Static and Dynamic VLAN Membership Explained
There are two types of VLAN membership: static and dynamic. In the static method, administrators manually add switch ports to VLANs. In the dynamic method, the switch automatically assigns appropriate VLANs to ports.

What VLAN membership is
A VLAN is a group of devices that share broadcast messages. By default, switches have only one VLAN, called VLAN-1. However, you can create and configure additional VLANs to limit broadcast messages and logically arrange devices in groups. After creating VLANs, you need to add desired ports to VLANs. VLAN membership is an authorization to be part of the VLAN. There are two ways to assign VLAN membership to switch ports: Static and Dynamic.
Static VLAN membership
It is an easy and straightforward method. In it, you manually add ports to VLANs. VLANs configured in this way are typically called port-based VLANs .
Let us take an example.
The following image shows an 8-port switch. With the default configuration, all ports belong to the same broadcast domain.

Now, suppose you want to break this network into two broadcast domains. You create two VLANs: VLAN-10 and VLAN-20 . You enter the sub-configuration mode of ports and configure VLANs. You configure VLAN-10 on ports 1, 2, 3, and 4, and VLAN-20 on ports 5, 6, 7, and 8. It is an example of static VLAN membership.

Advantages of static VLAN membership
The main advantages of static VLAN membership are the following.
Easy configuration
Configuring a static VLAN membership is easy. To configure a static VLAN membership, you run only one command [switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan VLAN_ID ] in the sub-interface configuration mode.
Easy management
Managing static VLAN membership is also easy. From the sub-interface configuration mode of the port, you can easily add, update, and remove VLAN membership.
Since you manually add, update, and remove static VLAN membership on all ports, the static VLAN membership is more secure than the dynamic VLAN membership.
Availability
Static VLANs are available on almost all Cisco switches. You do not need any high-end Cisco switch to use them. You can configure and use them on existing Cisco switches.
Disadvantages of static VLAN membership
The disadvantages of static VLANs are the following.
Scalability
Static VLAN membership is not scalable. If your network is small, you can choose it because of its easy configuration. But if your network is big, you can not use it alone. For example, if your network has thousands of devices, assigning and managing static VLAN membership for these devices on switches will be a difficult task.
Static VLAN membership is not movable. If you move a PC from a switch port to another switch port, you need to manually remove the VLAN membership from the current port and add it to the new port.
Dynamic VLAN membership
Dynamic VLAN membership works on a server-client model. In this model, a policy server called the VLAN membership policy server (VMPS) saves VLAN mapping information. VLAN mapping information contains VLAN IDs and MAC addresses of end devices.
All other switches act as VLAN client switches. They forward MAC addresses to the VMPS switch. The VMPS switch finds VLAN ID associated with each MAC address and passes that ID to the VLAN client switch.
The following image shows a simple network. It uses dynamic VLAN membership.

In the above network, when you add PC2 to the VLAN client switch's port-2, it forwards PC2's MAC address to the VMPS switch. VMPS switch finds the VLAN ID related to PC2's MAC address and provides that ID to the VLAN client switch. The VLAN client switch assigns the received VLAN ID to port-2.
Now suppose, you remove PC2 from port-2 and attach it to port3. In this situation, the switch will take the following steps.

- It removes configured VLAN on port-2 as soon as you remove the connected device.
- When you attach PC2 to port-3, it sends the PC2's MAC address to the VMPS switch.
- VMPS switch finds the VLAN ID related to the PC2's MAC address and provides it to the VLAN client switch.
- The VLAN client switch assigns the received VLAN ID to port-3.
Advantages of Dynamic VLAN membership
The advantages of dynamic VLAN membership are the following.
The main advantage of dynamic VLAN membership is movability. If you move an end device from a switch port to another switch port, the switch automatically updates the VLAN information on both ports.
Centralized management
Dynamic VLAN membership provides centralized management. You need to manage VLAN information only on the VMPS swtich. Other switches automatically receive the updated information from the VMPS swtich.
Fast implementation
Since VLAN client switches automatically implement dynamic VLAN membership, it is faster than static VLAN membership. In static VLAN membership, if you change VLAN information, you need to manually update that information on all ports. In dynamic VLAN membership, switches automatically update the information on all ports.
Disadvantages of Dynamic VLAN membership
The disadvantages of dynamic VLAN membership are the following.
Complex configuration
The configuration of dynamic VLAN membership is complex. You need to map the MAC addresses of all end devices to VLANs on the VMPS switch. You also need to configure all other switches to get VLAN information from the VMPS switch.
Add extra cost to the network
You cannot use low-end Cisco switches as VMPS server switch. You need a high-end Cisco switch such as Catalyst 6500 switch to configure VMPS. High-end Cisco switches are costly.
This tutorial is a part of the tutorial series on VLAN, VTP, and DTP Concepts and Configurations on Cisco Routers. Other parts of this series are the following.
Chapter 01 VLAN Basic Concepts Explained with Examples
Chapter 02 Advantages and Disadvantages of VLANs
Chapter 03 Static and Dynamic VLAN Membership Explained
Chapter 04 Access Link and Trunk Link Explained
Chapter 05 VLAN Tagging Explained with DTP Protocol
Chapter 06 DTP Modes and Protocol Explained
Chapter 07 802.1Q Native VLAN concept Explained
Chapter 08 Cisco Inter-Switch Link (ISL) Explained
Chapter 09 Trunk Tagging and Frame Tagging Explained
Chapter 10 VTP Modes and VTP Protocol Explained
Chapter 11 VTP Pruning on switches Explained
Chapter 12 VLAN Practice Lab Setup in Packet Tracer
Chapter 13 Configure VTP Server and Client in Switch
Chapter 14 VLAN Configuration Commands Step by Step Explained
Chapter 15 Router on Stick Configuration Explained
By ComputerNetworkingNotes Updated on 2024-06-09
ComputerNetworkingNotes CCNA Study Guide Static and Dynamic VLAN Membership Explained
- EtherChannel Load Distribution Explained
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) Explained
- Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) Explained
- EtherChannel Manual Configuration
- EtherChannel Basic Concepts Explained
- STP, RSTP, PVST, RPVST, and MSTP
- Similarities and Differences between STP and RSTP
- RSTP / RPVST Explained with Examples
- PVST/RPVST and EtherChannel Explained
- STP/RSTP Timers Explained
We do not accept any kind of Guest Post. Except Guest post submission, for any other query (such as adverting opportunity, product advertisement, feedback, suggestion, error reporting and technical issue) or simply just say to hello mail us [email protected]

CCNA 200-301 v1.1
- CCNA 200-301 Labs
- CCNP 350-401 ENCOR
- CCNP 350-401 ENCOR Labs
- CCNP 300-410 ENARSI
- CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure
- Cisco Packet Tracer Lab Course
- NRS II IRP Course
- NRS II MPLS Course
- NRS II Service Architecture
- Nokia Configuration Course
- Nokia SRC Program
- JNCIA Junos
- HCIA (HCNA)
- HCIA Configuration Course
- What is Huawei R&S Certification?
- Huawei ICT Certifications
- Python Course
- IPv6 Course
- IP Multicast Course
- NRS I Configuration Course
- Cisco Packet Tracer How To Guide
- Online Courses
- Udemy Courses
- CCNA Flashcard Questions
- Protocol Cheat Sheets
- Subnetting Cheat Sheet
- Linux Cheat Sheet
- Python Cheat Sheet
- CLI Commands Cheat Sheets
- Miscellaneous Cheat Sheets
- Cisco Packet Tracer Labs
- Cisco GNS3 Labs
- Huawei eNSP Labs
- Nokia GNS3 Labs
- Short Config Videos
- Network Tools
- IPCisco on Social Media
- Network Engineer Interview Questions
- Personality Interview Training
- Sign In/Up | Members
- Lost password
- Sign In/Sign Up
- ENROLL HERE

- VLAN Port Assignment and VLAN Port Types
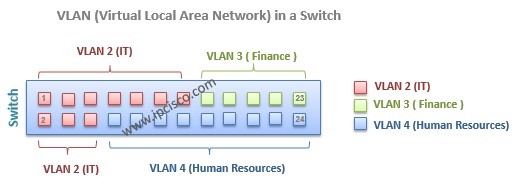
In this lesson, we will focus on some of the key lessons of VLANs. We will learn how to assign ports to VLAN, VLAN Port types and VLAn Tagging.
Table of Contents
Static and Dynamic VLAN Assignments
VLANs can be assigned statically and dynamically . Static configuration is more common, but dynamic is also used.
Static VLAN assignment is like its name. You will statically assign the ports to the VLAN.
Dynamic VLAN assignment can be done by VLAN Membership Policy Server(VMPS) . VMPS needs VLAN-MAC address relationship database. Here, we will use the static one, like many network engineer.
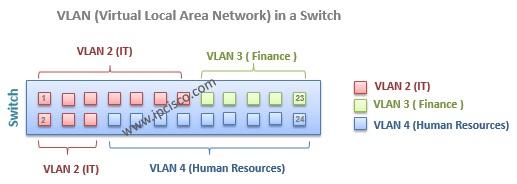
VLAN Port Types
There are two type port used in VLANs. These are: – Access Ports, – Trunk Ports
Access ports are the ports that are member of a single VLAN . Host devices are connected to it. This is also default Cisco switch port type.
Trunk ports are the ports that are member of more than one VLAN or all VLANs . This ports are used between switches. To span VLANs between more than one switch, some ports are needed to carry VLAN information accross the switches. These ports are trunk ports. You can also carry each VLAN without using any trunk port. But this way is not efficient and not common.
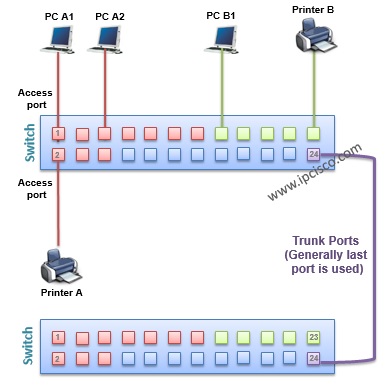
VLAN Frame Tagging
While carrying the frames between VLANs across multiple swithes, frame tagging is required. Because the other end switch need to understand that where the frame will go ( to which VLAN) on the other end. And tagging is used only for the frames going out a trunk port. This is not used for access ports, and anyway this is not necessary.
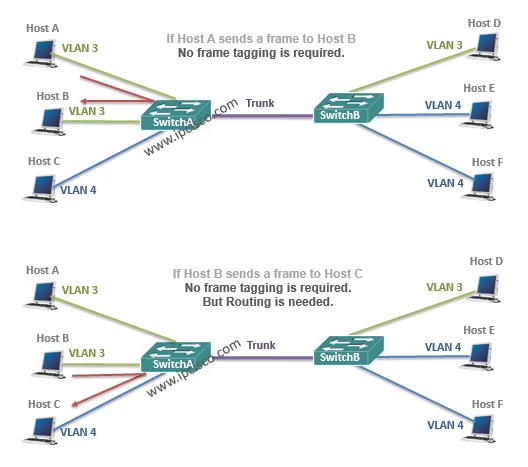
No VLAN Frame Tagging Require

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Network Fundamentals
- Collision Domain vs Broadcast Domain
- Coaxial Cable Details
- Types of Networks
- Top Internet Access Technologies
- WAN Topology Types
- Network Topology Architectures
- Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
- Ethernet Collisions and Troubleshooting
- Cisco NGFW and Cisco NGIPS
- Networking Connectors
- Ping Command
- Basic Cisco Router Configuration on Packet Tracer
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Network Cabling
- Network Devices
- TCP/IP Model
- OSI Referance Model
IPv4 Addressing
- Verify IP Parameters for Client OS
- Wildcard Mask
- VLSM Subnetting
- IPv4 vs IPv6 Comparison
- Cisco IP Address Configuration
- APIPA Address
- Private IP Address Ranges
- Subnetting Examples
- IP Addressing (IPv4)
- IP Subnetting and Subnetting Examples
IPv6 Addressing
- IPv6 Unique Local Address
- IPv6 Global Unicast Address
TCP and UDP
- TCP Header : Sequence & Acknowledgement Number
- TCP Handshake
- TCP versus UDP
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- TCP Header : TCP Options
- TCP Header : TCP Window Size, Checksum & Urgent Pointer
- TCP Header : TCP Flags
- Voice VLAN Configuration
- Packet Tracer VLAN Example 2
- How to Configure Cisco VLANs
- VTP Configuration with Packet Tracer
- VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)
- DTP and VLAN Frame Tagging protocols ISL, dot1.q
- Cisco Packet Tracer VLAN Configuration Example
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks)
Switching and LANs
- Ethernet Basics
- Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch
- Cisco Switch Configuration on Cisco Packet Tracer
- MAC Address Lookup
- What is a mac address
- Local Area Networks
- Network Topologies
- Hubs, Switches and Routers
Spanning Tree Protocol
- Loop Guard, Uplink Fast, Backbone Fast and UDLD
- Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- BPDU (Bridge Data Unit Protocol)
- STP Loop Guard
- STP BPDU Filter
- STP BPDU Guard
- STP Root Guard
- Portfast, Root Guard, BPDU Filter and BPDU Guard
- PVST+ and Rapid PVST+
- STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) Example on Packet Tracer
- RSTP Configuration on Packet Tracer
- STP Portfast Configuration with Packet Tracer
- Spanning Tree Protocol Operation
- Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)

Neighbor Discovery
- LLDP Configuration on Cisco IOS
- Neighbour Discovery Protocols
- CDP Configuration with Packet Tracer
EtherChannels
- PAgP Configuration on Cisco Devices
- LACP Configuration on Cisco Devices
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
Routing Fundamentals
- Route Summarization
- Link State vs Distance Vector Protocols
- Routing Path Determination
- Routing Table
- Static Routes
- IPv4 Floating Static Routes
- Inter VLAN Routing Configuration on Packet Tracer
- Switch Virtual Interface Configuration on Packet Tracer
- Switch Virtual Interfaces
- Inter VLAN Routing with Router on Stick
- IP and Layer 3 Overview
- Static Route Configuration on Cisco Routers
- Dynamic Routing Protocols
- OSPF Cost and SPF Algorithm
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example on Cisco IOS
- OSPFv3 (Open Shortest Path First Version 3)
- Cisco Single Area OSPF Configuration
- Other OSPF Key Points
- OSPF Network Types
- OSPF Area Types
- OSPF LSA Types
- OSPF Packet Types
- OSPF Adjacency
- OSPF(Open Shortest Path First) Overview
WAN (Wide Area Networks)
- MLPPP Configuration on Cisco Packet Tracer
- What is MLPPP?
- Metro Ethernet Technology
- WAN and WAN Technologies
DHCP and DNS
- DNS Configuration on Cisco Routers
- Domain Name System Overview
- Router DHCP Configuration with Packet Tracer
- DHCP IP Allocation Operation
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- NAT (Network Address Translation)
- PAT Configuration with Packet Tracer
- Dynamic NAT Configuration with Packet Tracer
- Static NAT Configuration with Packet Tracer
First Hop Redundancy
- HSRP Configuration on Cisco IOS
- HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)
- First Hop Redundancy Protocols (FHRPs)
Network Management
- Syslog Overview
- SSH Port and Secure Shell
- Configuration Register
- TFTP, FTP, SFTP and SCP
- SSH Configuration on Packet Tracer
- Syslog Configuration Cisco
- Cisco NTP Configuration
- NTP (Network Time Protocol)
- SNMP Overview
- SNMP Configuration On Cisco IOS
- Cisco Router Password Recovery
- IPv6 Floating Static Routes
- IPv6 Static and Default Route Configuration
- Stateless Address Auto Configuration
- IPv6 NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol)
- IPv6 Configuration on Cisco Packet Tracer
- What does IPv6 bring?
- Subnetting in IPv6
- IPv6 Address Types
- IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
- IPv6 and IPv6 Addresses
Quality of Service
- Network Traffic Types
- Policing and Shaping in QoS
- Classification and Marking in QoS
- Quality of Service Overview
- Radius Configuration for Wireless Users
- Cisco RADIUS Server Configuration on Packet Tracer
- TACACS+ Overview
- RADIUS Overview
- AAA Protocols : RADIUS and TACACS+
- Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA)
- WLAN Frequency Bands
- Other Wireless Network Extention Types
- Wireless Principles
- WLAN Components
- Wireless Network Design Models
- WLC Management Access Connections
- Wireless Access Point Modes
- Wireless Security Protocols
- WLAN Configuration on Packet Tracer
Security Fundamentals
- DHCP Snooping Configuration on Packet Tracer
- Cisco Banner Configuration on Packet Tracer
- What is DHCP Snooping?
- Access Control Lists
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Cyber Attacks, Network Attacks, Threats and Mitigation
- 802.1x (Port Based Network Access Control)
- Switch Port Security Configuration on Cisco Packet Tracer
- Switch Port Security
- Extended Access List Configuration With Packet Tracer
- Standard Access List Configuration With Packet Tracer
- Basic Cisco Router Security Configuration
Automation and Programmability
- Ansible vs Puppet vs Chef
- Generative AI vs Predictive AI
- Chef Overview
- Puppet Overview
- Ansible Overview
- Network Automation Tools
- Interpret JSON Encoded Data
- Cisco DNA Center
- Cisco SD-Access
- Data Serialization Languages: JSON, YAML, XML
- Traditional Network Management versus Cisco DNA Center
- Cisco DNA and Intent-Based Networking (IBN)
- How Network Automation Impacts Network Management
SDN (Software Defined Networking)
- What is SDN ?
- Traditional Network Drawbacks Versus SDN
- What Will SDN Bring?
- SDN Architecture Components
- SDN Terminology
- Virtualization
- Virtual Network Structure
Latest Lessons
- NETCONF Operation Steps Part of: CCNP Enterprise 350-401 ENCOR v1.1
- NETCONF Protocol Stack Part of: CCNP Enterprise 350-401 ENCOR v1.1
- NETCONF Overview Part of: CCNP Enterprise 350-401 ENCOR v1.1
- RESTCONF Protocol Part of: SDN Course
- RESTCONF Part of: CCNP Enterprise 350-401 ENCOR v1.1
- SSH Port and Secure Shell Part of: CCNA 200-301 v1.1
- EIGRP vs OSPF Part of: CCNP Enterprise 350-401 ENCOR v1.1
- Link State vs Distance Vector Protocols Part of: CCNA 200-301 v1.1
- Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) Part of: CCNA 200-301 v1.1
- Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch Part of: CCNA 200-301 v1.1
- More Lessons
Latest Blog Posts

WHAT YOU WILL FIND?
- 250.000+ Students All Over The World
- 8.000+ Questions & Answers
- 100+ Lab Files & Cheat Sheets
- 30+ IT/Network Courses
- A Real Desire To Help You
- Daily Social Media Shares
- %100 Satisfaction
- CISCO Courses
- NOKIA Courses
- HUAWEI Courses
- JUNIPER Courses
- PYTHON Course
- KEY Courses
- VIDEO Courses
- UDEMY Courses
- Cheat Sheets
- Configuration Files
- Interview Questions
- IPCisco On Social Media
- Pärnu mnt. 139c – 14, 11317, Tallinn, Estonia
- [email protected]

Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 35 million academic & study documents
Create vlan and assign port number to vlan cisco asmed education info.

Sign up to view the full document!

24/7 Study Help
Stuck on a study question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a study question?

Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 35 million study documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A study help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Security Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE 17.15.x (Catalyst 9600 Switches)
Bias-free language.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels
- Configuring Login Block
- Configuring Authentication
- Configuring Authorization
- Configuring Accounting
- Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
- Configuring AAA Authorization and Authentication Cache
- Configuring AAA Dead-Server Detection
- Configuring TACACS+
- Configuring RADIUS
- Configuring RadSec
- Configuring RADIUS Server Load Balancing
Configuring VLAN RADIUS Attributes
- Device Sensor
- Configuring MACsec Encryption
- Configuring Secure Shell
- Secure Shell Version 2 Support
- SSH Support Over IPv6
- Configuring SSH File Transfer Protocol
- X.509v3 Certificates for SSH Authentication
- SSH Algorithms for Common Criteria Certification
- Configuring Secure Socket Layer HTTP
- Object Groups for ACLs
- Configuring Reflexive Access Lists
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IPv6 First Hop Security
- Configuring Switch Integrated Security Features
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- IEEE 802.1X VLAN Assignment
- Web-Based Authentication
- Identity Based Networking Services Overview
- Change of Authorization Support
- Configuring Identity Control Policies
- Policy Classification Engine
- Configuring Identity Service Templates
- Interface Templates
- eEdge Integration with MACsec
- Critical Voice VLAN Support
- Configuring Local Authentication Using LDAP
- Web Authentication Redirection to Original URL
- Port-Based Traffic Control
- Port Security
- Configuring Control Plane Policing
- Configuring Lawful Intercept
- Configuring Authorization and Revocation of Certificates in a PKI
- Source Interface Selection for Outgoing Traffic with Certificate Authority
- Source Interface and VRF Support in LDAP
- Configuring IPv6 Support for LDAP
- Secure Operation in FIPS Mode
- Troubleshooting Security
Chapter: Configuring VLAN RADIUS Attributes
Restrictions for vlan radius attributes in access requests, vlan radius attributes, configuring vlan radius attributes in access requests, verifying vlan radius attributes in access requests, example: configuring vlan radius attributes in access requests, example: verifying vlan radius attributes in access requests, feature history for vlan radius.
The VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests feature enhances the security for access switches with the use of VLAN RADIUS attributes (VLAN name and ID) in the access requests and with an extended VLAN name length of 128 characters.
Dynamic VLAN assignment to critical authentication (inaccessible authentication bypass or AAA fail policy) VLAN is not supported.
If the RADIUS server becomes unavailable during an 802.1x authentication exchange, the current exchange times out, and the switch uses critical access control lists (ACLs) during the next authentication attempt.
Information About VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests
Authentication prevents unauthorized devices (clients) from gaining access to the network by using different methods to define how users are authorized and authenticated for network access. To enhance security, you can limit network access for certain users by using VLAN assignment. Information available in the access-request packets sent to the authentication server (AAA or RADIUS server) validates the identity of the user and defines if a user can be allowed to access the network.
The VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests feature supports authentication using IEEE 802.1X, MAC authentication bypass (MAB), and web-based authentication (webauth). The default order for authentication methods is 802.1X, and then MAB, then web-based authentication. If required, you can change the order or disable any of these methods.
If MAC authentication bypass is enabled, the network device relays the client's MAC address to the AAA server for authorization. If the client's MAC address is valid, the authorization succeeds and the network device grants the client access to the network.
If web-based authentication is enabled, the network device sends an HTTP login page to the client. The network device relays the client's username and password to the AAA server for authorization. If the login succeeds, the network device grants the client access to the network.
While performing authentications, the VLAN RADIUS attributes (name and ID of the VLAN) assigned to the hosting port is included in the RADIUS access requests and accounting requests. The VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests feature supports VLAN names accommodating 128-character strings.
With the use of VLAN RADIUS attributes in authentication requests, clients are authorized based on existing VLAN segmented networks. The existing VLAN provisioning is used as an indication of the location.
Based on RFC 2868 (RADIUS Attributes for Tunnel Protocol Support), support is provided for standard RADIUS attributes that exist for specifying the tunnel-type, medium and identifier.
Tunnel-Type (IEFT #64) = VLAN
Tunnel-Medium-Type (IEFT #65) = 802 (6)
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID (IEFT #81) = [tag, string]
How to Configure VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests
To create an attribute filter-list and to bind an attribute filter-list with authentication and accounting requests, perform the following task:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
| enable | Enter your password if prompted. |
|
| configure terminal | |
|
| access-session attributes filter-list list | |
|
| configure terminal | |
|
| exit | |
|
| access-session accounting attributes filter-spec include list | |
|
| end |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
| enable | Enter your password if prompted. |
|
| set platform software trace | |
|
| end |
Configuration Examples for VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests
The following is sample output from the set platform software trace command. The output provides debugging information used to verify VLAN RADIUS attributes in access requests.
This table provides release and related information for the features explained in this module.
These features are available in all the releases subsequent to the one they were introduced in, unless noted otherwise.
| Release | Feature | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS XE 17.13.1 | VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests | The VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests feature enhances the security for access switches with the use of VLAN RADIUS attributes. |
Was this Document Helpful?

Contact Cisco
- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract )

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Because spanning-tree PortFast mode is enabled by default on dynamic ports, port Fa2/1 connects immediately and begins forwarding. Step 4 Set the VMPS reconfirmation period to 60 minutes. The reconfirmation period is the number of minutes the switch waits before reconfirming the VLAN to MAC address assignments.
Configure the RADIUS (IETF) attributes used for dynamic VLAN Assignment on Cisco ISE. Step 1. Configure the Catalyst WLC as an AAA Client on the Cisco ISE server ... To allow multiple VLANs through the switch, you need to issue these commands to configure the switch port connected to the controller: Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk ...
Configuring Dynamic VLAN MembershipThese subsections describe how to configure a switch as a VMPS client and configure it. The following topics are included: Entering the IP Address of the VMPS, page 8-4. Configuring Dynamic Ports on VMPS Clients, page 8-5. Administering and Monitoring the VMPS, page 8-5.
VLAN membership is an authorization to be part of the VLAN. There are two ways to assign VLAN membership to switch ports: Static and Dynamic. Static VLAN membership. It is an easy and straightforward method. In it, you manually add ports to VLANs. VLANs configured in this way are typically called port-based VLANs. Let us take an example.
Step 4. When the port is in Trunk mode, it will be a member of this VLAN. Select the Native VLAN ID in the Native VLAN ID drop-down list. Note: In this example, we will be using VLAN 1 as the native VLAN ID. Step 5. Select User Defined radio button in the Tagged VLANs field. Then enter the VLAN ID's that you want this port to be a member of.
ISE Dynamic VLAN assignment. Dynamic VLAN assignment by a RADIUS server (e.g. Cisco ISE) can be useful when you want to assign a specific VLAN to a user or group of users. In order to achieve this the VLANS configured on the switches must be configured with a name, this name must be consistent across multiple switches.
There are two type port used in VLANs. These are: - Access Ports, - Trunk Ports. Access ports are the ports that are member of a single VLAN. Host devices are connected to it. This is also default Cisco switch port type. Trunk ports are the ports that are member of more than one VLAN or all VLANs. This ports are used between switches.
You will statically assign the ports to the VLAN. Dynamic VLAN assignment can be done by VLAN Membership Policy Server(VMPS). VMPS needs VLAN-MAC address relationship database. Here, we will use the static one, like many network engineer. ... This is also default Cisco switch port type. Trunk ports are the ports that are member of more than one ...
Dot1x Dynamic VLAN Assignment. Hi Team, Our dot1x is used for dyamic VLAN assignement and it works using this config: int fa0/12. switchport access vlan A. switchport mode access. switchport nonegotiate. authentication event fail action authorize vlan A. authentication event no-response action authorize vlan A.
Dynamic VLAN assignment is one such feature that places a wireless user into a specific VLAN based on the credentials supplied by the user. ... the operating system redirects all client transmissions to VLAN 100 even if the physical port to which VLAN 100 is assigned. When AAA Override is disabled, all client authentication defaults to the ...
Dynamic VLAN assignment - access switch ports. Hi guys, Looking for ideas/opinions on how to dynamically assign VLANS to access ports. End goal would be to detect an interface going up, discover the Mac OUI and dynamically assign the correct voice and data VLAN based on that OUI. Bonus points if I can assign other interface configs like QoS.
To select MAC-based authentication and the security group on the FortiSwitch unit: config switch interface. edit <interface_name>. config port-security. set port-security-mode 802.1X-mac-based. end. set security-groups <security-group-name>. end. Here, the switch assigns the returned VLAN only to this userʼs MAC address.
Our dot1x is used for dyamic VLAN assignement and it works using this config: int fa0/12. switchport access vlan A. switchport mode access. switchport nonegotiate. authentication event fail action authorize vlan A. authentication event no-response action authorize vlan A. authentication host-mode multi-host. authentication open.
Step 6. Use the switchport access vlan command to assign the port or range of ports into access ports. A port in access mode can have only one VLAN configured on the interface which can carry traffic for only one VLAN. SG350X (config-if-range)#switchport access vlan [vlan-id | none] The options are:
Configuring dynamic user VLAN assignment. Clients connecting to the WiFi network can be assigned to a VLAN. You can do this with RADIUS attributes when the user authenticates or with VLAN pooling when the client associates with a particular FortiAP. You cannot use both of these methods at the same time. VLAN assignment methods: VLAN assignment ...
Create vlan and assign interface vlan to cisco port FastEthernetEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Post a Question. Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private. Match with a Tutor. Studypool matches you to the best tutor to ...
Dynamic VLAN assignment to critical authentication (inaccessible authentication bypass or AAA fail policy) VLAN is not supported. ... (name and ID of the VLAN) assigned to the hosting port is included in the RADIUS access requests and accounting requests. The VLAN RADIUS Attributes in Access Requests feature supports VLAN names accommodating ...