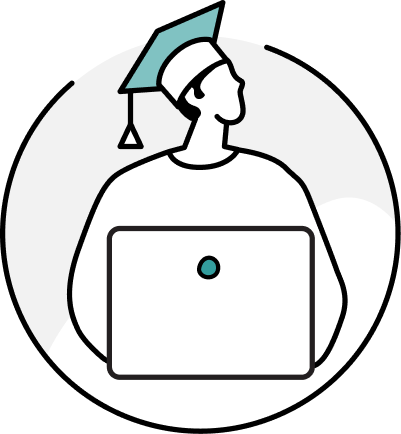
Written Business Communication


Assignment Letter Sample for Business and School
In business communication, an assignment letter holds a distinct and significant place. These formal documents are used to convey important messages related to the delegation of tasks, responsibilities, or projects within an organization. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of assignment letters, exploring their purpose, structure, key components, and best practices for drafting them effectively.
Assignment Letter Samples
There are various assignment letter sample/samples here, some of which are written to declare trademark registration, to submit assignment to a teacher or a lecturer or professor. The other letters are related to project assignment, task assignment and many others.
Trademark Assignment Letter Sample

Formal Assignment Submission Email Sample
This formal assignment submission email sample is so concise that it can save your time. Just write what the recipient needs to know.
From: [email protected]
Buy 119+ Effective Business Letter Samples here.
Dear Professor Hawkins,
My name is Christopher Williams, from your Applied Linguistics class. I am writing to submit the project you assigned to me. I attached the assignment file to this email as you instructed the class.
Best regards,
Christopher Williams
Download the letter here.
Formal Assignment Submission Email Template
To: [Recipient’s Email]
Dear Professor/Dr. [Last Name],
My name is [Your Name], from your [Class’s Name] class. I am writing to submit the project you assigned to me. I attached the assignment file to this email as you instructed the class.
[Your Name]
Job Assignment Letter
This letter is used to formally assign a specific job role or position to an employee, outlining their duties, responsibilities, and reporting structure.
[Employee’s Name] [Employee’s Address] [City, State, ZIP Code]
Dear [Employee’s Name],
I am pleased to officially assign you the role of [Job Title] within [Company Name], effective [Start Date]. This letter outlines the specific duties, responsibilities, and reporting structure associated with your new position.
Job Title: [Job Title] Department: [Department Name] Reporting To: [Supervisor’s Name] Start Date: [Start Date]
Duties and Responsibilities:
- Primary Responsibilities: In your role as [Job Title], you will be responsible for [Brief Description of Primary Responsibilities].
- Secondary Responsibilities: Additionally, you will be expected to [Brief Description of Secondary Responsibilities].
Reporting Structure:
You will report directly to [Supervisor’s Name], who will provide guidance, support, and periodic performance evaluations. Please be aware that your role may evolve as the needs of the department and company change.
We are confident that your skills and experience will be a valuable asset to our team, and we look forward to your contributions. If you have any questions or require further clarification regarding your new position, please do not hesitate to reach out to [Contact Person/HR].
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Company Name]
Project Assignment Letter
When assigning a specific project to an individual or team, this letter outlines the project’s objectives, scope, timeline, and resources available.
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Position] [Company Name]
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to formally assign the [Project Name] to your team at [Company Name]. This project holds significant importance for our organization, and I have full confidence in your team’s capabilities to execute it successfully.
Project Objectives: The primary objective of this project is to [state the project’s overarching goal and purpose]. It aligns with our strategic objectives and aims to [mention any specific outcomes or benefits].
Scope: The project scope encompasses [briefly describe the key deliverables, tasks, and boundaries]. It’s essential to maintain focus on these defined parameters to ensure project success.
Timeline: The project is expected to commence on [start date] and conclude on [end date]. Attached is a detailed project schedule outlining milestones and deadlines.
Resources Available: Your team will have access to [list the resources, both human and material, available for the project]. Please liaise with [point of contact] for any additional requirements.
Please confirm your acceptance of this project assignment at your earliest convenience. Regular progress updates will be expected to ensure the project remains on track.
I appreciate your dedication and commitment to our organization’s success. I am confident that your team will excel in delivering this project.
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Company Name] [Contact Information]
Task Assignment Letter
Used for delegating specific tasks or assignments within a project, this letter specifies the task’s details, deadlines, and expectations.
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company] [Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title] [Recipient’s Department] [Company Name]
I hope this letter finds you well. As we move forward with our project [Project Name], I would like to formally assign specific tasks to ensure its successful completion. Your expertise and dedication make you a valuable asset to our team, and I trust that you will excel in your assigned role.
Task Assignment Details: Task: [Task Name] Description: [Brief Task Description] Deadline: [Deadline Date] Expected Outcome: [Specify Desired Outcome]
Expectations:
- Please review the task details carefully and ensure a clear understanding of the objectives.
- Plan and execute the task efficiently, keeping quality and timeliness in mind.
- Regularly update me on your progress, addressing any challenges or concerns promptly.
- Collaborate with relevant team members for a smooth workflow.
- Submit the completed task by the specified deadline.
Your contribution is vital to the success of this project, and I have full confidence in your abilities. Should you require any support or clarification, do not hesitate to reach out.
Thank you for your commitment to our shared goals. Together, we will achieve excellence.
[Your Name] [Your Contact Information]
cc: [List of Relevant Team Members]
Sales Territory Assignment Letter
Sales organizations use this letter to assign specific territories to sales representatives, including geographical boundaries and sales goals.
Dear [Sales Representative’s Name],
I trust this letter finds you in good health and high spirits. As we continue to strive for excellence in our sales operations, I am pleased to inform you of your newly assigned sales territory.
Effective [Effective Date], you are entrusted with the responsibility of managing the [Territory Name] territory. This territory includes the geographical boundaries of [Geographical Boundaries], which have been carefully selected based on market analysis and growth potential.
Your primary objective within this territory is to achieve the following sales goals:
- Revenue Targets : Your annual revenue target for the [Territory Name] territory is [Dollar Amount]. This goal is set to capitalize on the region’s market potential.
- Market Share : We aim to capture a [Percentage]% market share in this territory within the next [Time Frame].
- Customer Acquisition : Focus on acquiring [Number] new customers within the first [Time Frame].
To support your efforts, you will have access to [Support Resources], including marketing materials and dedicated sales support. Regular performance reviews and coaching sessions will be conducted to ensure you are on track to meet and exceed these goals.
Your dedication and commitment are crucial in realizing the full potential of this territory. I have full confidence in your abilities and look forward to witnessing your success in this new role.
If you have any questions or require further clarification, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Congratulations, and best of luck in your new role!
Client Account Assignment Letter
You can write this letter to assign a particular client account to a team or individual, outlining the client’s needs and expectations.
[Your Company Letterhead]
[Client Name] [Client Address] [City, State, ZIP Code]
Dear [Client Name],
I trust this letter finds you well. We are excited to continue serving your esteemed organization as a trusted partner. At [Your Company Name], we are committed to delivering the highest level of service to meet your unique needs and expectations.
After careful consideration and analysis of your account requirements, we are pleased to inform you that your account will be assigned to our dedicated team led by [Team Leader’s Name]. This team comprises highly skilled professionals with a proven track record in delivering exceptional results to clients in your industry.
Our commitment to you includes:
- Personalized Service: Your dedicated team will work closely with you to understand your goals and requirements.
- Timely Communication: We will provide regular updates and ensure prompt responses to your inquiries.
- Customized Solutions: Tailoring our services to align with your specific needs.
- Continuous Improvement: We will proactively seek opportunities to enhance our partnership.
Please feel free to reach out to [Team Leader’s Name] or myself should you have any questions or require further clarification.
We look forward to a successful partnership and exceeding your expectations. Thank you for choosing [Your Company Name].
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company Name] [Contact Information]
[Enclosure: Additional Information or Documents, if applicable]
Employee Transfer Assignment Letter
When an employee is transferred to a different department or location, this letter communicates the details of the transfer, including the new position and reporting structure.
[Employee’s Name] [Employee’s Address] [City, State, Zip Code]
I hope this letter finds you in good health and high spirits. We are writing to inform you of an important development in your career here at [Company Name]. After careful consideration and based on your exemplary performance, we are pleased to announce your transfer to a new department/location, effective [Effective Date].
Your new position will be [New Position Title], reporting to [Supervisor’s Name], who will be your immediate supervisor in the [New Department/Location]. This transfer is part of our ongoing efforts to optimize our workforce and align talent with evolving business needs. We are confident that your skills and expertise will make a valuable contribution to the [New Department]’s objectives.
Please note that your terms and conditions of employment, including your compensation and benefits, will remain unchanged. You will receive detailed information regarding your new responsibilities and any necessary training in the coming days.
We appreciate your dedication and look forward to witnessing your continued success in this new role. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact [HR Contact Name] in our Human Resources department.
Congratulations on this exciting new chapter in your career, and we wish you all the best in your new role.
Property Assignment Letter
You can write this letter to assign company assets or property, such as laptops, vehicles, or office spaces, to employees. It includes terms and conditions for use and return.
[Employee’s Full Name] [Employee’s Address] [City, State, Zip Code]
Re: Assignment of Company Property
I am writing to officially assign the following company assets to you, in your capacity as [Employee’s Position] at [Company Name]:
- [List of Assigned Items, e.g., Laptop, Vehicle, Office Space]
You are hereby authorized to use these assets solely for company-related purposes during your employment with [Company Name]. Please take note of the following terms and conditions:
- Care and Maintenance: You are responsible for the proper care and maintenance of the assigned assets, ensuring they are used in a manner consistent with company policies and procedures.
- Return of Assets: Upon termination of your employment or at the company’s request, you must promptly return all assigned assets in good condition.
- Loss or Damage: Any loss, damage, or theft of assigned assets must be reported immediately to [Designated Contact].
- Personal Use: Personal use of company assets is strictly prohibited unless explicitly permitted by company policy.
Failure to comply with these terms may result in disciplinary action, including the potential recovery of costs associated with any damage or loss.
Please acknowledge your acceptance of these terms by signing and returning this letter within [Number of Days] days.
Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
[Employee’s Acknowledgment and Signature]
I, [Employee’s Name], acknowledge receipt of the above assignment of company property and agree to abide by the terms and conditions outlined herein.
Signature: ________________________
Date: ____________________________
Training Assignment Letter
When employees have to undergo specific training programs, this letter informs them about the training details, including dates, locations, and objectives.
[Your Company Logo]
We are pleased to inform you that you have been selected to participate in our upcoming training program. This initiative is aimed at enhancing your skills and knowledge to contribute effectively to our organization’s goals. Please find the details below:
Training Program: [Program Name] Date: [Start Date] to [End Date] Location: [Training Venue] Objective: The primary objective of this training is to [Specify Training Objectives].
- [Day 1]: [Agenda for Day 1]
- [Day 2]: [Agenda for Day 2]
- [Day 3]: [Agenda for Day 3]
Please arrive at the training venue on time and bring any materials or tools specified in the training agenda. Dress code is [Dress Code].
This training is a valuable opportunity to further develop your skills and contribute to the success of our company. We look forward to your active participation.
If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to contact [Training Coordinator’s Name] at [Training Coordinator’s Email] or [Training Coordinator’s Phone Number].
Thank you for your commitment to your professional development and our company’s success.
Contract Assignment Letter
In business contracts, one party may assign their rights and obligations to another party. This letter formalizes the assignment of the contract and notifies all relevant parties.
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Zip Code] [Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Address] [City, State, Zip Code]
Re: Contract Assignment Letter
I am writing to formally notify you of the assignment of the contract dated [Contract Date], between [Original Party Name], hereinafter referred to as the “Assignor,” and [Recipient’s Name], hereinafter referred to as the “Assignee.”
Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the contract, the Assignor hereby assigns all its rights, duties, and obligations under the aforementioned contract to the Assignee, effective as of [Assignment Effective Date]. This assignment includes but is not limited to [List Key Contractual Terms or Rights Being Assigned].
This assignment is made with the full consent and understanding of all parties involved. All future correspondence, payments, and obligations pertaining to the contract shall be directed to and assumed by the Assignee.
Please be advised that this assignment does not in any way alter the terms and conditions of the original contract, except for the change in the party responsible for its execution.
We kindly request you to update your records accordingly and acknowledge receipt of this letter at your earliest convenience.
Thank you for your prompt attention to this matter. Should you have any questions or require further information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [Your Contact Information].
Yours sincerely,
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Company Name] [Email Address] [Phone Number]
Copyright Assignment Letter
In creative industries, authors or creators may assign their copyright to a publisher or another entity. This letter details the transfer of copyright ownership.
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Zip Code] [Email Address] [Phone Number] [Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title] [Company or Organization Name] [Address] [City, State, Zip Code]
I, [Your Name], am the author/creator of the [Title of Work], which is a literary/artistic work registered under copyright number [Copyright Registration Number], dated [Date of Copyright Registration]. I am writing to formally assign all rights and interests in the aforementioned work to [Company or Organization Name], hereinafter referred to as the “Assignee.”
By this Copyright Assignment Letter, I acknowledge that I am the sole owner of all copyright interests in the work and have full authority to assign these rights to the Assignee. I hereby transfer, convey, and assign to the Assignee, its successors, and assigns, all rights, title, and interest in the work, including but not limited to:
- Exclusive copyright and reproduction rights.
- The right to distribute, display, and perform the work publicly.
- The right to create derivative works based on the original work.
- The right to enforce copyrights against third-party infringement.
This assignment is effective as of [Effective Date], and I understand that the Assignee will have full control over the work’s exploitation. In consideration of this assignment, I agree to receive [Agreed Compensation or Royalties] as per our separate agreement.
I warrant and represent that I have not previously assigned or encumbered the copyright interests in the work and that the work is original and does not infringe upon the rights of any third party. I further agree to cooperate with the Assignee in executing any additional documents necessary to perfect this assignment.
This Copyright Assignment Letter constitutes the entire agreement between the parties and supersedes all prior agreements, oral or written. Any modification to this agreement must be in writing and signed by both parties.
Please sign below to acknowledge your acceptance of this assignment.
[Your Signature]
Accepted by:
[Recipient’s Signature] [Recipient’s Name] [Date]
Vendor Assignment Letter
Businesses may assign their contracts or agreements with vendors to another company. This letter informs the vendor of the assignment and provides instructions for future interactions.
[Vendor’s Name] [Vendor’s Address] [City, State, ZIP Code]
Dear [Vendor’s Name],
We hope this letter finds you well. We are writing to inform you of an important change that will affect our ongoing business relationship. After careful consideration and in the interest of streamlining our operations, we have decided to assign all existing contracts and agreements between [Your Company’s Name] and [Vendor’s Name] to [Name of the Assignee Company], a reputable entity that has agreed to assume all rights and obligations outlined in our existing agreements.
This assignment will become effective on [Effective Date], and from that point forward, [Name of the Assignee Company] will be your primary point of contact for all matters related to the aforementioned contracts and agreements. They will honor all the terms and conditions previously established between [Your Company’s Name] and [Vendor’s Name].
We kindly request that you cooperate with [Name of the Assignee Company] as you have with us, ensuring a smooth transition of responsibilities. Should you have any questions or require further information regarding this assignment, please do not hesitate to reach out to [Contact Person at Assignee Company] at [Contact Email] or [Contact Phone Number].
We appreciate the cooperation and partnership we have enjoyed with you over the years and believe that this change will be beneficial for all parties involved. We look forward to continuing our business relationship through this transition and into the future.
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company’s Name] [Contact Email] [Contact Phone Number]
Beneficiary Assignment Letter
In insurance or financial services, this letter designates a beneficiary for a policy or financial account, specifying the beneficiary’s rights and responsibilities.
[Your Company Letterhead] [Date]
[Beneficiary’s Full Name] [Beneficiary’s Address] [City, State, Zip Code]
Dear [Beneficiary’s Name],
I hope this letter finds you in good health. We are writing to inform you about a significant update regarding your policy/account with [Your Company Name]. In accordance with your recent request, we have processed the beneficiary assignment for your policy/account number [Policy/Account Number], which has been updated effective [Effective Date].
This beneficiary assignment is a crucial step to ensure that your financial assets are passed on to the intended recipient in the event of your unforeseen absence. We understand the importance of this decision, and we are committed to making this process as seamless as possible for you.
Please take a moment to review the details of this assignment, which outline your rights and responsibilities as the designated beneficiary:
Beneficiary’s Rights:
- Claiming Benefits: As the designated beneficiary, you have the right to claim the benefits associated with the policy/account upon the insured or account holder’s demise. Please contact our claims department at [Claims Department Contact] to initiate the claims process.
- Beneficiary Designation Change: You have the option to change the designated beneficiary at any time by submitting a formal written request to [Your Company’s Address]. Changes will only take effect upon our receipt and verification of the request.
- Confidentiality: We respect your privacy and will maintain the confidentiality of your beneficiary designation.
Beneficiary’s Responsibilities:
- Notification: In the unfortunate event of the policy/account holder’s passing, it is your responsibility to promptly notify [Your Company Name] by contacting our claims department at [Claims Department Contact].
- Documentation: To initiate the claims process, you will be required to provide necessary documentation, including a copy of the policy/account holder’s death certificate, your identification, and any other documents requested by our claims department.
- Verification: All information provided during the claims process must be accurate and truthful. Falsifying information may result in a delay or denial of the claim.
We recommend that you keep a copy of this letter along with your policy/account documents in a secure location for your records.
Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our customer service team at [Customer Service Contact]. We are here to assist you and ensure a smooth beneficiary claims process.
Thank you for entrusting [Your Company Name] with your financial matters. We value your continued relationship with us and are committed to providing you with the highest level of service.
Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) Assignment Letter
When an NDA is assigned from one party to another, this letter communicates the change and the continued obligation to maintain confidentiality.
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company Name] [Your Company Address] [City, State, ZIP Code] [Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title] [Recipient’s Company Name] [Recipient’s Company Address] [City, State, ZIP Code]
I trust this letter finds you in good health and spirits. We are writing to inform you of a significant development concerning the Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) signed between [Your Company Name] and [Recipient’s Company Name] on [Date of NDA]. This letter serves as official notice of the assignment of NDA obligations.
Effective [Effective Date of Assignment], [Your Company Name] has transferred all rights, obligations, and responsibilities under the aforementioned NDA to [Assignee’s Company Name]. This assignment has been made in accordance with the terms and conditions outlined in the original NDA.
We wish to emphasize that, despite this assignment, your continued obligation to maintain the confidentiality of any and all confidential information disclosed during our prior business relationship remains unchanged. You are still bound by the terms and restrictions set forth in the NDA.
We kindly request your acknowledgment of this assignment in writing, and we remain available to address any questions or concerns you may have.
Thank you for your attention to this matter.
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company Name]
By signing below, you acknowledge the assignment of NDA obligations as described in this letter:
Recipient’s Signature: ______________________ Date: ___________
[Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title] [Recipient’s Company Name]
Non-Compete Agreement
Similar to the NDA, this letter communicates the assignment of a non-compete agreement, which restricts an individual from competing with their former employer.
I trust this letter finds you well. We are writing to formally inform you of the assignment of the Non-Compete Agreement (hereinafter referred to as “the Agreement”) originally entered into between [Former Employer’s Name] and yourself on [Date of Original Agreement]. We wish to apprise you that, as of [Effective Date of Assignment], all rights, obligations, and responsibilities under this Agreement have been assigned to [Your Company Name].
This assignment has been undertaken in accordance with applicable legal procedures and regulations. Henceforth, any inquiries, notifications, or matters related to the Agreement should be directed to [Your Company Name] at [Your Company Address].
We wish to reiterate our commitment to upholding the terms and conditions set forth in the Agreement, and we expect your continued compliance with its provisions. Should you have any questions or require clarification regarding this assignment, please do not hesitate to contact us at [Your Company Contact Information].
[Your Name] [Your Title] [Your Company Name] [Your Contact Information]
Note: This letter serves as a formal communication of the assignment of a Non-Compete Agreement and should be reviewed by legal counsel before use.
Related Posts
Business letter elements.
Business Letter Closings
Layout of Business Letters
Letter Phrases
Parts of Business Letters
Optional Business Letter Parts
Business Letter Book
Most Popular Posts and External Useful Links
Circular Letter Sample
Order Letter Sample
Invitation Letter Sample
Approval Letter Sample to Grant Request
Business Letter Resources

2 thoughts on “Assignment Letter Sample for Business and School”
Pingback: Resume Samples That Win the Job - Business Written Communication
Pingback: Approval Letter Sample for Leave, Loan, Mortgage, and Visa - Englet
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Crafting an Effective Letter of Assignment: A Comprehensive Guide with Sample

A letter of assignment is a critical document in various business, academic, and professional settings. It formally assigns responsibilities, tasks, or roles from one party to another. Understanding how to craft an effective letter of assignment can ensure clear communication and smooth transitions in responsibilities. This guide will explore the essential components of a letter of assignment, provide legal considerations, and offer a sample letter to help you draft your own.

Understanding the Letter of Assignment
What is a letter of assignment.
A letter of assignment is a document that formally assigns a specific task, responsibility, or job from one individual or organization to another. It is commonly used in settings such as journalism, where assignments are delegated to reporters, or in project management, where specific tasks are assigned to team members.
For more information on the role of assignments in organizational management, Harvard Business School provides a wealth of resources on organizational behavior.
Key Elements of a Letter of Assignment
Introduction : Clearly state the purpose of the letter.
Details of the Assignment : Specify the task or responsibility being assigned, including any relevant deadlines or expectations.
Resources and Authority : Outline any resources that will be provided to assist with the assignment and any authority the assignee has over others.
Expectations and Goals : Clearly define what success looks like for the assignment.
Duration of the Assignment : If applicable, state the start and end dates.
Contact Information : Provide contact details for someone who can offer assistance or answer questions related to the assignment.
To see a general template of business documents, including assignment letters, visit Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab.
Legal Considerations
When crafting a letter of assignment, it's essential to ensure that it does not violate any contractual agreements or employment laws. Consult legal resources or an attorney to confirm that all aspects of your letter are compliant with local and federal laws. The U.S. Small Business Administration offers guidelines on employment and labor laws that might be relevant.
Sample Letter of Assignment
Note: This sample is for illustrative purposes only and should be customized to meet specific needs and legal requirements.
[Your Name] [Your Position] [Your Company/Organization] [Your Address] [City, State, Zip Code] [Email Address] [Phone Number] [Date] [Recipient Name] [Recipient Position] [Company/Organization] [Recipient Address] [City, State, Zip Code] Dear [Recipient Name], Subject: Assignment of [Task/Responsibility/Project Name] I am writing to formally assign you the responsibility of [brief description of the task or responsibility]. This assignment will commence on [start date] and will conclude on [end date], unless extended by mutual agreement. Details of the Assignment: - **Task Description**: [Detailed description of the task, including any specific expectations or deliverables.] - **Resources Provided**: [List of resources or support to be provided, including access to systems, budget information, etc.] - **Authority**: You will have the authority to [describe any authority over staff, budgets, decisions]. - **Goals and Objectives**: The primary goal of this assignment is [describe what successful completion of the assignment looks like]. Please confirm your acceptance of this assignment by signing and returning a copy of this letter. Should you have any questions or require further clarification, do not hesitate to contact me directly at [your phone number] or [your email]. Thank you for your attention to this matter and your continued contribution to our team. Sincerely, [Your Signature (if sending a hard copy)] [Your Typed Name] [Your Position] [Enclosures: if any]
Best Practices for Letter of Assignment
Clarity and conciseness.
Ensure that the letter is clear and concise. Avoid ambiguity about the responsibilities or expectations to prevent misunderstandings.
After sending the letter, follow up to ensure that the recipient has understood everything and agrees to the terms laid out in the letter.
Record Keeping
Keep a copy of the signed letter for your records. This can be useful for future reference or in case of disputes.

50% OFF ONE WEEK ONLY
Quick Creator is the ultimate solution for digital marketers who need high-converting landing pages quickly and easily. Say goodbye to the old, time-consuming methods and hello to the future of digital marketing.

A well-crafted letter of assignment not only clarifies roles and responsibilities but also sets the stage for successful project execution and employee engagement. By adhering to legal standards and following the guidelines provided, you can ensure that these documents are both effective and compliant. For further reading on employment and assignment contracts, visit Harvard University's Employment and Labor Law page .
Create & Review All Your Contracts Online With LegalNow AI

© Copyright 2024 LegalNow - All Rights Reserved.
How to Write a Perfect Assignment: Step-By-Step Guide
Table of contents
- 1 How to Structure an Assignment?
- 2.1 The research part
- 2.2 Planning your text
- 2.3 Writing major parts
- 3 Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
- 4 Will I succeed with my assignments?
- 5 Conclusion
How to Structure an Assignment?
To cope with assignments, you should familiarize yourself with the tips on formatting and presenting assignments or any written paper, which are given below. It is worth paying attention to the content of the paper, making it structured and understandable so that ideas are not lost and thoughts do not refute each other.
If the topic is free or you can choose from the given list — be sure to choose the one you understand best. Especially if that could affect your semester score or scholarship. It is important to select an engaging title that is contextualized within your topic. A topic that should captivate you or at least give you a general sense of what is needed there. It’s easier to dwell upon what interests you, so the process goes faster.
To construct an assignment structure, use outlines. These are pieces of text that relate to your topic. It can be ideas, quotes, all your thoughts, or disparate arguments. Type in everything that you think about. Separate thoughts scattered across the sheets of Word will help in the next step.
Then it is time to form the text. At this stage, you have to form a coherent story from separate pieces, where each new thought reinforces the previous one, and one idea smoothly flows into another.
Main Steps of Assignment Writing
These are steps to take to get a worthy paper. If you complete these step-by-step, your text will be among the most exemplary ones.
The research part
If the topic is unique and no one has written about it yet, look at materials close to this topic to gain thoughts about it. You should feel that you are ready to express your thoughts. Also, while reading, get acquainted with the format of the articles, study the details, collect material for your thoughts, and accumulate different points of view for your article. Be careful at this stage, as the process can help you develop your ideas. If you are already struggling here, pay for assignment to be done , and it will be processed in a split second via special services. These services are especially helpful when the deadline is near as they guarantee fast delivery of high-quality papers on any subject.
If you use Google to search for material for your assignment, you will, of course, find a lot of information very quickly. Still, the databases available on your library’s website will give you the clearest and most reliable facts that satisfy your teacher or professor. Be sure you copy the addresses of all the web pages you will use when composing your paper, so you don’t lose them. You can use them later in your bibliography if you add a bit of description! Select resources and extract quotes from them that you can use while working. At this stage, you may also create a request for late assignment if you realize the paper requires a lot of effort and is time-consuming. This way, you’ll have a backup plan if something goes wrong.
Planning your text
Assemble a layout. It may be appropriate to use the structure of the paper of some outstanding scientists in your field and argue it in one of the parts. As the planning progresses, you can add suggestions that come to mind. If you use citations that require footnotes, and if you use single spacing throughout the paper and double spacing at the end, it will take you a very long time to make sure that all the citations are on the exact pages you specified! Add a reference list or bibliography. If you haven’t already done so, don’t put off writing an essay until the last day. It will be more difficult to do later as you will be stressed out because of time pressure.
Writing major parts
It happens that there is simply no mood or strength to get started and zero thoughts. In that case, postpone this process for 2-3 hours, and, perhaps, soon, you will be able to start with renewed vigor. Writing essays is a great (albeit controversial) way to improve your skills. This experience will not be forgotten. It will certainly come in handy and bring many benefits in the future. Do your best here because asking for an extension is not always possible, so you probably won’t have time to redo it later. And the quality of this part defines the success of the whole paper.
Writing the major part does not mean the matter is finished. To review the text, make sure that the ideas of the introduction and conclusion coincide because such a discrepancy is the first thing that will catch the reader’s eye and can spoil the impression. Add or remove anything from your intro to edit it to fit the entire paper. Also, check your spelling and grammar to ensure there are no typos or draft comments. Check the sources of your quotes so that your it is honest and does not violate any rules. And do not forget the formatting rules.
with the right tips and guidance, it can be easier than it looks. To make the process even more straightforward, students can also use an assignment service to get the job done. This way they can get professional assistance and make sure that their assignments are up to the mark. At PapersOwl, we provide a professional writing service where students can order custom-made assignments that meet their exact requirements.
Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
Want to write like a pro? Here’s what you should consider:
- Save the document! Send the finished document by email to yourself so you have a backup copy in case your computer crashes.
- Don’t wait until the last minute to complete a list of citations or a bibliography after the paper is finished. It will be much longer and more difficult, so add to them as you go.
- If you find a lot of information on the topic of your search, then arrange it in a separate paragraph.
- If possible, choose a topic that you know and are interested in.
- Believe in yourself! If you set yourself up well and use your limited time wisely, you will be able to deliver the paper on time.
- Do not copy information directly from the Internet without citing them.
Writing assignments is a tedious and time-consuming process. It requires a lot of research and hard work to produce a quality paper. However, if you are feeling overwhelmed or having difficulty understanding the concept, you may want to consider getting accounting homework help online . Professional experts can assist you in understanding how to complete your assignment effectively. PapersOwl.com offers expert help from highly qualified and experienced writers who can provide you with the homework help you need.
Will I succeed with my assignments?
Anyone can learn how to be good at writing: follow simple rules of creating the structure and be creative where it is appropriate. At one moment, you will need some additional study tools, study support, or solid study tips. And you can easily get help in writing assignments or any other work. This is especially useful since the strategy of learning how to write an assignment can take more time than a student has.
Therefore all students are happy that there is an option to order your paper at a professional service to pass all the courses perfectly and sleep still at night. You can also find the sample of the assignment there to check if you are on the same page and if not — focus on your papers more diligently.
So, in the times of studies online, the desire and skill to research and write may be lost. Planning your assignment carefully and presenting arguments step-by-step is necessary to succeed with your homework. When going through your references, note the questions that appear and answer them, building your text. Create a cover page, proofread the whole text, and take care of formatting. Feel free to use these rules for passing your next assignments.
When it comes to writing an assignment, it can be overwhelming and stressful, but Papersowl is here to make it easier for you. With a range of helpful resources available, Papersowl can assist you in creating high-quality written work, regardless of whether you’re starting from scratch or refining an existing draft. From conducting research to creating an outline, and from proofreading to formatting, the team at Papersowl has the expertise to guide you through the entire writing process and ensure that your assignment meets all the necessary requirements.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
How to Write an Email to a Professor (With Examples)

By Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
How to email a professor in 7 steps, email to professor examples.
Emailing your professor can be a daunting task.
Writing professional emails is never easy, but composing an email to a professor can feel especially nerve-racking. After all, your professors have a lot of control over your academic success and your future career, so you don't want to make a mistake.
So, how exactly do you write a successful email to a professor?
In this article, we’ll give you a step-by-step guide for how to write an email to your professor, plus a set of email templates you can use.
We’ve broken the process of emailing your professor into seven simple steps.
Step 1: How to Write the Subject Line
Start by writing a clear, concise subject line for your email.
Your subject line should be specific to your situation. Ideally, your professor should understand why you’re emailing them without even having to open the body of your message.

For example, if you’re emailing to request an extension for a research paper, you can use the subject line “Research paper deadline extension.” Or, if you’re emailing to ask for a clarification about the syllabus, you can use the subject line “Question about class syllabus.”
Step 2: How to Address a Professor in an Email
You should start your email with a formal salutation.
You can use formal greetings, such as “Dear” or “Hi,” followed by your teacher’s preferred title, whether that’s “Professor [Last Name],” “Mr. [Last Name],” “Ms. [Last Name],” or simply “[First Name].”
If you’re not sure about your professor’s title, “Dear Professor [Last Name]” is always a safe bet.
Step 3: How to Start an Email to a Teacher
Start your email by introducing yourself and explaining which class you’re in. For example, you might write, “My name is Hannah, and I’m a freshman in your ENGL 453 class.”
It’s common for professors to teach multiple classes, especially at large universities, so they don’t always know all their students by name. If you’re emailing from your academic account, they’ll likely be able to see your full name in the system, but it’s still better to be safe than sorry.
Of course, if you’ve already established a working relationship with your professor, and they know who you are, you don’t have to introduce yourself. Instead, you can start your email with a friendly greeting, such as “I hope your week is going well” or “Happy Friday!”

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Step 4: How to Explain Your Request
Now that you’ve finished your introduction, it’s time to explain all the essential information about why you’re writing this message.
Professors lead busy lives, so try to keep the body of your email as concise as possible. Don’t use a whole paragraph when a single sentence would do.
Try to keep a professional tone while you explain your request. You don’t need to sound overly stiff, but you should generally avoid using slang or making jokes.
If you’re writing about an issue that includes personal details, such as a health issue or the loss of a loved one, it’s okay to be vague when explaining your reasons. Don’t feel pressure to include details about your personal life that you’re not comfortable sharing.
Finally, be specific about what kind of follow-up action you’re requesting from your professor, if any. For example, you can write, “Please let me know if it would be possible to extend the deadline,” or “Please send me your feedback on this draft at your earliest convenience.”
Step 5: How to End an Email to a Professor
You can end the body of your email with a simple expression of gratitude. You can write something like, “Thank you for your understanding and support,” or simply “Thanks for your time.”
Step 6: How to Sign Off an Email
Sign off your email with a simple closing salutation, followed by your first name.
Keep it simple and polite. Popular choices include “Best,” “Thanks,” “Sincerely,” and “Regards.”

Step 7: Edit Your Email with ProWritingAid
You don’t want to send your professor an email riddled with grammar mistakes, especially if it’s your English professor! And even if they teach a different subject, like math or biology, you still want to make sure you’re putting your best foot forward.
Editing your email with ProWritingAid can help you avoid mistakes. Our editing tool will correct grammar errors, spelling typos, and weak word choices.
You can even ask the tool to help you ensure you’re using a formal tone so your email doesn’t come across as casual or unprofessional.
Now that we’ve gone over the seven steps for writing an email to a professor, let’s look at some examples.
Here are some email templates you can use, depending on your specific situation.
Sick Email to Professor Example
Subject line: Missing class today
Dear Professor [Last Name],
My name is [your name], and I’m a student in your class [class name]. I’m writing to let you know that I won’t be able to make it to class today, due to health issues. [Insert details if needed].
Please let me know what material we’ll be covering so I can make it up before the next class.
[Your name]
Sample Email to Professor Asking for Help
Subject line: Help with [class name]
My name is [your name]. I’ve been really struggling with your class [class name] this semester, and I’m having a hard time understanding [details].
Would you have time to sit down with me and help me better understand the material? I would welcome any support you can offer.
Thank you in advance! I look forward to hearing from you.
How to Email a Professor About a Grade
Subject line: My grade for [assignment/exam name]
I hope your week is off to a good start!
I recently received my grade for [assignment/exam name], and it was lower than I expected. Could you please tell me where I lost points?
I know you have a busy schedule, but I would really appreciate more details, since I’m sure that information could also help me improve my grades in the future.
Thank you so much for your time!
Sample Email to Professor for Research
Subject line: Research opportunities in your lab
I hope you’re doing well!
My name is [your name], and I’m a [year, major]. I’m writing to ask about research opportunities in your lab next semester.
I’m really interested in the topic you’re researching because [details], and I have experience conducting research with [previous experience, if any].
Please let me know if you have any openings that might be suitable for me. I look forward to hearing from you!
How to Write an Apology Email for Missing a Class
Subject line: Missing class yesterday
I hope your week is going well.
I’m writing to apologize for missing your class [class name] yesterday. I was unable to attend because [details].
I know it was an important class and that I shouldn’t have missed it. I’ll do my best to ensure this doesn’t happen again. Thank you for your support and understanding.
Extension Email to Professor Example
Subject line: Extension for [Assignment Name]
My name is [your name], and I’m a student in your class [class name]. I’m writing to request an extension for our assignment about [assignment details].
I’ve been struggling to complete the assignment in time because of [reasons]. I would really appreciate it if you could extend the deadline to [new deadline date], due to my situation.
Please let me know if that would be okay. Thank you so much for your flexibility.
Thanks again,
How to Write a Follow-Up Email to a Professor
Subject line: Follow-up re: [subject]
I recently emailed you about [topic].
I’m just writing to follow up on my previous email and make sure you’ve received it. If you have, please let me know when I can expect a reply.
Thank you again for your time!
Warm regards,
How to Email a Professor About Getting Into Their Class
Subject line: Joining your class [class name]
My name is [your name], and I’m a [year, major] at [school name]. I’m interested in joining your class [class name]. I’m really fascinated by [topic] because [reasons], and I’ve heard that your class is a must-take class for students interested in [topic].
I don’t know how much demand there is for the class, but I’m curious if there’s anything I should do in advance to increase my chances of getting into the class.
Thank you for your consideration! I look forward to hearing from you.
There you have it—our guide for composing a clear and professional email to a professor.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah Yang
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
- Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
| Please enter a username |
Writing an assignment letter

So, how detailed should an assignment agreement be? The answer is as detailed as possible. The assignment letter should be a legally binding document, confirming the agreement between the company and the assignee with respect to the terms and conditions of the assignment. In reality, the most common approach is that the assignee remains employed with the home company and the home employment contract remains in place. However, the assignment letter serves as an addendum to the employment contract and confirms the terms and conditions which vary from the normal contract while on assignment. Any terms and conditions not specifically varied therefore remain as per the home employment contract.
Most of the checklist items opposite will require considerable scoping – particularly if no assignment policy exists, but making well outlined provisions will prove worthwhile. The extent to which each item should be explained is illustrated below for three key areas.
Compensation, tax and pension arrangements
This is possibly the most complex and important part of the assignment letter and must clearly explain how the assignee will be compensated while on assignment. If the company uses a build-up or balance sheet approach, this section of the agreement will confirm details such as the home notional salary, cost of living adjustments, assignment and location allowances and, of course, the assignment salary. It should be confirmed whether the assignment salary is guaranteed net or gross, as well as where and how it will be delivered, i.e. through which payroll, in which currency, details of split pay arrangements, exchange rates, etc. If the company has a variable pay structure details of how bonus and incentive payments will be calculated and delivered while on assignment must also be included. The process for salary reviews must also be explained, as well as the treatment of assignment compensation for tax and social security. Assignees will normally remain in home country social security plans while on assignment, subject to the relevant regulations, and this should also be confirmed in the assignment letter. This section of the agreement will also give details of the tax services provided to the assignee, e.g. departure and arrival meetings, tax return preparation, etc. And finally, the pension arrangements should be confirmed. Of course, if the assignee is to be compensated according to a different approach, e.g. the assignment salary is based on the local compensation levels of the host location as opposed to the build-up method, similar details to the ones described above should be given, which confirm the assignment compensation and tax treatment
Assignment benefits
The most significant benefits, both in terms of cost to the company as well as value to the assignee, are education allowances for the assignee’s children and host country accommodation. The assignment letter should clearly explain the level of benefits provided and how they are delivered, i.e. in-kind or in cash, bearing in mind the most tax effective form of delivery for the company depending on host country tax legislation. Tax charged on assignment benefits can be considerable, sometimes up to 50% of total assignment costs. With education benefits it is important to state the type of schooling for which the company will provide assistance. If there are limits on the amount up to which the company will pay for education, or limitations on the choice of schools, this should be confirmed. Similarly, the limits up to which the company will pay for host country accommodation must be set out clearly. The letter should also clarify what happens if the assignee chooses accommodation below or above the set rental limits.
End of assignment
If there is the possibility of an assignment extension beyond the initially-agreed term, the applicable policy should be detailed here. Most importantly, a maximum duration beyond which the assignment will not be extended should be indicated. This avoids situations where employees become “permanent” assignees, remaining on assignment terms and conditions well beyond five years, which is generally the most common maximum assignment duration. It is also good practice to give details of the company’s localisation policy in this section. It may well suffice to confirm that a localisation policy may be applied once the maximum assignment duration has been reached, without having to give too many details on the actual process. But by mentioning the possibility of localisation in the letter, assignees’ expectations are managed and they are aware that assignment terms will not continue indefinitely. In the repatriation section the agreement should confirm the relocation assistance provided; e.g. shipping, temporary accommodation, relocation lump-sums, etc. Furthermore, this section should confirm the process and time scales for finding a suitable position for the assignee upon returning home. Finally, assignment letters rarely differentiate between terminating or resigning from the assignment, as opposed to terminating or resigning from the actual employment with the company. It is good practice to include the relevant terms and notice periods for each of these scenarios here and to differentiate accordingly. Terminating the employment of an assignee can be complicated and this section of the agreement should be very well thought through. Unfortunately, the governing labour law is often unclear or not straightforward to determine. A company should always seek legal advice should a labour dispute arise.
Need help with assignment letters? ECA's Consultancy & Advisory team are on hand to critique your company's assignment letters or create assignment letter templates in line with your policy, as well as offer expert advice and guidance on content so that your assignment letters accurately manage the expectations of the employee and the company. If you'd like to speak with one of our Consultants, you can request a callback here .

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.

4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
What is your plagiarism score?
Examples of business letter format.
In this section, you will find many instructional materials we’ve developed for our Writing Center teaching.
However, there are limitations to these materials. Assignments vary, and different instructors want different things from student writers. Therefore, the advice here may or may not apply to your writing situation.
Finally, handouts can give only a fraction of the customized guidance that an individual conference with a Writing Center instructor can provide. If you have questions about the information in our handouts, please make an appointment to see a Writing Center instructor.
5 Hill Street Madison, Wisconsin 53700
March 15, 2005
Ms. Helen Jones President Jones, Jones & Jones 123 International Lane Boston, Massachusetts 01234
Dear Ms. Jones:
Ah, business letter format-there are block formats, and indented formats, and modified block formats . . . and who knows what others. To simplify matters, we’re demonstrating the block format on this page, one of the two most common formats. For authoritative advice about all the variations, we highly recommend The Gregg Reference Manual, 9th ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001), a great reference tool for workplace communications. There seems to be no consensus about such fine points as whether to skip a line after your return address and before the date: some guidelines suggest that you do; others do not. Let’s hope that your business letter succeeds no matter which choice you make!
When you use the block form to write a business letter, all the information is typed flush left, with one-inch margins all around. First provide your own address, then skip a line and provide the date, then skip one more line and provide the inside address of the party to whom the letter is addressed. If you are using letterhead that already provides your address, do not retype that information; just begin with the date. For formal letters, avoid abbreviations where possible.
Skip another line before the salutation, which should be followed by a colon. Then write the body of your letter as illustrated here, with no indentation at the beginnings of paragraphs. Skip lines between paragraphs.
After writing the body of the letter, type the closing, followed by a comma, leave 3 blank lines, then type your name and title (if applicable), all flush left. Sign the letter in the blank space above your typed name. Now doesn’t that look professional?
John Doe Administrative Assistant
Indented Form
15 March 2005
Ah, business letter format–there are block formats, and indented formats, and modified block formats . . . and who knows what others. To simplify matters, we’re demonstrating the indented format on this page, one of the two most common formats. For authoritative advice about all the variations, we highly recommend The Gregg Reference Manual, 9th ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001), a great reference tool for workplace communications. There seems to be no consensus about such fine points as whether to skip a line after your return address and before the date: some guidelines suggest that you do; others do not. Let’s hope that your business letter succeeds no matter which choice you make!
If you are using the indented form, place your address at the top, with the left edge of the address aligned with the center of the page. Skip a line and type the date so that it lines up underneath your address. Type the inside address and salutation flush left; the salutation should be followed by a colon. For formal letters, avoid abbreviations.
Indent the first line of each paragraph one-half inch. Skip lines between paragraphs.
Instead of placing the closing and signature lines flush left, type them in the center, even with the address and date above, as illustrated here. Now doesn’t that look professional?

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

How to write a letter
HOW TO WRITE A LETTER: A GUIDE FOR TEACHERS AND STUDENTS

In this age of digital communication, writing letters is becoming something of a lost art. Emails and text messages can be sent instantly and for a fraction of the cost good old-fashioned snail mail can offer.
So, why bother teaching letter-writing at all? Well, though electronic ‘letters’ are often freer in formatting and language than physical letters, we can also apply letter-writing rules to electronic media. However, physical letters do offer some distinct benefits of their own too.
A WELL-WRITTEN LETTER CAN CHANGE THE WORLD.
Whilst we pride ourselves here on how to write a great essay, information report, or another text type that is primarily used in an educational setting, the ability to craft a powerful letter or email has literally changed people’s lives, altered the course of history and been the difference between life and death in some cases.
It can be the one opportunity to remove all the noise and confusion on any subject area and honestly tell someone how you feel straight from the heart. Pen to paper.
For whatever reason, a thousand emails, tweets, and likes will never have the same impact as a well-crafted handwritten letter. Its very creation and existence show your reader how passionate and genuine about what it contains.
Letters fall under the transactional writing category; if you want to know more about transactional texts, be sure to check out our in-depth guide here.

COMPLETE LETTER WRITING UNIT FOR STUDENTS

Over 100 PAGES of engaging RESOURCES , various letter SAMPLES , LESSON PLANS and INTERACTIVE DIGITAL RESOURCES to teach your students how to write amazing LETTERS and EMAILS .
Teach this life skill with confidence through this excellent ALL-IN-ONE RESOURCE . No preparation is required.
3 REASONS TO TEACH LETTER WRITING
1. the personal touch: .

Those of us who grew up in an age before the internet got going will remember the excitement of waiting for and receiving a letter. Many of us will have had childhood pen pals we never met or received love letters from our teenage sweethearts. Maybe some treasured letters are still securely stored in a bedside drawer.
There is something extremely personal and intimate about the letter that email cannot capture. Letters are physical, and their increasing rarity makes them seem even more intimate today.
In this day and age, receiving a personally written letter is something a unicorn in communication terms. Students who know how to produce a well-crafted letter can use it to their advantage. For example, any business hiring manager will undoubtedly be numbed by the constant torrent of emails flooding their inbox.
That mailed resume accompanied by a handwritten letter that waits for them on their desk in the morning will surely stand out and secure an attentive read. The letter, in its various forms, is guaranteed to stand out and make an impact in an age where the vast majority of communication is digital.
3. Handwriting

Just as letter writing has declined in popularity, so too has the emphasis on well-developed handwriting skills. You can, if you wish, take the opportunity here to have the students work on their handwriting skills.
While students may protest that they can accomplish the task much quicker by word-processing, another benefit of handwriting a letter is that the speed becomes almost meditative. This allows students to focus carefully on their grammar and punctuation without always resorting to the crutch of spell-checkers and grammar correction software.
FORMAL AND INFORMAL LETTER WRITING: WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
The table below outlines whether your letter should be written formally or informally, with some suggested prompts . Whilst there are many similarities, a formal letter should always be considered as a document with a real purpose and ramifications.
FORMAL LETTER FEATURES
USED FOR PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATION THESE DOCUMENTS FOLLOW A PRESCRIBED FORMAT. THEY ARE WRITTEN IN A PASSIVE VOICE FOR A SPECIFIC PURPOSE AND IN MANY CASES ARE LEGALLY BINDING. SOME EXAMPLES ARE.
INVITATION Make someone feel special about an upcoming event.
APPLICATION Write a professional letter of application for a job or group you wish to join.
REFEREE / REFERENCE Vouch for another’s skills, personality or credibility.
ACCEPTANCE & REJECTION Approve or deny an applicant in a professional manner.
MAKE AN OFFER Make a formal and binding offer in writing.
EXIT / RESIGNATION Formally leave or step down in a professional and dignified manner.
INFORMAL LETTER FEATURES
USED FOR PERSONAL COMMUNICATION THESE LETTERS HAVE NO PRESCRIBED FORMAT AND ARE WRITTEN IN AN ACTIVE VOICE.
THANK YOU Let someone know you appreciate their efforts.
CONGRATULATIONS Acknowledge someone’s achievements in life.
GRIEVANCE / LOSS Acknowledge someones personal loss or suffering and let them know you care.
FRIENDSHIP & LOVE Tell someone how special they are to you and why?
LETTER TO THE EDITOR / MAYOR ETC. Let someone know how their actions and adversely affect you and others.
LETTER TO SELF Give your older or younger self some words of advice and wisdom.
INFORMATIONAL UPDATE Write a letter back home telling them what you have been up to.
HOW TO WRITE FORMAL LETTERS
The writing process begins with planning.
As with all genres of writing, the process of formal letter writing should start with planning. This should involve sketching a brief outline from which to work rather than a comprehensive detailing of minutiae. The plan should include:
- Note addresses, names etc. – who are you writing to?
- Record the purpose of the letter – what do you want to say?
- List points to be made (each will form a paragraph) – how will you say it?
- State action point – what do you want the reader to do?
Formal letters can be written for a wide range of purposes and may come in various shapes, including a letter of complaint, a cover letter accompanying a job application, a letter of invitation, a reference letter, or a proposal letter – to name a few. Though each will adhere to its own rules of formatting and tone when writing formal letters, students should avoid using slang or contractions.
Language should be straightforward and polite. Encourage students to avoid bursts of purple prose in favor of direct, functional language. Usually, a formal letter will be written to achieve a particular end and should be written with that end foremost in mind. Students should avoid meanderings and stay firmly focused on the task at hand.
TIPS FOR WRITING GREAT FORMAL LETTERS

- The writer’s address should be in the top right-hand corner.
- The date should be written below the writer’s address
- The recipient’s name and address are below that on the left-hand side
- Use the correct opening (Dear Sir / Madam, Dear Mrs Ferguson, etc.)
- Use Standard English
- The opening sentence should explain the purpose of the letter
- Each paragraph should make a single specific point
- Use an appropriate formal tone and register in the wording of the letter
- Avoid contractions, slang, and abbreviations
- The concluding ‘action point’ paragraph states what you want the recipient to do
- The formal ending, such as Yours Sincerely or Yours Faithfully
A Note on Salutations
If the student knows the intended recipient’s name, start with Dear Mr. / Mrs Surname and end with Yours Sincerely. If they don’t know the recipient’s name, start with Dear Sir / Madam and end with Yours Faithfully.
Use of Rhetorical Devices
As mentioned, formal letter writing focuses on attempting to convince someone to take some course of action or other. To do this, it is helpful to employ some rhetorical devices to make the writing more persuasive . Some useful techniques to encourage your students to employ include:
Direct Address: Using the pronoun ‘you’ in a formal letter makes the reader feel that you are speaking directly to them. This helps to engage the reader and encourage them to continue reading the letter.

Emotive Language: Where students are trying to convince the reader to take a course of action, the use of emotive language can often be a powerful tool. Students can use either positive or negative colored words to create the desired response in the reader.
Facts and Figures: Another way to persuade and convince is to employ facts and figures to support the points made in the letter.
FORMAL LETTER STUDENT EXAMPLES

How to write an informal letter
Common features of informal letters:.
There are far fewer rules to follow when writing an informal letter, but there are still some practical guidelines to follow that will prove helpful for students engaged in writing informally.
As with any piece of writing, it is important to consider who the audience is and the reason for writing in the first place. In particular, this will help decide the tone and the language register. The more intimate the relationship, the more informal the language can be.
Though the letter will be informal, it will still have a purpose. Information should still be organized into paragraphs, as would be done with a formal, more ‘official’ letter. Students sometimes struggle with this aspect, as they often conflate ‘informal’ with ‘disorganized.’ Making them plan their informal letter before writing can help ensure it is sufficiently organized.
HOW TO START AN INFORMAL LETTER
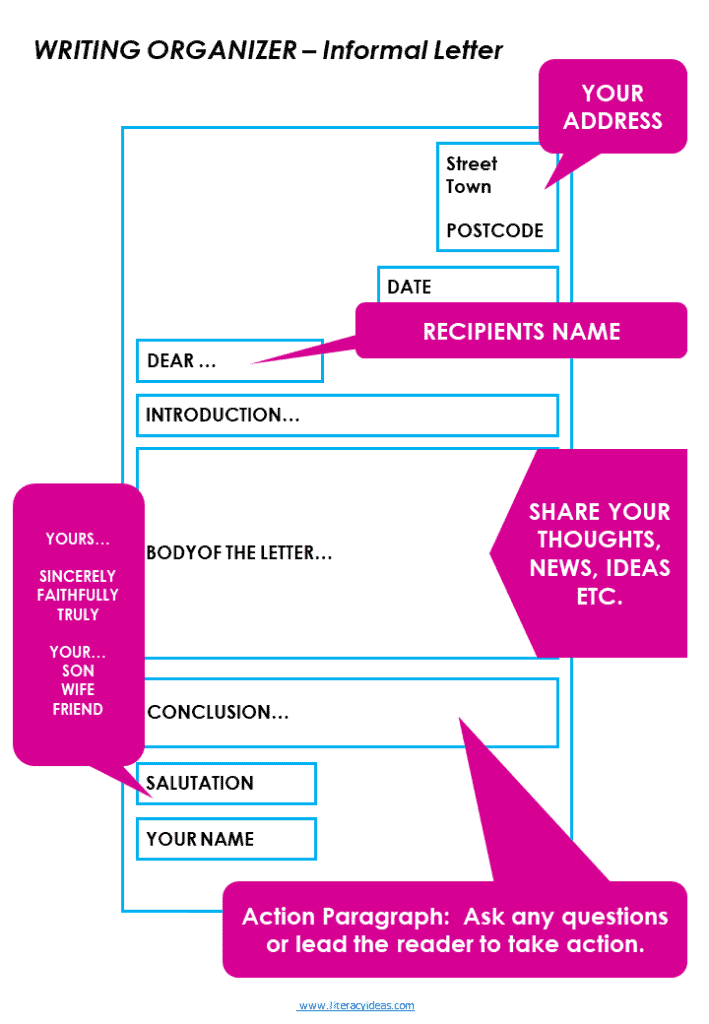
Informal letters will start with a greeting appropriate to how close the relationship is. For acquaintances, this may be ‘Dear Tom,’ (using the first name instead of the surname) to a very informal ‘Hi Jane,’. Don’t forget the comma after the name!
After the greeting, a general opening sentence should follow. Usually, this will be something like a ‘How are you?’ or a ‘How have you been?’. If the recipient is married or has kids, you may wish to ask how their spouse or children are.
Next, students should state the reason for writing. The language should be open and friendly in tone and, in contrast to the formal letter, colloquial language, idiomatic expressions, and contractions are perfectly okay and even desirable.
Just as the opening salutation to an informal letter is much more relaxed, so too will the closing salutation. There are many possibilities for the students to choose here, and their decision will depend on who they are writing to and their personal preferences. Some examples of possible closings include ‘Love’, ‘Best regards’, ‘All the best’, and ‘Thanks’.
INFORMAL LETTER STUDENT EXAMPLES

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
PRACTICE LETTER WRITING WITH THESE ACTIVITIES FOR STUDENTS
The most effective way for students to internalize all the features of letter writing, formal or informal, is to gain experience by writing various letters for differing purposes. The following activities offer some suggestions for students to get practising today:
1. FICTION AS A SPRINGBOARD
Have students write as if they were a character from a piece of fiction you have been reading in class. Choosing a dramatic point in the plot , ask students to imagine they are one of the characters writing a letter to another character in the story. This writer may be either formal or informal, depending on the scenario presented. This will give students realistic letter-writing practice while also getting them to engage closely with the text and respond imaginatively to its themes.
2. THE AGONY AUNT
Either offer a range of possible life predicaments or cut out the questions from the ‘agony aunt’ page of a local newspaper. Students must write back offering advice in response to the predicaments expressed in the question or predicament. The response should be written in full letter format. This activity also lends itself to several variations. The response may be written to a close friend, for example, or written from the perspective of a professional agony aunt employing a more formal tone and presentation.
3. A LETTER OF COMPLAINT
Have students think of their favorite candy bar or clothing item. Encourage them to imagine they have bought this product lately and found it to be substandard. Students must write a formal letter of complaint to the manufacturer outlining their complaint and recommending a course of action to satisfactorily resolve that complaint. They must use all the features of a formal letter as outlined above.

HOW TO MAKE YOUR HANDWRITTEN LETTERS LOOK OLD AND AUTHENTIC.
- Write in pencil or a calligraphy pen,
- screw them up tightly and carefully unfold and flatten.
- Lightly dab coffee stains over the paper to make it look aged.
- Carefully singe or burn the edges of your paper.
- Add some sepia-filtered photos for effect.
SIGNING-OFF
As students become more confident in their understanding of letter-writing formats, encourage them to exchange letters with each other for peer assessment. You may wish to provide them with a checklist of features to look for while reading over their partner’s work.
Letter-writing can also be a great way to partner up with schools overseas; often, children studying English as a second language will be delighted to receive letters from (and write to) students in English-speaking countries. And though email increasingly encroaches on the traditional territory of the letter, many of the skills garnered in the practice of letter writing are transferable to the modern manifestation. There is ample opportunity here to link letter-writing learning with approaches to writing emails too.
Letter-writing can provide a focus for a wide range of learning objectives while also teaching students valuable practical skills that will serve them well beyond their school years, both in their personal and work lives. And who knows, perhaps in years to come, one of the letters your student writes in your class may become a treasured keepsake in someone’s bedside drawer.
LETTER WRITING GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS (TEMPLATES)

WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
HOW TO WRITE A FORMAL LETTER TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO LETTER WRITING
Transactional Writing

Personal Narrative Writing Guide

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)
Content for this page has been written by Shane Mac Donnchaidh. A former principal of an international school and university English lecturer with 15 years of teaching and administration experience. Editing and support content has been provided by the literacyideas team.
- Product Development / Launch
- Critiques / Assessments
- Repositioning / Redesigning
- Print-to-Web / Multiplatform
- Promotion / Marketing
- Management Consulting
- Training / Facilitating
- Acoustic Guitar Magazine
- Afar Magazine
- Asiatica Magazine
- ConsumerReports.org
- Discovery.com
- Dwell Magazine
- Navigenics.com
- Surgical Techniques Online
- more projects
- About West Gold Editorial
- Michael Gold
ContentWise Blog
The assignment letter, an editor’s best friend.
By Susan West & Michael Gold on January 26, 2012
Sure, you and the writer had a long talk when you commissioned that story idea. But two months later the manuscript is on your desk, and who can remember what the article was supposed to be? That’s where an assignment letter comes in handy. After you and a freelancer have agreed on a story, recap the discussion in writing and send your letter (or e-mail message) to the writer. It will help you get the piece you want.
Once you’ve read through the guidelines below, have a look at our sample letter (a downloadable PDF document).
WHY WRITE IT?
- To build an editorial foundation for the story: A clear assignment letter puts you and the writer on the same wavelength. If your written description differs from the writer’s recollection, you have a chance to resolve the discrepancy before the first draft comes in. And when the manuscript arrives, the letter allows you to judge whether the writer delivered the story as promised. You can also circulate the letter to higher-ups to make sure they buy into the assignment and recall it later. When you distribute the manuscript to other editors for review, attach the letter so they too know what the idea was.
- To build a relationship with a writer: Writers want clear instruction; an assignment letter provides that and gives the writer something to refer to while reporting and writing. A careful summary of the story idea assures the writer that you’re a careful editor who wants to prevent those nasty surprises that so often pop up between writer and editor. The letter also lets you address a writer’s weaknesses—get two sources for every fact, avoid clichés, and so on.
WHAT’S IN IT?
- A clear, specific statement of the story’s concept, content, and approach: Quickly and specifically outline what the article will cover and the depth of information you expect, including perhaps the types of sources you desire (personal interviews, scientific studies, etc.). Send research materials you have collected. Enclose a sample story from your magazine that could serve as a model. Confirm the approach you have agreed to and, if you two have discussed them, outline the lead and structure.
- Your worries: Is the reporting going to be difficult? Say so. Are you concerned about the structure? Ask to see an outline. Are there points that absolutely have to be covered? Make sure the writer knows.
- Logistical information: Describe the magazine’s payment procedures, editing process, fact-checking needs; tell the writer if you’re going to be out of town and whether you prefer to work by phone or e-mail. You can create some of this information ahead of time to cut-and-paste into your assignment letters.
For more suggestions on working with writers, see our model rewrite letter and tips on getting the most from freelancers .
Posted in Magazines , Resources
Browse Blog by Topic
What’s new.

Connect With Us

Publishing Resources
- e-Newsletter
- ( For Clients Only )
Copyright © 2020 West Gold Editorial Consulting | Website by West Gold Editorial | Powered by WordPress
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing the Basic Business Letter

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Parts of a Business Letter
This resource is organized in the order in which you should write a business letter, starting with the sender's address if the letter is not written on letterhead.
Sender's Address
The sender's address usually is included in letterhead. If you are not using letterhead, include the sender's address at the top of the letter one line above the date. Do not write the sender's name or title, as it is included in the letter's closing. Include only the street address, city, and zip code.
The date line is used to indicate the date the letter was written. However, if your letter is completed over a number of days, use the date it was finished in the date line. When writing to companies within the United States, use the American date format. (The United States-based convention for formatting a date places the month before the day. For example: June 11, 2001. ) Write out the month, day and year two inches from the top of the page. Depending which format you are using for your letter, either left justify the date or tab to the center point and type the date. In the latter case, include the sender's address in letterhead, rather than left-justified.
Inside Address
The inside address is the recipient's address. It is always best to write to a specific individual at the firm to which you are writing. If you do not have the person's name, do some research by calling the company or speaking with employees from the company. Include a personal title such as Ms., Mrs., Mr., or Dr. Follow a woman's preference in being addressed as Miss, Mrs., or Ms. If you are unsure of a woman's preference in being addressed, use Ms. If there is a possibility that the person to whom you are writing is a Dr. or has some other title, use that title. Usually, people will not mind being addressed by a higher title than they actually possess. To write the address, use the U.S. Post Office Format. For international addresses, type the name of the country in all-capital letters on the last line. The inside address begins one line below the date. It should be left justified, no matter which format you are using.
Use the same name as the inside address, including the personal title. If you know the person and typically address them by their first name, it is acceptable to use only the first name in the salutation (for example: Dear Lucy:). In all other cases, however, use the personal title and last/family name followed by a colon. Leave one line blank after the salutation.
If you don't know a reader's gender, use a nonsexist salutation, such as their job title followed by the receiver's name. It is also acceptable to use the full name in a salutation if you cannot determine gender. For example, you might write Dear Chris Harmon: if you were unsure of Chris's gender.
For block and modified block formats, single space and left justify each paragraph within the body of the letter. Leave a blank line between each paragraph. When writing a business letter, be careful to remember that conciseness is very important. In the first paragraph, consider a friendly opening and then a statement of the main point. The next paragraph should begin justifying the importance of the main point. In the next few paragraphs, continue justification with background information and supporting details. The closing paragraph should restate the purpose of the letter and, in some cases, request some type of action.
The closing begins at the same vertical point as your date and one line after the last body paragraph. Capitalize the first word only (for example: Thank you) and leave four lines between the closing and the sender's name for a signature. If a colon follows the salutation, a comma should follow the closing; otherwise, there is no punctuation after the closing.
If you have enclosed any documents along with the letter, such as a resume, you indicate this simply by typing Enclosures below the closing. As an option, you may list the name of each document you are including in the envelope. For instance, if you have included many documents and need to ensure that the recipient is aware of each document, it may be a good idea to list the names.
Typist initials
Typist initials are used to indicate the person who typed the letter. If you typed the letter yourself, omit the typist initials.
A Note About Format and Font
Block Format
When writing business letters, you must pay special attention to the format and font used. The most common layout of a business letter is known as block format. Using this format, the entire letter is left justified and single spaced except for a double space between paragraphs.
Modified Block
Another widely utilized format is known as modified block format. In this type, the body of the letter and the sender's and recipient's addresses are left justified and single-spaced. However, for the date and closing, tab to the center point and begin to type.
The final, and least used, style is semi-block. It is much like the modified block style except that each paragraph is indented instead of left justified.
Keep in mind that different organizations have different format requirements for their professional communication. While the examples provided by the OWL contain common elements for the basic business letter (genre expectations), the format of your business letter may need to be flexible to reflect variables like letterheads and templates. Our examples are merely guides.
If your computer is equipped with Microsoft Office 2000, the Letter Wizard can be used to take much of the guesswork out of formatting business letters. To access the Letter Wizard, click on the Tools menu and then choose Letter Wizard. The Wizard will present the three styles mentioned here and input the date, sender address and recipient address into the selected format. Letter Wizard should only be used if you have a basic understanding of how to write a business letter. Its templates are not applicable in every setting. Therefore, you should consult a business writing handbook if you have any questions or doubt the accuracy of the Letter Wizard.
Another important factor in the readability of a letter is the font. The generally accepted font is Times New Roman, size 12, although other fonts such as Arial may be used. When choosing a font, always consider your audience. If you are writing to a conservative company, you may want to use Times New Roman. However, if you are writing to a more liberal company, you have a little more freedom when choosing fonts.
Punctuation
Punctuation after the salutation and closing - use a colon (:) after the salutation (never a comma) and a comma (,) after the closing. In some circumstances, you may also use a less common format, known as open punctuation. For this style, punctuation is excluded after the salutation and the closing.
- Sample Letters
FREE 9+ Sample Assignment Letter Templates in PDF | MS Word

An assignment letter is a document that is used mostly in situations such as business bankruptcy and insolvency. It is a legal document which can be presented in courts when handling different cases. Examples of scenarios whereby this paper comes in are when a business owner is assigning a portion of his or her assets to a trustee for selling purposes and also when assigning specific rights to another person such as collecting payment on your behalf.
Assignment Letter
Sample personal business letter - 9+ documents in pdf, word, sample thank you letter to boss - 22+ free documents download ..., sample trademark assignment form - 7+ examples in pdf.
Our assignment templates get designed in the best way possible to usher you properly when creating one. An assignment letter template may also be said to be a Professional Letter of assignment or an assignment letter sample.
Salary Assignment Letter
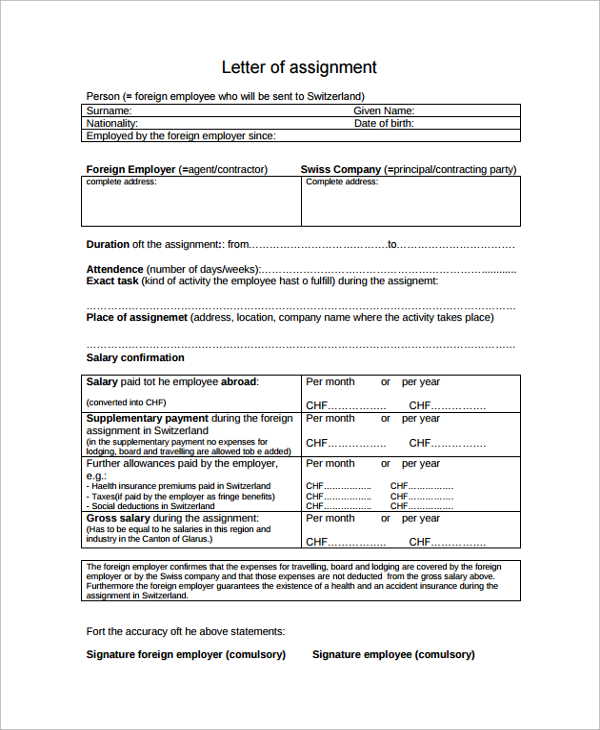
Size: 130 KB
The top of the page should have the name of the person or the entity issuing the letter together with their personal information such as the telephone number, email address, and the postal address. Below that it should indicate that it is a letter of assignment to give the form an identity. Next should be the full names of the people or entity in the agreement alongside their personal information.
After that, mention the duration of the assignment and the location of where the deal takes place. The body of the document should be concluded by listing all the details of the money that they parties will be handling. Finally, the parties involved should sign the paper to seal the agreement.
Appraisal Assignment Letter

Size: 38 KB
The top of the form should read that the document is an appraisal assignment letter for easier identification. The name plus the postal address of the person or company issuing the appraisals should be listed next. After that, a declaration statement mentioning the names of the parties involved in the agreement should be put down saying who has assigned rights to the other.
The agreement should always comply with the standards set by law. Other acknowledgments that each party is supposed to heed to should also get listed in this document. The model should conclude by stating the period when the agreement will be active.
Voided Assignment Letter

Size: 37 KB
The top of the model should read that it is a voided assignment letter for quick identification of the form. After that, on the left, the name of the person of corporate who is going to receive the document is listed together with other personal information such as a postal address and an email address.
The right should have the date of when the paper gets published. Finally, the reasons as to why there is a voided assignment letter must be on it and signatures of the parties involved should also be given to show that they agree with the stated reasons.
Incentive Assignment Letter

Size: 42 KB
The name of the company issuing the letter should be the first thing on the document and the date below that. Next should be the name and personal details of the person or entity meant to receive it. The incentive assignment should be listed giving all crucial information about it and contacts which the receiver can contact for further negotiations. Finally, it concludes with a short formal message to the receiver.
Professional Assignment Letter

Size: 355 KB
Buddy Assignment Letter

Size: 155 KB
Friendly Assignment Letter

Size: 31 KB
Sample Assignment Letter

Size: 137 KB
Assignment Letter from Trainee

Volunteer Assignment Letter

Size: 52 KB
What are the Advantages of Having our Assignment Letter Templates?
One may lack sufficient knowledge on what to include when forming this document; therefore, the main benefit of having our template is that it gives you the proper guidance on which information to include in your paper and an order of how to put it down.
Another advantage is that our templates are files which you can save on you PC; thus, you can make references from the file again in future when forming assignment letters. Finally, our templates are always designed to help you create one as per the standard legal requirements. You may also see Sample Personal Letters
How Have We Made our Assignment Letter Templates the Best for you?
Our models get worked on by the experts whom we have interviewed thoroughly and proven that they are talented. We also ensure that they have sufficient experience in the field for our templates to be as effective for you as possible. Another way we have made our templates the best for you is by making them editable such that you can do any modifications you prefer on them. Finally, they are printable for you to be able to make as many copies as you want. You may also see Friendly Letters
Which are the Most Crucial Aspects that I Should Entail in my Assignment Letter?
Always list the name of parties in the agreement and also sufficient personal information about them. Never forget to indicate the date you publish the model and the period of how long the contract will be valid. Ensure that both parties agree on what gets stated on the Professional Letters then seal the deal with signatures of each. Finally, since it is a legal document, always ensure that your agreement complies with the provisions of the law to avoid awful penalties.
We ensure that we meet the requirements of all our customers according to their needs. Those that would want a fully customed model can always communicate to us so that we can direct you to our experts to help them understand what kind of make you want. We have customer care agents that are always available to tend to all the inquiries you may have and the consultations you may need. Consider acquiring our accessible and affordable assignment letter template today, to guide you while creating the document you need.
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us !
Related Posts
Sample thank you letters to teacher, sample college letter of intent, sample reference letter templates, sample affidavit of support letter templates, resignation letter with reason samples, sample college acceptance letter templates, sample friendly letter templates, letter of intent for employment samples, letter of support samples & templates, sample business meeting invitation letter templates, sponsorship letter templates, sample contract agreement letter templates, sample proposal request letter templates, sample document request letter templates, sample job appointment letter templates, sample assignment of contract - 6+ free documents download in ..., sample assignment of mortgage template - 9+ free documents ..., sample assignment agreement template - 9+ free documents ..., sample appointment letter - 28+ download free documents in pdf ....
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Finding a Job
Letter Format Example and Writing Tips
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
What to Include in a Formal Letter
Written letter format, email letter format, letter template to download, professional written letter example, professional email example, tips for formatting your letter, proofread, spellcheck, and print, how to address the envelope.
Theresa Chiechi / The Balance
Letter format might not be top of mind when you begin writing an important letter or email, but an appropriate presentation is critical to ensure your message is ultimately well received. A printed letter is usually reserved for important professional communications, such as recommendation letters, cover letters, resignation letters, and business correspondence, so you'll want to know how to write one professionally.
Correct formatting is especially important if you're sending a hard copy to the recipient rather than an email because the letter needs to fit the page, look professional, and be clear, concise, and easy to read.
Review information on what you need to include when writing a professional letter, examples, and advice on the appropriate font, salutation, spacing, closing, and signature for business correspondence.
Key Takeaways
- A formal letter should include details about why you’re writing, an expression of your appreciation to the recipient for considering your request, and your contact information.
- Correspondence can be sent as a written letter or in an email. When sending an email message, list the reason you are writing in the subject line of the message.
- When writing a professional letter, carefully proofread and spellcheck before you print or send it.
Formal correspondence should include the details of why you’re writing, your contact information, a greeting and closing, and your signature.
Beginning of the Letter
Contact Information (Written Letter): A written letter should include the contact information of both yourself and the recipient (name, title, company name, address, phone number, email), followed by the date.
Contact Information (Email): When sending an email, you don’t need to include the recipient’s contact information. List your contact information at the end of the letter after your signature.
Greeting: Address the letter using a professional greeting and formal title ("Dear Mr./Ms./Dr.").
Body of the Letter
The first paragraph of your letter should provide an introduction as to why you are writing so your reason for contacting the person is clear.
In the following paragraphs , provide specific details about your request or the information you are providing.
The last paragraph of your letter should reiterate the reason you are writing and thank the reader for reviewing your request. If appropriate, it should also politely ask for a written response or the opportunity to arrange a meeting to further discuss your request.
Closing the Letter
Use a formal sign-off , such as "Sincerely" or "Best regards."
Signature (Written Letter): End the letter with your handwritten signature followed by your typed name.
Signature (Email): Include your typed name followed by your contact information.
It’s important to include enough detail so the recipient understands why you’re writing and the response you expect to the letter.
Here’s a template for each section of a formal letter:
Your Contact Information Name Address City, State Zip Code Phone Number Email Address
Recipient Contact Information Name Title Company Address City, State Zip Code
Greeting Dear Mr./Ms. Last Name,
Use a formal salutation , not a first name, unless you know the person well. If you do not know the person's gender, you can write out their full name. For instance, write, "Dear Pat Crody" instead of "Dear Mr. Crody" or "Dear Ms. Crody." If you do not know the recipient’s name, it’s still common and acceptable to use the old-fashioned “ To Whom It May Concern .”
Body of Letter
- Paragraph 1: State the reason you are writing, for example, you are asking for something or sharing a piece of information.
- Paragraph 2: Provide details about your request or the information you’re sharing.
- Paragraph 3: If necessary, include additional information on the purpose of your letter.
- Paragraph 4: Thank the reader for considering your request, and ask for a response to your letter.
Closing Best regards,
Signature Handwritten signature (use black or blue ink to sign a written letter)
Typed Signature Your typed name
Here’s a template for each section of a professional email:
Subject Line Subject: Your Name — Reason for Writing
Greeting Dear Mr./Ms. Last Name,
Body of Message Your message should generally be two or three paragraphs at most. Explain why you’re writing and what you’re requesting.
Closing Sincerely,
Typed Signature and Contact Information Mikala Schwartz mikala.schwartz@email.com 617-123-1234
When sending email correspondence, include the reason you are writing in the subject line of the message. List your contact information under your typed signature at the end of the message.
Here is a letter template that you can download (compatible with Google Docs and Word Online), or review the text version below.
Nicole Thomas 35 Chestnut Street Dell Village, Wisconsin 54101 555-555-5555 nicole@thomas.com
September 5, 2023
Jason Andrews Manager LMK Company 53 Oak Avenue, Ste 5 Dell Village, Wisconsin 54101
Dear Mr. Andrews,
I’m writing to resign from my position as customer service representative, effective September 16, 2023.
I’ve recently decided to go back to school, and my program starts in late September. I’m tendering my resignation now so that I can be as helpful as possible to you during the transition.
I’ve truly enjoyed my time working with you and everyone else on our team at LMK. It’s rare to find a customer service role that offers as much opportunity to grow and learn, and perhaps more rare to find such a positive, inspiring team of people to grow and learn with.
I’m particularly grateful for your guidance while I was considering furthering my education. Your support has meant so much to me.
Please let me know if there’s anything I can do to help you find and train my replacement.
Thanks and best wishes,
Signature (hard copy letter)
Nicole Thomas
Subject: Annual Meeting
Dear Kathleen,
Thank you so much for your assistance in planning our annual meeting. Your expertise in handling the meeting arrangements, booking the conference facilities and hotel, coordinating travel, scheduling events, and organizing the meeting is greatly appreciated.
I appreciate your help and advice, and I am hoping we can plan on having your assistance with next year’s event. It’s tentatively scheduled for January 16–20, 2025, in Tampa, Florida. If you can confirm your availability, I’ll be in touch when we’re ready to start planning.
I look forward to working with you in the future, and thank you again.
Best regards,
Peter Hancock
Professional letters should be simple, short, and written in business format using a traditional font.
- Length of the Letter: Most formal letters are no more than one typed page.
- Font Style and Size: Use a plain font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri. Your font size should be between 10 and 12 points.
- Margins: Use one-inch margins and left justify your text.
- Spacing: Single-space your letter, and leave a space between each paragraph. Use one-inch margins and align your text to the left. Leave an extra space after the salutation, before the closing, and before and after your handwritten signature in a printed letter.
- Printing the Letter: Business letters should be printed on plain white paper.
Once you have written your letter, proofread it and carefully spellcheck it on the screen. Then, print it out and read it aloud at least one more time, checking for any errors or typos. This is important as it's often easier to spot errors on a hard copy.
Reading your letter out loud is a good way to catch a mistake.
Check for formatting errors, such as two paragraphs that don’t have a space between them or lines that are indented incorrectly. Then, before putting your letter in an envelope, sign above your typed name using black or blue ink.
If you’re emailing your letter, send a copy to yourself to be sure it’s perfect. Then send the final version to the recipient.
Print a copy of your written letter so you have it for your records. Your email will be saved in your “sent” email folder.
When your letter is ready to mail, fold it in thirds so it fits into a business-size envelope. You can use your word-processing program to print the addresses on the envelope or handwrite them.
Print your name on the top-left corner of the front of the envelope. Print the recipient’s address in the center of the envelope, parallel with the long side. Add a stamp to the top right of the envelope.
NMU Writing Center. " Parts of a Business Letter ."
University of Arizona. " Writing a Professional Letter ."
USPS. " How to Send a Letter or Postcard: Domestic ."
Redirect Notice
Reference letters.
Some types of programs, such as fellowships and some career development awards, require the submission of reference letters by the referee. Referees must submit these letters by the application deadline in order to be considered with the application. Applications that have fewer than the required numbers of reference letters will not be reviewed.
Each funding opportunity will indicate whether Reference Letters are required.
Selecting a Referee
- At least three, but no more than five, reference letters are required unless otherwise specified in the funding opportunity.
- The letters should be from individuals not directly involved in the application, but who are familiar with the fellow/candidate's qualifications, training, and interests. Note that for postdoctoral grant applications that require submission of reference letters, a letter from the fellow/candidate's predoctoral thesis advisor is not required.
- The sponsor/co-sponsor(s) of the application cannot be counted toward the three required references.
- Resubmission applications do not need to use the same list of referees but do require new reference letters from all referees chosen.
- Make sure you include a list of referees (including name, departmental affiliation, and institution) in the cover letter of the application so NIH staff is aware of planned reference letter submissions.
Instructions to Provide to Referees
Fellows/candidates should provide their referees with the appropriate instructions. Remember to include your name as it is shown in your Commons account, your eRA Commons username, and the number of the funding opportunity (e.g., PA-21-048) to which you are applying.
Referees must submit letters directly to the eRA Commons
- Instructions for Fellowship Applicant Referees (16 KB)
- Instructions for Career Development Applicant Referees (17 KB)
Reference Letter Submission Process
- Referees must submit reference letters through the eRA Commons by the application due date. Note Referees DO NOT need need to login to eRA Commons to submit their letters.
- PI’s (fellow/candidate’s) eRA Commons username.
- PI’s first and last name as they appear on the PI’s eRA Commons account.
- Number of the funding opportunity (e.g., PA-21-048) to which you are applying.
- The confirmation sent to a referee includes the mentee and applicant’s names, a confirmation number, and the date the letter was submitted.
- The confirmation sent to a fellow/candidate includes the referee’s name and the date the letter was submitted.
- The eRA Commons links the reference letter up with the application based on eRA Commons username and funding opportunity number.
- The fellow/candidate may check the status of submitted letters by logging into their Commons account and accessing the “check status” screen for this application.
- While the fellow/candidate is able to check on the status of the submitted letters, the letters are confidential and the fellow/candidate will not have access to the letters themselves.
Contact the eRA Service Desk if you need assistance submitting your reference letter.
Transition your wardrobe with fall sneakers, chore jackets, more stylist picks — from $16
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
- TODAY Plaza
Hoda Kotb announces she is leaving TODAY: ‘I will miss you all’
Hoda Kotb has announced that she is leaving TODAY early next year, but will remain part of the NBC family.
She tearfully recounted on TODAY on Sept. 26 about how her 60th birthday celebration in August prompted a decision to make a change.
"I realized that it was time for me to turn the page at 60, and to try something new," she said. "I remembered standing outside looking at these beautiful bunch of people with these gorgeous signs, and I thought, 'This is what the top of the wave feels like for me.' And I thought it can't get better, and I decided that this is the right time for me to kind of move on."

Hoda's intention to spend more time with her daughters, Haley, 7, and Hope, 5 , also factored into her decision.
"Obviously I had my kiddos late in life, and I was thinking that they deserve a bigger piece of my time pie that I have," she said. "I feel like we only have a finite amount of time.
"And so, with all that being said, this is the hardest thing in the world."
She said she will remain with TODAY through early next year, and is going to stay in the NBC family in an unspecified role.
"It's kind of a big deal for me," she said through tears. "I've been practicing so I wouldn't cry, but anyway, I did."
Hoda has been part of the fabric at NBC News for nearly three decades , after previously working at “Dateline” and as the co-host of the fourth hour of TODAY with Kathie Lee Gifford and then Jenna Bush Hager. She and Savannah Guthrie have co-anchored TODAY for more than five years .
"We love you so much," Savannah tearfully said on TODAY. "And when you look around and see these tears, they're love. You are so loved. We don't want to imagine this place without you.
"So it's complicated because we love you so much, and we don't want you to ever go," she continued. "But also I just want to say I am so proud of my friend. You have guts. For someone to leave at the top of their game, to leave something that's wonderful that you love, where it's easy and comfortable and beautiful and fun, and say, 'But I dream bigger for myself into the great unknown.' You have so much guts. You inspire me. I love you."
The TODAY family all shared emotional messages with Hoda on the show.
"It's not over," Jenna Bush Hager said. "I'm going to be showing up at your house like the stalker you are to Zac Brown. I will be there on your doorstep, and we are your friends forever."
"Hoda has a relationship with every single person on this couch in her own way, so I think we're all just kind of wrestling with it inside," Sheinelle Jones said. "But we also know what a dynamic mom you are, and presence you are. And your whole movement with wellness, you are going to change the world. And we know it."
One of Hoda's oldest friends during her time with NBC has been weatherman Al Roker.
"I have never known anybody like you," Al said. "I've known you forever, and I love you."
Craig Melvin also paid tribute to Hoda's genuine friendship.
"People in this business, when that little red light, it goes off, they're different people," Craig said. "We've worked with all these people before. You're the opposite. That little red light goes off, you are exactly like people see you in the morning — just the biggest heart.
"You've been the heart of this show for a long time, and there's no replacing that."
She reflected on all her relationships with those behind the camera and the rest of the staff, plus the TODAY fans who gather every day in Rockefeller Plaza to brighten her morning.
Hoda also shared a letter to the TODAY staff on Sept. 26 about her decision to step down. Read it in full below.
To my TODAY family, As I write this, my heart is all over the map. I know I'm making the right decision, but it's a painful one. And you all are the reason why. They say two things can be right at the same time, and I'm feeling that so deeply right now. I love you and it's time for me to leave the show. My time at NBC has been the longest professional love affair of my life. But only because you've been beside me on this twenty-six-year adventure. Looking back, the math is nuts. 26 years at NBC News - Ten years at Dateline, seven on the seven o'clock hour, sixteen on the ten o'clock hour. I'm picturing your faces and your families and all the ways you've lifted me up and inspired me. That's my heart singing. So many of my professional relationships have become some of my most cherished friendships. Savannah: my rock. Jenna: my ride-or-die. Al: my longest friend at 30 Rock. Craig, Carson, Sheinelle and Dylan: my family. Libby, Mazz and Talia: my fearless leaders. I will miss each and every one of you at TODAY desperately. I’ve been weighing this decision for quite a while – Am I truly ready? But, my sixtieth birthday celebration on the Plaza felt like a shift. Like a massive, joyful YES, you are! I saw it all so clearly: my broadcast career has been beyond meaningful, a new decade of my life lies ahead, and now my daughters and my mom need and deserve a bigger slice of my time pie. I will miss you all desperately, but I’m ready and excited. Because I’ll be working through the beginning of 2025, there’s plenty of time to talk about what's ahead for all of us. But one thing I know for sure right now is this: everything’s going to be just fine. The Peacock’s feathers are never ruffled… no matter who comes or goes. TODAY and its amazing people — all of you — never waver. You always weather change with grace and guts. Happily and gratefully, I plan to remain a part of the NBC family, the longest work relationship I’ve been lucky enough to hold close to my heart. I’ll be around. How could I not? Family is family and you all will always be a part of mine. Love, Hoda
Scott Stump is a trending reporter and the writer of the daily newsletter This is TODAY (which you should subscribe to here! ) that brings the day's news, health tips, parenting stories, recipes and a daily delight right to your inbox. He has been a regular contributor for TODAY.com since 2011, producing features and news for pop culture, parents, politics, health, style, food and pretty much everything else.

COMMENTS
Assignment Letter Sample for Business and School In business communication, an assignment letter holds a distinct and significant place. These formal documents are used to convey important messages related to the delegation of tasks, responsibilities, or projects within an organization.
Understanding how to craft an effective letter of assignment can ensure clear communication and smooth transitions in responsibilities. This guide will explore the essential components of a letter of assignment, provide legal considerations, and offer a sample letter to help you draft your own.
Read information on how to structure an assignment and get familiar with main steps of assignment writing process!
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
In this article, we'll give you a step-by-step guide for how to write an email to a professor, plus a set of email templates you can use.
Check Assignment Instructions Instructors' guidelines supersede APA Style. Students should check their assignment guidelines or rubric for specific content to include in their papers and to make sure they are meeting assignment requirements. Tips for Better Writing Ask for feedback on your paper from a classmate, writing center tutor, or ...
Creating Effective Assignments Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an "assignment sheet" tend to produce the ...
The assignment letter should clearly explain the level of benefits provided and how they are delivered, i.e. in-kind or in cash, bearing in mind the most tax effective form of delivery for the company depending on host country tax legislation. Tax charged on assignment benefits can be considerable, sometimes up to 50% of total assignment costs.
Assignment formats Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
Step 1: Prewriting Before you start writing, you need to decide exactly what you'll write about and do the necessary research. Coming up with a topic If you have to come up with your own topic for an assignment, think of what you've covered in class— is there a particular area that intrigued, interested, or even confused you? Topics that left you with additional questions are perfect, as ...
To write a strong essay, you need an introduction, a main body organized into paragraphs, and a conclusion. See how it's done with examples.
Understand How Students Read Assignments Understanding the differences between how students and faculty look at writing assignments can help you create better assignments for your course.
Below we explain how to write a proper letter, no matter the type you need. We'll cover the correct format for a formal letter, such as a cover letter or job inquiry, as well as tips for writing a personal letter, with some helpful examples of each.
Examples of business letter format. In this section, you will find many instructional materials we've developed for our Writing Center teaching.
A sample letter of assignment is a document that outlines the details of a particular task or project being assigned to an individual or organization. This letter serves as an official communication to inform the recipient of their responsibilities, deadlines, and any other essential information. The primary purpose of a sample letter of assignment is to provide clear instructions and ...
How to write a letter. Formal, and Informal letters included. Planning tools, video tutorials, writing prompts, and teaching ideas for English teachers, students, and parents.
That's where an assignment letter comes in handy. After you and a freelancer have agreed on a story, recap the discussion in writing and send your letter (or e-mail message) to the writer. It will help you get the piece you want. Once you've read through the guidelines below, have a look at our sample letter (a downloadable PDF document).
Sample Letters If you are using letterhead, do not include the sender's address at the top of the letter; instead, begin with the date.
Leave a blank line between each paragraph. When writing a business letter, be careful to remember that conciseness is very important. In the first paragraph, consider a friendly opening and then a statement of the main point. The next paragraph should begin justifying the importance of the main point.
Our assignment templates get designed in the best way possible to usher you properly when creating one. An assignment letter template may also be said to be a Professional Letter of assignment or an assignment letter sample.
Here's how to format a letter, including spacing, font, salutation, closing, and what to include in each paragraph, as well as sample letters.
Writing a letter is easy. Writing an e-mail or text message? Piece of cake! Writing a formal letter… that's where things get complicated. You need to think about tone, word choice, formatting- the list goes
Writing a professional business letter can be an important part of a job. Learn how to write and format a basic business letter, with examples.
Resubmission applications do not need to use the same list of referees but do require new reference letters from all referees chosen. Make sure you include a list of referees (including name, departmental affiliation, and institution) in the cover letter of the application so NIH staff is aware of planned reference letter submissions.
Hoda also shared a letter to the TODAY staff on Sept. 26 about her decision to step down. Read it in full below. ... As I write this, my heart is all over the map. I know I'm making the right ...