- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper is the final section that ties together the findings, restates the main arguments, and provides closure for readers. A well-crafted conclusion not only summarizes the paper’s insights but also highlights its broader implications and suggests future research directions. This guide explores the steps involved in writing an effective conclusion, offering tips and examples to help you end your research paper on a strong note.
Purpose of a Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion serves several important purposes:
- Summarize Key Findings : Recap the main findings of the research in a concise way.
- Reinforce the Thesis : Remind readers of the main argument or research question.
- Highlight Implications : Discuss the broader significance of the findings.
- Suggest Future Research : Identify areas for further study or unresolved questions.
Structure of a Research Paper Conclusion
- Restate the Thesis : Briefly restate the research question or thesis statement, using different wording.
- Summarize Main Points : Highlight the key findings or arguments without going into detailed explanations.
- Discuss Implications : Explain what the findings mean in a larger context, considering their impact on the field or related areas.
- Recommend Future Research : Suggest potential directions for future studies based on any remaining questions or limitations in your work.
Steps to Write a Strong Research Paper Conclusion
Step 1: restate the thesis.
Begin the conclusion by rephrasing the research question or thesis statement. This reminds readers of the core argument and connects it to the findings.
Example : Original Thesis: “This study examined the effects of social media on adolescent mental health, focusing on its impact on self-esteem and anxiety levels.” Restated Thesis: “This research has highlighted the significant role that social media plays in shaping adolescent self-esteem and contributing to anxiety.”
Step 2: Summarize Key Findings
Next, summarize the most important findings or arguments from the paper. Keep this summary brief, as the main body has already provided details.
Example : “Analysis of the data revealed a clear correlation between high social media usage and low self-esteem among adolescents. Additionally, increased time spent online was associated with higher levels of anxiety, particularly among female participants.”
Step 3: Discuss the Broader Implications
In this section, explore the significance of the findings. Discuss how they contribute to the existing knowledge or impact the field. If applicable, address any potential practical or policy implications.
Example : “These findings underscore the need for educators, parents, and policymakers to develop strategies for supporting mental health among young people in a digital age. They suggest that moderating social media use may be beneficial for adolescent well-being.”
Step 4: Suggest Future Research Directions
Identify any gaps in the research or limitations that could be addressed in future studies. This section demonstrates the study’s contribution to ongoing research.
Example : “Future research should explore the long-term effects of social media use on mental health and examine potential moderating factors, such as family support and self-regulation strategies. A larger, more diverse sample would also enhance the generalizability of these findings.”
Examples of Research Paper Conclusions
Example 1: environmental science research paper conclusion.
Thesis Restatement : “This study has demonstrated the significant impact of deforestation on biodiversity loss in the Amazon rainforest.”
Summary of Findings : “The data shows that deforestation contributes directly to habitat loss, reducing species diversity and increasing the risk of extinction.”
Broader Implications : “These results emphasize the urgent need for stronger environmental protection policies to prevent further degradation of one of the world’s most vital ecosystems.”
Future Research Suggestions : “Future research should investigate the effects of deforestation on ecosystem services, such as water purification and carbon storage, which play a critical role in climate regulation.”
Example 2: Business Research Paper Conclusion
Thesis Restatement : “This research has explored how organizational culture influences employee satisfaction and retention.”
Summary of Findings : “The study found that companies with a supportive and inclusive culture reported higher employee satisfaction and lower turnover rates.”
Broader Implications : “These findings suggest that fostering a positive work environment not only benefits employees but also contributes to organizational success.”
Future Research Suggestions : “Future studies could examine how different types of leadership styles impact organizational culture and employee satisfaction across various industries.”
Example 3: Psychology Research Paper Conclusion
Thesis Restatement : “This research investigated the relationship between mindfulness practices and stress reduction among college students.”
Summary of Findings : “Participants who practiced mindfulness exercises reported lower levels of stress and improved mental clarity compared to the control group.”
Broader Implications : “These results highlight the potential of mindfulness programs as a simple, effective tool for stress management, especially in academic settings.”
Future Research Suggestions : “Further studies should explore how the duration and frequency of mindfulness practices influence their effectiveness and examine their long-term impact on mental health.”
Tips for Writing an Effective Conclusion
- Be Concise : Avoid re-explaining details from the body of the paper. Focus on the main takeaways and keep the conclusion brief.
- Stay Objective : Avoid introducing new arguments or data. Stick to summarizing and interpreting existing information.
- Use Strong Language : Convey confidence in your findings and their significance, while remaining balanced and objective.
- Avoid Redundancy : Do not repeat phrases or sentences verbatim from earlier sections. Rephrase to keep the conclusion fresh and engaging.
- End on a Positive Note : Aim to leave readers with a clear sense of the study’s contribution to the field and any actions that may result from the findings.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Introducing New Information : The conclusion is not the place to introduce new ideas or findings.
- Repeating the Introduction : Avoid copying the introduction’s content. Instead, synthesize the paper’s main points and implications.
- Being Overly General : Focus on specific conclusions rather than vague statements. Make sure your conclusions are directly related to your research.
- Ignoring Limitations : Address any limitations honestly, as they provide context for interpreting the results and contribute to transparency.
Writing a strong research paper conclusion involves restating the thesis, summarizing key findings, discussing implications, and suggesting future research directions. A well-written conclusion leaves a lasting impression, reinforcing the importance of the research and opening doors for further inquiry. By following these steps and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure that your conclusion effectively wraps up your study and communicates its significance.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research . University of Chicago Press.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Graff, G., & Birkenstein, C. (2017). They Say, I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing . W.W. Norton & Company.
- Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills . University of Michigan Press.
- Turabian, K. L. (2013). A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations . University of Chicago Press.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

APA Research Paper Format – Example, Sample and...

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples

Data Interpretation – Process, Methods and...


Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
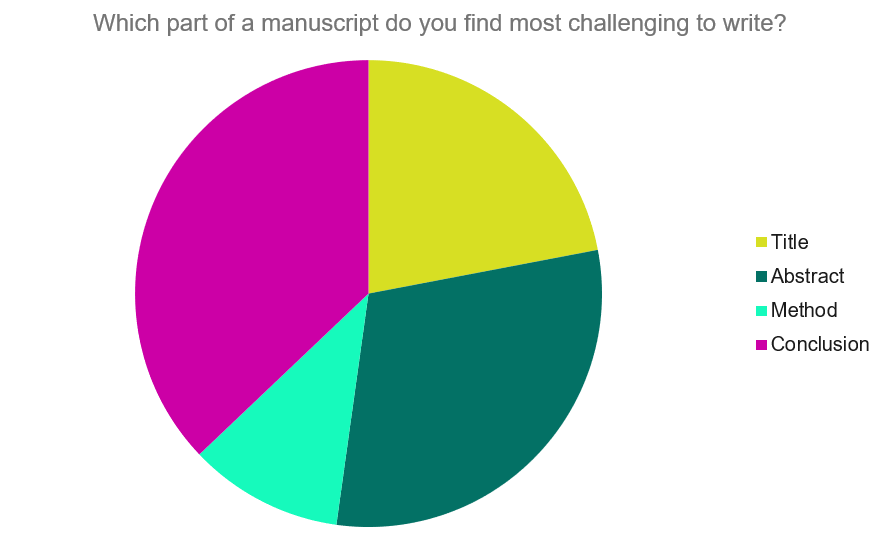
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
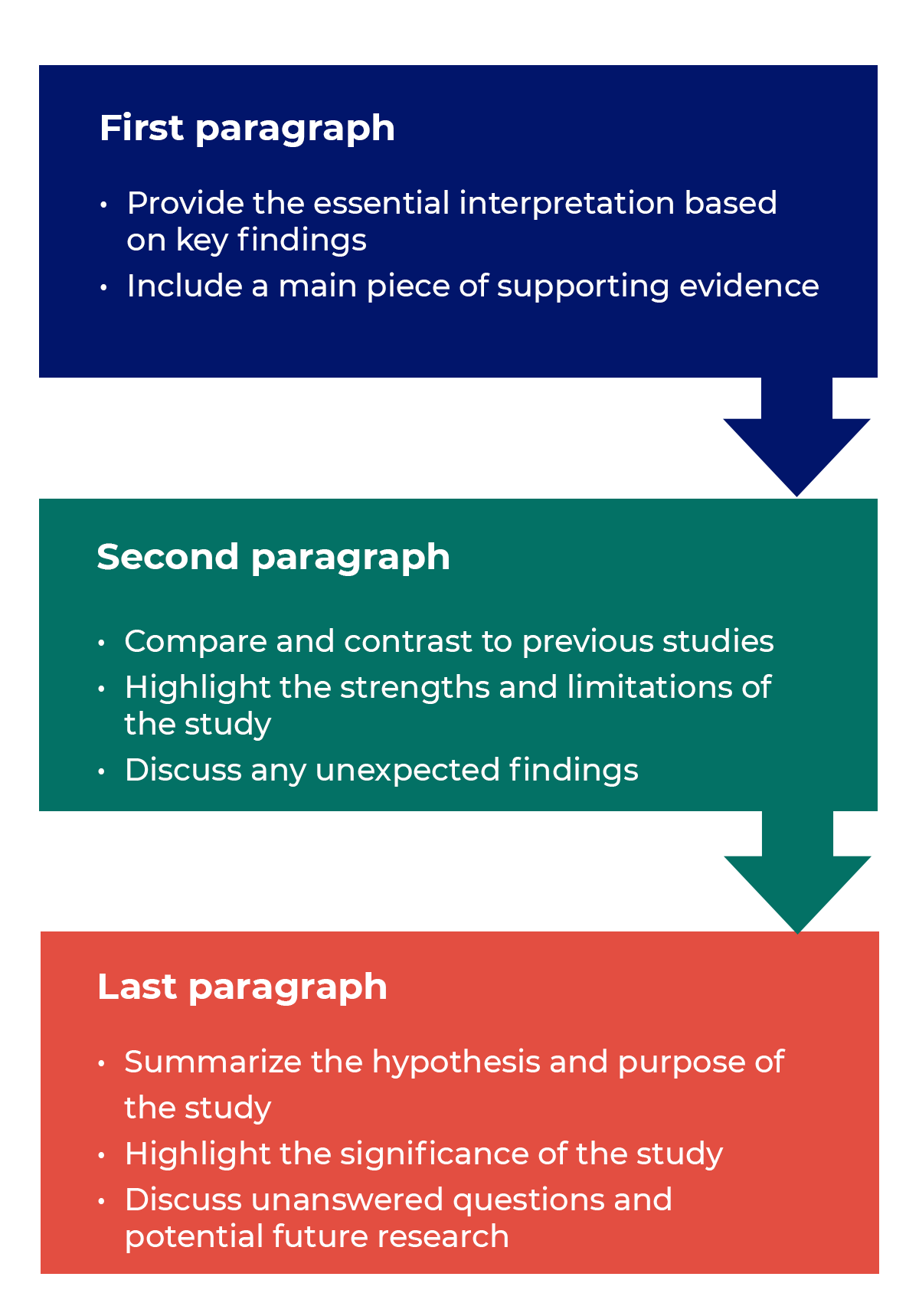
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

- 3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

IMAGES