

Entrepreneurship Project Business Plan- CBSE Class 12
Table of Contents
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Many people helped me through their support and guidance for the successful completion of this project.
First of all, I thank the Almighty God for his goodness and mercy in giving me the strength to complete this project.
I, at this moment, express my abundant and sincere gratitude to Mrs. SANILA MANOJ, Department of Commerce, Dr. GR PS, XTZ for her valuable guidance, constant encouragement, and creative suggestions rendered during this project.
I thank SISTER XTZ (Managing Trustee) Mrs. XYZ (Senior Principal) Mr. XYZ (Principal) for providing me with all facilities and also for the constant inspiration and encouragement for successful completion of this project.
I offer my deepest gratitude to my family members, whose prayers and blessings guided me for the successful completion of this project. I also owe my gratitude to my classmates, whose support was inevitable for the completion of the project.
INTRODUCTION
A business plan is a written description of the business further. That means a document that describes what plan to do and how to do it. Business plan com perform several tasks for those who write & read them. They are used by investment seeking entrepreneurs to convey their vision to potential investors. They may also be used by firms that are trying to attract key employees, the prospect for new business deals with suppliers, or simply to understand how to manage their companies cutter.
- To provide clarity of thought & purpose.
- To introduce the business models.
- To present examples, step by step explanation of the business plan.
- To define what the business plan is and who prepares it.
- To understand the scope and the value of the business
NEED AND SIGNIFICANCE
- It gives direction to the vision formulated by the entrepreneurs.
- To monitor the progress after implementing business plans.
- To persuade others to join the business.
- To seek loans from financial institutions.
- To identify the actual strength and weaknesses of the plan.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
“ELVAGO CANTINA” believes in its unique delivery to service as its policy is “Consumer is king’ It’s traditional, as well as members outlook gives you the feeling as if you are the members of its family.
Though we are now the love and taste in our foods will be abundant.
The location is just a half kilometer from the bus bay situated at the heart of Cobin city. It provides great facilities provided with first-class infrastructural facilities.
ABOUT THE COMPANY
“ELVAGO CANTINA’ is a first-class startup company with very good infrastructure. This company believes she is securing the society by organizing social activities such as entertainment programs for the Physically Challenged or differently-abled children.
It also has the policy to donate a part of income to various and all spread old age homes around the Rochi city also.
In the present situation, ‘ELVAGO’ consists of about too many employers overall.
There are about employees and so on the executive staff members. It is situated in the less bay in Vytilla in the heart of Kochi City.
ELVAGO CANTINA
‘ELVAGO CANTINA’ is something a place where the variety of goods are sold to the customers. The statement motivates us to go to the restaurant business in India. We have suggested this because there is no branded restaurant until now. The tag line for ELVAGO CANTINA is
” TASTY; BUT CHEAPER”
To become the most preferred restaurant among the people by treating the people in the way they like to be treated.
For every business, location plays a vital role. The success and the future of the company depend on that place from the selling of the product and availability of the required raw materials at least cost. The location of our restaurant is in the heart of Kochi, i.e., Vytilla.
BUSINESS OBJECTIVES
- To establish a working store for the restaurant.
- To provide the true flavor of India at reasonable costs.
- To understand the taste of the customers.
- To balance our business goal with one financial objective.
- To provide the best quality food to the customers.
MANAGEMENT SUMMARY
The initial summary of management depends on the founders, and there are various another working inside the company. As we grow, we will take an additional held in certain key areas.
At present, the ELVAGO CANTINA has two founders, Head offices, Eco, Sheffs, Managers, Waiting staff, etc.
The restaurant aims to be a stone in the community creating a neighborhood atmosphere where the customers feel safe and comfortable.
We target all the age groups of people from small children to teenagers and adults to the old aged people also. Our company’s culture is to satisfy in every way all the customs stepping into ‘ELVAGO’ especially with our special mems including:
- Muttons Biryani
- Elvago’s Special Biriyani
- Vegetable Biryani.
- Egg Biryani
- Elvago’s Special Fried Rice
- Green Chicken Rice.
- Chicken Chops
- Elvago’s Special Butter Chicken
- Elvago’s Special Chicken Curry.
MARKET & COMPETITION
We are the startup company and are looking forward to earning a good share of the market. The other important things are customer satisfaction. The competitions are common in every society between Various enterprises
Our competitors are: –
Pai Brothers.
Sardarji ka Dhabha.
INFRASTRUCTURE
ELVAGO CANTINA provides great infrastructural facilities. Over 45 seats and family rooms are provided with a good air conditioning system. The infrastructure in our restaurant is very attractive. The restaurant has mainly two floors for the customers.
PHYSICAL PLANT
Area: – The piece of land which is required to organize the whole set up is about 1,600 sq. feet
MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT
- Refrigerators
FINANCIAL RESOURCES
It is SBA’s most basic and common loan program. These loans are mostly available through various commercial institutions, and most American banks participate as lenders in this program. Lenders typically grand loans up to £ 2,00,000.
FRIENDS & FAMILIES
Friends and family members might be the most lenient member of the ELVAGO CANTINA launch. They don’t tend to make you pledge your house and may even agree to sell their interest in your company back to you for a nominal return.
PERSONNEL PLAN
The personnel plan is based on operating 24/7 hrs and falls in with how EAVAGO CANTINA operates throughout the week.
Any additional price will be part-time & devoted to expansion on any catering functions, as well as increased capacity of private party function.
The enterprise currently has 100 employees. There are about 100 employees & 30 executive staff.
| Shift Manager | 26,000 |
| CEO | 75,000 |
| Chef | 50,000 |
| Assistant Chef | 28,000 |
| Waiting Staff | 17,000 |
| Others | 15,000 each |
MARKET STRATEGY
Our strategy is based on serving our markets well. The concentration will be on providing fresh & quality good items.
A combination of local media & local store marketing programs will be utilized at each location. By providing a fun & entertaining environment with high-quality goods (foods at a reasonable rate, we will be coming shortly on top of the town.
UNIQUE SELLING PROPORTION
There are many restaurants in India. What gives a competitive advantage to the product of “ELVAGO CANTINA” is that it produces good and quality food. When compared to other restaurants, what makes us special is that we have many varieties of foods. The other restaurants charge a very high price in their foods; we charge only a reasonable price.
By analyzing the product,
- I could easily find the customer’s taste and preferences in the area.
- It could also analyze the price of Various products.
- By writing a business plan, it is necessary to know about the starling of a business enterprise.
CONCLUSIONS
A Business plan is an important document that is essential for every business firm. This is valuable not only for the entrepreneurs but also for all the stakeholders who access the firm directly or indirectly. There are various components of a business plan which is prepared to depend upon the entrepreneur’s enterprise and knowledge.
CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the project is an authentic record of the work done by ROHITH S. BOBBY , class XII.D during 2017-2018 towards the partial fulfillment of the AISSCE course prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). The student has done the project with his/her effort & with the guidance of a concerned teacher.
Teacher In-charge
External Examiner
DECLARATION
I, XYZ do at this moment declare that the project entitled “BUSINESS PLAN” is a bonafide record of the project work done by me and was under the guidance of Mrs. SANILA MANOJ, also declare this project or any part of it has not been submitted by me fully or partially for any other examination before.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- NCERT textbook (Class XII) –
- [email protected]
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Entrepreneurship Project Business Plan- CBSE Class 12 PDF
Related articles.

Social Science Project Topics For Class 10 CBSE

Solar Vacuum Cleaner & Floor Cleaner Robot Project

Cam Shaft Mechanism DIY Ventilator Project

Android Hostel Management System
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Entrepreneurial Planning Class 12 Entrepreneurship Important Questions
Students can read the important questions given below for Entrepreneurial Planning Class 12 Entrepreneurship . All Entrepreneurial Planning Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 12 Entrepreneurship Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Entrepreneurship Question Bank Class 12 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Related Posts
The d and f block elements class 12 chemistry important questions, aldehydes ketones and carboxylic acids class 12 chemistry important questions.

Business Arithmetic Class 12 Entrepreneurship Important Questions
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Company summary | Brief overview (one to two paragraphs) of the problem, solution, and potential customers |
| Customer analysis | Description of potential customers and evidence they would purchase product |
| Market analysis | Size of market, target market, and share of market |
| Product or service | Current state of product in development and evidence it is feasible |
| Intellectual property | If applicable, information on patents, licenses, or other IP items |
| Competitive differentiation | Describe the competition and your competitive advantage |
| Company founders, management team, and/or advisor | Bios of key people showcasing their expertise and relevant experience |
| Financials | Projections of revenue, profit, and cash flow for three to five years |
| Amount of investment | Funding request and how funds will be used |
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Executive Summary Component | Content |
|---|---|
The Concept | La Vida Lola is a food truck serving the best Latin American and Caribbean cuisine in the Atlanta region, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes, with a festive flair. La Vida Lola offers freshly prepared dishes from the mobile kitchen of the founding chef and namesake Lola González, a Duluth, Georgia, native who has returned home to launch her first venture after working under some of the world’s top chefs. La Vida Lola will cater to festivals, parks, offices, community and sporting events, and breweries throughout the region. |
Market Advantage | Latin food packed with flavor and flair is the main attraction of La Vida Lola. Flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture can be enjoyed from a menu featuring street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes from the González family’s Puerto Rican and Cuban roots. craving ethnic food experiences and are the primary customers, but anyone with a taste for delicious homemade meals in Atlanta can order. Having a native Atlanta-area resident returning to her hometown after working in restaurants around the world to share food with area communities offers a competitive advantage for La Vida Lola in the form of founding chef Lola González. |
Marketing | The venture will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will comprise a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Much of the promotion mix will center around dual-language social media. |
Venture Team | The two founding members of the management team have almost four decades of combined experience in the restaurant and hospitality industries. Their background includes experience in food and beverage, hospitality and tourism, accounting, finance, and business creation. |
Capital Requirements | La Vida Lola is seeking startup capital of $50,000 to establish its food truck in the Atlanta area. An additional $20,000 will be raised through a donations-driven crowdfunding campaign. The venture can be up and running within six months to a year. |
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Business Description | La Vida Lola will operate in the mobile food services industry, which is identified by SIC code 5812 Eating Places and NAICS code 722330 Mobile Food Services, which consist of establishments primarily engaged in preparing and serving meals and snacks for immediate consumption from motorized vehicles or nonmotorized carts. Ethnically inspired to serve a consumer base that craves more spiced Latin foods, La Vida Lola is an Atlanta-area food truck specializing in Latin cuisine, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes native to the roots of the founding chef and namesake, Lola González. La Vida Lola aims to spread a passion for Latin cuisine within local communities through flavorful food freshly prepared in a region that has embraced international eats. Through its mobile food kitchen, La Vida Lola plans to roll into parks, festivals, office buildings, breweries, and sporting and community events throughout the greater Atlanta metropolitan region. Future growth possibilities lie in expanding the number of food trucks, integrating food delivery on demand, and adding a food stall at an area food market. After working in noted restaurants for a decade, most recently under the famed chef José Andrés, chef Lola González returned to her hometown of Duluth, Georgia, to start her own venture. Although classically trained by top world chefs, it was González’s grandparents’ cooking of authentic Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes in their kitchen that influenced her profoundly. The freshest ingredients from the local market, the island spices, and her attention to detail were the spark that ignited Lola’s passion for cooking. To that end, she brings flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture to a flavorful menu packed full of street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes. Through reasonably priced menu items, La Vida Lola offers food that appeals to a wide range of customers, from millennial foodies to Latin natives and other locals with Latin roots. |
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategy | According to ’ first annual report from the San Francisco-based Off The Grid, a company that facilitates food markets nationwide, the US food truck industry alone is projected to grow by nearly 20 percent from $800 million in 2017 to $985 million in 2019. Meanwhile, an report shows the street vendors’ industry with a 4.2 percent annual growth rate to reach $3.2 billion in 2018. Food truck and street food vendors are increasingly investing in specialty, authentic ethnic, and fusion food, according to the report. Although the report projects demand to slow down over the next five years, it notes there are still opportunities for sustained growth in major metropolitan areas. The street vendors industry has been a particular bright spot within the larger food service sector. The industry is in a growth phase of its life cycle. The low overhead cost to set up a new establishment has enabled many individuals, especially specialty chefs looking to start their own businesses, to own a food truck in lieu of opening an entire restaurant. Off the Grid’s annual report indicates the average typical initial investment ranges from $55,000 to $75,000 to open a mobile food truck. The restaurant industry accounts for $800 billion in sales nationwide, according to data from the National Restaurant Association. Georgia restaurants brought in a total of $19.6 billion in 2017, according to figures from the Georgia Restaurant Association. There are approximately 12,000 restaurants in the metro Atlanta region. The Atlanta region accounts for almost 60 percent of the Georgia restaurant industry. The SAM is estimated to be approximately $360 million. The mobile food/street vendor industry can be segmented by types of customers, types of cuisine (American, desserts, Central and South American, Asian, mixed ethnicity, Greek Mediterranean, seafood), geographic location and types (mobile food stands, mobile refreshment stands, mobile snack stands, street vendors of food, mobile food concession stands). Secondary competing industries include chain restaurants, single location full-service restaurants, food service contractors, caterers, fast food restaurants, and coffee and snack shops. The top food truck competitors according to the , the daily newspaper in La Vida Lola’s market, are Bento Bus, Mix’d Up Burgers, Mac the Cheese, The Fry Guy, and The Blaxican. Bento Bus positions itself as a Japanese-inspired food truck using organic ingredients and dispensing in eco-friendly ware. The Blaxican positions itself as serving what it dubs “Mexican soul food,” a fusion mashup of Mexican food with Southern comfort food. After years of operating a food truck, The Blaxican also recently opened its first brick-and-mortar restaurant. The Fry Guy specializes in Belgian-style street fries with a variety of homemade dipping sauces. These three food trucks would be the primary competition to La Vida Lola, since they are in the “ethnic food” space, while the other two offer traditional American food. All five have established brand identities and loyal followers/customers since they are among the industry leaders as established by “best of” lists from area publications like the . Most dishes from competitors are in the $10–$13 price range for entrees. La Vida Lola dishes will range from $6 to $13. One key finding from Off the Grid’s report is that mobile food has “proven to be a powerful vehicle for catalyzing diverse entrepreneurship” as 30 percent of mobile food businesses are immigrant owned, 30 percent are women owned, and 8 percent are LGBTQ owned. In many instances, the owner-operator plays a vital role to the brand identity of the business as is the case with La Vida Lola. Atlanta has also tapped into the nationwide trend of food hall-style dining. These food halls are increasingly popular in urban centers like Atlanta. On one hand, these community-driven areas where food vendors and retailers sell products side by side are secondary competitors to food trucks. But they also offer growth opportunities for future expansion as brands solidify customer support in the region. The most popular food halls in Atlanta are Ponce City Market in Midtown, Krog Street Market along the BeltLine trail in the Inman Park area, and Sweet Auburn Municipal Market downtown Atlanta. In addition to these trends, Atlanta has long been supportive of international cuisine as Buford Highway (nicknamed “BuHi”) has a reputation for being an eclectic food corridor with an abundance of renowned Asian and Hispanic restaurants in particular. The Atlanta region is home to a thriving Hispanic and Latinx population, with nearly half of the region’s foreign-born population hailing from Latin America. There are over half a million Hispanic and Latin residents living in metro Atlanta, with a 150 percent population increase predicted through 2040. The median age of metro Atlanta Latinos is twenty-six. La Vida Lola will offer authentic cuisine that will appeal to this primary customer segment. La Vida Lola must contend with regulations from towns concerning operations of mobile food ventures and health regulations, but the Atlanta region is generally supportive of such operations. There are many parks and festivals that include food truck vendors on a weekly basis. |
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
| Operations and Management Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Key Management Personnel | The key management personnel consist of Lola González and Cameron Hamilton, who are longtime acquaintances since college. The management team will be responsible for funding the venture as well as securing loans to start the venture. The following is a summary of the key personnel backgrounds. Chef Lola González has worked directly in the food service industry for fifteen years. While food has been a lifelong passion learned in her grandparents’ kitchen, chef González has trained under some of the top chefs in the world, most recently having worked under the James Beard Award-winning chef José Andrés. A native of Duluth, Georgia, chef González also has an undergraduate degree in food and beverage management. Her value to the firm is serving as “the face” and company namesake, preparing the meals, creating cuisine concepts, and running the day-to-day operations of La Vida Lola. Cameron Hamilton has worked in the hospitality industry for over twenty years and is experienced in accounting and finance. He has a master of business administration degree and an undergraduate degree in hospitality and tourism management. He has opened and managed several successful business ventures in the hospitality industry. His value to the firm is in business operations, accounting, and finance. |
Advisory Board | During the first year of operation, the company intends to keep a lean operation and does not plan to implement an advisory board. At the end of the first year of operation, the management team will conduct a thorough review and discuss the need for an advisory board. |
Supporting Professionals | Stephen Ngo, Certified Professional Accountant (CPA), of Valdosta, Georgia, will provide accounting consulting services. Joanna Johnson, an attorney and friend of chef González, will provide recommendations regarding legal services and business formation. |
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
| Marketing Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Overview | La Vida Lola will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will include a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Given the target millennial foodie audience, the majority of the promotion mix will be centered around social media platforms. Various social media content will be created in both Spanish and English. The company will also launch a crowdfunding campaign on two crowdfunding platforms for the dual purpose of promotion/publicity and fundraising. |
Advertising and Sales Promotion | As with any crowdfunding social media marketing plan, the first place to begin is with the owners’ friends and family. Utilizing primarily Facebook/Instagram and Twitter, La Vida Lola will announce the crowdfunding initiative to their personal networks and prevail upon these friends and family to share the information. Meanwhile, La Vida Lola needs to focus on building a community of backers and cultivating the emotional draw of becoming part of the La Vida Lola family. To build a crowdfunding community via social media, La Vida Lola will routinely share its location, daily if possible, on both Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Inviting and encouraging people to visit and sample their food can rouse interest in the cause. As the campaign is nearing its goal, it would be beneficial to offer a free food item to backers of a specific level, say $50, on one specific day. Sharing this via social media in the day or two preceding the giveaway and on the day of can encourage more backers to commit. Weekly updates of the campaign and the project as a whole are a must. Facebook and Twitter updates of the project coupled with educational information sharing helps backers feel part of the La Vida Lola community. Finally, at every location where La Vida Lola is serving its food, signage will notify the public of their social media presence and the current crowdfunding campaign. Each meal will be accompanied by an invitation from the server for the patron to visit the crowdfunding site and consider donating. Business cards listing the social media and crowdfunding information will be available in the most visible location, likely the counter. Before moving forward with launching a crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will create its website. The website is a great place to establish and share the La Vida Lola brand, vision, videos, menus, staff, and events. It is also a great source of information for potential backers who are unsure about donating to the crowdfunding campaigns. The website will include these elements: . Address the following questions: Who are you? What are the guiding principles of La Vida Lola? How did the business get started? How long has La Vida Lola been in business? Include pictures of chef González. List of current offerings with prices. Will include promotional events and locations where customers can find the truck for different events. Steps will be taken to increase social media followers prior to launching the crowdfunding campaign. Unless a large social media following is already established, a business should aggressively push social media campaigns a minimum of three months prior to the crowdfunding campaign launch. Increasing social media following prior to the campaign kickoff will also allow potential donors to learn more about La Vida Lola and foster relationship building before attempting to raise funds. |
Facebook Content and Advertising | The key piece of content will be the campaign pitch video, reshared as a native Facebook upload. A link to the crowdfunding campaigns can be included in the caption. Sharing the same high-quality video published on the campaign page will entice fans to visit Kickstarter to learn more about the project and rewards available to backers. |
Crowdfunding Campaigns | Foodstart was created just for restaurants, breweries, cafés, food trucks, and other food businesses, and allows owners to raise money in small increments. It is similar to Indiegogo in that it offers both flexible and fixed funding models and charges a percentage for successful campaigns, which it claims to be the lowest of any crowdfunding platform. It uses a reward-based system rather than equity, where backers are offered rewards or perks resulting in “low-cost capital and a network of people who now have an incentive to see you succeed.” Foodstart will host La Vida Lola’s crowdfunding campaigns for the following reasons: (1) It caters to their niche market; (2) it has less competition from other projects which means that La Vida Lola will stand out more and not get lost in the shuffle; and (3) it has/is making a name/brand for itself which means that more potential backers are aware of it. La Vida Lola will run a simultaneous crowdfunding campaign on Indiegogo, which has broader mass appeal. |
Publicity | Social media can be a valuable marketing tool to draw people to the Foodstarter and Indiegogo crowdfunding pages. It provides a means to engage followers and keep funders/backers updated on current fundraising milestones. The first order of business is to increase La Vida Lola’s social media presence on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Establishing and using a common hashtag such as #FundLola across all platforms will promote familiarity and searchability, especially within Instagram and Twitter. Hashtags are slowly becoming a presence on Facebook. The hashtag will be used in all print collateral. La Vida Lola will need to identify social influencers—others on social media who can assist with recruiting followers and sharing information. Existing followers, family, friends, local food providers, and noncompetitive surrounding establishments should be called upon to assist with sharing La Vida Lola’s brand, mission, and so on. Cross-promotion will further extend La Vida Lola’s social reach and engagement. Influencers can be called upon to cross promote upcoming events and specials. The crowdfunding strategy will utilize a progressive reward-based model and establish a reward schedule such as the following: In addition to the publicity generated through social media channels and the crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will reach out to area online and print publications (both English- and Spanish-language outlets) for feature articles. Articles are usually teased and/or shared via social media. Reaching out to local broadcast stations (radio and television) may provide opportunities as well. La Vida Lola will recruit a social media intern to assist with developing and implementing a social media content plan. Engaging with the audience and responding to all comments and feedback is important for the success of the campaign. Some user personas from segmentation to target in the campaign: |

Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jun 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Syllabus 2024-25 (PDF Download)
Cbse class 12 entrepreneurship syllabus 2024-25, course structure theory paper.
Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 70
| -->
|
|
|
|
| Unit 1 | Entrepreneurial Opportunity | 40 | 30 |
| Unit 2 | Entrepreneurial Planning | 40 | |
| Unit 3 | Enterprise Marketing | 40 | 20 |
| Unit 4 | Enterprise Growth Strategies | 20 | |
| Unit 5 | Business Arithmetic | 40 | 20 |
| Unit 6 | Resource Mobilization | 20 | |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 40 | 30 | |
|
|
|
|
COURSE CONTENT
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Sensing Entrepreneurial Opportunities · Environment Scanning · Problem Identification · Idea fields · Spotting Trends · Creativity and Innovation · Selecting the Right Opportunity | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Comprehend the concept and elements of business opportunity · Discuss the process of sensing opportunities · Understand the need to scan the environment ·Enlist the various forces affecting business environment · Identify the different idea field |
| · Understand the concept of opportunity and market assessment · Appreciate the ways in which trends can be spotted · Understand the process of creativity and innovation · Transform ideas into business opportunities | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Forms of business organization- Sole proprietorship, Partnership, Company | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Recall the meaning of the various forms of business organization · Understand the characteristics of the various forms of business organization · Understand the difference between a Public and Private Company · Appreciate the reasons for a private company being more desirable · Appreciate the concept and importance of a Business Plan · Describe the various components of Business plan · Differentiate among the various components of Business plan · Develop a Business Plan |
| · Business Plan: concept, format. | |
| · Components: | |
| Organisational plan; | |
| Operational plan; | |
| Production plan; | |
| Financial plan; | |
| Marketing plan; | |
| Human Resource plan | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Marketing and Sales Strategy · Branding, Logo, Tagline ·Promotion Strategy | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Discuss the various marketing strategies used in a business · Explain Marketing Mix. · Understand the concept of Branding, Packaging and Labeling · Describe the various methods of Pricing · Discuss the various factors affecting the channels of distribution · Understand the concept and types of sales strategy · Discuss different tools of promotion · Appreciate the objectives and different modes of Advertising · Understand the concept of personal selling, sales promotion, public relations · Discuss the various techniques of sales promotion |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Franchising: Concept and types · Franchising: Advantages and limitations to franchisor and franchisee. · Mergers and Acquisition: Concept, reasons and types. · Reasons for mergers and acquisitions | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the concept of growth & development of an enterprise · Discuss the concept, types, advantages and limitations of franchising · Appreciate growth of business through mergers and acquisitions · Discuss the different types of mergers and acquisitions · Discuss the reasons for mergers and acquisitions |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Unit of Sale, Unit Cost for multiple products or services · Break even Analysis for multiple products or services · Computation of Working Capital · Inventory Control and EOQ · Return on Investment (ROI) and Return on Equity (ROE) | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the concept of Unit Cost and Unit Price · Calculate Break-even point for Multiple products and services. · Understand the concept of Inventory Control · Compute the working capital of a business. · Calculate Return on Investment; Return on Equity and Economic Order Quantity |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| · Capital Market: Concept · Primary market: Concept, methods of issue · Angel Investor: Features · Venture Capital: Features, funding. | After going through this unit, the student/ learner would be able to: · Understand the need of finance in Business · Discuss the various sources of funds required for a firm · Understand the ways of raising funds in primary market · Appreciate the Angel Investors and Venture Capitalists as a source of business finance. |
PROJECT WORK
Students have to do TWO projects in the entire academic session.
TOPICS FOR THE PROJECT:
- Business Plan
- Market Survey
- 10 Marks each for 02 Projects
- 5 Marks for Numerical Assessment
- 5 Marks for Viva
Note: Students need to complete both the projects. Guidelines for both projects are given in the CBSE Textbook.
Download PDF
| Download Syllabus PDF | |
| Complete Syllabus |
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook chapter 2 - Enterprise Planning [Latest edition]
Online mock tests.

Advertisements
Solutions for chapter 2: enterprise planning.
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CBSE CBSE for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook.
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Very Short Answers (10 words) [Page 88]
Give any two contents of business plan.
Who can write the business plan?
How many formats are available to design a successful business plan?
What is the meaning of shipping in the process of operational plan?
What is a proforma income statement?
What is a proforma income statement?
What is break even analysis?
What is meant by a target market?
What is TAN?
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Short Answers (50 words) [Page 88]
What is a Business Plan?
What is elevator pitch?
What is production plan ?
Name the factors which affect the operational plan.
How many sources of funds are available for arranging funds for business enterprises?
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Short Answers (75 words) [Page 88]
Briefly, explain the objectives of operational plan.
Describe the contents of organizational plan.
Which common techniques are required to calculate the forecasting income?
Write the steps in preparing the marketing plan.
What is PAN? Why is it required?
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Long Answers (100 words) [Page 88]
What is an operational plan? Discuss its blue print.
Define organisational plan? A business can be classified in how many categories?
How many choices are there to start a business by a business man? Explain each of them
What are the key areas, for a sound financial plan to work?
What are the major financial items that should be included in the financial plan?
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Long Answers (250 words) [Page 88]
What is a business plan? Explain its importance.
Describe the different elements of an operational plan.
What is a financial plan? What are its objectives?
Explain the investment decision under the financial plan? In which areas should the investment should be on the basis of priority?
What is manpower planning? Why is it necessary for every business unit?
What is a marketing plan? Why is it required in business enterprises?
Explain, in detail, the various formalities required to start a business.
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Hots Questions [Page 89]
A person has decided to start a small leather belt manufacturing unit. He/she is not aware of the various formalities involved in the process of setting up the unit. Explain to him/her the procedure.
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook Chapter 2 Enterprise Planning Value Based Questions [Pages 89 - 90]
The first stage of a business plan is to come up with a business name supposing you are an entrepreneur, who is in the stage of deciding abusiness name for your enterprise would you : (i)Keep the name of your enterprise, similar to one of the enterprises that are already doing really well in the same line of business? (ii)Select/create a completely new name for your enterprise and create a brand name of your own? Give reasons. (Honestly)
An entrepreneur is doing an industry analysis. While he/she is analyzing his/her competitions in his/her line of business, he realises that the competitors are far better in their business plans and their execution. Should the entrepreneur add unique selling point in the existing plan to get a creative niche above others or should he/she go for a completely different line of business where the competition is less and he/she is easily able to place his/her feet in the market? Give reasons. (creativity and problem solving)
You are an entrepreneur who is deciding the operational plan for your business. While deciding the technology to be used, you come across three alternatives: a) Use a cheaper technology which lets you dispose of the waste water and lets you fix the price of your product low. b) Use a technology that is a little expensive as it lets you recycle that waste water into water fit for drinking. In this case, you will have to fix the price a little higher in order to earn profits. c) Use the technology that recycles the waste, do not change the price. And go about cost cutting though efficient utilization of resources.
An individual wants to start an enterprise that manufactures steam iron which can be imported from Germany. The material available in Germany is a little better in quality. However, there are no safety issues with the one available in India which material would you go for and why? (Social responsibility, import substitution).
While doing the manpower planning an entrepreneur, decides to keep less qualified manpower and give them low wages and salaries to enable higher profits. Do you think his/her approach is correct and justified, why?
According to you, what kind of organisational set up is better – an autocratic form of an organization where there is absolute centralization of power and the communication from is from top to bottom. Or A democratic form of an organization where power is decentralized and communication from both the ends. Justify?
Raghav, an entrepreneur realises that the enterprise he wants to start has a potential risk of fire because the production process poses such a threat. Should he develop strategies to : (i)Prevent the risk (ii)Respond to the risk (iii)Prevent as well as respond to the risk? Give reasons.
CBSE solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook chapter 2 - Enterprise Planning
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. CBSE solutions for Mathematics Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook CBSE 2 (Enterprise Planning) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. CBSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook chapter 2 Enterprise Planning are Types of Economic Activities, Business Organization, Forms of Enterprises, Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Joint Stock Company, Description of Venture/Business Venture, Production Plan, Operational Plan, Financial Plan, Components of Financial Plan, Manpower Planning, Marketing Plan, Joint Hindu Family / Firm (HUFs), Co-operative Organisations, Business Plan, Introductory Profile /General Introduction, Elements of Operational Plan, Organizational Plan, Assessment of Risk, Appendix.
Using CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook solutions Enterprise Planning exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in CBSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook students prefer CBSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Enterprise Planning Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook additional questions for Mathematics Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.

- Maharashtra Board Question Bank with Solutions (Official)
- Balbharati Solutions (Maharashtra)
- Samacheer Kalvi Solutions (Tamil Nadu)
- NCERT Solutions
- RD Sharma Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions
- TS Grewal Solutions
- ICSE Class 10 Solutions
- Selina ICSE Concise Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- CBSE Study Material
- Maharashtra State Board Study Material
- Tamil Nadu State Board Study Material
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Study Material
- Mumbai University Engineering Study Material
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Entrance Exams
- Video Tutorials
- Question Papers
- Question Bank Solutions
- Question Search (beta)
- More Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Shaalaa App
- Ad-free Subscriptions
Select a course
- Class 1 - 4
- Class 5 - 8
- Class 9 - 10
- Class 11 - 12
- Search by Text or Image
- Textbook Solutions
- Study Material
- Remove All Ads
- Change mode
Entrepreneurial Planning, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 Revision Notes PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
A business plan usually consists of the following elements.
- A general introduction about the venture
- Planning related to the Business venture
- Planning related to the Organization
- Planning related to the Production
- Planning related to the operations
- Planning related to the human resources
- Planning related to the Marketing and promotional activities
- Planning related to the Financing
- Any other miscellaneous planning elements and appendix
In your opinion who should prepare the business plan?
Ideally the business owner/the entrepreneur should prepare the business plan. They can consult other experts during the course of preparation. However, they should take the sole responsibility of preparing the business plan themselves.
What are the various formats available to present an effective business plan? Watch Video
The following are the various formats available for preparing an effective business plan.
- Elevator pitch: It is a precise summary of the business plan’s execution.
- Oral/In person presentation: The presentation containing the key elements of the business plan is presented to the potential investors.
- Written/Documented presentation: This is targeted for external customers.
- Operational plan: This is targeted for the internal management team. (not for external stakeholders)
How is shipping considered while preparing an operational plan?
Shipping represents a sequence of steps to accomplish a business transaction. When properly planned for, it helps in completing a business trasaction with optimum efficiency and least expenses. Shipping primarly depends on the
- Nature of business
- Type of the product or service
- Whether the business is operating at a small scale or large scale
- Usage of technology
What is significance of proforma income statement?
Proforma income statement is used to provide the summary of all the profits earned by a new enterprise, in the first year. It projects the profit computed by subtracting projected costs and expenses from the projected revenue. Projected net profit = Projected Revenue – Projected cost. While preparing the proforma income statement, the first thing to be computed is the ‘sales by month’. Any of the following available forecasting techniques are used for this purpose.
- Consumer opinion Surveys
- Expert opinions
- Financial data available from start-up ventures in the same industry or sector.
- Industry sales
- Marketing research.
- Our own experience or others’ experience.
While preparing the proforma income statement one need not be conservative for the sake of initial planning. However if the estimates are conservative and result in substantial profits, it adds credibility to the bright future prospects of the enterprise.
Give an analysis of the break even point.
Break even point occurs when the enterprise is earning an income equivalent to its expenses. In other-words, at break-even point represents a state of the business where in it is neither making profits nor incurring losses. Put it differently, the revenue and the cost are equal in magnitude. Break-even point is critical to any business due to the following reasons.
- It gives an estimate of minimum number products to be produced or services to be delivered.
- Any deviation in the output will directly affect the profits.
- It is used to determine the selling price of a product or amount to be charged for a service.
- Helps in determining which options or processes or methodologies in the production results in a profit.
Break-even analysis is used in deciding how much sales volume helps the business to break-even. The volume of sales thus computed help the business to get an estimate of the number of sales to be made to meet the total of variable and fixed expenses. You’ve already studied about break-even point in class xi. To refresh your memory refer back to the Business Finance and Arithmetic lesson
Give a brief of the “target market”.
Target market refers to the group of specific potential customers who are interested in availing the products or services provided by the enterprise. Deciding the “target market” is a very complex task. Deciding on the target market involves
- Deciding the basis on which the entrepreneurs or general market pursue through market research or analysis of the industry. The industry analysis or market research need to be performed by the entrepreneurs themself or by highly experienced professionals.
- Geographic such as city, state, country
- Demographic such as age, gender etc
- Psycho-graphic such as life style, personality, education etc
- Buying conditions (time available etc)
- Desired features and specifications of a product
- Choosing the segment that need to be targeted
- Prepare a marketing plan based on the product, sale price, promotion, delivery logistics etc.
What is the significance of TAN?
TAN is acronym for Tax deduction and collection Account Number. It is 10 digit long and is a combination of alphanumeric characters. Every one who are responsible or required for deducting or collecting the tax at source, on behalf of Income Tax Department, should apply for and obtain the TAN. It is mandatory to furnish TAN while filing the TDS or TCS returns either directly or online. It should be quoted while paying any TDS/TCS challan or certificate.
Give a very short definition of the business plan.
A business plan is a document, generally prepared by the entrepreneur himself/herself, documenting all the internal and external elements essential to setup an enterprise. The business plan projects
- The business goals
- The factors that favor the achievement of these goals
- The plans to achieve the goals
- Details of the organizations
- Details about all the team involved in achieving the goals.
What do you know about Elevator pitch?
Elevator pitch is shorter version of the executive summary of the business plan. When presented to someone it is usually seen that the elevator pitch finishes in around 3 minutes. It is used to give a quick introduction about the enterprise to the potential investors, partners and even customers. The primary motive of elevator pitch is usually to grab the attention of the audience and attract them towards the upcoming venture.
Give a brief about the production plan.
According to Alford and Beatty production planning is defined as The technique of forecasting or picturing ahead, every step in a long series of separate operations,
- in the right place
- of the right degree
- and at the right time
- and each operation to be done at maximum efficiency.
Production planning should give a clear picture of the following.
- Machinery, tools and equipment
- Manufacturing processes and techniques
- Production schedule and/or budget
- Plant layout
- Time, motion and word study
An enterprise which is not manufacturing any products can completely eliminate this from the business plan.
Which factors highly affect the operational plan? The following factors highly affect the operational plan.
- Nature of product or service
- Whether the business is Small/Medium/Large scale
- Technology used.
What are the different sources of funds to finance an enterprise?
There are typically two sources of funds available for an enterprise to finance its needs. They can be summarized into two types.
- Owners i.e. Owner’s funds
- Outsiders i.e. funds raised from the investors/financial institutions etc
An entrepreneur should not completely rely on on source of financing i.e. Along with their own funds they should invest the outsider funds so as to make up the complete capital. The ratio in which the owner funds and the outsider funds should be calculated so that
- the cost of capital and the financial risk is lowest
- Return on Investment (ROI) and the profits are highest
Which objectives does an operational plan deal with?
The operational plan is prepared with due consideration to the following objectives.
- Planning for production well ahead of operations.
- Determine the exact route taken by each part or item in the assembly line.
- Come up with the timeline regarding the exact start date and ending date for each critical assignment or task.
- Controlling and ensuring that the goods are moving through the manufacturing cycle in systematic way. This will ensure that there is systematic approach followed right from the procuring of the materials to the distribution of the end product.
What does an organizational plan contain?
The organizational plan consists of the following details documented in high clarity. By reading the organizational plan the potential investors can get a clear picture of the associated rights or authorities or roles and responsibilities of each member in the organization.
- Authority and responsibilities of each member of the new enterprise.
- Bio-data i.e. name, role, contact details and resume of each of the member
- Conflict/dispute (in case any arise in future) resolution procedure
- Delegated rights to each of the members. Rights related voting, management controlling etc fall into this category.
- Each member’s roles and responsibilities.
- Form of payment to all the members
- Gross stake of each member in the enterprise.
- High level details of terms and conditions
When you are asked to prepare the income statement which forecasting techniques do you use to prepare the ‘Sales by Month’?
We have the following most popular forecasting techniques at our disposal for forecasting the income while preparing the ‘Sales by Month’ as part of proforma income statement.
What are all the various steps that should be considered while preparing the marketing plan.
The following are the various steps that should be considered while preparing the marketing plan.
- Analysis of the business situation
- Broad identification the target market
- Conduct SWOT analysis
- Detailed goal establishment
- Enlist the marketing strategy
- Foolproof implementation and monitoring of the plan
Define PAN. What is its significance?
PAN is acronym for Permanent Account Number. It is issued by the income tax department and consists of alphanumeric characters. It should be quoted in all the transactions performed by a person with the income tax department. For instance, it should be quoted in the following instances.
- tax payment
- TDS/TCS credits
- communication with income tax department
- Other mentioned transactions
All documents related to financial transactions should compulsorily include the PAN number. PAN number is issued to a person when they fall into one or more of the following categories.
- All existing assessee or persons or taxpayers who need to submit the income tax returns. They should possess PAN even if they are submitting these returns on behalf of others.
- A business man or a professional whose annual gross receipts or turnover or total sales is beyond 5 lakh rupees, in the previous year.
- When a person is dealing with the financial transactions where in it is mandatory to mention the PAN
- PAN can be issued to any person by an assessing officer, on his/her own decision. It can also be allocated to a person who has requested for PAN
Define operational plan.
Operational plan can be defined as the planning and control of each and every operation in production, at every step of the manufacturing process to result in a coordinated and smooth completion of work withing a factory. Operational plan ensures that the final product is as per the plan.
The operational plan is a blueprint devised much before the actual operations begin. Justify this statement.
The operational plan is indeed a blueprint of the actual operation and is produced well before the actual operations begin. The following facts support this statement.
- The operational plan ensures that there is an organized process flow from the starting (where the raw material is procured) to the final stage(where the end product is produced)
- continuous production
- less work-in-progress (WIP)
- less wastage
- Purchasing/Procuring
- Engineering
- Manufacturing/Production
- Inventory management
- Supply chain or distribution of goods from the plant to the consumer
- Ensures efficient quality control
- Adopting the more efficient/latest and cost effective manufacturing methods and policies
What is an organizational plan?
The organizational plan is a part of the business plan that details the enterprise’s form of ownership. It provides detailed information about the who has what kind of authority in the enterprise and how each member of the enterprise deal with other while executing their managerial functions.
Into how many categories can you segregate the types of businesses? What are they?
Businesses in general can be segregated into four basic categories. They are as follows.
- Manufacturing: Any business that produces a tangible product will fall into this category.
- Service: Any business that offers something that is intangible such as expertise (An accountant’s expertise) or time (a teachers time) or advice (a lawyer’s advise).
- Wholesale: Any business that purchases the products from the manufacturer in buld and then sells the product in small quantities to the retailers.
- Retail: Any business that sells a product directly to the end consumer whose need is satisfied by the product.
For an entrepreneur to start a business what type of business options are available.
For an entrepreneur to start a business the following forms of business are available.
The following forms are business are available as a choice for a business man to start a new venture..
- Sole proprietorship: This form of business is owned, managed and controlled by a single person, responsible for procuring all the required funds. The business can not be transferred into others’ name. The owner is liable for all the losses and all the profits are enjoyed by the owner only. This kind of business is easier to start and shut down. It has very limited liability.
- Partnership: This form of business is owned, managed and controlled by two or more persons. These persons enter a mutual oral or on paper agreement to form the partnership and share the profits and losses together. This form of ownership has unlimited liability. Each partner enjoys implied authority. Each partner is liable for their and others’ actions. Partners can transfer their shares or sell them after getting a consent from other partners. Partners can discontinue the partnership by giving a notice. It continues as long as all the partners are willing to continue.
- Joint Hindu Family Business/firm (HUFs): Joint Hindu Family or Hindu Undivided Family Business is prevailing only in India. It is governed by Hindu law. This form of business is owned, managed and controlled by male members of a joint Hindu family. HUFs have been defined under Hindu law as a family comprising male who have a common ancestor, including their wives and unmarried daughters. This form of partnership is formed by the status or operation of Hindu law. Only members born in the family can become partners. Others can also become partners but only if they are adopted by someone in the family. Only the eldest male member has rights to manage or verify the accounts of the business. Liability is defined by the share a partner has in the business. However, the eldest member, also known as Karta, has unlimited liability. Any new born male can become the member. The business can be shut down only if all the members provide their consent.
- Cooperative: A cooperative form of business is formed by a society. Its primary object is mutual help. Profit is secondary objective. Members can join or leave at their own will. The members select the management committee which will be responsible for managing the affairs of the business. The capital is procured from the members. Shares can not be transferred. This form of enterprise is limited by the Cooperative societies act and the State cooperative societies act. Profits are limited to 9% of the share. Excessive profits are shared among members depending on their contribution to the society.
- Joint Stock Company: For a private company minimum two persons are required and for a public company minimum seven persons are required. In addition to this, the company exists as an individual and has its own personality. Thus the company will have a common seal which is used as a signature of the company. The company neither has any liability nor it can have any shares. The company is managed by the directors. The actions of the company are governed by The Indian Companies Act, Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association. The company can be liquidated through legal proceedings.
While preparing a financial plan, which areas should be giving at-most consideration for it to be effective?
While preparing the financial plan, the following areas should be dealt with at-most consideration as they form the key areas.The following are the areas which need to be given due consideration while preparing a financial plan. The more the emphasis is laid on these areas the more will be the effectiveness of the financial plan.
- All the areas which require financing
- Sources from where the investments or funds can be procured.
- cash flow considerations
- inventory requirements
- loan and other investment options
- Timely procurement of funds.
What are the key components that should be part of the financial plan?
The following are the key components that should be part of the financial plan.
- Break-even Analysis
- Proforma Balance sheet
- Proforma Cash flow
- Economic and social factors
- Proforma financing decisions
- Proforma income statements
- Proforma investment decisions
Define and describe the significance of the business plan.
Business Plan: A business plan is formal document prepared by the entrepreneur consisting of all the extensive details of internal and external elements to be considered for starting a new business. The business plan covers
- A list of business goals.
- All the factors that support the fact that these goals can be realized.
- Road-map or plan for accomplishing these goals
- The background information of the enterprise
- The team involved to realize these goals.
Thus a business plan is a detailed document consisting of all the tasks performed as part of the business. Along this information it also serves as
- A means to understand the viability and feasibility of the proposed business.
- Helps in planning for bottlenecks and implementation of the idea.
- Gives an idea about risks associated and the possibility of successful establishment of the business.
Significance of business plan: A business plan is significant to all the stakeholders who are interested to get an insight of the
- business/venture
- and its objectives
The business plan is very handy to
- get a clear picture of the viability of the venture in a specific market sector.
- identification of the required resources
- Procure the license, depending on the need
- complete the legal formalities imposed by the government
- clarify the queries, issues or concerns of all the parties interested in the proposed venture.
- perform self-evaluation and self-assessment. This will enable the entrepreneur consider various alternate solutions to avoid/mitigate risk.
- identify the risk which can not be dealt with and drop off the plan. However this is very rare scenario.
- Contribution of equity
Thus it helps in convincing the investors/lenders and procure the required funds.
Specify the various components of an operational plan.
The following are the various components of an operational plan.
- Routing: Routing deals with the work flow of a product or service from the stage the raw materials are procured to the stage the final product is produced/service is accomplished.
- Scheduling: Scheduling deals with the exact start and end time of each operation. Indirectly, scheduling is concerned with the duration required to complete each operation.
- information
- instructions
- and orders are issued thus giving the desired shape to the production plan.
- the materials
- work-in-progress (WIP)
- finished products
- Identify the steps to improve the performance of the poorly performing departments.
- suggesting alternate courses of action to overcome the obstacles in the production line.
- Inspection: Inspection deals with the established standards to ensures that these standards are maintained in the materials or product or performance. Inspection ensures that there are separate laboratories or processes established to ensure that the product or service is within the prescribed quality standards.
- Shipping: Shipping deals with the deliver of the finished product or service to the consumer.
What is a financial plan? Watch Video at the financial plan definition part
Financial plan is a representation of critical financial data related to
- The total possible funding required to establish the new enterprise
- Feasibility of the enterprise to become economically successful.
at the objectives of financial plan part
What are the primary objectives of the financial plan?
The objective of the financial plan is to ensures that all the interested stakeholders get a clear idea of
- Total funds required for smooth running of all the business operations without any impact. This includes the funds required for purchasing assets, day-to-day expenses etc.
- Sources such as Banks, financial institutions, angel investors, equity financiers, venture capitalists from where the funds can be procured.
- Disbursement of funds. Give details of how the funds are managed effectively so as to minimize the expenses and maximize the profits.
- Liquid cash available at disposal
- An estimate of the possible revenue generation at least after completing a year. This section is very important as it plays key role to make the investors confident about the entrepreneur and gives them an idea about the returns on their investments.
Thus it facilitates the timely gathering of the funds and there by becoming a key factor in the success of the enterpreneur and enterprise. By reading the financial plan, the stakeholders can get detailed information regarding
- how all financial requirements are fulfilled
- how the enterprise can successfully generates good returns on all the investments made
- how the entrepreneur maintains liquidity to cover the debts
Thus with a well documented financial plan and executing it, the entrepreneur will be able to pu the critical resources i.e. materials, men, machines and methods to produce goods and services on time.
What are the investment decisions?
Investment decisions under financial plan refers to the strategies with which the funds are wisely invested in various assets. A well planned and investigated investment decision can generate maximum income and thus contribute to maximum returns on all the investments. In the financial plan the investment decisions are documented under the proforma investment decisions section. The divestment of investment under the working capital and fixed assets is estimated and should be clearly documented in this proforma.
What is the priority in which the investments are distributed and documented in proforma investment decisions.
The priority in which the proforma investment decisions are made is as follows.
- Investment on the Land and building
- Investment on the tools, machinery and plant
- Setup or installation expenses
- Initial or preliminary expenses
- Margin allocated for the working capital.
- Expenses for performing the research and development activities.
- Investments made on the short-term assets like raw material, level of cash etc.
A properly formatted investment decision gives an idea about the exact amount funds to be raised so as start the venture. This will be of great help for efficiently running the enterprise. Any insufficiency or surplus of funds can have an adverse impact on the success of the enterprise. So, proforma investment decision plays a critical role in estimating the exact amount of funds required and how they should be distributed based on the priority. For this reason due attention should be paid while preparing the proforma investment decisions.
- possess the desired skill set
- available at the right time
- available at the right place to perform the assigned job
- they do the work most appropriate for what they are paid for.
Why is the manpower critical for every enterprise?
- Which type of human resources are required to perform the job.
- As the roles of the human resources vary, it should be clearly specified about the position for which the human resources are recruited for i.e., Unskilled employees, skilled employees, technicians, engineers, managers, administrators etc.
- The type of business determines the type of human resources required.
- the amount of work done
- work done by an individual in a given period.
- Number of leaves allocated
- The rate at which the manpower leaves the organization and the rate at which the new workforce is recruited (this is called attrition).
- The current size of the organization.
- Future growth and diversification
- Recruitment process
- Selection process
- Training the recruited or existing employees
Explain what you understood by the term ‘marketing plan’?
- Brief history of the market place
- The strengths and weaknesses of the business in the market.
- Risks and opportunities
- Future direction: This section covers the goals and objectives of the enterprise to be achieved in the next 1 year.
- The strategies to be executed to reach the goals.
- Time frame to achieve the goals
- Delegation of the responsibilities to various personnel to take the ownership and monitor the progress.
Why is the marketing plan called as one of the the critical elements of the business plan?
- It helps in convincing the investors regarding how the entrepreneur is going to drive the business towards success.
- It analyses the current business situation.
- It helps in identifying the target market and prepare the strategies to reach the target market.
- Contains the details of the SWOT (Strengths – Weaknesses – Opportunities – Threats) analysis details.
- It emphasizes the entrepreneur to establish the goals to be achieved in the next one year.
- Defines the marketing strategies to achieve the established goals.
- It helps in identifying the qualified personnel to delegate the marketing goals who in turn can take the ownership and start monitoring the progress.
- Apply for PAN: PAN can be obtained from the Income Tax Department. This is essential as the entrepreneur has to submit the PAN in all the documents dealing with financial transactions.
- ID Proof like Driving license or passport or voter Id card or PAN card
- Address proof: Any utiltity bill like telephone or electricity bill.
Private or public limited companies need to furnish the following documentation in addition to the above.
- Certificate of incorporation and starting of the business.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Authorising document from the board resolution approving the opening and opertaing of the account.
- Filled in Form 60
- Name of the business or company
- e-filing through the MCA website for registration
- Apply for DIN
- Procure DSC
- Submit DSC in the MCA portal
- Submit the application for getting the approval for the name of the company
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- Verification of all the forms needed for the incorporation of the company.
- Register for service tax: Need to register for service tax so as to authorize the company to collect service tax.
- Register for Sales tax/VAT: The company should register for VAT so as to procure authorization to collect VAT. Also, if the product is sold for the first time then the company should have registered for service tax and obtained the Sales tax Identification number.
- Excise duty: Where applicable the company should register for excise duty.
- Customs duty: This is applicable for import/export business.
- Submit the entrepreneurship memorandum at DIC: This is not mandatory and can be applied optionally.
- Apply for TAN: The business should apply for and procure TAN if the business requires deducting or collecting the tax.
- Submit the application for the plot/shed, offer letter, payment of earnest money deposit.
- Approval from the authorities regarding the allotment of plot/shed, balance payment, taking the possession
- Application to procure NOC/SSI
- Obtain lease agreement
- Approval for water connection during construction.
- Approval for power connection during construction.
After the construction is completed, the following approvals should be procured.
- Building completion
- Tree plantation
- Drainage completion.
- Approval for mortgage
- NOC from the pollution control board
- Fire clearance certificate
- NOC from the environmental department
- Industrial safety certification
- Issue of permanent power supply.
- Issue of permanent water supply and sewerage.
- Employee’s provident fund(EPF): This is required for business who have a work force of 20 or more people.
- Employee’s state insurance scheme (ESI): This is required for non-seasonal business units that have a workforce of 10 or more. However for businesses like shops, hotels, cinemas or preview theatres etc, this is required if the workforce is 20 or more.
FAQs on Entrepreneurial Planning, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 Revision Notes
| 1. What is entrepreneurial planning? |
| 2. What is the importance of entrepreneurial planning? |
| 3. How does entrepreneurial planning help in minimizing risks? |
| 4. What are the key components of a business plan in entrepreneurial planning? |
| 5. How does entrepreneurial planning contribute to business growth and expansion? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
practice quizzes
Mock tests for examination, shortcuts and tricks, study material, entrepreneurship, extra questions, entrepreneurial planning, video lectures, past year papers, class 12 revision notes, objective type questions, viva questions, sample paper, semester notes, previous year questions with solutions, important questions.

Revision Notes - Entrepreneurial Planning, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 Free PDF Download
Importance of revision notes - entrepreneurial planning, entrepreneurship, class 12, revision notes - entrepreneurial planning, entrepreneurship, class 12, revision notes - entrepreneurial planning, entrepreneurship, class 12 class 12 questions, study revision notes - entrepreneurial planning, entrepreneurship, class 12 on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
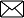
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Notes
Entrepreneurship encompasses the academic study of the processes, principles, and practices involved in starting, managing, and growing new ventures. It combines insights from various disciplines such as business management, economics, finance, marketing, innovation, and strategy to provide a comprehensive understanding of how entrepreneurial ventures operate. Entrepreneurship as a subject is not only relevant for aspiring entrepreneurs but also for individuals interested in working in startups, corporate innovation, venture capital, or small business management.

Entrepreneurship Class 12 Course Structure 2024-25
Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70
| S.No. | Unit | No. of Periods | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| Entrepreneurial Opportunity | 40 | 30 |
|
| Entrepreneurial Planning | 40 | |
|
| Enterprise Marketing | 40 | 20 |
|
| Enterprise Growth Strategies | 20 | |
|
| Business Arithmetic | 40 | 20 |
|
| Resource Mobilization | 20 | |
|
| 40 | 30 | |
| TOTAL | 240 | 100 |
Entrepreneurship Question Paper Design
| S.No. | Competencies | Total Marks | % Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, listing elements, terms and basic concepts. Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas. |
20 | 28.5% |
| 2. | Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in different ways. | 30 | 43% |
| 3. | Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations, integrated learning; Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions . |
20 | 28.5 |
| TOTAL | 70 | 100% |
Unit 1: Entrepreneurial Opportunity
The Entrepreneurial Opportunity unit for CBSE Class 11 is crafted to introduce students to the foundational concepts of identifying and evaluating entrepreneurial opportunities. The unit aims to foster an entrepreneurial mindset among students and equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary for recognizing and capitalizing on opportunities in today’s dynamic business environment.
- Business Opportunity
- Environment Scanning
- Problem Identification
- Idea Generation
- Idea Fields
- Product Identification
- Market Assessment
- Trend Spotting
- Creativity and Innovation
Unit 2: Entrepreneurial Planning
The Entrepreneurial Planning unit for CBSE Class 11 is meticulously designed to introduce students to the process of planning and strategizing for entrepreneurial ventures. Planning is a crucial aspect of entrepreneurship, laying the groundwork for success by outlining goals, strategies, and actions required to achieve them.
- Activities, Business, and Enterprises in Entrepreneurship
- Sole proprietorship in Entreperneurship
- Partnership in Entreperneurship
- Joint Stock Company in Entreperneurship
- Joint Hindu family / firm (HUFs) in Entreperneurship
- Co-operative Organisations in Entreperneurship
- Business Plan
- Production Plan in Entrepreneurship
- Operational plan in Entrepreneurship
- Organizational plan in Entrepreneurship
- Financial plan in Entrepreneurship
- Manpower planning in Entrepreneurship
- Marketing plan in Entrepreneurship
Unit 3: Enterprise Marketing
The Enterprise Marketing unit for CBSE Class 11 is tailored to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of marketing principles and strategies tailored specifically for entrepreneurial ventures. In today’s competitive business landscape, effective marketing plays a pivotal role in the success of any enterprise.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Branding , Logo, Tagline
- Promotion Strategy
Unit 4: Enterprise Growth Strategies
The Enterprise Growth Strategies unit for CBSE Class 11 is crafted to provide students with insights into the various strategies and approaches that entrepreneurs can employ to scale their ventures and achieve sustainable growth.
- Franchising: Concept and types
- Franchising: Advantages and limitations to franchisor and franchisee.
- Mergers and Acquisition: Concept, reasons and types.
- Reasons for mergers and acquisitions
Unit 5: Business Arithmetic
The Business Arithmetic unit for CBSE Class 11 is designed to provide students with a solid foundation in mathematical concepts and techniques essential for business and entrepreneurship. In today’s data-driven and competitive business landscape, proficiency in arithmetic skills is crucial for making informed decisions, managing finances, and analyzing business performance.
- Unit of Sale, Unit Cost for multiple products or services
- Break even Analysis for multiple products or services
- Computation of Working Capital
- Inventory Control and EOQ
- Return on Investment (ROI) and Return on Equity (ROE)
Unit 6: Resource Mobilization
The Resource Mobilization unit for CBSE Class 11 is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the process of acquiring and managing resources essential for entrepreneurial ventures.
- Capital Market : Concept
- Primary market : Concept, Methods of Issue
- Angel Investor: Features
- Venture Capital: Features, Funding
Project Work
| Marks | Constituent |
|---|---|
| 20 | Students need to complete two projects in total, 10 marks each |
| 5 | Numerical Assessment |
| 5 | Viva Voce |
Topics for the Project
1. Business Plan
2. Market Survey
Similar Reads
Please login to comment....
- Top Language Learning Apps in 2024
- Top 20 Free VPN for iPhone in 2024: October Top Picks
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Enterprise Growth Strategies
September 30, 2019 by Bhagya
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Chapter-4 Enterprise Growth Strategies
Textbook questions solved.
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Question 1. What are the two ways in which an organisation can expand? Answer. Internal Expansion and External Expansion are the two ways in which an organisation can expand.
Question 2. Who is a franchisor? Answer. The owner or person offering the franchise is known as the franchisor.
Question 3. Who is a franchisee? Answer. The franchisee is the person who purchases the franchise and is given the opportunity to enter a new business with a better chance to success than if he or she were to start a new business from nothing.
Question 4.What is franchising? Answer. Franchising is an arrangement through which the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trademarked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures.
Question 5. Which is the most popular form of franchising? Answer. Business format franchise opportunity is the most popular form of franchising.
Question 6. What is acquisition? Answer. Acquisition or take over is enveloping in itself a range of acquisition transactions by a firm.
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-I Question 1. Explain in brief the three ways in which an organisation can expand externally. Answer. The three ways in which an organisation can expand externally are:
- Franchising: Franchising is an arrangement through which the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trademarked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures,
- Merger: It is the combining of two firms into a single large firm.
- Acquisition: Acquisition or takeover is enveloping in itself a range of acquisition transactions by a firm.
Question 2. Enumerate the importance of franchising. Answer. Importance of Franchising:
- Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market and is also known.
- Profit from brand recognition: Franchises develop an image in the marketplace. This saves both time and money of advertising, promotion, recognition, etc. Image of the product is a favourable one and is in the minds of consumers.
- Recognized brand name and trademarks: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brandname and trademarks. Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchise.
- Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, help setting up the business, a manual telling how to run the business and ongoing advice.
- Exclusive rights of the territory: The franchisor can’t sell any other franchises in the same territory which leads to the creation of monopoly power in the territory.
- Easier Financing: Financing the business becomes easier due to the associated brand name. Banks are more likely to lend money to buy a franchise with a good reputation.
Question 4. Name the two forms that merger can take place. Answer. Two forms of merger are:
- Amalgamation: Amalgamation is a union of two or more companies, made with an intention to form a new entity or company.
- Absorption: It means an existing company taking over one or more company. In this case one or more company will close down their business and this business will be continued by the name of the existing company.
Question 5. Explain the types of acquisition. Answer. There are four types of acquisitions:
- Friendly acquisition: Here, both the companies approve of the acquisition under friendly terms. There is no use of force or pressure and every thing gets over cordially.
- Reverse acquisition: Here, a private company takes over a public company.
- Rack flip acquisition: Here, the purchasing company becomes a subsidiary of the purchased company.
- Hostile acquisition: Here, the entire process is based on force. The smaller company is forced to say yes to the acquisition or the bigger company just buys off all its share.
Question 6. What is value addition? Explain by giving examples. Answer. Value addition refers to creation of a competitive advantage by, combining, packaging features and benefits or through any other method that results in greater customer acceptance. Its examples are:
- Offering one year of free support on a new computer would be a value-added feature.
- Turning cotton into fabric. Here, fabric has more usefulness than cotton.
- Turning milk into cheese. Cheese has got more specific uses than milk.
- Packaging ready-to-use grated cheese into serving size packets.
- Turning wood into paper. Utility of paper is more than wood.
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Question 1. Explain the types of franchising. Answer. Following are the types of franchising:
- Product Franchise Business Opportunity: Here, the manufacturers use the product franchise to govern how a retailer distributes their products. The manufacturer grants a store owner the authority to distribute goods by the manufacturer and allows the owner to use the name and trademark owned by the manufacturer. The store owner purchases the inventory in return for these rights. Example: Some tire stores.
- Manufacturing Franchise Opportunity: It provides an organisation with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the franchisor’s name and trade mark. This type of franchising is very common. For example, in the food and beverage industry, bottlers of soft drinks, etc.
- Business Franchise Opportunity Ventures: Here, a business owner purchases and distributes the products for one specific company. The company provides customers or accounts to the business owner. In return, the business owner pays a fee as compensation. Example, vending machine routes and distributorships.
- Business Format Franchise Opportunity: Here, a company provides a business owner with a proven method for operating a business using the name and trade mark of the company. The company provides a significant assistance to the business owner in starting and managing the company. The business owner pays a fee or royalty in return.
Question 2. What are the disadvantages of franchising to the franchisee? Answer. Disadvantages of franchising :
- Higher cost: Costs may be higher than expectations. The costs include initial costs of buying the franchise, you pay continuing management service fees and you may have to agree to buy products from the franchisor, this may be more than the expectations.
- Huge restrictions: The franchise agreement usually includes strong restrictions on how to run the business. Franchise might not be able to make changes to suit the local market.
- Risk: There is a risk that the franchisor might go out of business and in this case a huge risk is involved.
- Bad reputation: Other franchisees could give the brand a bad reputation, so the selection process needs to be perfect.
- No sale option: Franchise finds it difficult to sell to someone if willing to sell due to any reason. It can only be sold to someone approved by the franchisor.
Question 3. What is synergy? In what forms can it take place? Answer. Synergy is the benefit that results when two or more firms together achieve something either one couldn’t have achieved on its own. It’s the concept of the whole being greater than the sum of its parts. For example, if firms A and B merge and the value of the combined entity— V(AB)—is expected to be greater than (VA+VB), the sum of the independent values of A and B, the combined entity is said to be benefitting through synergy. Synergy can take place in two forms:
- Operating synergy: This refers to the cost savings that come through economies of scale or increased sales and profits. It involves raising scale of production by changing all factors of productions of the firm. It leads to the overall growth of the firm.
- Financial synergy: It is the type of synergy which is due to financial factors such as lower taxes, higher debt capacity or better use of idle cash. When a loss making firm merges with a profitable firm and the combined firm can set off such losses against its profits, a financial synergy, known as tax shield, occurs.
Question 4. What are the different types of value added? Answer. The different types of value added are as follows:
- Quality Added Value: It is adding convenience, ease of use, etc. that customers value. For example, turning a commodity into a branded product or design enhancements.
- Environmental Added Value: It is value added which employs methods or systems that do not harm the environment. For example, using less fuel, using recycled material for packaging.
- Cause-related Added Value: Here, the business contributes part of the revenue from a commodity to a cause. For example, a business may donate a percentage of revenue from each transaction to a orphanage.
- Cultural Added Value: It uses methods or systems of production involving cultural aspects. For example, using a combination of English and the regional language in written communications.
D. VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Question 1. Explain the advantages of franchising, both for the franchisor and franchisee. Answer. Merits of Franchising:
- Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market.
- Recognized brand name and trademarks: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brand name and trademarks. Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchise.
- Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, help setting up the business, a manual telling how to run the business and ongoing advice.
Question 2. Explain in detail the types of mergers. Answer.
- Conglomerate: Here, two totally unrelated business activities mearge. Pure conglomerate mergers is between the firms with nothing in common. Mixed conglomerate mergers involve firms which are going for product extensions or market extensions. Example: Walt Disney Company and the American Broadcasting Company. Here the new company formed had to face tough competition in both the products.
- Horizontal merger: This merger is between companies in the same industry. It is a type of business consolidation that occurs between firms which are competitors and offering the same goods or service. It is in the condition where competition tends to be higher and the potential gains in market share are much greater for merging firms in such an industry. Example: A merger between Coca-Cola and the Pepsi beverage division, would create a new, larger organisation with more market share.
- Market extension mergers: It takes place between two companies that deal in the same products but in different markets. This merger is to make sure that the merging results in a bigger market and a bigger client base. Example: The acquisition of Eagle Bancshares Inc. by the RBC gave RBC a chance to deal in the financial market of Atlanta, which is among the leading upcoming financial markets in the USA. RBC has thus diversified due to this move.
- Product extension mergers: A product extension merger takes place between two business organizations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. The product extension merger allows the merging companies to group together their products ‘ and get access to a bigger set of consumers. This ensures that they earn higher profits. Example: The acquisition of Mobilink Telecom Inc. by Broadcom Broadcom deals in the’ manufacturing of Bluetooth personal area network hardware systems and chips for IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN. Mobilink Telecom Inc. deals in the manufacturing of product designs meant for handsets that are equipped with the Global System for Mobile Communications technology. It is expected that the products of Mobilink Telecom Inc. would be complementing the wireless products of Broadcom.
- Vertical merger: A merger between two companies producing different goods or services for one specific finished product. A vertical merger occurs when two or more firms, operating at different levels within an industry’s supply chain, merge operations. Most often the logic behind the merger is to increase synergies created by merging firms that would be more efficient operating as one. Example: A vertical merger joins two companies that may not compete with each other, but exist in the same supply chain. An automobile company joining with a parts supplier would be an example of a vertical merger. Such a deal would allow the automobile division to obtain better pricing on parts and have better control over the manufacturing process. The parts division, in turn, would be guaranteed a steady stream of business.
Question 3. What do you think are the reasons for failure of merger and acquisition? Answer. Following are the reasons for failure of merger and acquisition:
- Unrealistic price paid for target: Merger and acquisition involves valuation of the target company and paying a price. Many a time the price paid to the target company is much more than what should have been paid. Shareholders of the target company are benefited, the shareholders of the acquirer end up on the losing side.
- Difficulties in cultural integration: Merger involves combining of two or more different companies with different corporate cultures, styles of leadership, differing employee expectations etc. If the merger is not dealing sensitively with the companies people and their different corporate cultures, the merger may be a disaster. For example, the merger of Daimler Benz with Chrysler. While Daimler-Benz’s culture stressed on a more formal and structured management style, Chrysler favoured a more relaxed and freewheeling style.
- Overstated synergies: Mergers and acquisitions assumed to be for creating synergies through increased revenue, reduced costs and improvement in the investment intensity. Overestimation can lead to failure.
- Integration difficulties: The combined firm or entity has to adapt to a new set of challenges given by the new circumstances. Plans are thus prepared to integrate the operations of the combining entities. This is done on the present information. If the information available is inadequate, integration becomes difficult. (a) Poor business fit: Mergers and acquisitions also fail when the products of the merging firms do not fit into the acquirer’s overall business plan.
- Inadequate due diligence: Due diligence helps in detecting financial and business risks that the acquirer inherits from the target company. Inaccurate estimation of the related risk can result in failure of the merger.
Question 4. What is meant by moving up the value chain? Explain with the help of an example. Answer.
- Moving-up the value chain is a value chain in the whole series of activities that create and build value at every step. The total value delivered by the company is the sum total of the value built up gradually all throughout the company.
- It is the primary and secondary facilitations offered by a company. Low facilitation to highest facilitation by a company then leads to movement from low level to highest level. For example, in a steel industry, if they make specialized steel for automobiles, rather than selling basic steel, which is taken by another company who makes specialized steels to automobiles. Since the company makes it directly now, they get more money for their product, and thus higher revenues. This will eventually lead to higher profits. The value chain concept separates useful from the wasteful activities which hinder the company from becoming a leader in the market. Focusing on the value-creating activities gives the company many advantages. It involves primary activities like Inbound logistics, Operations, Outbound logistics, Marketing, sales, Services, etc. and Support activities like Procurement, Technological development, Human resource management etc. Value chain management requires coordination and collaboration, Technology investment, Organizational process, Leadership, Employee/ Human resources and Organizational culture and attitudes. For example: The ability to charge higher prices; lower cost of manufacture; better brand image, faster response to threats or opportunities. Outsourcing: The fragmentation of the production process across various countries has given rise to restructuring in firms including the outsourcing and off shoring of certain functions. Outsourcing involves the purchase of intermediate goods and services from outside specialist providers, while off shoring refers to purchases by firms of intermediate goods and services from foreign providers, or to the transfer of particular tasks within the firm to a foreign location. Off shoring includes both international outsourcing where activities are contracted out to third parties abroad and international in-sourcing to foreign affiliates.
Question 5. Explain in detail Porter’s Generic Value Chain with the help of a diagram. Answer. Michael Porter gave the value chain analysis concept in his 1985 book ‘The Competitive Advantage’. He suggested that activities within an organisation add value to the service and products that the organisation produces and all these activities should be run at optimum level if the organisation is to gain any real competitive advantage. If these activities are run efficiently, the value obtained exceed the costs of running them and customers return to the organisation and transact freely and willingly. He suggested that the organisation is split into ‘primary activities’ and ‘support activities’.
- Primary activities include: (a)Inbound logistics: Here, goods are obtained from the suppliers and are used for producing the end product. (b)Operations: Here, raw materials and goods are manufactured into the final product. (c)Outbound logistics: Distribution of finished goods is known as outbound logistics. (d)Marketing and sales: Here, marketing mix is used to form an effective strategy to the target group through the promotional mix. (e) Services: After the product/service has been sold, sales training, guarantees and warranties etc. play its part.
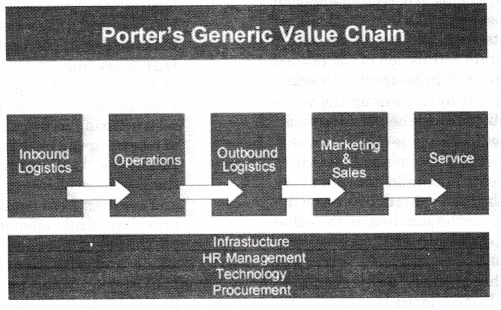
Question 6. Explain the requirements for value chain management. Answer. Following are the six requirements for value chain management:
- Coordination and collaboration: It is essential to increase efficiency within an organization. Care should be taken that efforts are not duplicated. Firm is greater than the sum of its parts for achieving a common goal of the firm.
- Technology investment: With outdated technology, like old computers or machinery, an organization’s competitiveness is weakened due to a loss in productivity. This devoids the firm from gaining advantage.
- Organisational process: Improvement in processes through better technology and greater procedural knowledge is essential for the present and future success of a company. Continuity is to be maintained for the improvement and is to be made an integral part of the system.
- Leadership: Strong leaders adds to the successions value chain management. Good leaders earn the respect of their employees through neutral, effective and sound management practices. Conflict management, motivation and direction are the essential requirements of strong leaders.
- Employee/human resources: Without a knowledgeable and active human resources department, employees may feel they don’t have a voice within the company and this may lead to lack in belongingness from the employees. Also, an employee hesitant to go directly to the ultimate superiors with issues act as a hurdle in many situations.
- Organisational culture and attitudes: Organisations that foster strong cultural identity with positive attitudes tend to attract and retain top employees. Regular sponsored activities are suggested to help build cultural unity and keep attitudes positive while boosting productivity of the firm.
E. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS In the following cases identify the type of merger: Question 1. A merger between firms that are involved in totally unrelated business activities. Answer. It is Conglomerate merger.
Question 2. A merger occurring between companies in the same industry. Answer. It is Horizontal merger.
Question 3. It takes place between two companies that deal in the same products but in separate markets. Answer. It is Market extension merger.
Question 4. It takes place between two business organisations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. Ans. It is Product extension merger.
Question 5. It is between two companies producing different goods or services for one specific finished product. Answer. It is Vertical merger.
F. APPLICATION BASED QUESTIONS Question 1. ABC Company, manufacturing shoes, has taken over XYZ Company which also manufactures shoes at a small scale. What do you think will be the reason for this kind of takeover? Answer. Following can he reasons for the take over:
- ABC Company may have decided to expand in terms of its production and wanted to raise its sales and turnover.
- ABC Company may have decided to expand its area of sales and so may be desirous to take over the marketing area of XYZ Company.
- ABC Company may have wanted to use the research and development of the XYZ company for raising its output and sales.
Question 2. Vimal Company Ltd., were earlier producing pencils, now they have decided to further venture into the field of notebooks and paper. What do you think is the company attempting to do? Identify and explain the concept. Answer. The concept is of diversification. It is a process of adding new products or markets to the existing, by an enterprise. Here, the enterprise thus is able to produce more types of products e.g. not only washing soap, but toilet soaps, shampoos, detergents, washing powders etc. are produced by such enterprises. For example, Samsung not only produces TV but washing machines, copying machines, printers, etc. Usefulness of diversification for an enterprise:
- Risk is reduced: If one type of product is not sold then other products can be sold. This reduces the chances of incurring overall loss to the enterprise.producers are producing the product.
- Continuous revenue: By diversification an enterprise continuously receives payments. This makes the inflow a continuous process. The financial obligations of the company can thus be easily met.
- Financial obligations can be met easily: Due to a variety of products being sold the cash flow becomes regular. This helps in fulfilling the financial obligations like installments premium, payment for power, payment for raw material, etc.
- Helps in branding: When one product is able to gain faith of consumers, then this faith can be utilized for increasing the sale of other products. Thus, a brand name comes into existence.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

COMMENTS
Business plans are crucial for entrepreneurial ventures. It helps businesses to identify possible problems and design practical solutions. It helps in critical decision-making. This is a pragmatic approach and helps the business in the long run. Another critical aspect of a business plan is it helps in identifying short-term goals and long-term ...
There are various components of a business plan which is prepared to depend upon the entrepreneur's enterprise and knowledge. CERTIFICATE This is to certify that the project is an authentic record of the work done by ROHITH S. BOBBY , class XII.D during 2017-2018 towards the partial fulfillment of the AISSCE course prescribed by the Central ...
Welcome to our Class 12 Entrepreneurship series! In this video, we dive deep into the essential topic of "Components of a Business Plan." Whether you're a st...
Entrepreneurial Planning - CBSE Notes for Class 12 Entrepreneurship 1. Entrepreneurial activities are of three major categories: Manufacturing, trading and service providing. 2. Business is 'A state of being busy or occupied'. 3. Activities undertaken to earn monetary benefits are called economic activities. 4. Activities done out of love and affection and not to earn […]
Explore the key components of entrepreneurial planning and business plans in this comprehensive video for Class 12 EP students.
SHIP CLASS XI-XII (2024-25) (CODE NO. 0. 6) RationaleSchool curriculum is a dynamic process. It continuously evolves i. self reflecting the needs and aspirations of learners. In recent times, our society is influence. by knowledge creation and technological advancements. Competencies affecting Innovation and creativity have become impo.
A business plan is a comprehensively written down document prepared by the entrepreneur describing formally all the relevant external and internal elements involved in starting a new venture. The business plan: (i) Viability: It helps in finding the viability of the venture in a designated market. (ii) Guidance: It helps in providing guidance ...
Ans. Entrepreneurial planning refers to the process of creating a strategic roadmap for an entrepreneur or business owner to achieve their goals and objectives. It involves identifying opportunities, setting objectives, formulating strategies, and allocating resources to effectively manage and grow a business. 2.
Introduction of NCERT Textbook - Entrepreneurial Planning in English is available as part of our Entrepreneurship Class 12 for Commerce & NCERT Textbook - Entrepreneurial Planning in Hindi for Entrepreneurship Class 12 course. Download more important topics related with notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship. In this page, each and every question originate with a step-wise solution. Working on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 will help students to get an idea about how to solve the problems. With the help of these NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship you can easily grasp basic concepts better and faster. . Moreover, it is a perfect guide to help ...
Answer: (i) A business plan is a comprehensively written down document prepared by the entrepreneur describing formally all the relevant external and internal elements involved in starting a new venture. (ii) It is a 'road map' required by the venture to evolve from an early start up to a mature business.
Entrepreneurship is a process of developing a business plan, launching and running a business using innovation . to meet customer needs and to make a profit. Let us read a story to further understand the meaning . of entrepreneurship and who is an entrepreneur. Pratap, the Vegetable Seller. Pratap was a vegetable seller in Agra. He was well
Rice University's Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51, 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2.
CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Syllabus 2024-25 Course Structure Theory Paper. Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 70. S.No. Unit. No. of Periods. Marks. Unit 1. Entrepreneurial Opportunity. 40. 30. ... · Describe the various components of Business plan · Differentiate among the various components of Business plan · Develop a Business Plan ...
Helps in Reducing Uncertainty. One of the importance of a business plan is it helps in reducing uncertainty. Uncertainty is a widespread issue in all types of businesses. In case of uncertainty, a business plan is a solution. A company can eliminate uncertainty by pointing out its future actions. A business plan is a blueprint for the future.
EduRev's Entrepreneurship Class 12 Course for Commerce is a comprehensive program that equips students with the knowledge and skills required to be successful entrepreneurs. The course covers various aspects of entrepreneurship, including idea generation, market research, business planning, funding, and marketing. It also provides students with real-world examples and case studies to help them ...
The first stage of a business plan is to come up with a business name supposing you are an entrepreneur, who is in the stage of deciding abusiness name for your enterprise would you : ... Using CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Textbook solutions Enterprise Planning exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve ...
in the growth and economic development of the nation.To promote Entrepreneurship as life-skills to improve quality of life, skills. l pursuits.COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS-XI (2020-21) The course content of Entrepreneurship is divi. ed into 7 units and the project work given as follows. Each unit of the course is accompanied by the comprehensive ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Chapter-1 Entrepreneurial Opportunity TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED A.VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q1. What is a business opportunity? Ans. It refers to an attractive and accessable economic idea which could be implemented to create a business, earn maximum profit, and leads to further growth. National Career Service (NCS) aims to […]
The "Revision Notes - Entrepreneurial Planning, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 Class 12 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 12 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics.
CBSE Class 12 Entrepreneurship Notes. Entrepreneurship encompasses the academic study of the processes, principles, and practices involved in starting, managing, and growing new ventures. It combines insights from various disciplines such as business management, economics, finance, marketing, innovation, and strategy to provide a comprehensive ...
An entrepreneur has a dual role to play— as a leader and as a manager. Leader provides direction and energy while the Manager processes the input and gives the production or output. To ensure the continued efficiency and profitable functioning and growth of enterprise, extra managerial ability is required. Question 3.