essay introduction examples. Let’s start by understanding how to write an introduction for an essay.
Optimize your essay with our expert essay editing services! Learn more
How to start an essay
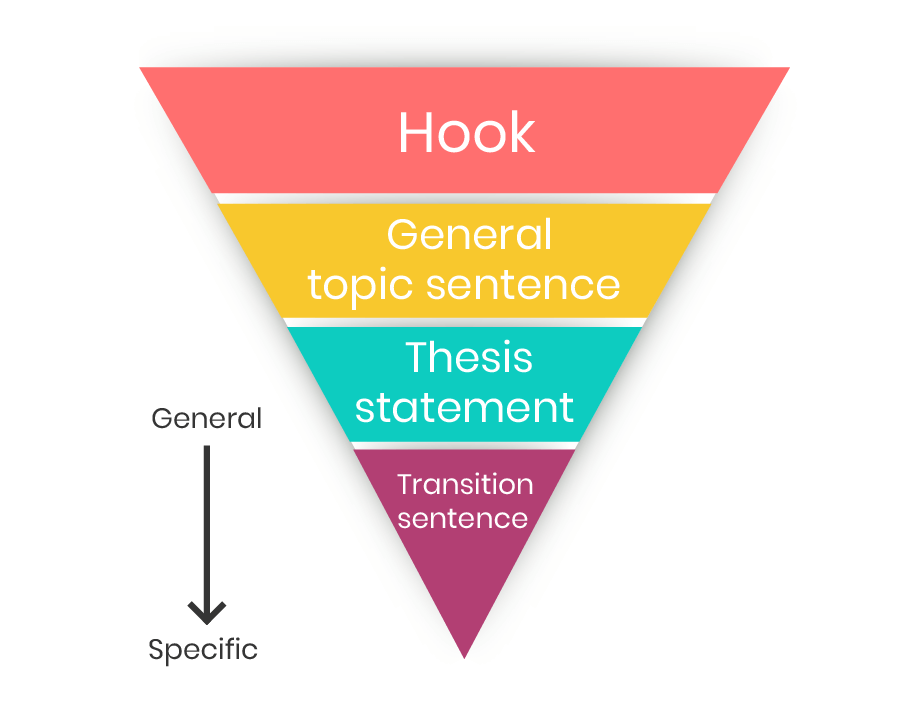
In order to understand how to start an essay, we need to first take a look at its different components. The introduction to an essay consists of three main parts:
1. Hook: Attractive opening line that draws the reader’s attention
2. Background information: Relevant information that revolves around the thesis statement
3. Thesis statement: The main argument or idea of your essay
You can also provide an overview, which gives the reader a glimpse of what is to come. But make sure that this structure is very brief.
There are several ways to start an essay. But, any changes to the content of your essay may lead to significant revisions in your introduction.
We suggest that you simply develop a rough thesis statement and save the essay introduction paragraph for the end. Once you have completed the rest of your work, you can use the following steps to understand how to start an essay introduction:
1. Begin with an attractive hook
In order to understand how to start an introduction in an essay, we must first focus on the hook. An effective opening statement, or a “hook”, aims to intrigue the reader. An attractive opening statement essentially hooks the reader to your essay. It should be fairly concise but should still provide insight into the main point of your essay.
Although the goal of the opening statement is the same for all essay types, different essays use different types of hooks. Since essay types are highly diverse, an opening statement that works for one type of essay may not always work for the other. Hence, it’s crucial to refer to different types of opening statements.
Let’s understand this with the help of the following opening statements:
A. Interesting fact or statistic
Begin your essay with a shocking, seemingly unbelievable fact that makes the reader want to delve further into your essay. This type of opener is especially useful for persuasive and expository essays .
A key thing to consider while using this opener is to make sure it ties to the rest of your introduction. Relevancy is key to an effective opener.
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
The richest 1% of the world’s population owns more wealth than the remaining 99% combined. As the gap between the ultra-rich and the rest of society continues to widen, questions about fairness, social mobility, and the sustainability of such a system become increasingly critical to address.
Approximately 450 million people worldwide are currently living with mental health disorders, yet stigma and discrimination persist, preventing many from seeking the help they desperately need.
The universe is estimated to contain more than 2 trillion galaxies, each harboring billions of stars. With such mind-boggling vastness, the question arises: Are we alone?
B. Question
Wondering how to start an introduction in an essay using a unique format? Just ask a question! Starting off your essay with a question makes your essay more interactive, as it directly addresses the reader. It adds an element of interest to your essay making it much more engaging as compared to a passive, boring statement.
It also encourages the reader to form their own opinion on a particular topic. This type of opener is best suited for persuasive and argumentative essays .
Here are a few examples:
Are we playing with nature’s blueprint while unlocking unprecedented medical breakthroughs? Delving into the ethical considerations surrounding genetic engineering opens up Pandora’s box of questions about the balance between scientific progress, ethical boundaries, and the long-term consequences for humanity.
Is personal privacy a casualty of the digital age, or can we strike a balance between technological convenience and safeguarding our personal information? Examining the implications of surveillance, data collection, and cybersecurity challenges us to reassess the boundaries of privacy in an interconnected world.
Can machines truly possess intelligence and consciousness? Exploring the ethical and philosophical implications of AI raises fundamental questions about the nature of humanity and the boundaries of technological advancement.
C. Dramatized opening
We’ve already taken a look at how to start an essay introduction for different types of academic essays. Hence, we must also figure out how to start a paragraph in an essay when it comes to creative writing.
Innovative and dramatic opening statements are key factors in creative essay types. These openings are used to create a scene that the reader can step into.
This type of opening is commonly used in personal essays , narrative essays , and descriptive essays. However, they can also be used in persuasive essays to put across your point.
Let’s take a look:
In the depths of a moonlit forest, a lone figure emerged, carrying the weight of a secret that would unravel the very fabric of their existence.
Nestled amidst emerald green hills, a quaint village exuded an old-world charm. Its cobblestone streets were lined with charming cottages adorned with cascading flowers.
The ancient ruins stand stoic and weathered, their crumbling stone walls echoing the whispers of history. For centuries, this city has invited visitors to step back in time and unravel their enigmatic stories.
D. Impactful quote
Another key technique to kick off your opening statement is to impart knowledge from experts. This can be done with the help of a powerful quote that foreshadows the theme and topic of your essay.
This technique is highly versatile and can be used for all essay types. However, it is key to take into account that your opening quote is relevant to the rest of your essay. An unrelated quote may have the opposite effect and may confuse the reader!
Here are a few impactful opening quotes:
According to Winston Churchill “The Industrial Revolution was a revolution of profound consequences, an age of wonders that turned the wheels of progress and forever changed the course of human history.” According to the recent evidence, this statement seems to ring true.
“The pain of mental illness knows no boundaries of age, and in the battle against depression, it is our duty to lend a helping hand and provide a ray of hope to the young souls navigating through the darkness.” A profound statement quoted by first lady, Michelle Obama. Mental health disorders affect millions of people worldwide, and the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized the global burden of mental health as a significant public health challenge. However, many people do not receive the necessary mental health care they need due to various social, and economic barriers.
As famous anthropologist Jane Goodall correctly pointed out, “Genetic modification holds the key to unlocking the mysteries of life, but we must tread cautiously, for with great power comes great responsibility.” While genetic modification holds tremendous potential to improve agriculture, healthcare, and overall human well-being, we can’t turn a blind eye to the potential dangers and ethical concerns associated with this practice.
E. Main idea
Some essays require no beating around the bush and should get straight to the point. The goal is to be as clear, concise, and succinct as possible.
In such cases, it is a good idea to simply begin your essay with the main idea. This sort of opening statement is especially useful for analytical and argumentative essays as it immediately conveys your stance on an argument.
Here are a few succinct opening statements:
Smoking should be universally prohibited due to its severe health risks for both smokers and involuntary bystanders, its strain on public healthcare systems, and its negative impact on societal well-being.
Subsidized college education is crucial to the development of society. It enhances accessibility, promotes social mobility, reduces disparities, and empowers individuals to contribute to the economy.
Dismissing emotional support animals as a scam overlooks their well-documented therapeutic benefits of providing genuine support to individuals with mental health issues.
Now that we’ve understood how to start a paragraph in an essay with the help of a hook, let’s move on to providing the necessary context.
2. Provide essential background information
The introduction to an essay consists of more than just a hook and the main idea. In order to learn how to start an introduction for an essay, it is crucial to understand what background information needs to be included in your introduction. The goal is to acquaint the reader with the background of your topic or argument without getting into the specifics. The background information may include:
- Historical and social background
- Geographical facts
- Past research or theories on a particular argument
- Definition of terminologies in case of a highly technical essay
Although the background information provides context to your thesis statement, it should be highly generalized. It is a good idea to save the more detailed bits for the body paragraphs. The length and scope of your background information depend on the complexity of your essay. But keep it fairly broad and do not delve into the specifics.
Let’s take a look at a few examples of background information:
The following example provides background information for the topic “Why Domestication of Wild Animals Should Be Prohibited”.
Wild animals play critical roles in maintaining ecological balance within their natural habitats. Removing them from their natural environments disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to potential negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Here’s an essay introduction example on the topic “Experiencing the Beauty of Hana Matsuri in Japan”:
Hana Matsuri, also known as the “Flower Festival” or “Buddha’s Birthday,” is a significant annual festival celebrated in Japan to commemorate the birth of Siddhartha Gautama, who later became known as Buddha. The festival takes place on April 8th or the nearest Sunday, depending on the region.
The final example is based on the topic ”Changes in the Post-Covid Work Culture”.
Pre-pandemic, many organizations had a traditional office-based work culture, where employees would commute to a physical workspace and work regular hours. This allowed for face-to-face interactions, team collaboration, and a sense of community among coworkers.
3. Present your main idea or thesis statement
In order to construct an impactful introductory paragraph, its foundation must be strong. It is crucial to construct a rough idea of your thesis statement even before writing an introducton paragraph. A good thesis statement should be broad enough to be elaborated on. But you need to make sure that it’s not too broad since an overabundance of information will make the essay tedious to work upon.
The thesis statement is the most important part of your essay. It is the premise or argument upon which the entire essay is based. A good thesis statement summarizes the main argument of your essay in just a few sentences.
Let’s take a look at a few impactful thesis statements:
The following thesis statement is based on the topic “Harvesting the Rain”.
Rainwater harvesting represents a sustainable and effective solution to combat water scarcity by capturing and utilizing rainfall, thereby alleviating the pressures on traditional water sources, promoting self-sufficiency, and fostering long-term environmental and societal resilience.
Here’s an example of a thesis statement for the topic “Unveiling the Mysteries of the Medieval World”:
The medieval period, characterized by its rich tapestry of cultural, social, and political developments, shaped the course of history through its influence on governance, religion, arts, and the emergence of a distinct feudal system.
Here’s one on the topic “Tracing the Journey of Canine Domestication”:
The domestication of dogs, a complex process spanning thousands of years, not only transformed wolves into loyal companions but also had profound impacts on human society.
4. Provide a general overview
Although this step is optional, it is a good idea to provide a general overview of your essay in the introduction paragraph. This is especially beneficial for longer essays. It gives the reader a gist of what is to be expected and the points that you will be covering.
Let’s take a look at a few examples:
The following overview is for the topic “Life in the Victorian Era”.
The essay begins with a discussion of social segregation and class division in the Victorian era. It then highlights the impact of the industrial revolution on Victorian society. Finally, it discusses the influence of Victorian morals, values, and art on modern society.
Now that we’ve figured out how to write introductions for essays let’s take a look at a few introduction examples for essays.
Essay introduction examples
To guide you in your essay writing journey, we’ve also provided a few good introductions for essays. Since different essay types have different types of introduction paragraphs, we’ve provided examples of how to start an essay for the four main essay types (narrative, descriptive, argumentative, and expository essay).
Narrative essay introduction example
The following narrative essay introduction example revolves around the everyday struggles faced by a person of color living as an immigrant in a foreign nation.
- Background information
- Thesis statement
As the sun rose on a seemingly ordinary day, little did I know that it would mark the beginning of a journey that would shape my identity, challenge my perceptions, and lead me to discover the profound significance of being a person of color. In a world that prides itself on diversity and equality, the lived experiences of individuals from marginalized communities often remain obscured, untold, and overshadowed by dominant narratives. However, I am unafraid to delve into the depths of my personal journey. Through the exploration of pivotal moments, encounters, and self-reflection, I will unveil the complexities and nuances of my life, shedding light on the triumphs, struggles, and transformative experiences that have shaped my understanding of self, others, and the world around me.
Descriptive essay introduction example
The following descriptive essay introduction highlights the beauty of a leisurely walk through the park.
In the hustle and bustle of modern life, where time slips through our fingers like grains of sand, there exists a tranquil refuge—a haven where the frenetic pace slows and the soul finds solace. This refuge is none other than a park—a sanctuary of greenery, a tapestry of serenity nestled within the heart of urban landscapes. It is a place where nature’s gentle symphony mingles with the whispers of the wind, where vibrant hues dance on the canvas of the sky, and where the weary spirit finds respite in the embrace of tranquility. Through the lens of this leisurely stroll, we can unravel the secrets of nature’s embrace, illuminating how a simple walk in the park can rejuvenate our senses, soothe our souls, and reconnect us with the innate beauty of the natural world.
Argumentative essay introduction example
The following argumentative essay introduction revolves around the age-old debate of nature vs. nurture.
The eternal question of whether our genes or our environment shape us as individuals has sparked a timeless debate—the battle between nature and nurture. The nature versus nurture debate revolves around the influence of our genetic inheritance (nature) and the impact of our environment (nurture) on our development, behavior, and essence. The nature perspective argues for the predominance of our innate characteristics determined by our genes, while the nurture perspective emphasizes the crucial role of external factors such as upbringing, social interactions, and cultural influences in shaping our identities. However, a deeper exploration reveals a dynamic interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental factors in human development. The integration of both nature and nurture is essential for comprehending the complexities of individual growth, transcending the boundaries of a simplistic dichotomy.
Expository essay introduction example
The following expository essay introduction describes the world before the advent of the internet and other digital devices.
- Background information
Picture a world without smartphones, social media, or instant connectivity—a time when information was sought from physical encyclopedias, conversations happened face-to-face, and the written word carried a tangible weight. Before the digital age emerged communication, information retrieval, and daily life unfolded through traditional means. Printed books, landline telephones, handwritten letters, and physical newspapers formed the foundation of knowledge dissemination and interpersonal connections. During this analog era, people relied on physical maps for navigation, shopping in brick-and-mortar stores, and cherished personal photo albums to safeguard memories. It was an era that demanded patience and perseverance to acquire information and establish connections. The pre-digital age offered a distinctive combination of challenges and opportunities, providing a glimpse into a simpler, more deliberate way of life. Through an exploration of its defining characteristics, we can gain deeper insights into the impact of the digital revolution on society.
Now that you’ve discovered how to write an essay introduction, you can use this information to create an engaging introduction. After you create your introduction and write the rest of the essay, you’ll also need to edit your essay. Since we provide essay editing services , we’d love to make your work easier.
We’ve also created many resources to help you write high-quality essays and resolve any confusion you may have. Bookmark the resources given below to write the best essay!
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a good essay introduction, what is the purpose of the introduction in an essay, how to write an introduction for an argumentative essay, which statement best describes the introduction of an argumentative essay, what is a good example of a persuasive essay introduction.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Additional Resources
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Essay Writing Guide
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Citation and Referencing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Excellent Essay Introduction

- 3-minute read
- 27th September 2022
Love it or hate it, essay writing is a big part of student life. Writing a great essay might seem like a daunting task, especially when you’re staring at a blank document, but there are formulas you can follow to make sure your paper hits the mark.
When you plan your essays , don’t neglect your introduction! It might seem like a trivial part of the paper, but it can make it or break it. A badly written introduction can leave your reader feeling confused about the topic and what to expect from your essay.
To help your writing reach its full potential, we’ve put together a guide to writing an excellent essay introduction.
How to Write an Essay Introduction
An essay introduction has four main steps:
● Hook your reader
● Provide context
● Present your thesis statement
● Map your essay
Hook Your Reader
The first part of your introduction should be the hook. This is where you introduce the reader to the topic of the essay. A great hook should be clear, concise, and catchy. It doesn’t need to be long; a hook can be just one sentence.
Provide Context
In this section, introduce your reader to key definitions, ideas, and background information to help them understand your argument.
Present Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences.
Map Your Essay
Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your reader a sense of direction.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction:
Hook: Suspense is key for dramatic stories, and Shakespeare is well-known and celebrated for writing suspenseful plays.
Context: While there are many ways in which Shakespeare created suspension for his viewers, two techniques he used effectively were foreshadowing and dramatic irony. Foreshadowing is a literary device that hints at an event or situation that is yet to happen. Dramatic irony is a literary technique, originally used in Greek tragedy, by which the full significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience or reader, although it is unknown to the character.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Thesis statement: Foreshadowing and dramatic irony are two powerful techniques that Shakespeare used to create suspense in literature. These methods have been used to keep the reader intrigued, excited, or nervous about what is to come in many of his celebrated works.
Essay mapping: In this essay, I will be detailing how Shakespeare uses foreshadowing and dramatic irony to create suspense, with examples from Romeo and Juliet and Othello.
Pro tip: Essays take twists and turns. We recommend changing your introduction as necessary while you write the main text to make sure it fully aligns with your final draft.
Proofread and Editing
Proofreading is an essential part of delivering a great essay. We offer a proofreading and editing service for students and academics that will provide you with expert editors to check your work for any issues with:
● Grammar
● Spelling
● Formatting
● Tone
● Audience
● Consistency
● Accuracy
● Clarity
Want 500 words of your work proofread completely free of charge?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Essay Introduction Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Always have a road map for an essay introduction . Having a strong essay introduction structure is critical to a successful paper. It sets the tone for the reader and interests them in your work. It also tells them what the essay is about and why they should read it at all.
It shouldn't leave the reader confused with a cliffhanger at the end. Instead, it should generate interest and guide the reader to Chapter One. Using the right parts of an essay introduction can help with this.
Check out an effective essay introduction structure below. It’s a road map for writing an essay—just like the parts of essay introductions are road maps for readers.
Essay Introduction Structure
Attention-grabbing start
Outline of argument
Thesis statement
Some academics find the beginning the most difficult part of writing an essay , so our editors have created some examples of good essay introductions to guide you. Let's take a look at the samples below to see how the essay introduction structures come together.
If you are unsure about your paper, our essay editors would love to give you some feedback on how to write an essay introduction.
[1] According to Paul Ratsmith, the tenuous but nonetheless important relationship between pumpkins and rats is little understood: "While I've always been fascinated by this natural kinship, the connection between pumpkins and rats has been the subject of few, if any, other studies" (2008). [2] Ratsmith has been studying this connection, something he coined "pumpkinology," since the early 1990s. He is most well known for documenting the three years he spent living in the wild among pumpkins and rats. [3] Though it is a topic of little recent interest, the relationship has been noted in several ancient texts and seems to have been well understood by the Romans. Critics of Ratsmith have cited poor science and questionable methodology when dismissing his results, going so far as to call pumpkinology "rubbish" (de Vil, 2009), "stupid" (Claw, 2010), and "quite possibly made up" (Igthorn, 2009). [4] Despite these criticisms, there does appear to be a strong correlation between pumpkin patches and rat populations, with Ratsmith documenting numerous pumpkin–rat colonies across North America, leading to the conclusion that pumpkins and rats are indeed "nature's best friends" (2008).
Let's break down this example of a good essay introduction structure. The beginning hooks our attention from the get-go in section one. This is because it piques our curiosity. What is this strange relationship? Why has no one studied it? Then, section two gives us context for the topic. Ratsmith is an expert in a controversial field: pumpkinology. It's the study of the connection between pumpkins and rats.
The second half of the paragraph also demonstrates why this is a good essay introduction example. Section three gives us the main argument: the topic is rarely studied because critics think Ratsmith's work is "rubbish," but the relationship between pumpkins and rats has ancient roots. Then section four gives us the thesis statement: Ratsmith's work has some merit.
The parts of an essay introduction help us chart a course through the topic. We know the paper will take us on a journey. It's all because the author practiced how to write an essay introduction.
Let’s take a look at another example of a good essay introduction.
[1] Societies have long believed that if a black cat crosses one's path, one might have bad luck—but it wasn't until King Charles I's black cat died that the ruler's bad luck began (Pemberton, 2018). [2] Indeed, for centuries, black cats have been seen as the familiars of witches—as demonic associates of Satan who disrespect authority (Yuko, 2021). Yet, they have also been associated with good luck, from England's rulers to long-distance sailors (Cole, 2021). [3] This essay shows how outdated the bad luck superstition really is. It provides a comprehensive history of the belief and then provides proof that this superstition has no place in today's modern society. [4] It argues that despite the prevailing belief that animals cause bad luck, black cats often bring what seems to be "good luck" and deserve a new reputation.
This example of a good essay introduction pulls us in right away. This is because section one provides an interesting fact about King Charles I. What is the story there, and what bad luck did he experience after his cat passed away? Then, section two provides us with general information about the current status of black cats. We understand the context of the essay and why the topic is controversial.
Section three then gives us a road map that leads us through the main arguments. Finally, section four gives us the essay's thesis: "black cats often bring what seems to be 'good luck' and deserve a new reputation."
Still feeling unsure about how to write an essay introduction? Here's another example using the essay introduction structure we discussed earlier.
[1] When the Lutz family moved into a new house in Amityville, New York, they found themselves terrorized by a vengeful ghost (Labianca, 2021). Since then, their famous tale has been debunked by scientists and the family themselves (Smith, 2005). [2] Yet ghost stories have gripped human consciousness for centuries (History, 2009). Scientists, researchers, and theorists alike have argued whether ghosts are simply figments of the imagination or real things that go bump in the night. In considering this question, many scientists have stated that ghosts may actually exist. [3] Lindley (2017) believes the answer may be in the quantum world, which "just doesn’t work the way the world around us works," but "we don’t really have the concepts to deal with it." Scientific studies on the existence of ghosts date back hundreds of years (History, 2009), and technology has undergone a vast evolution since then (Lamey, 2018). State-of-the-art tools and concepts can now reveal more about ghosts than we've ever known (Kane, 2015). [4] This essay uses these tools to provide definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm.
This example of a good essay introduction uses a slightly different strategy than the others. To hook the reader, it begins with an interesting anecdote related to the topic. That pulls us in, making us wonder what really happened to the Lutzs. Then, section two provides us with some background information about the topic to help us understand. Many people believe ghosts aren't real, but some scientists think they are.
This immediately flows into section three, which charts a course through the main arguments the essay will make. Finally, it ends with the essay's thesis: there is definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm. It all works because the author used the parts of an essay introduction well.
For attention-grabbing introductions, an understanding of essay introduction structure and how to write an essay introduction is required.
Our essay introduction examples showing the parts of an essay introduction will help you craft the beginning paragraph you need to start your writing journey on the right foot.
If you'd like more personalized attention to your essay, consider sending it for Essay Editing by Scribendi. We can help you ensure that your essay starts off strong.
Image source: Prostock-studio/Elements.envato.com
Let’s Get Your Essay Ready to Wow an Audience
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

How To Start An Essay (With 20 Great Examples)
Facing a blank page and unsure how to start your essay? Crafting a compelling essay isn’t innate for everyone. While it’s about presenting clear ideas, even top students can struggle. For many, meeting deadlines or ensuring quality becomes daunting, leading them to consult professionals like do my essay cheap . These experts whip up top-tier essays swiftly. A standout essay can elevate your academic status, with the introduction being the pivotal hook. Many opt to hire essay writers for that impeccable start. But crafting an engaging intro is doable. Want to captivate your readers immediately? Or impress academic panels? If the task still feels daunting, there’s always the option to buy assignments online for guaranteed quality. But let’s explore ways to start an essay on your own.
How to start your essay? – The most straightforward advice
How to begin your essay – the lengthier and more appropriate advice, but regardless of the format of the essay , the introduction should still have these basic ingredients:, how long should an essay introduction be.
It all depends on the overall length of your essay. If it’s a standard, five-paragraph college essay , the introduction should only take one paragraph or 60-80 words. But if you’re writing something longer, for example, a five-page interpretation of a literary work, the introduction could take two to three paragraphs or 120-150 words. You can measure the length using a simple word counter but don’t obsess too much about the number. The crucial thing is to say what you need to say and impact the reader.
The aim of the introductory paragraph
If you truly want to learn how to begin an essay, there are three best ways to do it:, 20 great examples and tips on how to start an essay:, 1. describe a setting and start with an emotional punch, 2. start with a deeply personal story from your childhood, 3. create a mysterious atmosphere.
“Moths that fly by day are not properly to be called moths; they do not excite that pleasant sense of dark autumn nights and ivy-blossom which the commonest yellow-underwing asleep in the shadow of the curtain never fails to rouse in us.” – Virginia Woolf – Death of the Moth
4. Throw the reader straight into the middle of the events
5. start with universal questions of life and death, 6. start with a question and then answer it, 7. start with irony.
“In Moulmein, in Lower Burma, I was hated by large numbers of people – the only time in my life that I have been important enough for this to happen to me.” – George Orwell – Shooting an Elephant
8. Begin by creating great expectations of what’s to come (use the introduction as bait)
9. start with a puzzle (notice how you start to wonder who is she talking about in this introduction), 10. start with dark humor.
“When I was young, I thought Life: A User’s Manual would teach me how to live and Suicide: A User’s Manual how to die.” – Édouard Levé – When I Look at a Strawberry, I Think of a Tongue
11. Start with an unusual question that will pull the readers in
12. commence by taking the reader into the world of mystery and awe, 13. state your thesis at the very beginning – be clear about it.
“Science has beauty, power, and majesty that can provide spiritual as well as practical fulfillment. But superstition and pseudoscience keep getting in the way providing easy answers, casually pressing our awe buttons, and cheapening the experience.” – Carl Sagan – Does Truth Matter – Science, Pseudoscience, and Civilization
14. Start with the obvious that’s not so obvious after all
“To do something well you have to like it. That idea is not exactly novel. We’ve got it down to four words: “Do what you love.” But it’s not enough just to tell people that. Doing what you love is complicated.” – Paul Graham – How To Do What You Love
15. Be unpredictable and highly intellectual
“Once, in a dry season, I wrote in large letters across two pages of a notebook that innocence ends when one is stripped of the delusion that one likes oneself. Although now, some years later, I marvel that a mind on the outs with itself should have nonetheless made painstaking record of its every tremor, I recall with embarrassing clarity the flavor of those particular ashes. It was a matter of misplaced self-respect.” – Joan Didion – On Self Respect
16. Get straight to the point
17. start in a deeply emotional, poetic manner, 18. begin by describing the place and circumstances in great detail.
“Two blocks away from the Mississippi State Capitol, and on the same street with it, where our house was when I was a child growing up in Jackson, it was possible to have a little pasture behind your backyard where you could keep a Jersey cow, which we did. My mother herself milked her. A thrifty homemaker, wife, and mother of three, she also did all her cooking. And as far as I can recall, she never set foot inside a grocery store. It wasn’t necessary.” – Eudora Welty – The Little Store
19. Start by presenting an original idea (frame it in a way that the reader never considered before)
“Saints should always be judged guilty until they are proved innocent, but the tests that have to be applied to them are not, of course, the same in all cases. In Gandhi’s case the questions one feels inclined to ask are: to what extent was Gandhi moved by vanity — by the consciousness of himself as a humble, naked old man, sitting on a praying mat and shaking empires by sheer spiritual power — and to what extent did he compromise his principles by entering politics, which of their nature are inseparable from coercion and fraud?” – George Orwell – Reflections on Gandhi
20. Be clear-headed and approach the subject as objectively as possible
Rafal reyzer.
Hey there, welcome to my blog! I'm a full-time entrepreneur building two companies, a digital marketer, and a content creator with 10+ years of experience. I started RafalReyzer.com to provide you with great tools and strategies you can use to become a proficient digital marketer and achieve freedom through online creativity. My site is a one-stop shop for digital marketers, and content enthusiasts who want to be independent, earn more money, and create beautiful things. Explore my journey here , and don't miss out on my AI Marketing Mastery online course.
How to Write an Essay Introduction?
16 January, 2021
8 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
You have been assigned to write an essay but you’re not quite sure how to get started. Don’t worry, after reading this introduction, you will have a better grasp on what you should do. The introduction of an essay is the first thing that a reader will see, so it can influence how your entire essay is received. Be sure to take your time to make it effective. Before you start, you should first identify the purpose of your introduction.

Why do I Need an Introduction Paragraph?
You’re writing an introduction to your essay for two reasons. First, its purpose is to hook your readers so that they will read on and see what you have to say. Second, it will provide a guideline for your topic and main argument, known as the thesis statement. Your first sentences should pull the readers in – this is the hook that tells your readers something they didn’t know before. It can be an interesting fact, a surprising statistic, or a quote from a well-known person. Basically, it can be anything that has the ability to catch your readers’ attention. Choose the right hook based on your topic and style. Your readers need enough information to understand the background of your essay. Make sure, however, to keep it short, too, not to lose their interest. Your thesis statement, on the other hand, should provide an answer to the main problem of your essay.

How Long Should an Essay Introduction Be?
This depends on the overall length of your essay. There is no set rule for how long an introduction should be. For a 2- to a 3-page essay, the appropriate length is usually one paragraph. But in case the overall length of your essay is more, for example, 4−5 pages, two paragraphs is considered more appropriate. A general rule is that your introduction should be between 5 and 10 percent of the overall length of your essay.
How to Write a Good Essay Introduction?
Being able to write a good essay is an essential skill for your future. As many as 80 percents of corporations with employment growth potential assess their applicants’ writing skills during the hiring process.
To write a good introduction paragraph, you need to first identify your audience. You want your essay to evoke emotions and to keep your readers interested from start to finish. Before you can do that, you need to know who your readers are. If you’re writing an essay as a class assignment, you don’t necessarily have to write for your instructor. Choose your audience based on the subject matter of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about career paths, you may want to identify students and young professionals as your target audience. Your target audience determines what information you should include and what you can leave out.
To make the introduction of your essay effective, you can appeal to your readers’ emotions. This is a good strategy, especially when writing a persuasive essay introduction about a personal topic. It will help you get your audience emotionally involved in the topic. For example, if you’re writing an essay about foreign aid, you can describe the tragedy of undernourished children to evoke some emotions in your readers. Another strategy is to ask thought-provoking questions. This way, you will draw your readers in by making them think about your subject matter. As long as these questions are intriguing enough, your readers will want to find out the answers.

Move From the General to the Specific
Perhaps you have heard of the upside-down pyramid. Place your hook at the top, and use 2 to 3 sentences to describe the wider context of your thesis. You should try to make each sentence more specific than the one before it. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the crimes committed by refugees, you could start with an anecdote about a victim of these crimes. Then you could provide statistics about the problem in a specific country, and finally narrow it down to a particular age group or social group.
Make a Smooth Transition to the Body
In many cases, you can move straight from your introduction to the first paragraph of your body. Sometimes, however, you may need a transition sentence to move naturally to the rest of your essay. You can test whether you need this transition sentence by reading your introduction and the first paragraph of your body out loud. If you find yourself pausing between the two paragraphs, it’s better to write a transition sentence.
Pay Attention to Your Structure
Keep in mind that it’s not necessary to write the introduction first. In fact, it’s often easier to write it after writing the body and conclusion. On the other hand, others find it convenient to write the introduction first and use it as an outline for the rest of the essay.
While your introduction needs to be short, it should also convey a lot of information. The first sentence is your hook that catches your readers’ attention. The next sentences build a bridge between your hook and the general topic of your essay. The ending sentence of your introduction should include your thesis statement or points that you will discuss in more detail in the body and which support the main argument of your essay.
Remember to Revise
This is important for those who prefer to write their introduction first. Since it’s not uncommon to deviate from your outline, make sure that your introduction is in line with your completed essay. Make every sentence count and remove any unnecessary parts.
In case you’re struggling to find the time for your essay, you can always contact our essay writer . We have been in the business long enough to know the ins and outs of a perfect essay. Save your time and let us ease your burden.
Check Some Essay Introduction Examples
Now that you know the theory behind writing an effective essay introduction, it’s time to see things in practice. Samples are useful for learning how to put all the information into action. Check the samples below to figure out what your introduction should look like.
Argumentative Essay Introduction
In an argumentative essay introduction, you should present your own personal opinion on the topic based on your evaluation which you will present in the body.

You can also check this argumentative essay sample.
Persuasive Essay Introduction
Persuasive essay introduction also should attempt to convince readers to believe in an idea or opinion. It needs to showcase some personal attitude to the topic.

You can also check more in-depth instructions for writing a persuasive essay.
Compare and Contrast Essay Introduction
A compare and contrast essay introduction should describe two sides of a problem. It’s easier to consider two very different things. You can start with a brief description of the problem and then move on to talk about the two things.

You can also check topic ideas for your compare and contrast essay.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Essay Writing Guide
How To Start An Essay
How to Start an Essay? Tips for an Engaging Start
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 370+ Essay Topics for Students
Common Types of Essays - Sub-types and Examples
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
How to Write an Essay Outline in 5 Simple Steps
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
Tips On How to Make an Essay Longer: 15 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay Properly- An Easy Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
A Guide to Writing a Five-Paragraph Essay
How To Write A Strong Body Paragraph
Starting an essay can often feel like the hardest part of writing. You may have a well-structured outline and a clear idea of what you want to convey, yet struggle to find the perfect opening lines.
This is a common challenge that many writers face, but it’s necessary to overcome it to set the tone for a compelling essay.
In this blog, we will explain everything about starting an essay. We will discuss how to begin different parts of essays and what are some common ways to start an essay. Additionally, we'll highlight some common mistakes to avoid in your essay's introduction.
So let's get started!
- 1. 7 Tips to Start an Essay
- 2. Words To Start An Essay Introduction
- 3. Sentences To Start An Essay
- 4. How to Start an Essay - Examples
- 5. Mistakes to Avoid When Starting an Essay
7 Tips to Start an Essay
When writing an essay a good opening is like setting the stage for a performance—get it right, and you’ll have your audience hooked from the start.
Let's look at some useful methods to start your essay strongly.
Tip 1. Start with a Hook
The first stage in writing a compelling essay opening is to hook your reader. This could be a surprising fact, a provocative question, a quote, or even a vivid description that grabs attention.
For example, you might start with a startling statistic: "Did you know that 90% of startups fail within their first year?" Such a fact immediately intrigues the reader and sets the stage for discussing entrepreneurial challenges.
Tip 2. Provide Context or Background
Once you’ve hooked your reader, it’s important to provide some context or background information relevant to your topic. This helps orient your reader and sets up the framework for your thesis.
For instance, if your essay is about the impact of social media on mental health, you might briefly outline the rise of social media platforms and their pervasive influence on society today.
Tip 3. State Your Thesis Clearly
Next, state your thesis statement clearly and concisely. Your thesis should outline the main argument or position you will be discussing in the essay. This acts as a roadmap for your readers, guiding them through the points you will explore.
For example, in an essay arguing for stricter gun control laws, your thesis might assert: "Effective gun control measures are necessary to reduce firearm-related violence and ensure public safety."
Tip 4. Use Narrative or Anecdotal Openings
Another effective strategy is to start your essay with a narrative or anecdote. This approach works well for personal essays or when you want to humanize your topic.
For instance, you could begin with a personal story about an experience that shaped your views on environmental conservation if your essay discusses sustainability issues.
Tip 5. Pose a Thought-Provoking Question
Engage your reader by posing a thought-provoking question that encourages them to think critically about your topic. This technique is particularly effective in persuasive essays where you want to prompt your reader to consider your argument.
For example, in an essay advocating for universal healthcare, you might ask: "Should access to healthcare be considered a basic human right?"
Tip 6. Use a Relevant Quote
Drawing on the wisdom of others can lend authority and depth to your essay introduction. Choose a quote that resonates with your topic and supports your thesis. Make sure it's relevant and enhance the reader's understanding of your argument.
For instance, if your essay explores the theme of perseverance in the face of adversity, you might begin with a quote from Nelson Mandela: "It always seems impossible until it's done."
Here are some more examples to clear your understanding of how to start an essay with a quote:
- "‘The only limit to our realization of tomorrow will be our doubts of today.’ — Franklin D. Roosevelt. This quote reminds us that our beliefs about what's possible can shape our future."
- "‘In three words I can sum up everything I've learned about life: it goes on.’ — Robert Frost. This quote reflects the resilience of life and encourages us to keep moving forward."
- "‘You must be the change you wish to see in the world.’ — Mahatma Gandhi. Gandhi’s quote challenges us to take action and be proactive in creating the changes we want to see around us."
Tip 7. Directly State Your Argument
Finally, consider starting your essay by directly stating your main point or argument. This approach is straightforward and works well for analytical essays where clarity and precision are key.
For example, in an essay analyzing the impact of globalization on cultural identity, you might open with a declarative statement: "Globalization has irrevocably altered traditional cultural practices worldwide."
Words To Start An Essay Introduction
Here are some effective words and phrases to begin an essay introduction:
- Intriguingly: Intriguingly, the concept of...
- Unquestionably: Unquestionably, the most critical issue is...
- Surprisingly: Surprisingly, the data reveals...
- Notably: Notably, this phenomenon has far-reaching implications.
- Evidently: Evidently, the evidence suggests...
- Arguably: Arguably, one of the most contentious topics is...
- It is imperative to: It is imperative to address the issue of...
- Historically: Historically, this problem has persisted for centuries.
- In today's context: In today's context the relevance of this cannot be overstated.
- To illustrate: To illustrate, consider the following example….
- In contemporary society: In contemporary society, the issue of...
- Remarkably: Remarkably, few have explored the implications of...
- Undoubtedly: Undoubtedly, this problem warrants immediate attention.
- Consequently: Consequently, this leads us to question...
- In light of this: In light of this, it becomes evident that...
- Fundamentally: Fundamentally, the core issue revolves around...
- In recent years: In recent years, there has been a growing interest in...
- In an ever-changing world: In an ever-changing world, it is crucial to consider...
- To shed light on: To shed light on this matter, we will delve into...
- As a result: As a result, we are compelled to explore the implications of…
Sentences To Start An Essay
Here are some interesting sentences to start an essay:
- Have you ever wondered about the impact of climate change on our planet?
- In a remote village nestled among the mountains, a young girl's journey began.
- "The only thing we have to fear is fear itself," said Franklin D. Roosevelt.
- Shockingly, 70% of marine life is threatened by plastic pollution.
- While some embrace technology, others yearn for a simpler, analog life.
- Democracy, the cornerstone of modern societies, is often misunderstood.
- A tranquil dawn, with the sun's first rays painting the sky in hues of gold.
- Did you know that octopuses have three hearts and blue blood?
- As a child, I often marveled at the stars, wondering about the cosmos.
- Society teeters on the brink of a digital revolution that will redefine human existence.
How to Start an Essay - Examples
Examining various essay introduction examples provides valuable insights into captivating your reader's interest right from the start.
Check out these examples for guidance on crafting powerful opening lines.
How to Start an Essay Introduction?
To start an essay introduction, begin with a hook that grabs the reader's attention. Next, provide some background information on the topic. Finally, clearly state your thesis to outline the main argument of your essay.
Here is an example of how to write an essay introduction to help you understand this better.
Expository Essay Introduction
Argumentative Essay Introduction
How to Start a Paragraph in an Essay?
The best way to start a paragraph in an academic essay is to write the topic sentence. The topic sentence tells the reader what the paragraph is going to be about. After the topic sentence, the supporting details are further provided.
Read this example to know how to start a paragraph.
How to Start a Paragraph in an Essay?
How to Start a Conclusion in an Essay?
To start a conclusion in an essay, you should write a rephrased thesis statement first. As it is the crux of your whole essay. Further on, the points discussed in the essay can be summarized one by one in the concluding paragraph.
Here is an example of how to write a conclusion to help you understand this better.
How to Start a Conclusion in an Essay?
Mistakes to Avoid When Starting an Essay
Here are a few mistakes that should be avoided for writing a great essay introduction.
- Starting Without a Plan: Launching into your essay without a clear outline is a recipe for confusion.
- Weak, Generic Hooks: Using clichés or dull openings that fail to grab your reader's attention.
- Excessive Formality: Overloading your intro with formal language can bore your audience.
- Info Overload: Bombarding readers with too much background information can overwhelm them.
- Unclear Thesis: Failing to state your essay's purpose upfront leaves readers puzzled.
- Irrelevant Quotes: Using quotes that don't connect directly to your topic is a misstep.
- Ignoring Your Audience: Neglecting your audience's interests can lead to disengagement.
- Procrastinating Intro: Leaving the intro for last often results in rushed, ineffective beginnings.
- Repetitive Content: Repeating what's in the body of your essay makes the intro redundant.
- Skipping Proofreading: Overlooking errors in grammar and punctuation undermines your intro's credibility.
Still confused about how to begin your essay? Don't worry—help is just a click away! At MyPerfectWords.com , we specialize in offering professional paper writing services that provide 100% custom assistance.
If you're thinking, "Who can help me do my essay ?"—we've got you covered. Our expert online essay writers are available 24/7 to craft high-quality, custom essays that will earn you top grades.
Place your order now and get an amazing essay written in no time, guaranteed to impress your teachers!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction sentence for an essay.
A good instruction sentence for an essay is one that captures the reader's attention with an interesting hook. After writing the hook, give them some context by providing background information that will help set up what is to come in later paragraphs or sections of the paper/essay.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a thesis statement that states both concisely and specifically what main point(s) are being made about this topic along with why it matters.
What are 3 ways of starting your essay?
The three most recommended ways to start off an essay are:
- Quotation: By a famous person that fits the context of your essay.
- Question: That engages the reader to find the answer in your essay.
- Facts or Statistics: That is startling so that the reader’s attention can be grabbed.
What words can you use to start an essay?
Some words that can be used to start an essay are once, next, then, in fact, similarly, or a time word like first, second, third. You can also use sequential transitions to merge your hook to the rest of the introduction paragraph. These transition words include, for example, consequently, for this reason, or another addition transition.
What is a good paragraph starter?
A good paragraph starter is a brief yet complete topic sentence. The topic sentence should adequately give the reader an idea about what is going to be discussed in the rest of the paragraph. The topic sentence should also prove your thesis statement.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- [email protected]
- (650) 338-8226
Cupertino, CA

- Our Philosophy
- Our Results
- News, Media, and Press
- Common Application
- College Application Essay Editing
- Extracurricular Planning
- Academic Guidance
- Summer Programs
- Interview Preparation
Middle School
- Pre-High School Consultation
- Boarding School Admissions
College Admissions
- Academic and Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
- Senior Editor College Application Program
- Summer Program Applications
- Private Consulting Program
- Transfer Admissions
- UC Transfer Admissions
- Ivy League Transfer Admissions
Graduate Admissions
- Graduate School Admissions
- MBA Admissions
Private Tutoring
- SAT/ACT Tutoring
- AP Exam Tutoring
- Olympiad Training
Academic Programs
- Passion Project Program
- Science Research Program
- Humanities Competitions
- Ad Hoc Consulting
- Athletic Recruitment
- National Universities Rankings
- Liberal Arts Colleges Rankings
- Public Schools Rankings
Acceptance Rates
- University Acceptance Rates
- Transfer Acceptance Rates
- Supplemental Essays
- College Admissions Data
- Chances Calculator
- GPA Calculator
National Universities
- College Acceptance Rates
- College Overall Acceptance Rates
- College Regular Acceptance Rates
- College Early Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Overall Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Regular Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Early Acceptance Rates
Public Schools
- Public Schools Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Overall Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Regular Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Early Acceptance Rates
Liberal Arts
- Liberal Arts Colleges Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Overall Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Regular Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Early Acceptance Rates

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips + Examples

By Eric Eng

A 2019 study found that over 70% of students struggle with academic writing, and synthesis essays are no exception. If you’re having trouble thinking of how to write a synthesis essay, think of it like making a pizza. You can have all the ingredients separately, but combining them creates something that’s even more awesome. A synthesis essay blends different sources to build a strong, unified argument or analysis. When done right, the result is cohesive and compelling.
In this blog, you’ll discover a step-by-step guide on how to write a synthesis essay, complete with tips and tricks to make the process easier. By the end, you’ll have the skills and confidence to tackle any synthesis essay confidently.
What Is a Synthesis Essay?
How to start a synthesis essay, how to write a synthesis paragraph, synthesis essay example, tips for writing a killer synthesis essay, frequently asked questions.

A synthesis essay is a type of writing where you take information from different sources and use it to support a central idea or argument. The goal is to combine facts, data, and viewpoints from these sources to show how they connect and build a stronger case for your own perspective. Instead of just summarizing what each source says, you analyze and pull everything together to form a clear, unified argument.
A successful synthesis essay will:
- Present a clear thesis that states your main argument or claim.
- Use information from multiple sources to support that argument.
- Show how these sources connect and relate to one another.

The biggest challenge for many students? Getting started. Once you know how to begin, the rest falls into place! Here’s a foolproof guide to nailing your intro.
1. Begin with a hook.
Your first sentence should grab attention. Think of something surprising, thought-provoking, or intriguing. This could be an interesting statistic, a bold claim, or even a rhetorical question. The idea is to pique the reader’s interest so they feel compelled to keep reading.
Example of a hook:
“ Did you know that 60% of today’s workforce prefers remote work over traditional office settings? That statistic may surprise you, but it reflects a major shift in how we think about work in the 21st century. “
2. Introduce the topic.
After your hook, you’ll want to ease into your topic. Give a bit of background information so your readers understand what the essay is going to be about. This is where you can introduce the main sources or themes you’ll be synthesizing.
3. End with a thesis.
Your thesis statement is the backbone of your essay. It should clearly tell the reader what your essay will argue. Think of it as the roadmap for your paper. Without it, your reader will be lost!
Example of a thesis:
“ While both traditional office work and remote work offer their own advantages, a hybrid model that blends both approaches is the most effective in promoting productivity and work-life balance. “
The hook grabs attention, the topic is introduced, and the thesis makes it clear what the essay will argue. Having a hook is important because it grabs the reader’s attention right away, making them want to keep reading. It sets the tone for your essay and gives the reader a reason to stay engaged.

The body of your essay is where you’ll really dig into your argument, using your sources to back up your points. Each paragraph should be well-structured so your essay doesn’t feel like a random collection of facts. Here’s a simple breakdown for writing a strong synthesis paragraph:
1. Start with a topic sentence.
This sentence should introduce the main point of the paragraph. It acts as a mini-thesis for that section.
2. Provide evidence from your sources.
Now, it’s time to bring in the sources you’ve found during your research. Ideally, you’ll want to use at least two sources per paragraph to show how different authors or experts agree (or disagree) on your point. Always remember to properly cite your sources!
3. Analyze and synthesize.
The key to a synthesis essay is not just throwing in a bunch of quotes but showing your readers how these sources connect. How does one source support the other? Are they offering different perspectives that, when combined, give a fuller picture of your argument?
4. Conclude the paragraph.
Wrap up the paragraph by linking back to your main thesis. This reinforces how this particular point supports your overall argument.
Now that you’ve got the basics of a synthesis essay down, jump into some examples to see them in action. Use these examples to help you nail a strong introduction and a killer conclusion, so you can ace your AP Lit class!
The benefits of joining a sorority in college
Topic sentence
“ One of the key benefits of joining a sorority is the strong sense of community and support it provides. “
Evidence from sources
“ A 2021 study by the National Association of Student Affairs Professionals found that students involved in Greek life , particularly sororities, reported higher levels of social support and belonging compared to their non-Greek peers (Johnson, 2021). Additionally, research from the University of Southern California showed that sorority members were 25% more likely to graduate on time, citing strong mentorship and academic support within the organization (Davis, 2020). “
“ These studies demonstrate that sororities offer a built-in network of friends and mentors, which helps members navigate the challenges of college life. From emotional support to academic guidance, the sense of community within sororities fosters personal growth and success. “

Concluding sentence
“ Thus, joining a sorority can provide valuable resources and a strong support system, contributing to both academic achievement and personal development. “
Why the example works
This is a good example since it follows the structure of a strong paragraph while effectively supporting the argument. The topic sentence about how sororities provide a strong sense of community and support introduces the main idea and sets up the discussion.
Evidence from sources strengthens the claim by citing credible research, such as the study from the National Association of Student Affairs Professionals and the University of Southern California. These studies provide concrete data demonstrating how sorority members benefit academically and socially.
The analysis explains the connection between the evidence and the main argument and shows how the support system in sororities can help members succeed. The concluding sentence ties everything together and reinforces that joining a sorority can benefit academic and personal growth. This example flows well, uses reliable sources, and clearly supports the thesis.

Now that we’ve walked through the process, here are some tips to make sure your essay stands out :
1. Choose credible sources.
When you’re writing a synthesis essay, choosing reliable sources is crucial. Stick to reputable sources like academic articles, peer-reviewed studies, and books written by experts in the field.
Suppose you’re writing about the effects of climate change, in that case, an article from a scientific journal or a report from an organization like the EPA will carry much more weight than a random blog post or a website without proper credentials.
Think of your sources as the foundation of your essay. If they’re shaky or unverified, your argument won’t be as convincing. Avoid websites that don’t provide the author’s credentials or have questionable information. Trustworthy sources help build your credibility and make sure your essay is based on facts, not opinions or unreliable data.
If you’re looking for credible sources for your research, there are a bunch of great online tools you can use. Google Scholar is a reliable source of tons of academic articles, and JSTOR gives you access to journals and primary sources. For access to free, peer-reviewed articles in all sorts of fields, check out the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ).
2. Stay organized.
Working with multiple sources can get messy fast, especially when you’re juggling facts, quotes, and different perspectives. A great way to stay on top of things is to organize your sources by the sections of your essay.
For example, if you’re writing a paragraph about the benefits of online learning, make a note of which studies or articles you’ll pull from to support that point. You could use a digital tool like Google Docs or Evernote, or even just a notebook, to track your sources.
Jot down key facts and which source they came from so you’re not scrambling later. Staying organized helps ensure you don’t accidentally misattribute information or lose track of key data, making your writing process smoother and your essay more cohesive.
3. Be clear and concise.
It’s easy to get excited about all the interesting facts you find during your research, but remember that less is more. Every piece of information you include should directly support your thesis.
Let’s say you’re writing about the impact of technology on education. Instead of throwing in every statistic you come across, focus on the ones that strengthen your argument, like a study showing how virtual classrooms increase student engagement.
Resist the urge to overload your readers with too much information or veer off-topic. Keep it simple, and only include facts that are directly relevant to the point you’re trying to make. Your readers will thank you for staying on track, and your essay will be much more focused and persuasive.
4. Don’t forget to synthesize.
The key to a great synthesis essay is smoothly blending your sources into one cohesive argument. You don’t want your essay to feel like a random list of summaries or unrelated ideas. Instead, treat it like your sources are having a conversation.
Think of it this way, if one source talks about how social media is great for networking and another points out its negative impact on mental health, don’t just list them separately. Show how they’re connected.
You can do this by discussing how social media has its perks while also presenting the downsides that people need to balance. This approach helps your essay feel more connected and shows that you really understand the different perspectives. In a synthesis essay, it’s all about making those connections, not just throwing out facts.
1. How do I choose sources for a synthesis essay?
Select sources that are credible and relevant to your topic. Look for a mix of perspectives, such as scholarly articles, books, and reliable websites. The key is to find sources that provide valuable information to support your argument.
2. What is the best way to structure a synthesis essay?
A synthesis essay typically follows a standard structure. It has an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs that integrate and analyze your sources, and a conclusion that summarizes your main points and restates the thesis.
3. How do I write a strong thesis statement for a synthesis essay?
Your thesis should clearly present the main argument or point of view you’ve formed after analyzing your sources. It should reflect the central theme of your essay and guide the reader on what to expect from your synthesis.
4. How can I avoid summarizing sources instead of synthesizing them?
Instead of just restating what each source says, focus on finding connections between them. Compare and contrast the viewpoints, and discuss how they complement or contradict each other to build your own argument.
- A synthesis essay combines information from different sources to support a central argument or analysis. It’s not about summarizing sources but about connecting them to form a unified point of view.
- Start with a compelling hook to grab attention, introduce your topic clearly, and end with a solid thesis statement that outlines your main argument.
- Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence, use evidence from multiple sources, and synthesize those sources by showing how they relate to and support your argument.
- Use reputable, relevant sources, and keep your essay well-organized and concise, always linking back to your thesis. The key is synthesizing, not just summarizing.
- Need help with writing your synthesis essay? You can seek the help of a private consultant to give you feedback on your work.
Want to assess your chances of admission? Take our FREE chances calculator today!

Why College Admissions Isn’t Perfect

US News Rankings

The Personal Statement: The Holy Grail of College Admissions

The Modern Day 4.0 and 1600 SAT Score Student Is No Longer Impressive

The Competitive Nature of College Admissions for Asian Americans

The College Application

Our Comprehensive Approach

Ivy League Schools

How Early Should You Prepare for College?

Featured in US News & World Report Best Colleges Publication
Congratulations to AdmissionSight Students and their Acceptances!

College Rejection

College Rankings

College Consultants Could Make A Difference

College Admissions Scandal and Higher Education

How to Ask Someone to Be a Reference: Sample Email + Tips

How Many Times Can You Take the LSAT? Study Tips + Insights

What Is A DBQ Essay? Tips + Examples

Top 20 Colleges with the Lowest Acceptance Rates

How to Nail Your Overcoming a Challenge Essay: Advice and Tips

What Happens If You Fail a Class in College? Insights + Tips

Do You Need a Bachelor’s to Get a Master’s Degree?

Top 7 Hidden Ivies in the US: Stats + Tips

What Can You Do with a Philosophy Degree? Job Prospects + Insights

Top 16 National Awards for High School Students

Top 10 Best Sororities in the US

How to Superscore Your SAT: Insights + Tips

Life after College: Insights and Advice

11 Best STEM Colleges in the US

Best Law Student Jobs to Make Money During Law School
How to get into yale: admission requirements and tips, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Articles

How to Ask Someone to...

How Many Times Can You...

What Is A DBQ Essay?...

Top 20 Colleges with the...

How to Write a Synthesis...

How to Nail Your Overcoming...

What Happens If You Fail...

Do You Need a Bachelor’s...

Top 7 Hidden Ivies in...

What Can You Do with...

Top 16 National Awards for...

Top 10 Best Sororities in...
Sign up now to receive insights on how to navigate the college admissions process..

Admissions Counseling
- Academic & Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
Copyright © AdmissionSight 2024
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
Home > Blog > Expository Essay Examples: Top Tips To Improve Your Grade

Expository Essay Examples: Top Tips To Improve Your Grade
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: September 24, 2024
- General Guide About Content and Writing
Are you struggling to complete your expository essay and need help creating an outline? Then the expository essay tips in this article will help you overcome any problems you might have.
We’ll guide you on how to start your expository essay, discuss its structure, offer you expository essay examples, and include a section on the top mistakes you must avoid making so you can improve your writing flow . Let’s get started!

What Is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a form of writing that aims to explain, inform, or clarify a specific topic or idea. Unlike persuasive essays, which seek to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, expository essays are grounded in facts and objective analysis. The primary goal is to present information clearly and logically to enable the reader to understand the subject better.
Expository essays usually include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. They begin with a thesis statement that outlines the main topic or argument. Then each body paragraph develops a distinct aspect of the thesis.
Furthermore, there is a lot of supporting evidence evidence such as statistics, examples, or expert quotes. This is the core of the work that you’ll need to do during expository essay writing. Hence, the research phase is important to ensure that you have all the information you need.
Different Types of Expository Essays
Now let’s turn our attention to the various types of expository essays that you might come across. This will help you get ready for one of these assignments in your academic writing classes. Here’s a list of expository writing types:
- Descriptive essay: A descriptive essay vividly portrays a person, place, event, or object using sensory details. This is done by appealing to the reader’s senses, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. Hence, the writer creates a vivid image that engages emotions, so descriptive language is key to getting a passing grade.
- Cause and effect essays: This essay explores the reasons behind an event and its consequences. You’ll need to analyze a specific cause and its effects, and the writer clarifies complex relationships. Effective organization and supporting evidence help readers understand the connections between events.
- Process essay: A process essay outlines the steps needed to complete a specific task. It provides clear and chronological instructions, which often include details and explanations for each step. The goal is to guide readers through the process easily.
- Comparison and contrast essay: As the name suggests, this essay examines the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It can discuss each subject separately or address points of comparison and contrast in a structured manner.
- Definition essay: A definition essay explains the meaning of a term or concept and goes beyond a simple dictionary definition. Hence, it provides a comprehensive understanding through examples, anecdotes, and analysis of the term’s implications.

Structure of an Expository Essay: What To Consider First
An expository essay is one of the most common types of essays, according to MasterClass . Hence, looking at an expository essay example and learning how to start this type of essay makes it easier. After all, learning by example allows you to see the best practices to get top grades.
In the following sections, we’ll share the first few parts of an expository essay outline and include a few examples.
Choose a Clear Topic
The first step in writing an expository essay is selecting a clear and focused topic. The topic should be specific enough to allow for in-depth exploration but broad enough to provide ample information. For example, you might opt for “the role of bees in pollination.”
This topic allows you to delve into the specific contributions of bees, their impact on ecosystems, and their importance to agriculture. There’s enough depth here to provide a solid foundation for your essay. Furthermore, a clear topic guides your research and helps you develop a focused thesis statement.
Conduct Thorough Research
After selecting a topic, conduct thorough research to gather relevant information. You’ll need to utilize credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites to ensure the accuracy of your data.
For instance, if your topic is “the role of bees in pollination,” look for studies on bee populations, articles discussing their ecological significance, and statistics on agricultural reliance on pollinators. Make sure to take notes and organize the information into categories that align with your main points.
Furthermore, comprehensive research strengthens your argument and provides a wealth of evidence to support your claims to enhance the essay’s credibility.
Create an Outline
Creating an outline is crucial for organizing your ideas and structuring your expository essay. Begin with an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement. Then, outline the body paragraphs, where each one covers a specific aspect of your topic.
As an example, you might have one paragraph discussing the biology of bees, another on their pollination process, and a third on their economic importance. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis.
Generally, an outline provides a clear roadmap for your writing and makes it easier to complete your work in the correct expository essay format.
Write a Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly express the main idea or argument of your essay. It typically appears at the end of your introduction and sets the tone for the entire piece. You can look at expository essay examples to get a better idea of how to write a winning thesis statement.
For instance, if your topic is “the role of bees in pollination,” your thesis might be: “Bees play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting agricultural production through their pollination activities, making their conservation vital for environmental health and food security.”
A strong thesis statement provides clarity and guides your research and writing. Consequently, you’ll ensure all your content aligns with this central argument.
Craft a Compelling Introduction
Your introduction should grab the reader’s attention and provide background information on your topic. Start with a good essay hook , such as a surprising fact or a relevant quote. For example, you could begin with: “Did you know that one in every three bites of food we eat relies on pollinators like bees?”
Follow the hook with context about the importance of bees and their role in ecosystems. Finally, introduce your thesis statement, giving readers a clear overview of what to expect. Get it right, and the introduction will set the stage for your essay and engage your audience right from the start.

How To Start an Expository Essay: Examples for 3 Different Essay Types
In this section, we will discuss how to start an expository essay with examples of different thesis statements.
For each example, we’ll start with a thesis statement and then share how you would approach tackling the topic. Read these if you want to know how to write an expository essay and get top marks.
1. Descriptive Essay Example
Thesis statement: The vibrant atmosphere of a bustling farmer’s market showcases the richness of local culture and community.
In this descriptive essay about a farmer’s market, the writer should vividly portray the sights, sounds, and smells of the environment. This captures the vibrant colors of fresh produce, the enticing aromas of baked goods, and the lively chatter of vendors and customers.
Furthermore, through detailed sensory descriptions, you can immerse the reader and illustrate the market’s unique atmosphere.
2. Cause and Effect Essay Example
Thesis statement: Human activities are the primary drivers of climate change, which leads to severe environmental consequences.
A cause and effect essay on climate change examines the factors leading to global warming and its impacts. You could discuss causes like industrial pollution and deforestation. Then explain how they contribute to rising temperatures.
Additionally, you can explore effects such as extreme weather patterns, melting ice caps, and biodiversity loss. Therefore, by highlighting these connections, the essay emphasizes the urgent need for environmental action and raises awareness about the consequences of human activities.
3. Definition Essay Example
Thesis statement: Success is a multifaceted concept that varies widely based on individual values, goals, and perspectives.
In a definition essay defining “success,” you can explore various interpretations of the term. The essay can discuss societal standards, such as wealth and career achievements. Furthermore, you can emphasize personal definitions that include happiness and fulfillment.
Additionally, by incorporating quotes from influential figures and personal anecdotes, you can illustrate the subjective nature of success. This encourages readers to reflect on their values and what success means in their own lives.

5 Mistakes To Avoid When Writing Expository Essays
Now let’s focus on the top things you need to avoid when working on your expository essay. This will help you steer clear of the mistakes that many other students have made before you. Furthermore, avoiding these common writing mistakes increases the chances of getting a top grade in your class.
Here are the top expository essay mistakes to avoid:
- Lack of a clear thesis statement: A weak or unclear thesis statement can confuse readers and undermine your essay’s purpose. therefore, the thesis should concisely express the main idea and guide the direction of your writing.
- Insufficient research: Failing to conduct thorough research can lead to inaccuracies and a lack of depth in your writing. Also, relying on limited or unreliable sources may weaken your argument and diminish your credibility. Hence, make sure to gather information from credible sources, such as academic journals and books.
- Weak organization: Poor organization can make your essay difficult to follow. Therefore, each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence and relate back to your thesis. Make sure to use a logical structure. This might be a chronological order or a cause-and-effect format.
- Overly complex language: Using overly complex language or jargon can alienate readers and obscure your message. While it’s essential to demonstrate knowledge of the topic, clarity should always come first. Therefore, strive for straightforward language that conveys your ideas effectively.
- Lack of evidence or examples: Failing to support your claims with evidence and examples can weaken your argument significantly. An expository essay relies on factual information to inform and educate the reader. Therefore, always include relevant data, statistics, and real-life examples to back up your points.

Frequently Asked Questions
How do i choose a topic for an expository essay.
Choosing a topic for an expository essay involves selecting something specific, relevant, and engaging. Therefore, consider your interests and areas of knowledge. Additionally, ensure the topic allows for sufficient research and exploration.
Topics can range from scientific concepts to social issues. Try to stick with a topic that you find interesting since that will shine through in the end result.
What is the purpose of a thesis statement in an expository essay?
The thesis statement in an expository essay serves as the central argument or main idea. It guides the direction of the essay. Furthermore, it concisely summarizes the topic and sets the tone for the discussion.
Generally, a strong thesis helps readers understand what to expect and ensures that the content remains focused throughout the essay.
What are some common types of expository essays?
Common types of expository essays include descriptive essays, cause and effect essays, process essays, comparison and contrast essays, and definition essays. Each type has a unique focus so the approach and research will have a different format.

Get Top Marks in Your Expository Essay With Smodin AI
The expository essay samples in this article will help you with everything from writing the introductory paragraph to compiling the body paragraphs. An expository essay generally is all about the facts, so make sure to do extensive research.
Furthermore, you can learn from the countless number of expository essay examples in this article. They share the approach you need to take and how you should think about crafting each section of the essay.
Do you want help writing a high-quality expository essay? Then take advantage of Smodin AI. We offer extensive assistance for writing different types of essays, including expository essays to get you the grade you need. Our AI-based tool will help you come up with compelling titles and content that will captivate your readers.
Start using Smodin AI today and excel in your essays!
How to Start a Scholarship Essay That Gets Noticed
%20(1).webp)
Starting a college scholarship essay can feel like a big deal, and it is! Your words are the first thing standing between you and the chance to graduate without student debt. In fact, research shows that students who win scholarships are 40% more likely to graduate debt-free. That’s a huge weight lifted off your shoulders.
But here’s the thing: your introduction paragraph isn’t just about making a good impression — it’s about standing out in a pile of applications.
To help you out, this article will break down an example of how to start a scholarship essay that grabs scholarship provider attention right from the first sentence. We'll show you the strategies for opening with impact, setting the tone for your essay, and aligning your story with what scholarship committees care about.
And look, if after all this you’re still not sure how to hit that perfect note, DoMyEssay is always ready to step in and help. No messy drafts, no pulling your hair out. Just clear writing that does the heavy lifting for you.
Turn Heads, Not Pages
Your story, our words — let’s create an essay that demands attention!

Understanding the Prompt
First things first: don’t rush past the scholarship essays prompt. It’s easy to think you know what the scholarship committee is looking for, but really reading it carefully makes all the difference. Missing a small detail could mean crafting an essay that doesn’t even answer what they’re asking.
Break the prompt down and look closely at what the committee is asking for. Do they want to hear about your leadership experience? Your career goals for the future? Maybe how you’ve dealt with tough situations? Whatever it is, your essay should focus on that. Think of the prompt as a checklist of what the committee wants to see. If you stick to it, you’re already ahead.
If you’re not sure how to organize your thoughts, check out this essay structure guide to help keep everything on track and make sure you’re hitting all the important points.
Brainstorming Ideas
Before you even think about writing, it’s helpful to spend some time brainstorming and just getting all your thoughts out so you have something to work with. Trust me, it’s way easier to start writing when you’ve got a bunch of ideas ready rather than staring at a blank page hoping inspiration will strike.
Here are a few simple ways you can do it:
- Mind mapping : Grab a pen and paper, put your main idea in the middle, and start branching off with related thoughts or stories. It’s a quick and easy way to organize everything visually.
- Free writing : Set a timer for 10 minutes and just write. Don’t worry about making sense or grammar, just write whatever comes to mind. You’ll be surprised at what you can come up with when you stop overthinking.
- Make a list : Sometimes the simplest way works best. Write a quick list of anything relevant to the topic: stories, achievements, challenges. This helps you see what you’ve got and what could be useful.
Crafting a Strong Hook
The hook is the first sentence of your college scholarship essay, and it’s important because it pulls the reader in right from the start. You want them to be curious, interested, and ready to learn more about you. A strong hook sets the tone and gets the reader wanting to read further.
Here are 5 examples of different types of hooks you could use:
- Personal anecdote : “I never thought a broken bicycle could teach me so much about persistence, but that’s exactly what happened one summer afternoon.”
- Bold statement : “I’ve failed more times than I can count, but every failure has led me to where I am today.”
- Surprising fact : “Only 3% of foster kids go on to graduate from college. I’m determined to be part of that 3%.”
- Question that makes them think : “What would you do if you had to choose between paying rent or buying textbooks?”
- Quote : “‘The best way to predict the future is to create it,’ said Abraham Lincoln, and that’s the mindset I’ve carried through every challenge.”
Whatever hook you choose, make sure it connects with the main idea of your essay. It should lead naturally into your story or the point you’re going to make, setting up the rest of your essay with a strong start.
Introducing Yourself
When introducing yourself in a college scholarship application or essay, first impressions matter. You want to stand out in a way that makes the reader remember you. It’s all about finding the right balance between sharing personal stories and showcasing your achievements. Too much focus on one or the other can make your essay feel incomplete.
For example, if you’ve led a community project, don’t just list it. Talk about why it mattered to you and how it shaped who you are. Instead of saying, “I’m hardworking,” show it through a story, like how you worked two jobs while maintaining a top GPA. This way, the committee sees both your personality and your qualifications in action.
And keep the tone in mind as well. You want to come across as authentic and confident, without sounding overly formal or casual.
Aligning with the Scholarship’s Mission
When writing a college scholarship essay, it’s super important to know who’s giving you the scholarship and what they stand for. Every organization has its own values and goals, and they want to support students who align with that. So, before you start writing scholarship essays, do a little research on the organization to understand what matters most to them.
Once you know their values, tweak your essay intro paragraph to reflect that. If they care about leadership, show how you’ve led. If they focus on community service, talk about your volunteer work. The goal is to subtly weave their mission into your story — without overdoing it.
Here’s how you can connect your intro to the scholarship’s values:
| Scholarship Focus | How to Match Your Intro | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership 🏆 | Mention a time when you took charge and made an impact. | “In high school, I led a team to organize a local fundraiser, raising $3,000 for the community food bank.” |
| Community Service 🤝 | Talk about your involvement in helping others and how it shaped you. | “Volunteering at my neighborhood center taught me the value of compassion and the power of small actions.” |
| Academic Excellence 📚 | Highlight your dedication to college education and learning and how it drives you forward. | “My passion for science led me to start a tutoring group, helping classmates while deepening my own knowledge.” |
| Environmental Awareness 🌍 | Share your personal efforts toward sustainability or protecting the planet. | “Starting a recycling initiative at my school showed me how small changes can create a larger environmental impact.” |
Developing a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is basically the main point of your essay wrapped up in one sentence. It tells the reader what your essay is really about and gives them an idea of where you’re going with your story.
In a college scholarship essay, the thesis should clearly show your goal and how it connects to the scholarship program's mission. Here’s how to keep it simple:
- Focus on your main message.
- Be specific: don’t just say “I want to help people.” Say how and why .
- Make sure it ties directly to the prompt or what the scholarship values.
Here are some examples of clear, strong thesis statements:
- “My goal is to become a first-generation college graduate and use my degree to open doors for underrepresented students like me.”
- “Growing up in a small rural community taught me the value of access to healthcare, and I’m determined to become a doctor who serves similar communities.”
- “Through my experience leading environmental clean-up efforts, I’ve realized my passion for sustainability and plan to pursue a career in environmental policy.”
Mistakes to Avoid in the Introduction
Your introduction matters. It’s your first chance to grab the reader’s attention, and starting off on the wrong foot can hurt your chances.
Let’s talk about some common mistakes students make and how you can avoid them by being clear, using specific examples, and using active voice.
Being Too Generic
Starting with something like, “I’ve always wanted to help people ” or “I’m dedicated” is just toooo broad. It doesn’t tell the reader anything unique about you. Instead, get specific and personal. Share a moment that shaped you — something only you could say.
- Weak Example : "I’m passionate about making a difference."
- Stronger Example : "Helping my elderly neighbor fix his roof after a storm made me realize how much small acts of kindness can impact a community."
Using Clichés
Clichés like “I want to change the world” or “I’ve always loved learning” can make your article sound like everyone else’s. The reader has seen it all before. Be original and avoid overused phrases by focusing on your real, specific life experiences.
- Weak Example : "I want to change the world."
- Stronger Example : "After tutoring kids in my neighborhood, I realized how much a little guidance can change someone’s entire academic path."
Starting with a Boring Fact or Statement
Avoid starting a great essay with something dry like, “My name is Sarah, and I’m applying for this scholarship.” This isn’t a form. Your essay should grab attention right from the start. Begin with a personal story, a strong statement, or something that makes the reader curious about you.
- Weak Example : "I’m applying for this scholarship because I need financial aid."
- Stronger Example : "Working two part-time jobs in high school taught me how to balance responsibility and ambition, and now I’m ready to take that to the next level in college."
Finally, don’t overlook the power of proper punctuation ! Using it correctly can make your writing clearer and more impactful.
Bring Your Ideas to Life
Turn your ideas into a powerful scholarship essay. We make it easy!

Scholarship Essay Introduction Example
Here’s an example of how to start a college scholarship application essay that feels real, gets attention, and flows naturally:
- Start with a personal, real-life hook : "When my little brother was diagnosed with autism, our whole family had to learn how to live in a completely different way. I didn’t really get it at first — why he couldn’t just communicate like the rest of us — but over time, I became the one who helped him in a world that wasn’t built for him."
- Explain how this shaped you : "Taking on this role made me see the gaps in how we treat people with disabilities. It wasn’t just about my brother — it was about everyone like him. I became his biggest advocate, not just because he’s my brother, but because I knew kids like him deserved more."
- End with a strong, clear thesis : "This scholarship for the Speech and Language Pathology program will give me the chance to study special education so I can help kids like my brother get the support they need, and make sure they don’t have to face the same struggles alone."
This way, the introduction now clearly ties the story to the specific program you’re applying for.
Let’s Bring It Home
Alright, you’ve got everything you need to write a strong college scholarship essay. Start with a hook that grabs attention, tie it to your personal story, and end with a clear thesis that connects your future goals with the scholarship’s mission. Follow those steps, and you’re setting yourself up for success.
But if you still need some extra help, DoMyEssay’s scholarship essay writing service is here to make the process of college admissions even easier. Less stress, more results!
How Do You Write a Good Introduction for a Scholarship Essay?
What is a good hook for a scholarship essay.
- The College Investor. (n.d.). How to graduate college without student loan debt . The College Investor. https://thecollegeinvestor.com/38787/graduate-college-no-student-loan-debt/
- Children's Rights. (n.d.). College graduation: A bittersweet success for former foster youth . Children's Rights. https://www.childrensrights.org/news-voices/college-graduation-a-bittersweet-success-for-former-foster-youth
%20(1).webp)

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
3 Strong Argumentative Essay Examples, Analyzed
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Lab Report Format

The Ultimate Guide to Lab Report Format: Simple Steps to Follow
12 min read
Published on: Sep 28, 2024
Last updated on: Sep 28, 2024

People also read
Write Your Lab Report Like a Pro with this Helpful Guide
Share this article
Ever found yourself staring at a blank page, wondering how to start your lab report? It’s a common struggle, especially when you’re unsure of the right format to follow.
This confusion can lead to frustration, as you know that a poorly structured report could affect your grades or the clarity of your findings.
But don’t worry—getting your lab report format right doesn’t have to be a headache. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential elements of a lab report format, so you can tackle your next assignment with confidence.
Ready to dive in? Let's start by understanding what a lab report actually is.
On This Page On This Page -->
What Is A Lab Report? - A Simple Definition
A lab report is a detailed document that explains an experiment you've conducted in a scientific setting. It serves as a record of what you did, how you did it, what you observed, and what your results mean.
The main purpose of a lab report is to communicate your findings clearly and logically, so others can understand your process and replicate your experiment if needed. It typically includes sections like the introduction, methods, results, and discussion, each serving a specific role in telling the story of your experiment.
In essence, a lab report is your way of sharing scientific knowledge in a structured format, making your research accessible and understandable to others.
Lab Report Format Template
When it comes to writing a lab report, following a clear and organized format is essential. Each section of your report serves a specific purpose and helps present your experiment and findings in a logical manner.
Below, we'll break down each component of a lab report, so you know exactly what to include and how to structure your work. By following this format, youâll ensure that your report is comprehensive and easy to understand.
The title page is the first impression of your report. It should include the title of your experiment, your name, the date, and any other relevant information like your instructorâs name or course details. Keep it simple and professional.
The abstract is a brief summary of your entire report, usually no more than 100-200 words. It highlights the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of your experiment. Think of it as a snapshot that gives readers a quick overview of what to expect.
Introduction
In the introduction, you provide background information on the experiment, state the problem youâre investigating, and explain why itâs important. This section sets the stage for the reader, offering context and defining the scope of your report.
Your hypothesis is an educated guess about the outcome of your experiment. It should be clear, testable, and based on existing knowledge or theories. This section outlines what you aim to prove or disprove through your conducted experiment.
Materials and Methods (Procedures and Equipment)
This section details the materials, tools, and methods you used in your experiment. Itâs important to be precise so that someone else can replicate your experiment based on your description. Include step-by-step procedures and a list of equipment.
Experimental Design
Here, you explain how you structured your experiment, including the variables you tested and the controls you used. This section should clarify how you ensured the reliability and accuracy of your results.
Results/Data Analysis
In the results section, you present the data you collected during your experiment. Use tables, infographics, and charts to make your findings clear and easy to interpret. Avoid drawing conclusions hereâjust present the raw data.
Calculations
If your experiment involves calculations, this section is where you'll show your work. Include all formulas and steps used to arrive at your results. Clear and accurate calculations are crucial for supporting your findings.
This is where you interpret your results and explain what they mean. Here, you'll compare your findings with your hypothesis and discuss any anomalies or unexpected outcomes. The discussion section allows you to explore the implications of your results.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of your experiment and their significance. Restate whether your hypothesis was supported and suggest any further research that could be conducted. This section should neatly wrap up your report
Documentation
If your experiment involved specific protocols, safety measures, or compliance with regulations, detail them in the documentation section. This ensures transparency and adherence to standards.
The references section lists all the sources you cited in your report. Use the appropriate citation style as required by your instructor or field of study. Proper citation and referencing adds credibility to your work.
The appendix includes any additional material that supports your report, such as raw data, detailed calculations, or supplementary information. Itâs a useful place to include material that is too lengthy or detailed to fit in the main sections.
By following this structured format, your lab report will be well-organized and easy to follow. Next, we'll walk through a complete lab report example that incorporates all these sections, so you can see how it all comes together in practice.
Lab Report Format Example
Understanding the format of a lab report is essential, but seeing an example in action can be even more helpful. Here, we'll walk through a complete lab report, section by section, using a simple experiment as an example.
This example will show you how to apply the format we discussed earlier, ensuring that your report is clear, detailed, and easy to follow.
: The Effect of Light on Plant Growth |
This experiment aimed to determine the effect of different light conditions on the growth of bean plants. Three groups of plants were exposed to full sunlight, partial sunlight, and no light over two weeks. The growth was measured by height and leaf count. Results showed that plants in full sunlight grew the most, while those in no light showed minimal growth. The conclusion supports the hypothesis that light is essential for optimal plant growth. |
Plants rely on light for photosynthesis, the process that allows them to produce energy. This experiment investigates how varying light levels affect the growth of bean plants. Understanding the relationship between light and plant growth is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices. The experiment will test the hypothesis that more light results in greater plant growth, providing insights into how light influences plant health. |
The hypothesis for this experiment is that bean plants exposed to full sunlight will grow taller and develop more leaves than those exposed to partial sunlight or no light. |
: : |
The experiment was designed to test the effect of light on plant growth by controlling the light exposure for three groups of bean plants. The independent variable was the light condition (full sunlight, partial sunlight, no light), while the dependent variables were plant height and leaf count. Each group contained three plants to account for variability and increase reliability. |
: Average height 15 cm, average leaf count 10. Average height 10 cm, average leaf count 7. Average height 2 cm, average leaf count 2.: The data showed a clear trend where plants exposed to more light grew taller and developed more leaves. The full sunlight group had the most growth, while the no light group showed stunted growth. |
: (15 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = 0.71 cm/day (10 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = 0.36 cm/day (2 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = -0.21 cm/day |
The experimentâs results support the hypothesis that light significantly influences plant growth. Plants in full sunlight showed the highest growth rate, confirming that light is crucial for photosynthesis and energy production. The stunted growth in the no-light group highlights the importance of light in maintaining plant health. Unexpectedly, the partial sunlight group showed less growth than anticipated, suggesting that light intensity might also play a role. Further research could explore the effects of different light wavelengths on plant growth. |
In conclusion, this experiment demonstrates that light is a vital factor in plant growth, with full sunlight leading to the most significant growth. The hypothesis was supported by the data, confirming that light exposure directly impacts plant development. This information could be useful in agricultural practices where light conditions can be controlled to optimize growth. |
All safety protocols were followed during the experiment, including proper handling of plants and equipment. The experiment was conducted in a controlled environment, ensuring accurate results. |
|
: Raw data tables for plant height and leaf count. |
Now that youâve seen a complete lab report example, you can better understand how to apply this format to your own work. In the next section, weâll provide different detailed lab report format examples, showing how all these elements come together in a real-world scenario.
Additional Lab Report Format PDF Examples
Sometimes, seeing multiple examples can make all the difference in mastering the structure and format of a lab report. In this section, weâll provide links to a variety of PDF examples that showcase different types of lab reports across various scientific disciplines.
Lab Report Format Chemistry
Lab Report Format Physics
Pathology Lab Report Format
Medical Lab Report Format
Lab Report Format University
College Lab Report Format
APA Lab Report Format
MLA Lab Report Format
Best Practices For Writing A Lab Report That Stands Out
Here are some practical tips to help you write an outstanding lab report:
- Plan and Prepare Thoroughly: Before you start writing, make sure you understand the experiment and the requirements of the report. Gather all relevant data, notes, and observations. Creating an outline can help you organize your thoughts and ensure you cover all necessary sections systematically.
- Use Third-Person Pronoun: Write your report in the third person to maintain a formal and objective tone. Avoid using first-person pronouns like "I" or "we". For example, instead of saying " We conducted the experiment, " write " The experiment was conducted ".
- Employ Past-Passive Tense: Use the past passive tense to describe the procedures and results. This approach helps to focus on the actions and results rather than the researcher. For instance, instead of " We mixed the solutions ," write " The solutions were mixed ".
- Be Clear and Concise: Ensure that your writing is clear and to the point. Avoid unnecessary jargon and complex sentences that might confuse the reader. Each section of your report should be straightforward and focused on conveying the relevant information.
- Follow a Structured Format: Adhere to the standard lab report structure: Title Page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, References, and Appendices. Consistent formatting helps readers follow your report easily and understand your findings.
- Include Accurate Data and Analysis: Present your data clearly using tables, graphs, or charts as needed. Ensure that your analysis is accurate and directly addresses the research question. Discuss the significance of your results and how they relate to your hypothesis.
- Review and Revise: Proofread your lab report to correct any grammatical errors, typos, or inconsistencies. Revising your report helps to ensure clarity and accuracy. Consider having a peer review of your work to get additional feedback.
By applying these tips, you can enhance the quality of your lab report and effectively communicate your research findings. Following a structured approach and focusing on transparency and precision will help you produce a professional and credible report.
Writing a well-structured and insightful lab report is essential for communicating your research effectively. By following the outlined format, you can ensure your report is comprehensive and professionally presented.
Moreover, adhering to the tips and techniques mentioned will further enhance the clearness and impact of your report. Selecting a relevant and engaging topic will help in producing a report that is both informative and compelling. Remember, the key to a successful lab report lies in its ability to purely convey the objectives, methods, and findings of your research.
If you need further assistance with the ' write my lab report' task, or if you're looking for help with other academic writing tasks, our expert essay writing service is here to support you 24/7. Reach out to us to ensure your work meets the highest standards of excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do a lab report and a research paper differ.
A lab report is a detailed document that describes the process and results of an experiment, focusing on practical aspects and procedures. In contrast, a research paper is a more comprehensive analysis that includes a literature review, methodology, results, and discussion, often aiming to contribute new knowledge or insights to a field.
What distinguishes the results section from the discussion section inside a lab report?
In a lab report, the results section presents the raw data and findings from the experiment or investigation, while the discussion section interprets these results, exploring their significance, implications, and how they fit with other research or theories.
Which format, MLA or APA, is commonly used for lab reports?
Lab reports can be written in either APA or MLA style, depending on the instructor's preference or the specific requirements of the course. Both styles are suitable for lab reports, but APA is more commonly used in scientific disciplines for its emphasis on data presentation and clarity.
What is the typical length of a lab report?
The length of a lab report can vary depending on the complexity of the experiment and the instructor’s requirements, but it typically ranges from 5 to 10 pages. This includes sections such as the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
| Part | Content |
|---|---|
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to write an effective introduction paragraph for your academic essay with this guide. It covers the goals, structure, and tips of a good introduction, and provides examples from different topics.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
One straightforward way to begin is to get right to the point. But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...". "It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving."
Intriguing ways to start an essay. There are many different ways to write an essay introduction. Each has its benefits and potential drawbacks, and each is best suited for certain kinds of essays.Although these essay introductions use different rhetorical devices and prime the reader in different ways, they all achieve the same goal: hooking the reader and enticing them to keep reading.
Note that the meta essay can sometimes work (you'll see a couple examples below), but has a higher degree of difficulty. The Quote: While quoting famous people who have said something cool in the past may seem like an appealing way to start your essay, remember that colleges want to hear YOUR thoughts. Don't use the words of another person ...
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
1. Begin with an attractive hook. In order to understand how to start an introduction in an essay, we must first focus on the hook. An effective opening statement, or a "hook", aims to intrigue the reader. An attractive opening statement essentially hooks the reader to your essay.
Do your research and gather sources. Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
Essay mapping: In this essay, I will be detailing how Shakespeare uses foreshadowing and dramatic irony to create suspense, with examples from Romeo and Juliet and Othello. Pro tip: Essays take twists and turns. We recommend changing your introduction as necessary while you write the main text to make sure it fully aligns with your final draft.
Our essay introduction examples showing the parts of an essay introduction will help you craft the beginning paragraph you need to start your writing journey on the right foot. If you'd like more personalized attention to your essay, consider sending it for Essay Editing by Scribendi. We can help you ensure that your essay starts off strong.
This college essay tip is by Abigail McFee, Admissions Counselor for Tufts University and Tufts '17 graduate. 2. Write like a journalist. "Don't bury the lede!" The first few sentences must capture the reader's attention, provide a gist of the story, and give a sense of where the essay is heading.
3. Create a mysterious atmosphere. "Moths that fly by day are not properly to be called moths; they do not excite that pleasant sense of dark autumn nights and ivy-blossom which the commonest yellow-underwing asleep in the shadow of the curtain never fails to rouse in us.". - Virginia Woolf - Death of the Moth. 4.
The Bottom Line: How to Start a College Essay. The college essay introduction should hook your reader and make her want to know more and read more. Good personal statement introductions will contain the following features: A killer first line. A detailed description of an experience from your life.
Place your hook at the top, and use 2 to 3 sentences to describe the wider context of your thesis. You should try to make each sentence more specific than the one before it. For example, if you're writing an essay about the crimes committed by refugees, you could start with an anecdote about a victim of these crimes.
Smith College. Each year, Smith asks its applicants to answer a different prompt with a 200-word essay. Here are six of these short essays answering the 2014 prompt: "Tell us about the best gift you've ever given or received." 6 "best gift" essays from the class of 2018. You really can find everything at the library.
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
7 Tips to Start an Essay. When writing an essay a good opening is like setting the stage for a performance—get it right, and you'll have your audience hooked from the start.. Let's look at some useful methods to start your essay strongly. Tip 1. Start with a Hook . The first stage in writing a compelling essay opening is to hook your reader. This could be a surprising fact, a provocative ...
Below you'll find examples of sentence starters relevant to specific contexts. Topic sentence starters for essays. Topic sentences are like the sentence starters of an entire essay—they introduce what the paragraph or entire text is about so the readers know what to expect. This paper discusses . . . In this paper . . . Here, we discuss . . .
The body of your essay is where you'll really dig into your argument, using your sources to back up your points. Each paragraph should be well-structured so your essay doesn't feel like a random collection of facts. Here's a simple breakdown for writing a strong synthesis paragraph: 1. Start with a topic sentence.
How To Start an Expository Essay: Examples for 3 Different Essay Types. In this section, we will discuss how to start an expository essay with examples of different thesis statements. For each example, we'll start with a thesis statement and then share how you would approach tackling the topic. Read these if you want to know how to write an ...
Ideally, you should start brainstorming college essay topics the summer before your senior year. Keep in mind that it's easier to write a standout essay with a unique topic. ... In the example below, the essay concludes by returning to the "museum" metaphor that the writer opened with. Example Thank you for your attention. This completes ...
Weak Example: "I want to change the world." Stronger Example: "After tutoring kids in my neighborhood, I realized how much a little guidance can change someone's entire academic path." Starting with a Boring Fact or Statement. Avoid starting a great essay with something dry like, "My name is Sarah, and I'm applying for this scholarship."
Argumentative Essay Example 2. Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through female Anopheles mosquitoes. Each year, over half a billion people will become infected with malaria, with roughly 80% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Start excelling today! Discover the essential lab report format design with detailed examples and best practices to write an effective and professional report. Start excelling today! ... our expert essay writing service is here to support you 24/7. Reach out to us to ensure your work meets the highest standards of excellence.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay. General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body. The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis.